Yoga is also a sport in Physical Education. Nowadays, Yoga has become very popular throughout the world. The present age can be said the age of stress, tension and anxiety. So, most of the persons have not been living a happy and fruitful life. In western countries, Yoga has become a way of life. It has a vital significance in the life of human beings.
Explore about Yoga and its different Kinds
History of Yoga
The history of Yoga is indeed ancient. Nothing can be said firmly about the origin of Yoga. Only it can be noted that Yoga originated in India. The available evidence shows that the history of Yoga is related to Indus valley civilization. At that time, people used to do Yoga based on a secondary source. It can allude that Yoga originated approximately 3000 BC in India. Patanjali wrote the first book on Yoga in 147 BC. Yoga is derived from a Sanskrit word ‘”Yoj’ which means union or join.
- 1. According to Patanjali, yoga means to control the desires of a human being.
- 2. The system of yoga is built on the three main structures: exercise, breathing and meditation.
- 3. The practices of yoga are designed to put pressure on the glandular systems of the body, increase its efficiency and total health. The body is looked upon as the primary instrument that enables us to work, and so a yoga student treats it with great care and respect.
- 4. Breathing techniques are based on the concept that breath is the source of life in the body. The yoga student gently increases breath control to improve health.
- 5. The two systems of exercise and breathing prepare the body and mind for meditation, and the student finds a straightforward approach to a quiet mind that allows silence and healing from day-to-day stress.
- 6. Regular daily practice of all three parts of this structure of yoga produces a clear, bright mind and a healthy, capable body and mind.
Elements
The eight steps or elements of classical yoga are:
| Steps of Yoga | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 1. Yama | Refraining from violence,lying, stealing and hoarding. |
| 2. Niyama | Purity, contentment,tolerances and remembrance |
| 3. Asana | Physical exercise |
| 4. Pranayam | Breathing techniques. |
| 5. Pratyahara | Preparation for meditation described as ‘withdrawl of the mind from the senses. |
| 6. Dharana | Concentration being able to hold the mind on one object for a specified time. |
| 7. Dhyana | Meditation,the ability to focus on one thing (or nothing) indefinitely. |
| 8. Samadhi | Absorption, or realization of the essential nature of the self. |
Types (Kinds)
| Yoga Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Hatha Yoga | Some of the most well-known types of yoga are described below most people associate with yoga practice. |
| Raja Yoga | It incorporates exercise and breathing practice with meditation and study producing a well-rounded individual. |
| Jnana Yoga | The path of wisdom. |
| Bhakti Yoga | The practice of extreme devotion in one pointed concentration upon one’s concept of God. |
| Bhakti Yoga | All the movements and all work of any kind is done with the mind centered on a personal concept of God. |
Asanas
Asanas are the first and the most important stage of yoga. They are specific body postures practised to keep the body healthy. Asanas help in exercising every muscle, nerve and gland of the body and are thus highly useful in maintaining physical fitness. Mentioned below are the Sanskrit names (along with the English name) of the major asanas.
| Sanskrit name | English Name |
|---|---|
| Surya Namaskar | Sun salutuation |
| Anjaneya asana | Salutation Posture |
| Ardha chandra asana | Half-moon Posture |
| Padma asana | Lotus Posture |
| Vajra asana | Diamond Posture |
| Sirsha asana | Head stand Posture |
| Tada asana | Mountain Posture |
Some of the asanas are discussed below:
Padmasana
Padmasana means lotus posture. This asana gives the appearance of a lotus. It is the best asana for contemplation.
Steps to follow
- Sit on the ground by spreading the legs forward.
- Place the right foot on the left thigh and the left foot on the right thigh.
- Place the hands on the knee joints as shown in the figure.
- Keep the body,back and head hand erect.
- Eyes should be closed.
Benefits
- It helps in improving concentration and memory.
- It helps to preserve vital fluids in the body.
- It prevents abdominal disease and female disorders.
- It brings peace and longevity
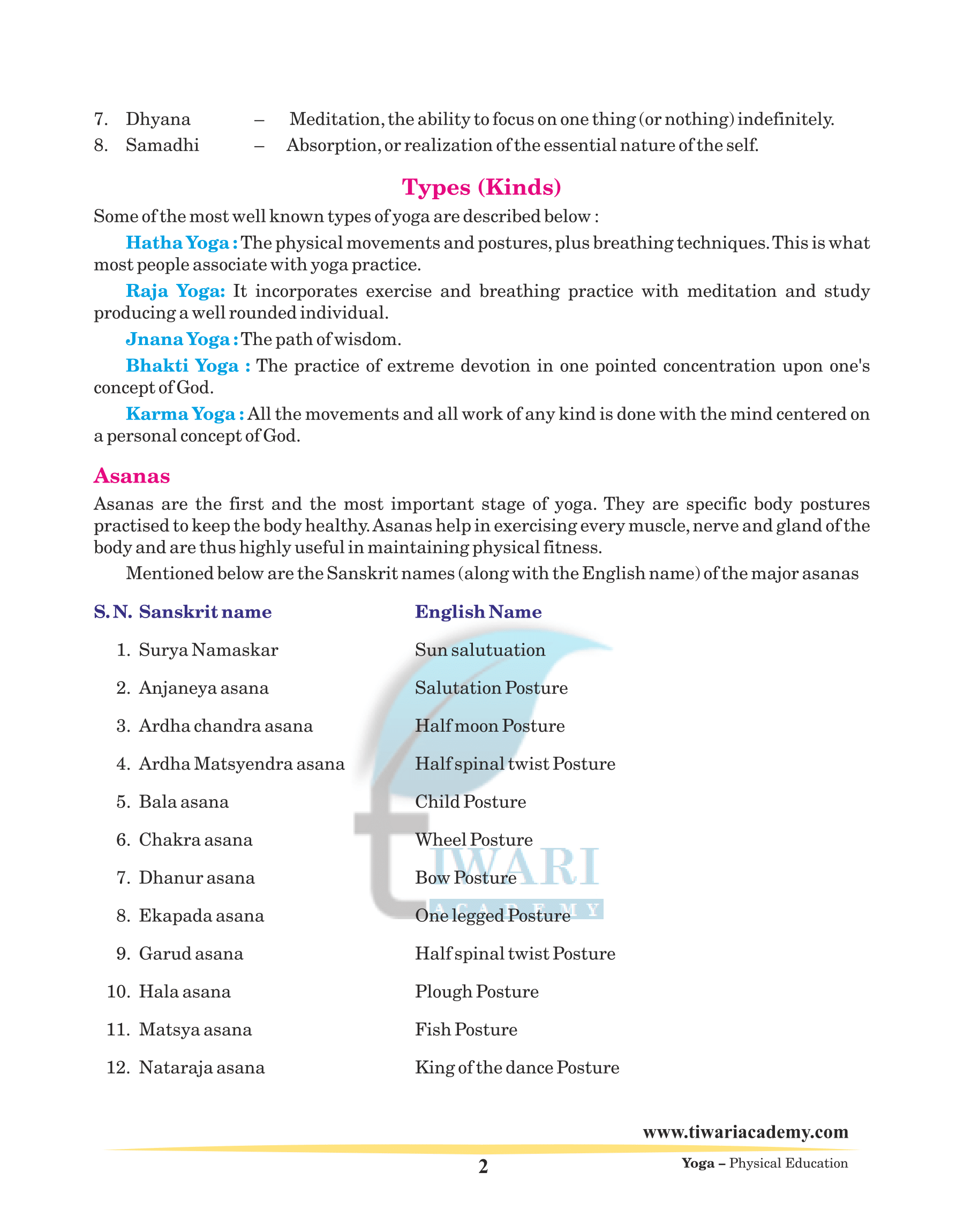
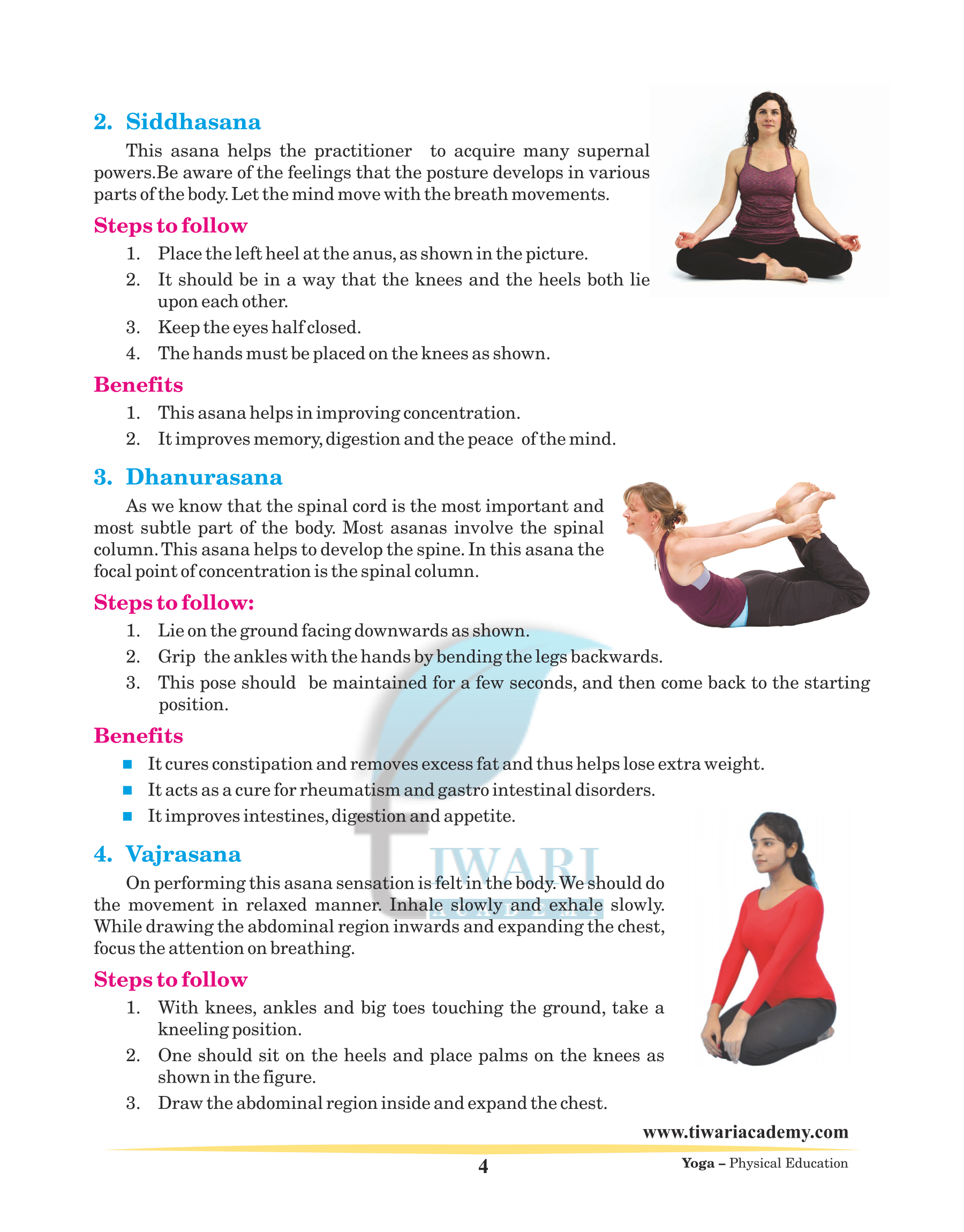
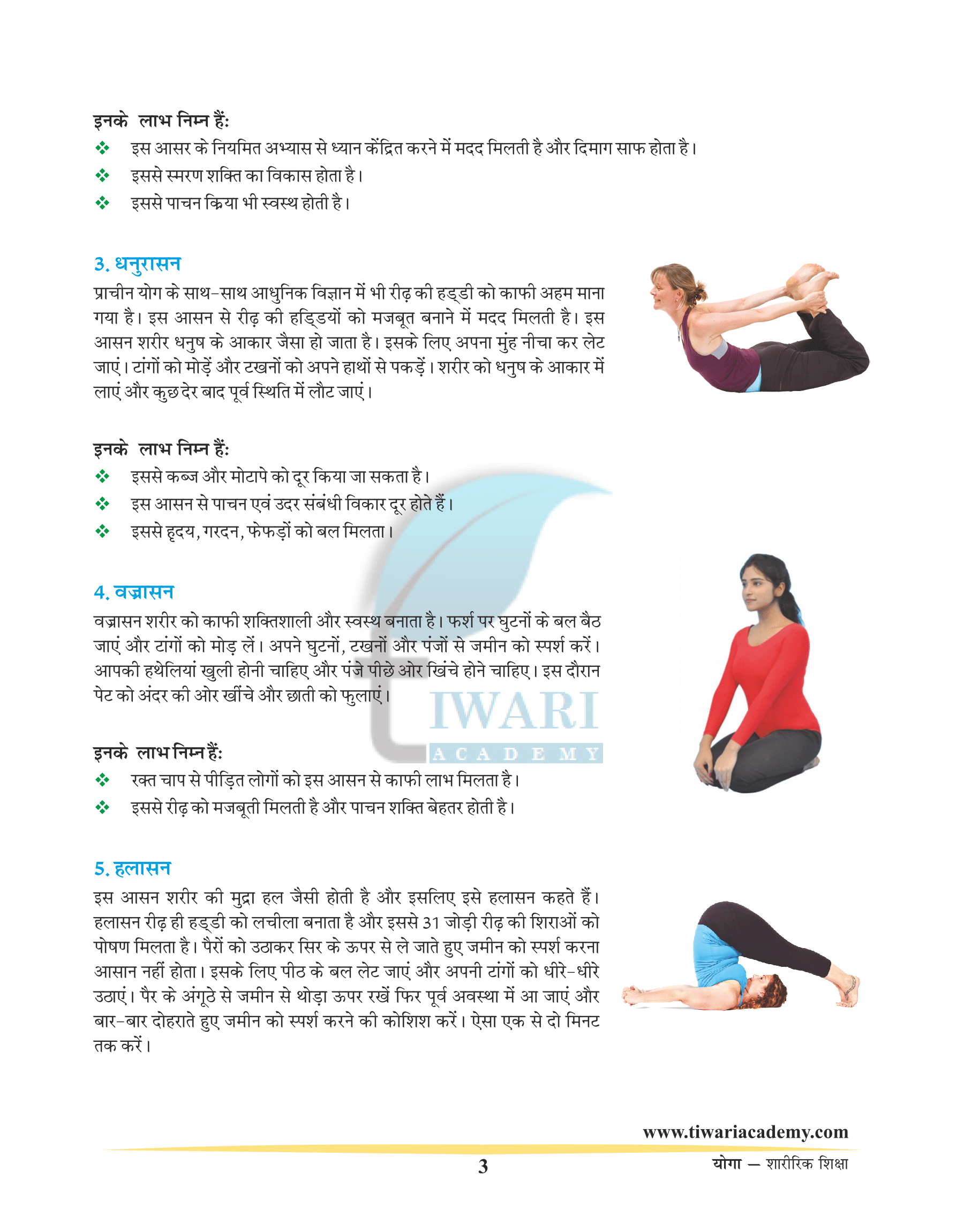
Vajrasana
On performing this asana sensation is felt in the body.We should do the movement in relaxed manner. Inhale slowly and exhale slowly. While drawing the abdominal region inwards and expanding the chest, focus the attention on breathing.
Steps to follow
1. With knees, ankles and big toes touching the ground, take a kneeling position.
2. One should sit on the heels and place palms on the knees as shown in the figure.
3. Draw the abdominal region inside and expand the chest.
Benefits
1. The blood pressure patients will benefit from this asana.
2. It also strengthens the spine.
Surya Namaskar
Also known as sun salutation, the Surya Namaskar is one of the best exercises that one can perform.The benefits accruing from these exercises are unique and excellent. The Surya Namaskar is performed usually early in the morning facing the morning rising sun. It is done in 12 steps, each step having its own posture with its own breathing pattern.
Steps to follow
- 1. Stand erect facing the sun with palms folded and both the thumbs touching the chest. Breathing: Inhale while raising the hands and exhale as hands are brought down.
- 2. Raise hands upward, with feet firmly on the ground and bend backwards and stretch arms
Breathing: Inhale - 3. Slowly bend forward,hands touching the earth,head touching the knees. Breathing:Exhale
- 4. Set both hands with palms down firmly on the ground, pull the left leg backward, raise the head looking the sun. Breathing: Inhale.
- 5. Bring right leg back close to left leg keeping hands and leg straight.Bend the body at the hip forming an arch. Breathing:Exhale.
- 6. Stretch yourself fully on the ground in the saashtanga Namaskar pose. Feet, knees,thighs, chest and forehead touch the ground with the hands stretched out. Now slowly turn the head to the sides first to left and then to right. Breathing inhale first and then exhale fully.
- 7. Slowly raise the head bend backward as much as possible, hands straight. Breathing Inhale.
- 8. Parvatasana – same as step 5. Breathing: exhale.
- 9. Same as step 4 with the difference that the right leg is brought forward Breathing: inhale
- 10. Same as step 3 – Breathing: exhale
- 11. Same as step 2 – breathing: inhale
- 12. Same as step 1- Breathing, exhale: inhale and exhale.
Benefits
1. Surya Namaskar improves the physical body prana (breathing) mind, intellect and the bliss components of the entire human personality. It can be used as a personality development tool.
2. It also reduces the extra fat from your body.
3. It improves body posture.
4. It strengthens the body muscles.