The Olympic Games are a great international event. In this sport, thousands of athletes participate in various types of competition. The Olympic Games are considered the most important sporting event in the world and more than 200 nations participate. The Games are currently held alternately with the Summer and Winter Olympics every two years, although they take place every four years at their respective regional games. Initially, the ancient Olympic Games were held in Olympia, Greece from the 8th century BCE. Until the IV century d. C. The International Olympic Committee (IOC) was established in 1894 by Baron Pierre de Kuebertin. Since then, the IOC has become the governing body of the Olympic Games. The Olympic schedule, which includes sports played in the Games, is also determined by the IOC.
History of Popular EVents in Games
History of Olympics
The Olympics are an invention of modern Greek. Despite the harsh living conditions at the dawn of history, men found time to enjoy a variety of sports. These were given importance as a means of developing the ability to hunt or prepare for war and appease angry gods.
The ancient Olympic Games were a series of competitions held between representatives of the various city-states and the states of ancient Greece, which consisted mainly of sports competitions, but also fights and chariot races during the Olympic Games. All fights against the participating city-states were postponed until the Games ended. The origin of these Olympic Games is mystery and legend.
The most accepted date for the start of the ancient Olympic Games is 776 BC. C. It is based on an inscription found at Olympia. The old games included racing events: a pentathlon included a jumping event, discus and javelin throw, a foot race and boxing, wrestling and horse riding competitions. Ellis is believed to have been the first Olympic champion, Colobus, a cook in the city. The ancient Olympics were of fundamental religious importance with sporting events as well as rituals. The winners of the events were praised and immortalized in poems and statues. The Games were held every four years, and the Greeks used this period known as the Olympiad as one of their units of measurement of time. The games were part of a cycle known as the Panhellenic Games.
The Ancient Olympic Games
The ancient Olympic Games reached their peak in the 6th and 5th centuries BCE, but then gradually declined in importance as the Romans gained power and influence in Greece. There is no consensus on officially ending the Games. The most common date is 393 AD. When Emperor Theodosius I announced that all pagan defects and practices would be abolished. After the demise of the Olympic Games, they were not held again until the end of the 19th century.
Winter Olympic Games
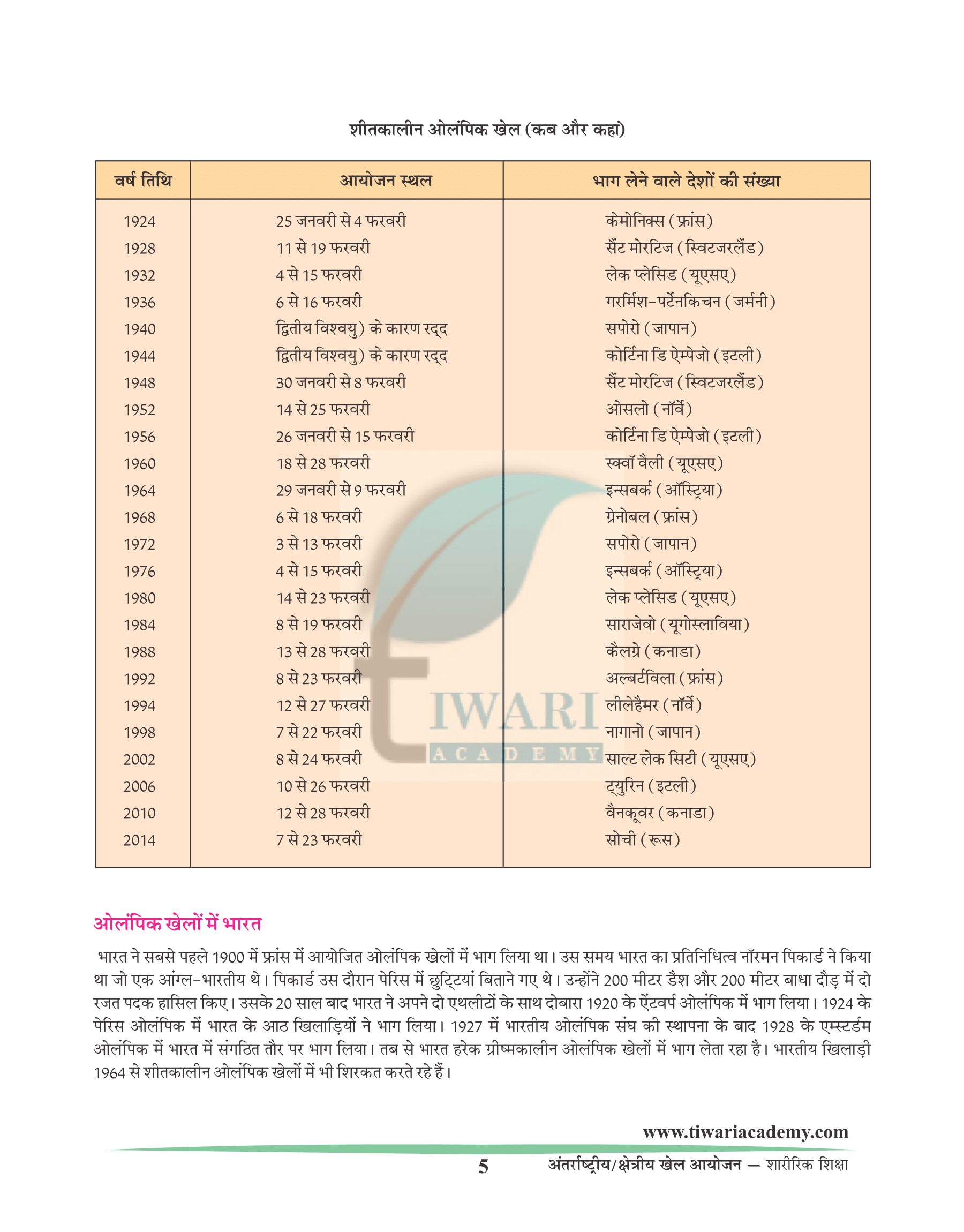
The Winter Olympics (first held in Chamonix France, in 1924) were created to feature snow and ice sports that were logistically impossible to hold during the Summer Games. At the 1921 Olympic Congress, in Lausanne, it was decided to hold a winter version of the Olympic Games. A winter sports week was held in 1924 in Chamonix, France. This event became the first winter Olympic Games. The IOC decided that the winter Games be celebrated every four years in the same year as their summer counterpart. This tradition was upheld until the 1992 Games; after that, beginning with the 1994 Games the winter Olympics are held on the third year of each Olympic.
Celebration of Olympic Games
The celebration of the Olympic Games is marked by many rituals and symbols such as the Olympic flag and torch, as well as the opening and closing ceremonies, medal presentation etc.
Olympic Motto
Olympic Motto comprises of three Latin Words Citius, Altius, Fortius which means faster, higher stronger, respectively. The Motto was coined by a French educator, Dather Didon in 1895. The Motto was introduced in 1924 at the olympic Games in Paris.
Olympic Flag
Olympic flag is based on a model designed by Baron Pierre-de Coubertin in 1914. It was first hoisted in 1920 at Antwerp (Belgium) Olympics. It is made of white silk. In the centre of the flag there are five interlocked rings of different colours in the spirit of friendship.
The colours are:
| Color | Continent |
|---|---|
| Blue | American Continent |
| Black | African Continent |
| Red | Australian Continent |
| Yellow | Asian Continent |
| Green | European Continent |
Olympic Rings
The five rings are arranged in the shape of a ‘W’. The blue ring shall be high on the left nearer the flag pole. The five Olympic Rings represent the five Continents involved in the Olympics.
Olympic Emblems
Each Olympic Game has its own Olympic emblem, which is a design integrating the Olympic rings with one or more distinctive elements. They are created and proposed by the organising committee or the National Olympic Committee of the host country. It is the responsibility of the International Olympic committee to approve Olympic emblems for the Olympic Games. The Olympic emblems are used in the promotional materials by sponsors of the Olympics on the uniforms of every Olympic competitor.
Olympic Flame
The modern tradition of moving the Olympic flame via a relay system from Greece to the Olympic venue began with the Berlin Games in 1936. Months before the Games are held the Olympic flame is lit on a torch with the rays of the sun concentrated by a parabolic reflector, at the site of the Ancient Olympics in Olympia, Greece. The torch is then taken out of Greece most often to be taken around the country or continent where the Games are held. The Olympic torch is carried by athlete’s leaders, celebrities and ordinary people alike. On the final day of the torch relay, the day of the opening ceremony the flame reaches the main stadium and is used to light a cauldron situated in a prominent part of the venue to signify the beginning of the games.
Olympic Medals
The Olympic medals awarded to winners are another symbol associated with the Olympic Games. The medals are made of gold-plated silver (commonly described as gold medals), silver or bronze and awarded to the top 3 finishers in a particular event. Each medal for an Olympiad has a common design, decided upon by the organizers for the particular games.
Opening Ceremony
The Olympic torch or flame is first of all burnt by sunrays in olympic village (Greece) and it is brought to that city where the Olympic Games are going to be held. The president or prime Minister declares the games open. Before this process all the sports persons take part in the march past and they take an oath. Later on recreational and cultural programmes are organised. Olympic flag is hoisted and Olympic flame of this stadium is kindled by the torch.
Closing Ceremony of Olympic Games
Sports persons from all the countries who have participated in the games assemble in the stadium for the closing ceremony. The Mayor of that city and the President of managing committee escort, the President of International Olympic Committee to the stadium. He declares the games closed. After that, Olympic flag is lowered and it is given to the Mayor of the city. Various cultural programmes are organised. The Olympic Flame is extinguished. At last the games come to an end with the Olympic Song.
Medal Presentation
A medal ceremony is held after each Olympic event is concluded. The winner, second and third place competitors or teams stand on top of a three–tiered rostrum to be awarded their respective medals. After the medals are given out by an IOC member the national flags of the three medalists are raised while the national anthem of the gold medalist’s country is played.
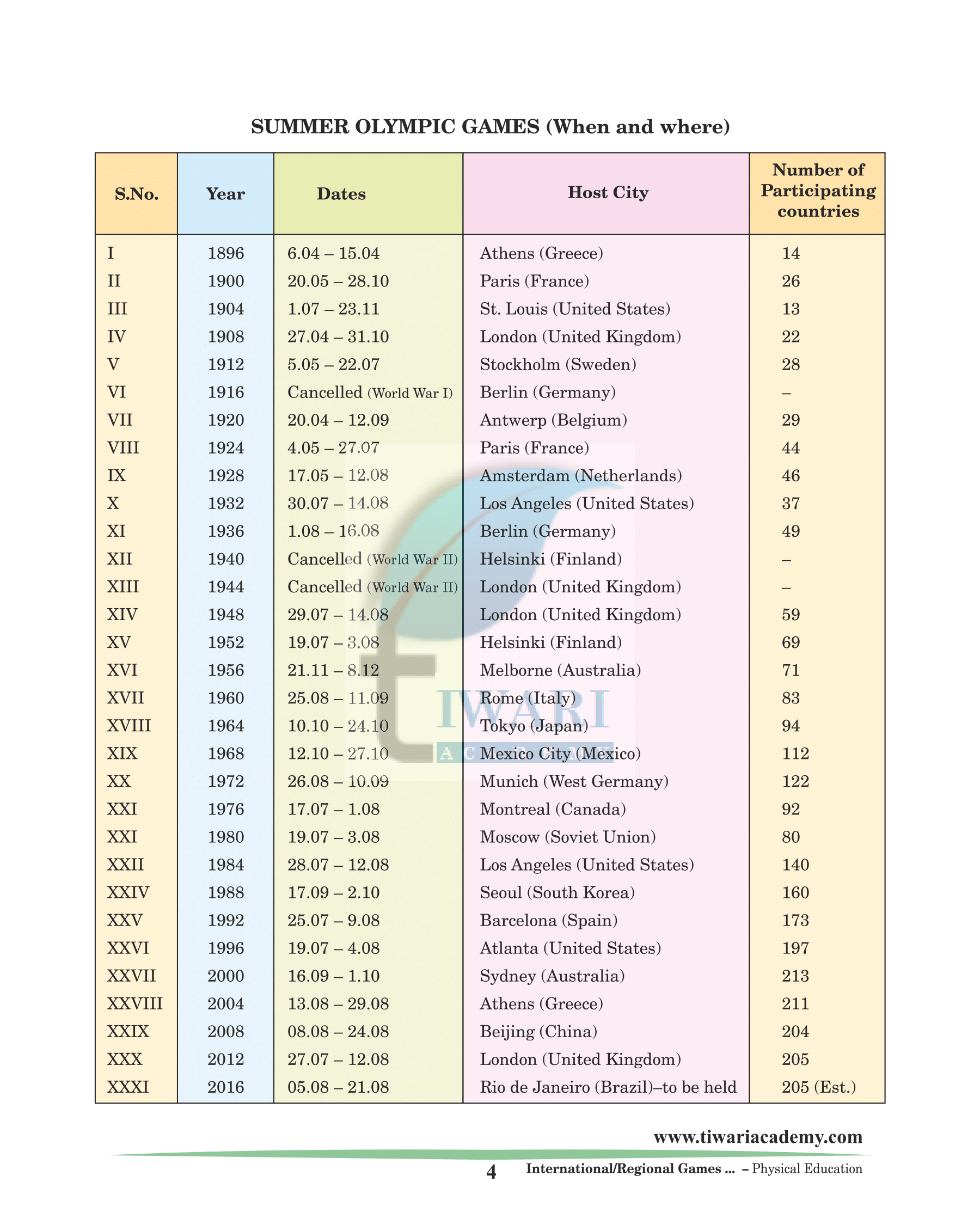
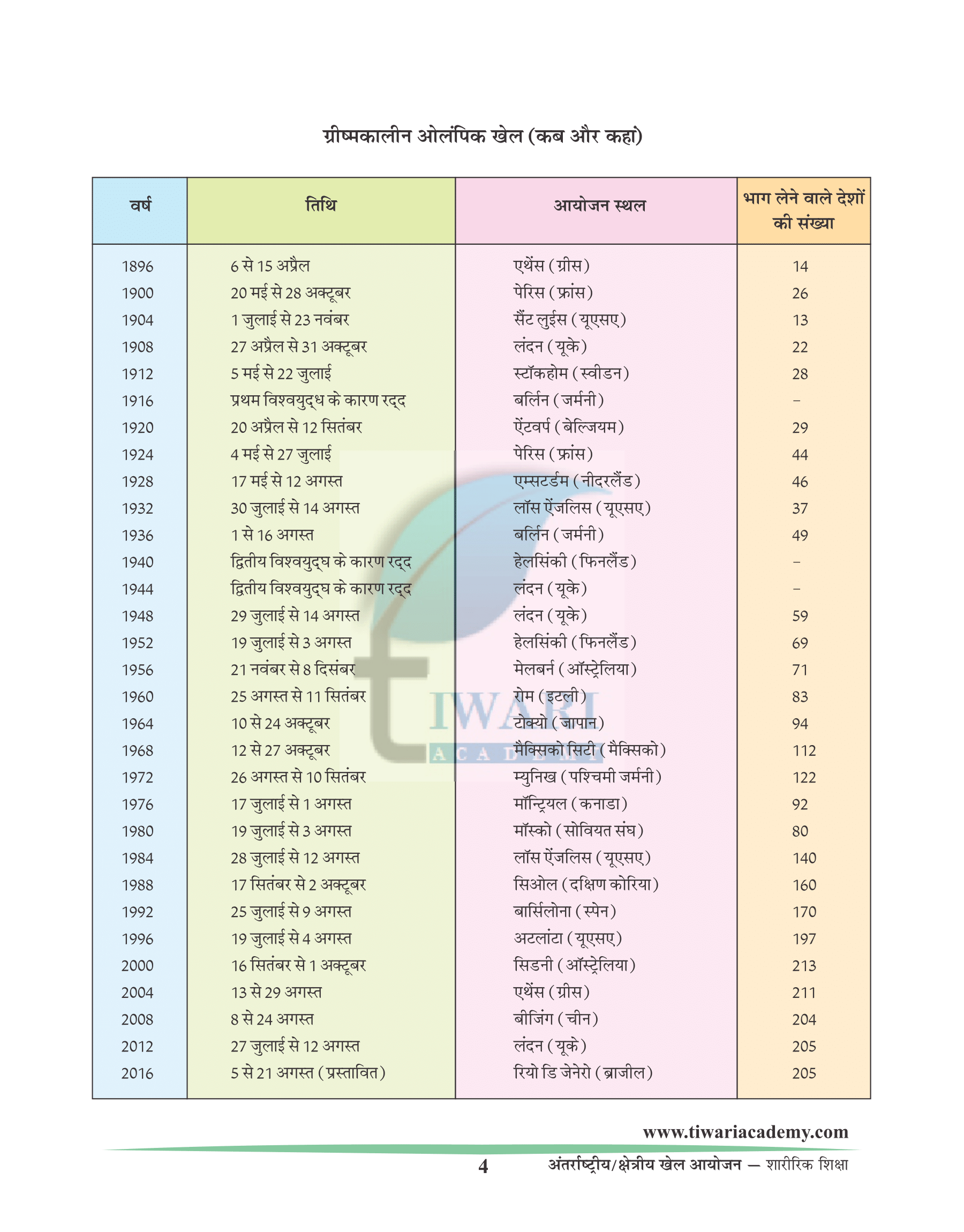
SUMMER OLYMPIC GAMES (When and where)
| Year | Dates | Host City |
|---|---|---|
| 1996 | 19-07 – 4-08 | Atlanta (United States) |
| 2000 | 16-09 – 1-10 | Sydney (Australia) |
| 2004 | 13-08 – 29-08 | Athens (Greece) |
| 2008 | 08-08 – 24-08 | Beijing (China) |
| 2012 | 27-07 – 12-08 | London (United Kingdom) |
| 2016 | 05-08 – 21-08 | Rio de Janeiro (Brazil) |
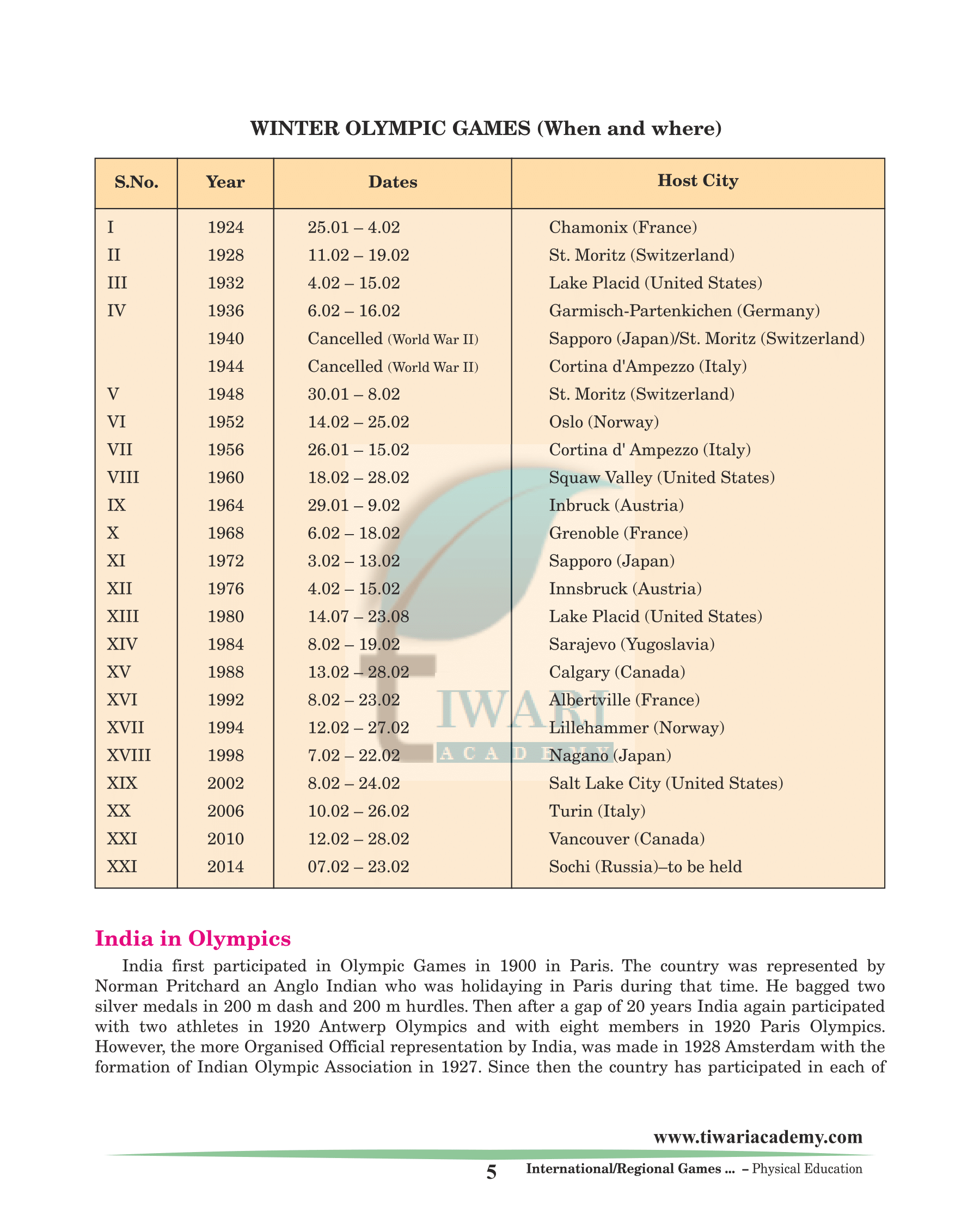
WINTER OLYMPIC GAMES (When and where)
| Year | Dates | Host City |
|---|---|---|
| 1998 | 7.02 – 22.02 | Nagano (Japan) |
| 2002 | 8.02 – 24.02 | Salt Lake City (United States) |
| 2006 | 10.02 – 26.02 | Turin (Italy) |
| 2010 | 12.02 – 28.02 | Vancouver (Canada) |
| 2014 | 07.02 – 23.02 | Sochi (Russia) |
India in Olympics
India first participated in Olympic Games in 1900 in Paris. The country was represented by Norman Pritchard an Anglo Indian who was holidaying in Paris during that time. He bagged two silver medals in 200 m dash and 200 m hurdles. Then after a gap of 20 years India again participated with two athletes in 1920 Antwerp Olympics and with eight members in 1920 Paris Olympics. However, the more Organised Official representation by India, was made in 1928 Amsterdam with the formation of Indian Olympic Association in 1927. Since then the country has participated in each of the Olympic Summer Games. Indian has also participated in Several Winter Olympic Games since 1964.
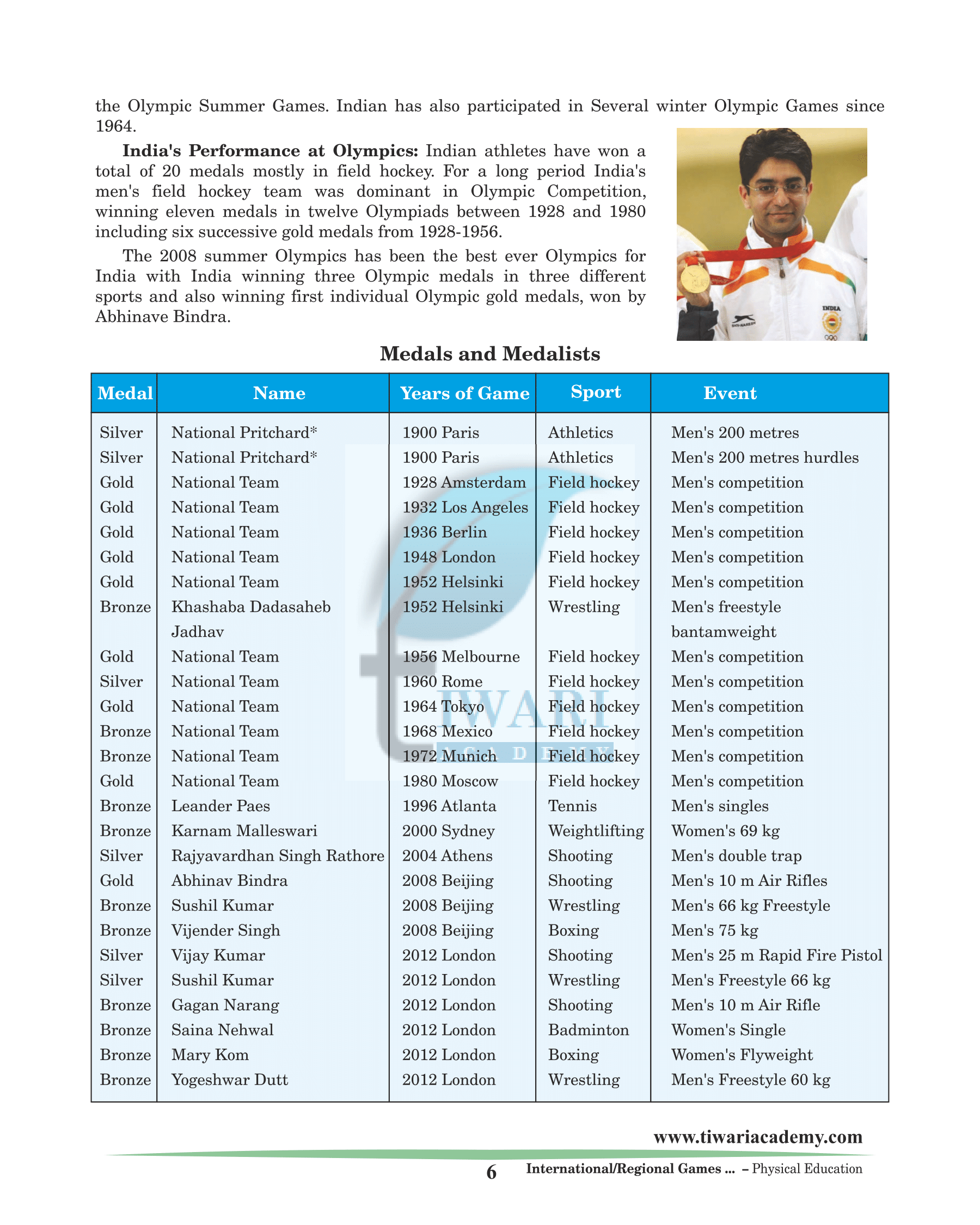
India’s Performance at Olympics
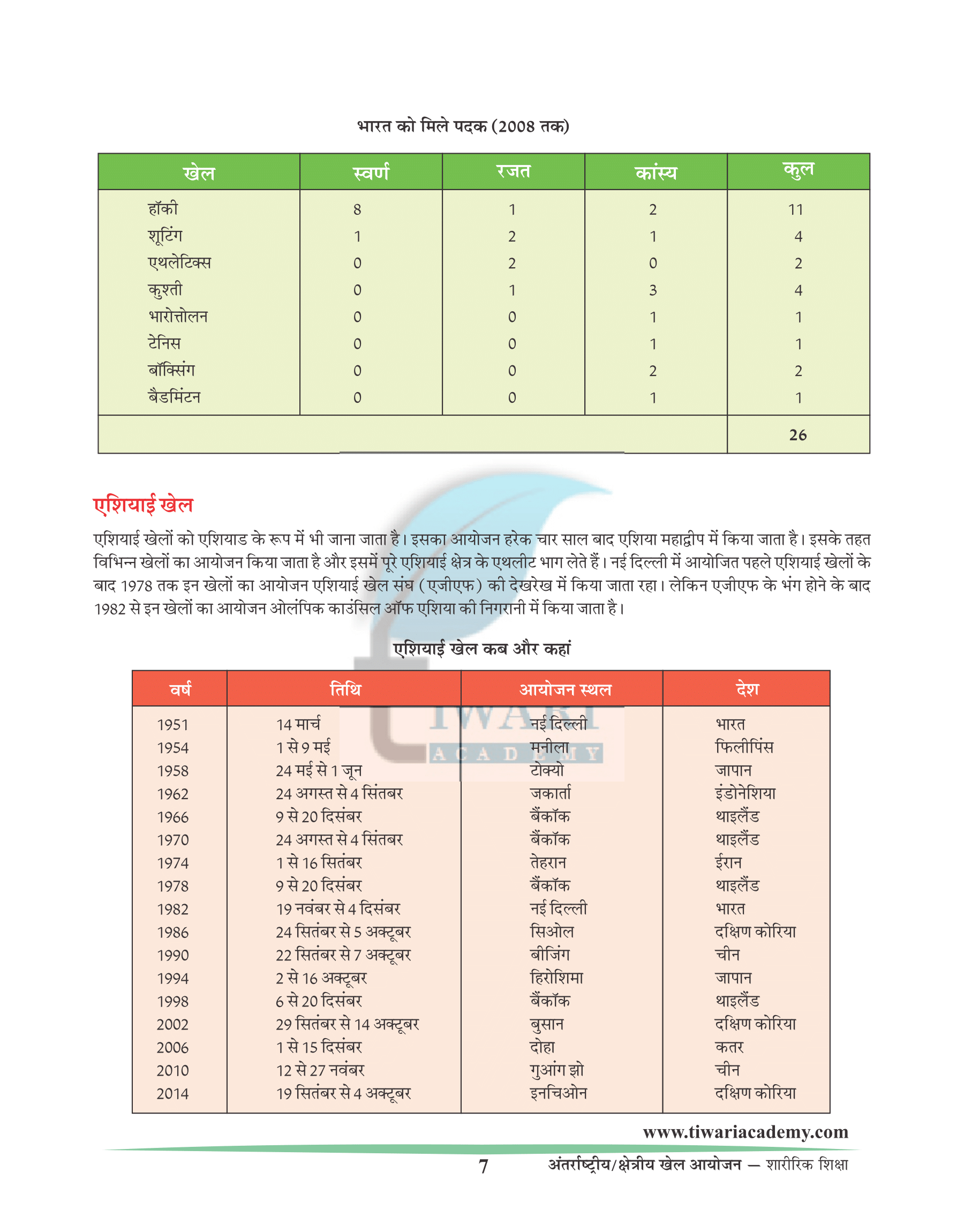
Indian athletes have won a total of 20 medals mostly in field hockey. For a long period India’s men’s field hockey team was dominant in Olympic Competition, winning eleven medals in twelve Olympiads between 1928 and 1980 including six successive gold medals from 1928-1956.
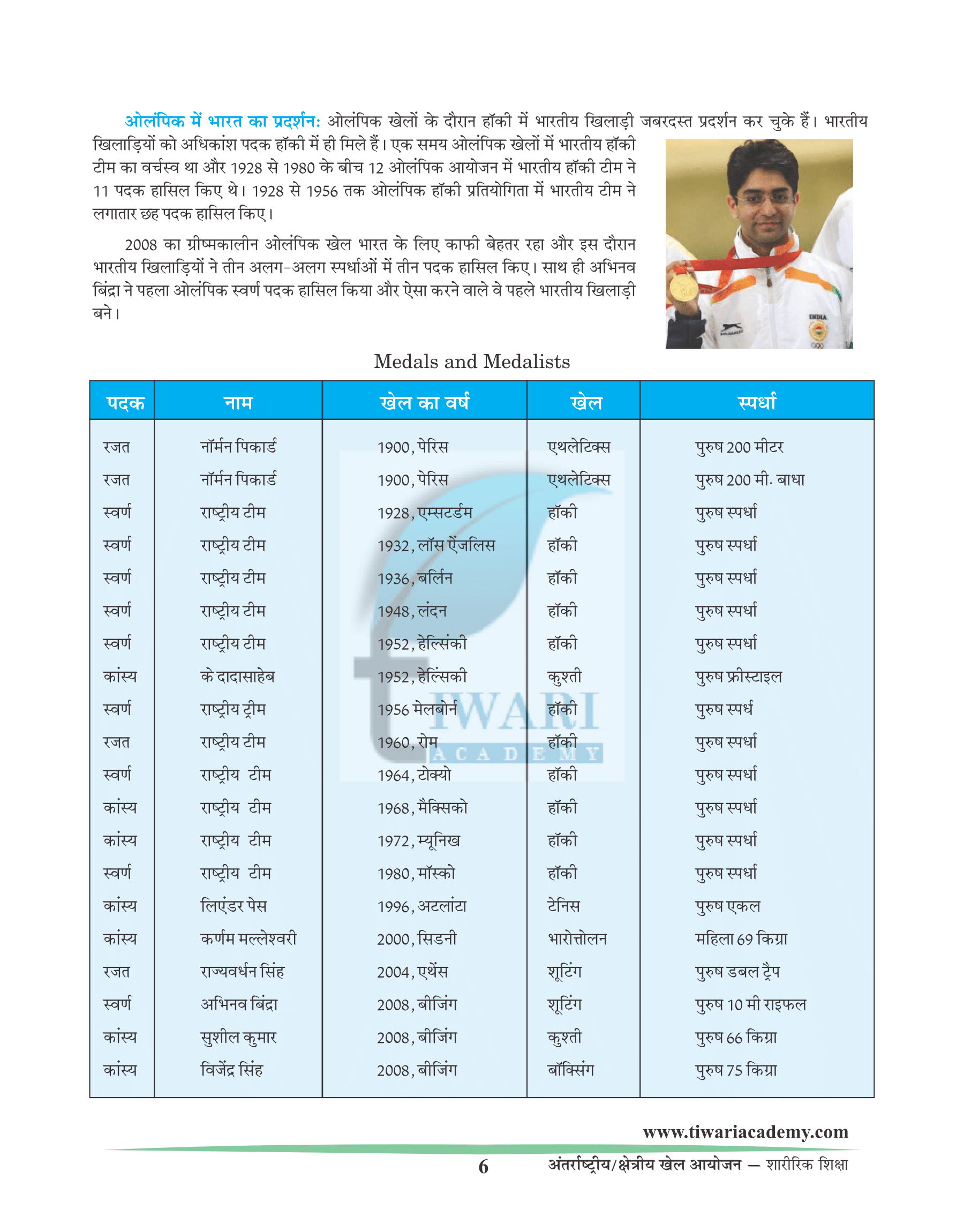
The 2008 summer Olympics has been the best ever Olympics for India with India winning three Olympic medals in three different sports and also winning first individual Olympic gold medals, won by Abhinave Bindra.
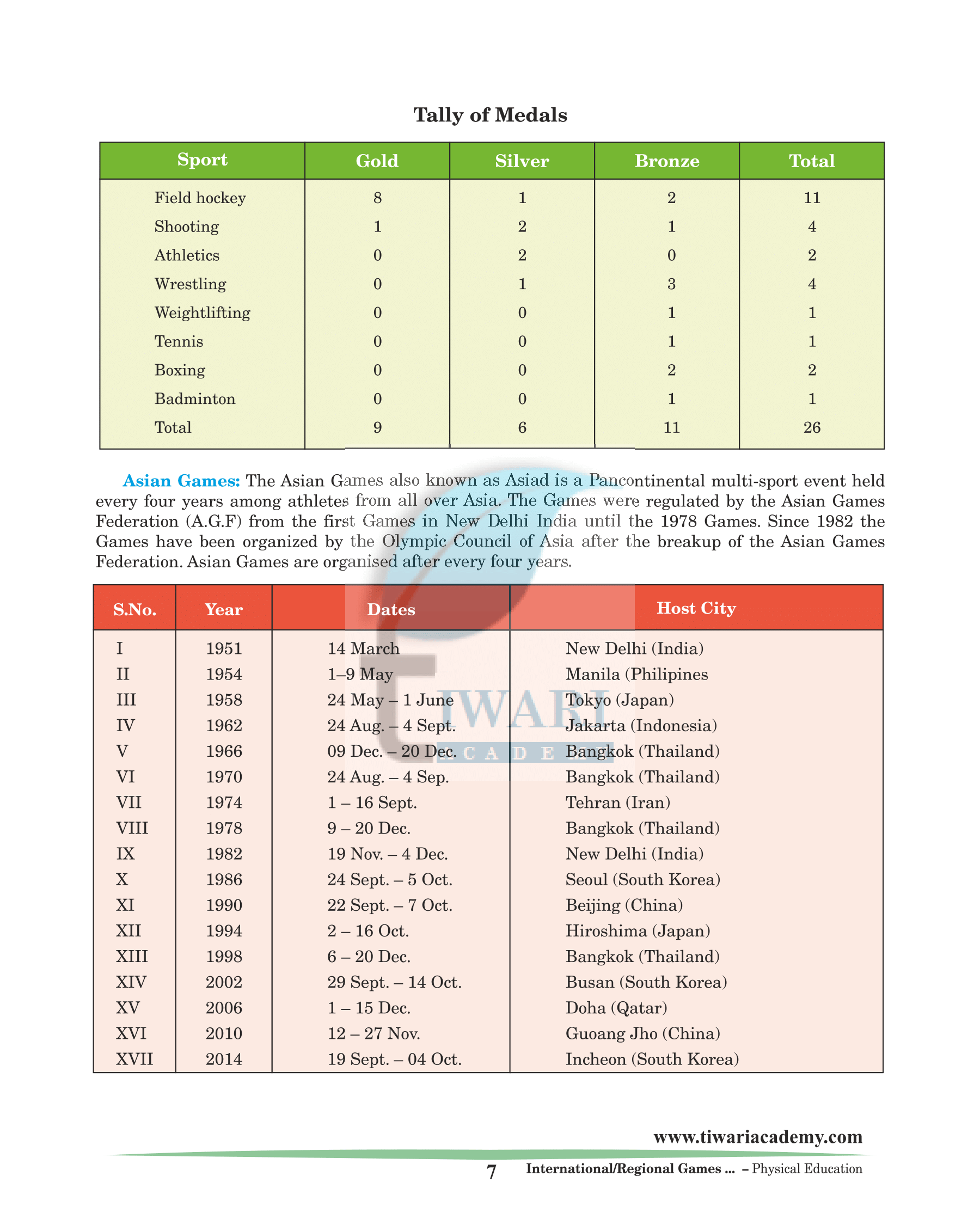
Tally of Medals
| Sports | Gold | Silver |
|---|---|---|
| Field hockey | 8 | 1 |
| Shooting | 1 | 2 |
| Athletics | 0 | 2 |
| Wrestling | 0 | 1 |
| Weightlifting | 0 | 0 |
| Tennis | 0 | 0 |
| Boxing | 0 | 0 |
| Badminton | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 9 | 6 |
| Sports | Bronze | Total |
|---|---|---|
| Field hockey | 2 | 11 |
| Shooting | 1 | 4 |
| Athletics | 0 | 2 |
| Wrestling | 3 | 4 |
| Weightlifting | 1 | 1 |
| Tennis | 1 | 1 |
| Boxing | 2 | 2 |
| Badminton | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 11 | 26 |
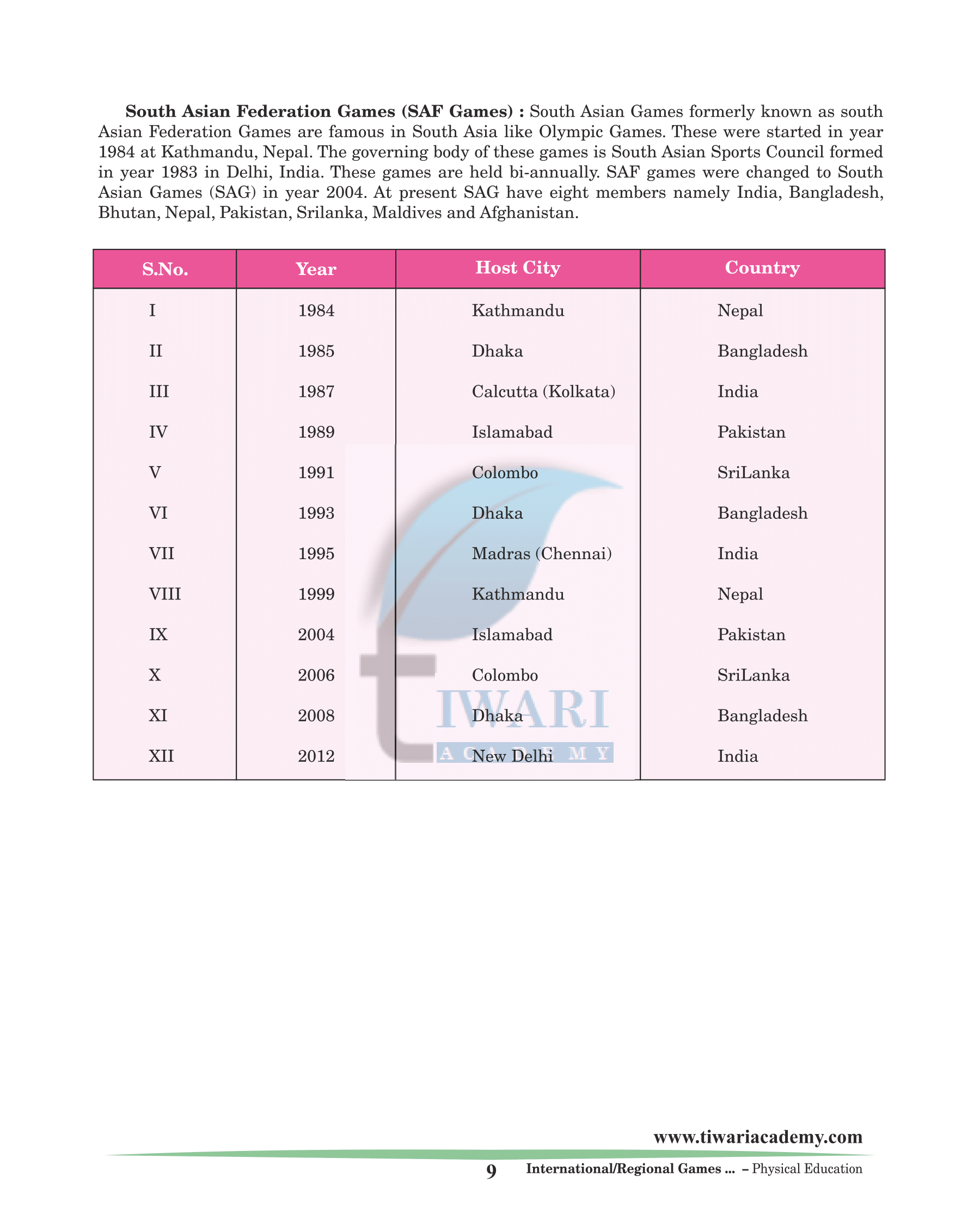
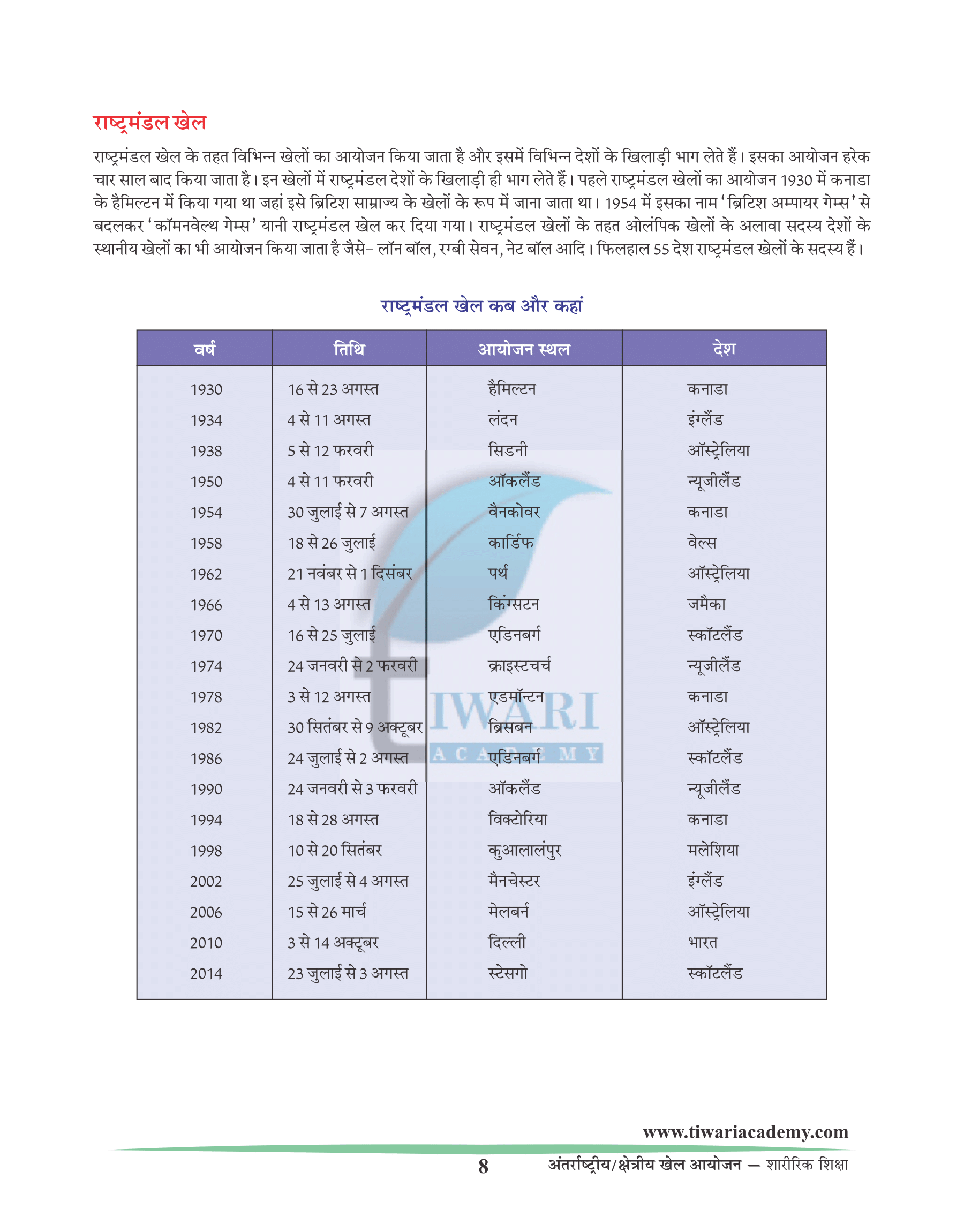
Asian Games
The Asian Games also known as Asiad is a Pan-continental multi-sport event held every four years among athletes from all over Asia. The Games were regulated by the Asian Games Federation (A.G.F) from the first Games in New Delhi India until the 1978 Games. Since 1982 the Games have been organized by the Olympic Council of Asia after the breakup of the Asian Games Federation. Asian Games are organised after every four years.
| Year | Dates | Host City |
|---|---|---|
| 1998 | 6 – 20 Dec. | Bangkok (Thailand) |
| 2002 | 29 Sept. – 14 Oct. | Busan (South Korea) |
| 2006 | 1 – 15 Dec. | Doha (Qatar) |
| 2010 | 12 – 27 Nov | Guoang Jho (China) |
| 2014 | 19 Sept. – 04 Oct. | Incheon (South Korea) |
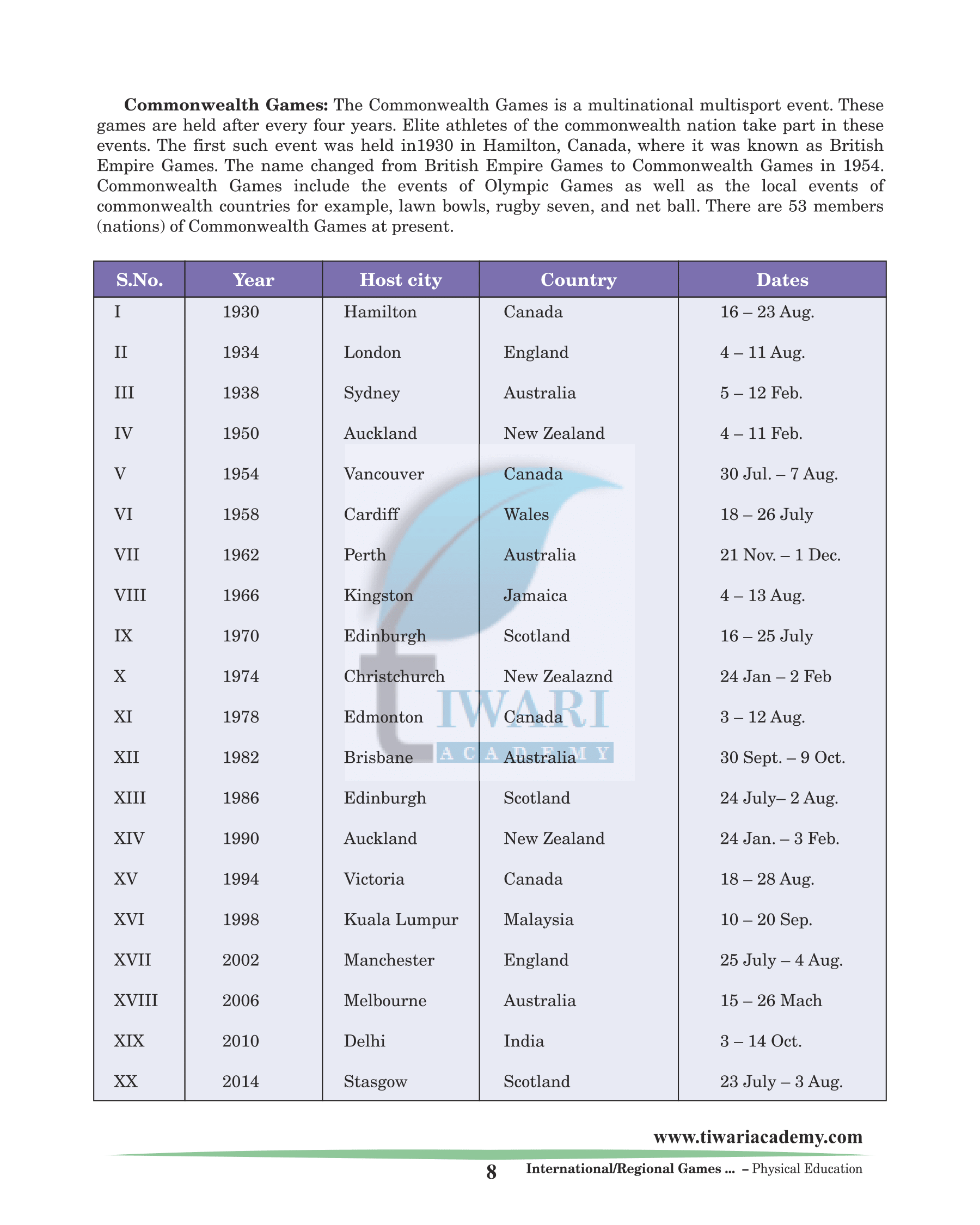
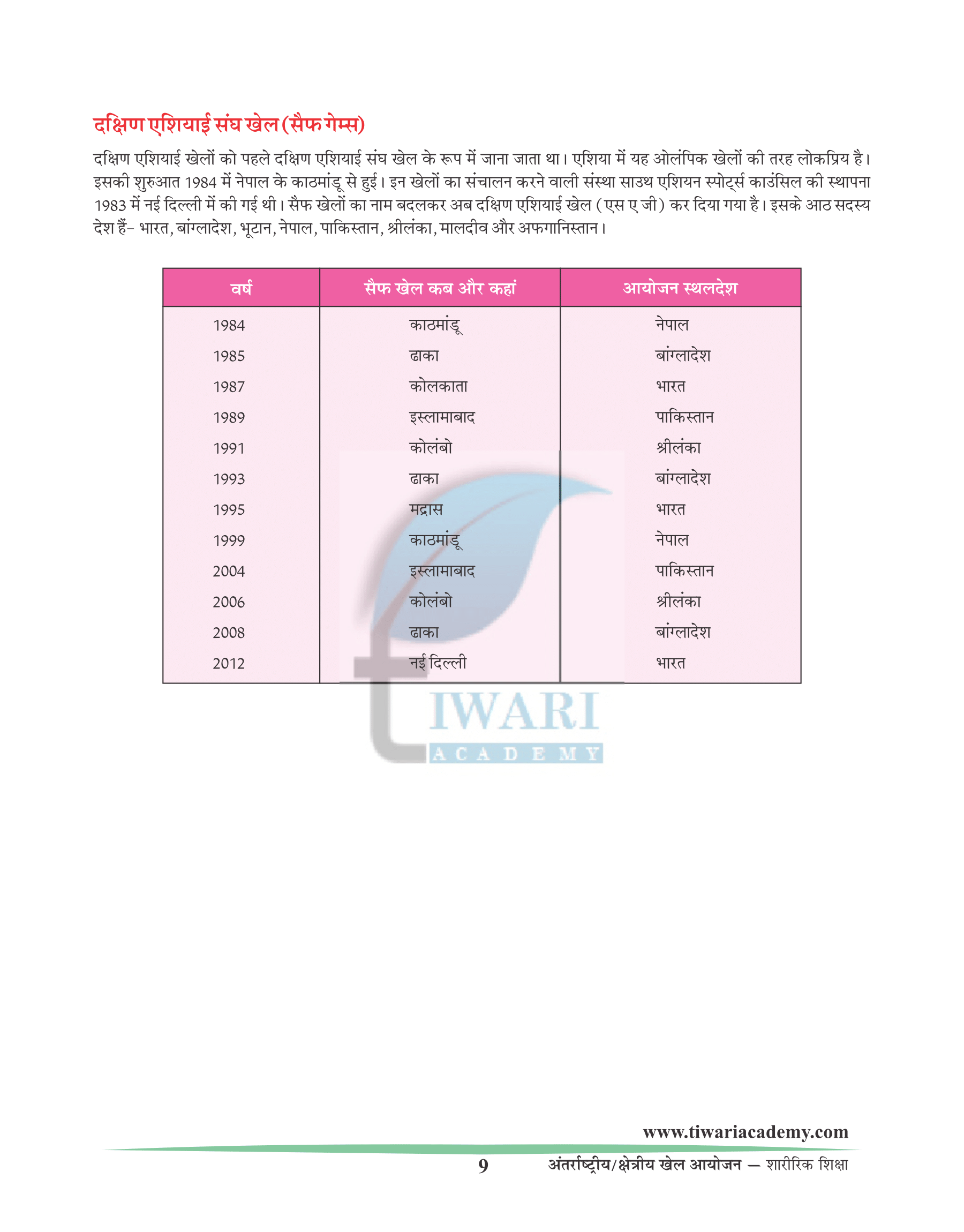
Commonwealth Games
The Commonwealth Games is a multinational multisport event. These games are held after every four years. Elite athletes of the commonwealth nation take part in these events. The first such event was held in1930 in Hamilton, Canada, where it was known as British Empire Games. The name changed from British Empire Games to Commonwealth Games in 1954. Commonwealth Games include the events of Olympic Games as well as the local events of commonwealth countries for example, lawn bowls, rugby seven, and net ball. There are 53 members (nations) of Commonwealth Games at present.
| Year | Dates | Host City |
|---|---|---|
| 1998 | 10 – 20 Sep. | Kuala Lumpur (Malaysia) |
| 2002 | 25 July – 4 Aug. | Manchester (England) |
| 2006 | 15 – 26 March | Melbourne (Australia) |
| 2010 | 3 – 14 Oct. | Delhi (India) |
| 2014 | 23 July – 3 Aug. | Stasgow (Scotland) |