NIOS Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Light Energy in Hindi and English Medium revised and updated for new academic session 2025-26. The solutions of NIOS Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Question Answers simplified for upcoming exams.
Light Energy: A Comprehensive Overview
The Essence of Light: Light, a form of energy, renders objects visible to us, shaping our perception of the world. This energy, whether emanating from luminous objects like the sun and candles or reflected by other surfaces, plays a pivotal role in visual perception. The phenomenon of light reflection and refraction not only contributes to our basic visual capabilities but also explains various natural occurrences and the functioning of optical devices.
Reflection and Its Laws
Reflection occurs when light bounces off surfaces, a phenomenon governed by precise laws. These laws, first articulated by ancient scholars like Euclid and later refined by Alhazen, underpin the behavior of light upon encountering reflective surfaces. The process, depending on the surface’s nature, can be categorized into regular (mirror-like reflection) and diffused (scattered reflection) types. The study of reflection extends to understanding image formation through plane and spherical mirrors, contributing significantly to optical science.
Mirrors and Image Formation
Mirrors, whether plane or spherical (convex and concave), have the unique ability to form images through the reflection of light. The formation of images by mirrors is a foundational concept in optics, explaining how we perceive reflected images. Plane mirrors produce virtual images identical in size to the objects they reflect, while spherical mirrors can create varied images depending on the object’s position relative to the mirror’s focal point.
Refraction: Bending Light
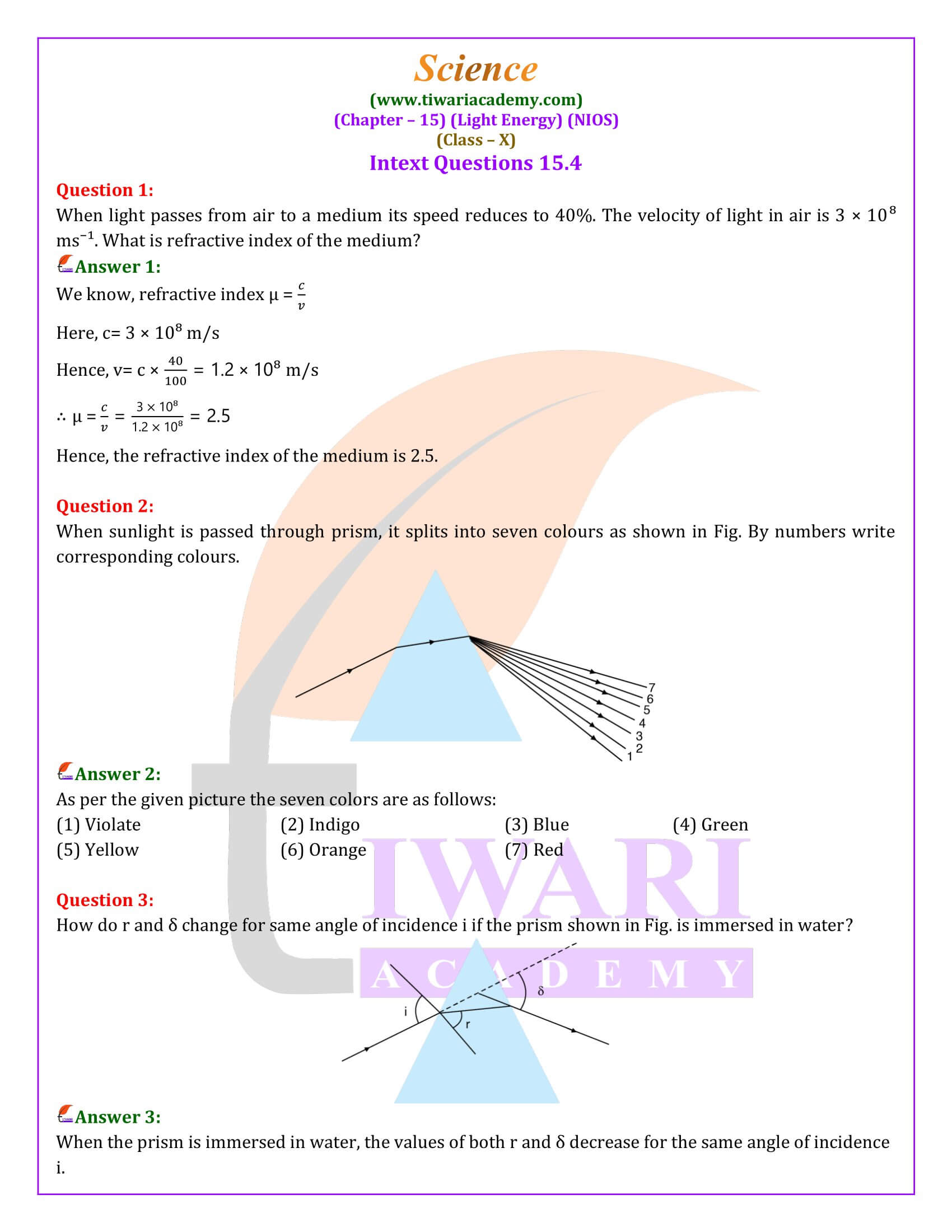
Refraction, the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another, underlies many optical phenomena and technologies. This process is governed by Snell’s law, which relates the angles of incidence and refraction to the refractive indices of the involved media. Refraction’s effects are evident in everyday experiences, such as the apparent bending of a straw in water and the dispersal of light into a spectrum when passed through a prism.
Lenses: Focusing Light
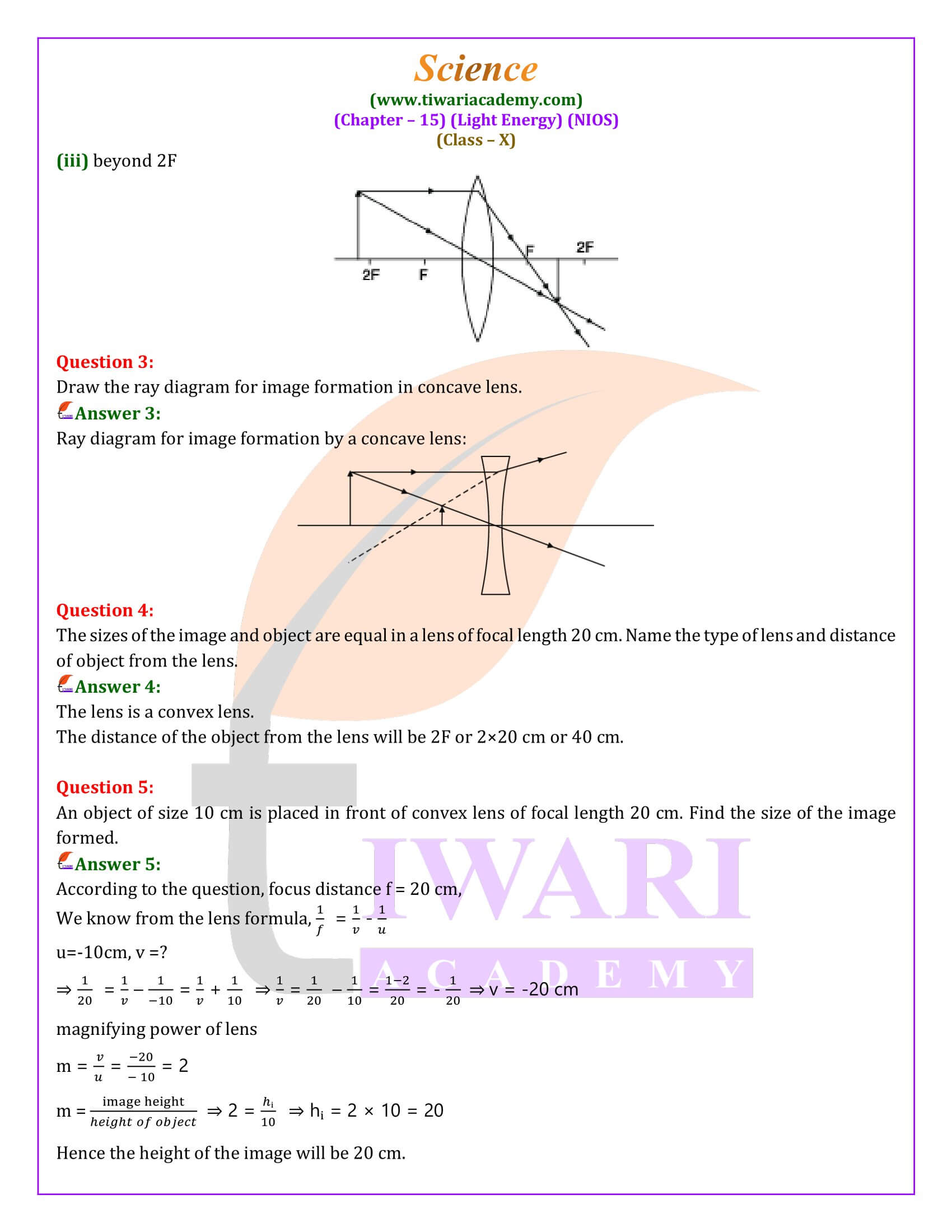
Lenses, crafted from transparent materials, are designed to either converge or diverge light rays. Convex lenses, or converging lenses, focus light rays to a point, whereas concave lenses, or diverging lenses, spread them apart. The behavior of lenses is crucial for various applications, including vision correction, magnification, and the focusing of light for imaging purposes.
Vision and Optical Corrections
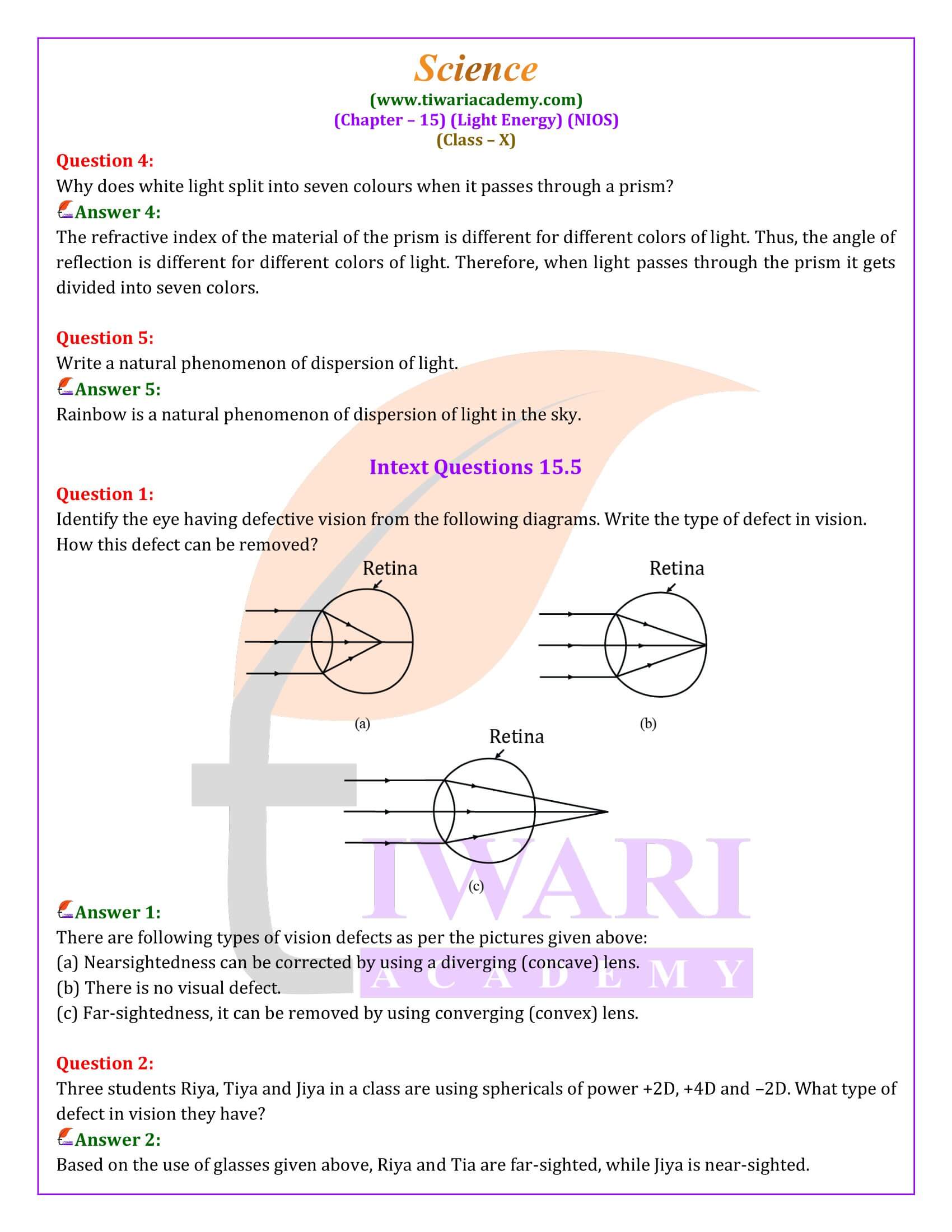
The human eye, a marvel of nature’s design, relies on refraction to focus light onto the retina. However, vision imperfections such as myopia (shortsightedness) and hypermetropia (farsightedness) necessitate optical corrections. These corrections are achieved through the use of specific lenses that adjust the eye’s focusing ability, enabling clear vision across different distances.
Dispersion: The Spectrum of Light
Dispersion, the splitting of white light into its constituent colors, illustrates the wavelength-dependent refractive index of materials. This phenomenon, observable in rainbows and through prisms, highlights the diverse nature of light and its integral role in the colorful visual experiences of the natural world.
Light energy, with its dual nature of reflection and refraction, not only illuminates the world around us but also provides the basis for a myriad of natural phenomena and technological advancements. From the simple reflection in a mirror to the complex mechanisms of the human eye, the study of light continues to be a source of fascination and innovation, illuminating the path to understanding the visual universe.