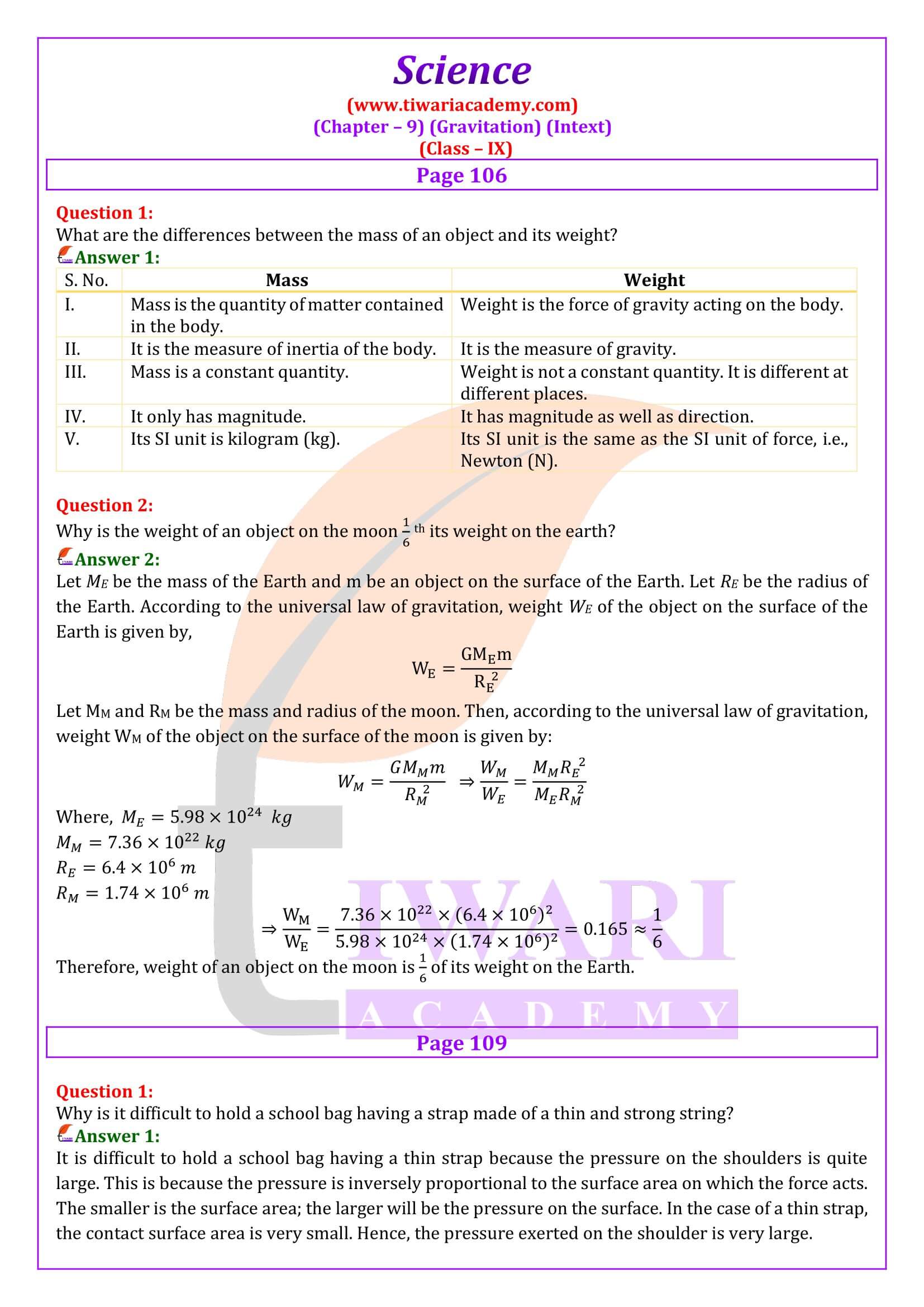
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Gravitation in Hindi and English Medium updated for academic session 2025-26. The question answers and explanation is modified according to new rationalised NCERT Books issued for 2025-26 exams.
Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Question Answers
- Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Exercises
- Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Intext Questions
- Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Extra Questions
- Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Hindi Medium
- Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Notes in English
- Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Notes in Hindi
- Class 9 Science Chapter 9 NCERT Book
- Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 all Subjects NCERT Solutions
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 9
Class IX Science chapter 9 answers of intext questions given on Page 134 or Page 136 or Page 138 or Page 141 or Page 142 or Exercises. Download Class 9 Science chapter 9 UP Board Solutions in Hindi Medium also. You can download Page 149 ke Uttar or Page 152 ke uttar or Page 153 ke Uttar or Page 157 ke Uttar or Page 158 ke Uttar or Abhyaas ke Uttar in Hindi Medium free to use. NCERT Solutions Apps for class IX are also available for download free based on latest CBSE Syllabus.
| Class: 9 | Science |
| Chapter 9: | Gravitation |
| Content: | Exercise and Intext Answers |
| Content Mode: | Text, PDF and Videos |
| Session: | 2025-26 |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
9th Science Chapter 9 Answers in English & Hindi Medium
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Gravitation Intext Questions and Exercise questions are given below in Hindi and English Medium updated for session 2025-26. Solutions are based on latest CBSE Books 2025-26 based on new CBSE Syllabus 2025-26.
Extra Questions on 9th Science Chapter 9
A particular is dropped from a tower 180 m high. How long does it take to reach the ground? What is the velocity when it touches the ground?
Take g = 10 m/s².
Answer:
6 s, 60 m/s
How much would a 70 kg man weigh on moon? What will be his miss mass on earth and moon? Given g on moon = 1∙7 m/s².
119 N, 70 kg, 70 kg
Calculate the value of acceleration due to gravity on Moon. Give n mass of moon = 7.4 x 10²² kg, radius of moon = 1740 km.
1.63 m/s²
A car weighs 1200 kg. This weight is evenly distributed on 4 wheels. If the pressure in each Tyre is 15 kg wf/cm², what is the area of each Tyre in contact.
20 cm²
Why are sleeper used below the rails?
Sleeper are placed below the rails to increase area (A) and to consequently decrease pressure (P) due to weight (W) of a train on the rails as P= F/A = W/A (∙.∙ F = W). This prevents the railways line from sinking into ground.
The mass of a block made of certain material is 13.5 kg and its volume is 15 x 10-³ m³. Will the block float or sink in water? Give reason for your answer.
The block floats.
Relative density of silver is 10.8. The density of water is 10³ kg/m³. What is the density of silver in SI units?
10.8 x 10³ kg/m³
Questions for Practice on 9th Science Chapter 9
Question 1:
A boy weighing 60 kg f is wearing shoes with heel area of cross-section 20 cm² while a girl weighing 45 kg f wearing shoes with heel of area of cross-section 1.5 cm². Compare the pressure exerted on ground by their heels when they stand on the heel of one foot.
Answer 1:
The girl’s shoe heel exerts a pressure 10 times more than the boy’s shoes heel.
Question 2:
A car falls off a ledge and drops to the ground in 0.5 s. Let g = 10 m/s² (for simplifying the calculations).
(a) What is its speed on striking the ground?
(b) What is its average speed during 0.5 s?
(c) How high is the ledge from the ground?
Answer 2:
(a) 5 m/s (b) 2.5 m/s (c) 1.25 m
Question 3:
A block of wood is kept on a table top. The mass of the wooden block is 5 kg and its dimensions are 40 cm x 20 cm x 10 cm. Find the pressure exerted by the wooden block on the table top if it is made to lie on the table with its sides of dimensions (a) 20 cm x 10 cm (b) 40 cm x 20 cm. given g = 9.8 m/s².
Answer 3:
(a) 2450 Pa (b) 612.5 Pa
Important Questions on 9th Science Chapter 9
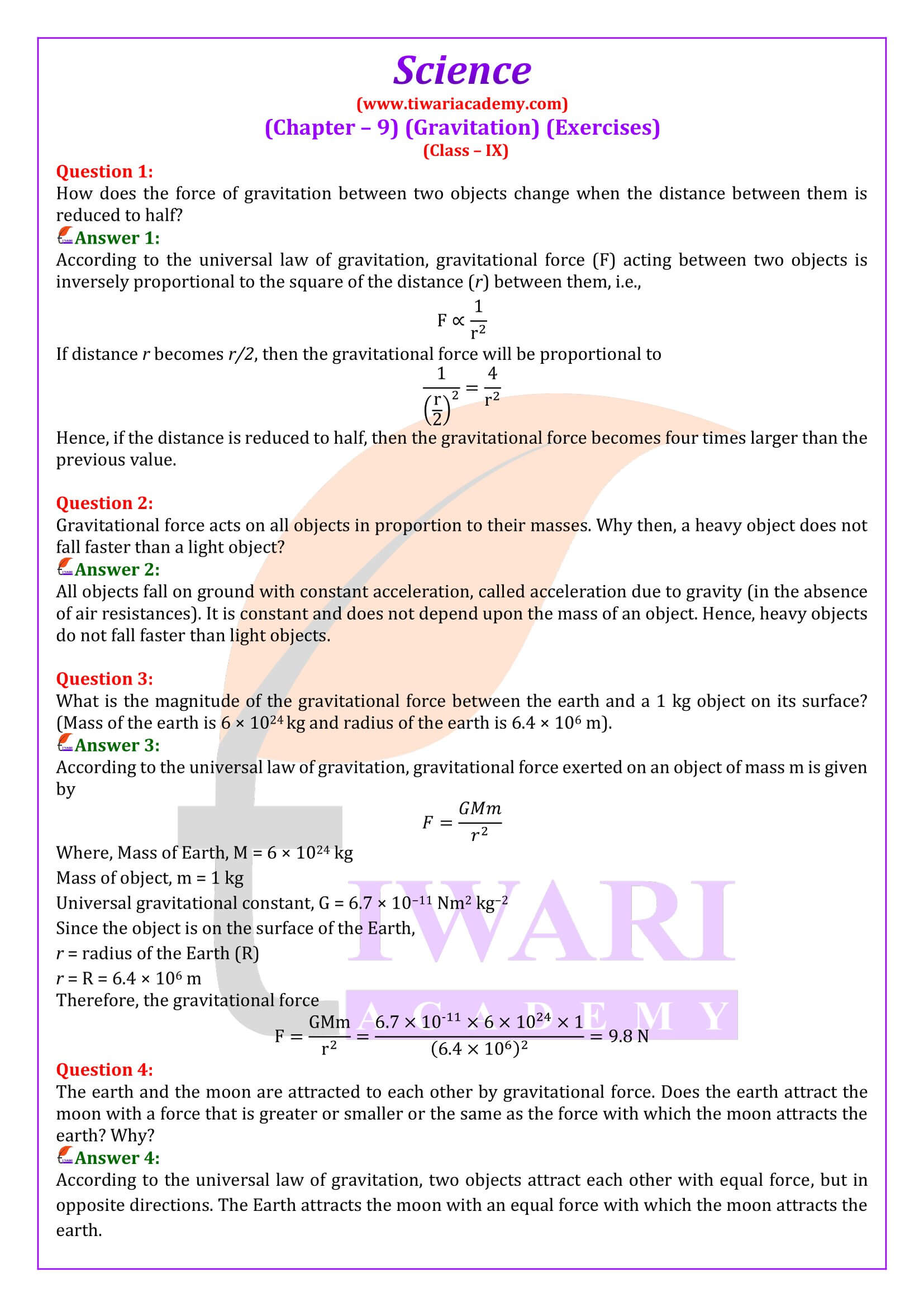
Gravitational force acts on all objects in proportion to their masses. Why then, a heavy object does not fall faster than a light object?
All objects fall on ground with constant acceleration, called acceleration due to gravity (in the absence of air resistances). It is constant and does not depend upon the mass of an object. Hence, heavy objects do not fall faster than light objects.
The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does the earth attract the moon with a force that is greater or smaller or the same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth? Why?
According to the universal law of gravitation, two objects attract each other with equal force, but in opposite directions. The Earth attracts the moon with an equal force with which the moon attracts the earth.
If the moon attracts the earth, why does the earth not move towards the moon?
The Earth and the moon experience equal gravitational forces from each other. However, the mass of the Earth is much larger than the mass of the moon. Hence, it accelerates at a rate lesser than the acceleration rate of the moon towards the Earth. For this reason, the Earth does not move towards the moon.
What is the importance of universal law of gravitation?
The universal law of gravitation proves that every object in the universe attracts every other object.
What do we call the gravitational force between the Earth and an object?
Gravitational force between the earth and an object is known as the weight of the object.
Why will a sheet of paper fall slower than one that is crumpled into a ball?
When a sheet of paper is crumbled into a ball, then its density increases. Hence, resistance to its motion through the air decreases and it falls faster than the sheet of paper.
In what direction does the buoyant force on an object immersed in a liquid act?
An object immersed in a liquid experiences buoyant force in the upward direction.
Why does a block of plastic released under water come up to the surface of water?
Two forces act on an object immersed in water. One is the gravitational force, which pulls the object downwards, and the other is the buoyant force, which pushes the object upwards. If the upward buoyant force is greater than the downward gravitational force, then the object comes up to the surface of the water as soon as it is released within water. Due to this reason, a block of plastic released under water comes up to the surface of the water.