NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Work and Energy in Hindi and English Medium updated for CBSE session 2025-26. The question answers and solutions of chapter 10 class 9 Science is modified according to new rationalised NCERT textbooks published for academic year 2025-26.
Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Question Answers
- Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Exercises
- Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Intext Questions
- Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Extra Questions
- Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Hindi Medium
- Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Notes in English
- Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Notes in Hindi
- Class 9 Science Chapter 10 NCERT Book
- Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions
- Class 9 all Subjects NCERT Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10
Class IX Science chapter 10 Intext question answers on Page 148 or Page 149 or Page 152 or Page 156 or Exercises. Download CBSE and UP Board Hindi Medium Solutions of Class 9 Science chapter 10 Page 164 ke Uttar or Page 165 ke Uttar or Page 169 ke Uttar or Page 174 ke Uttar or Abhyaas ke Uttar to study online or in PDF format. Download NCERT Solutions and Solutions Apps for class 9 other subjects also.
CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Work and Energy all Intext Questions and exercises question answers given at the end of chapter are given below to free download. Visit to Discussion Forum to share your knowledge or ask your doubts with our experts and your classmates. Tiwari Academy NCERT Solutions and Offline Apps are free to use for all users.
| Class: 9 | Science |
| Chapter 10: | Work and Energy |
| Content: | Intext and Exercises Solution |
| Content Type: | Text and Videos Format |
| Session: | 2025-26 |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
Extra Questions on 9th Science Chapter 10
A boy of mass 55 kg runs up a flight of 40 stairs, each measuring 0.15 m. calculate the work done bye the boy.
3300 J
What is the difference between potential energy and kinetic energy?
Potential energy of a body is by virtue of its position or shape whereas kinetic energy of a body is by virtue of its motion.
Why do some engines require fuels like petrol and diesel?
Internal combustion heat engines use the chemical energy of fossil fuels (petrol and diesel) for their operation. These engines first convert the chemical energy of the fuels into heat energy which is later on converted into mechanical energy.
A porter lifts a luggage of 15 kg from the ground and puts it on his head 1.5 m above the ground. Calculate the work done by him on the luggage.
225 J
A bullet of mass 20 g is found to pass two points 30 m apart in 4 s? Assuming the speed to be constant, find its kinetic energy.
0.5625 J
Two girls, each of weight 400 N, climb up a rope through a height of 8 m. We name one girl A and the other girl B. Girl A takes 20 s while b takes 50 s to accomplished this task. What is the power expended by each girl?
160 W, 64 W
Questions for Practice on 9th Science Chapter 10
Important Questions on 9th Science Chapter 10
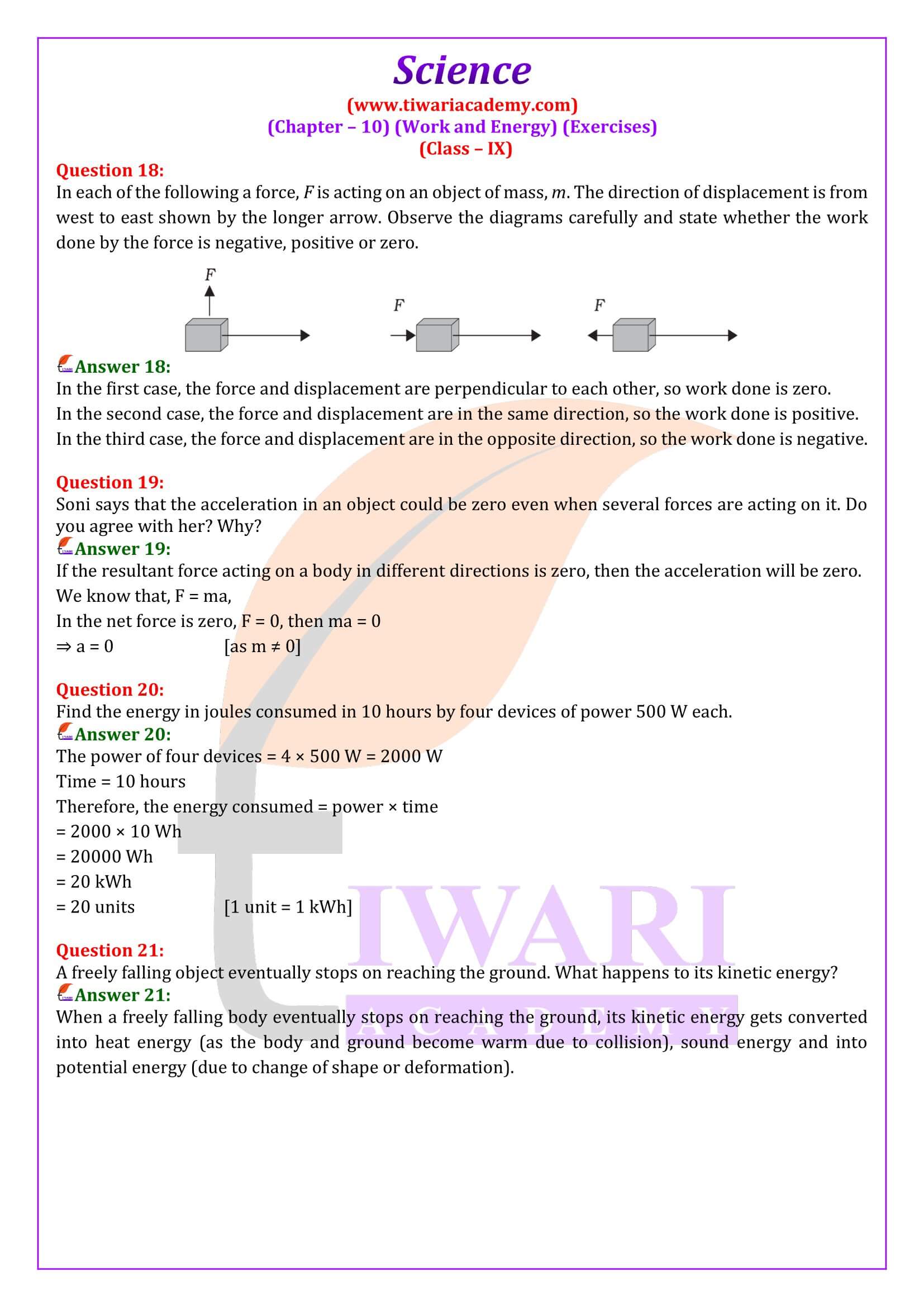
An object thrown at a certain angle to the ground moves in a curved path and falls back to the ground. The initial and the final points of the path of the object lie on the same horizontal line. What is the work done by the force of gravity on the object?
When the object moves upwards, the work done by gravity is negative (as the direction of gravitational force is towards the Earth’s center) and when the object come downwards, there is a positive work done. So, the total work down is zero in throughout the motion.
A battery lights a bulb. Describe the energy changes involved in the process.
Battery converts chemical energy into electrical energy. This electrical energy is further converted into light and heat energy.
A mass of 10 kg is at a point A on a table. It is moved to a point B. If the line joining A and B is horizontal, what is the work done on the object by the gravitational force? Explain your answer.
The work down by the gravitational force acting on the body is zero because the direction of force is vertically downward and the displacement is horizontal i.e. force and displacement are perpendicular to each other.
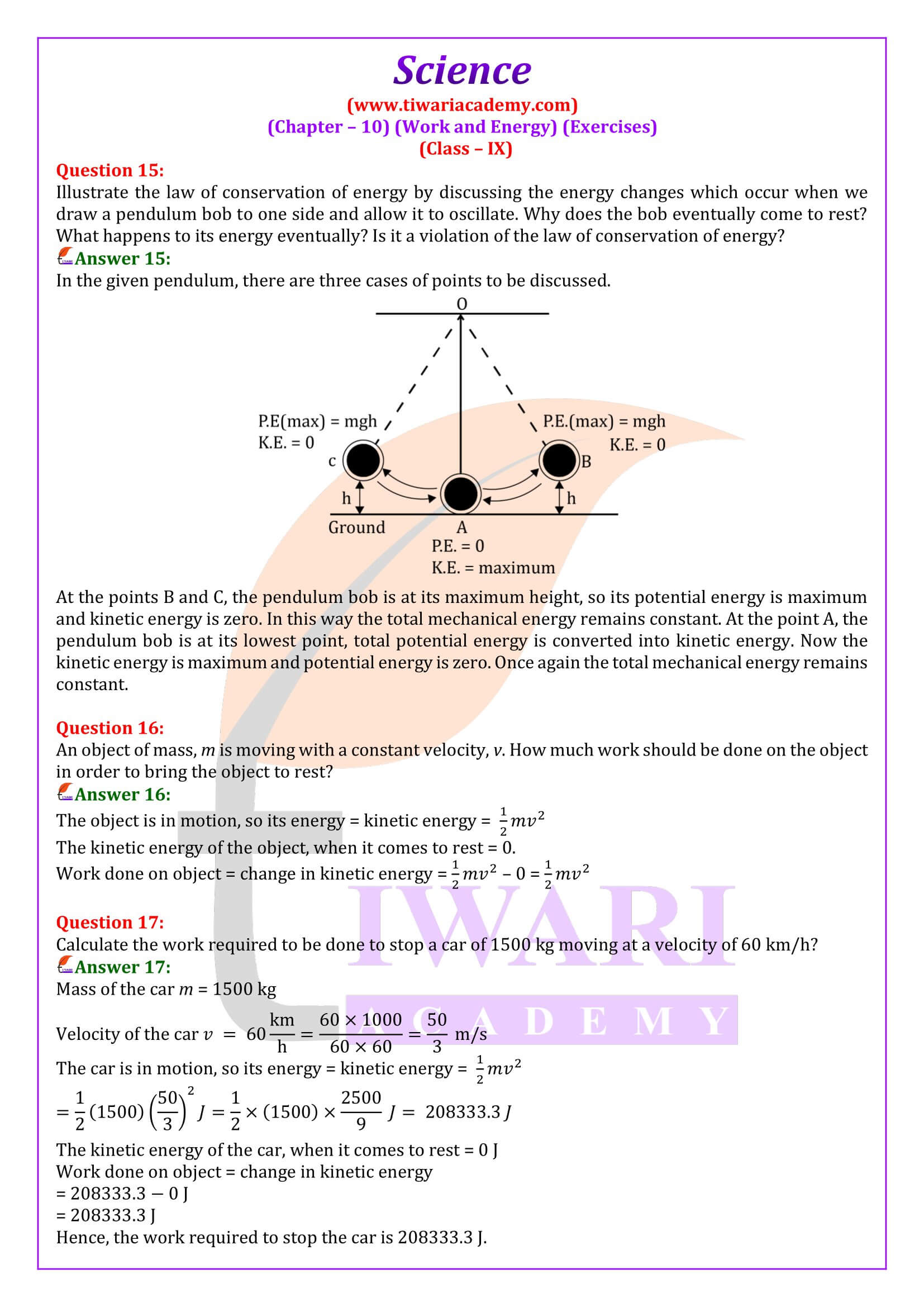
The potential energy of a freely falling object decreases progressively. Does this violate the law of conservation of energy? Why?
The potential energy of freely falling object decreases and its kinetic energy increases (as its velocity increases) progressively. So, in this way the total mechanical energy (Kinetic energy + potential energy) remains constant. Thus, the law of conservation of energy is not violated.
What are the various energy transformations that occur when you are riding a bicycle?
The muscular energy of the cyclist is converted into kinetic (rotational) energy of wheels of cycle which is further converted into kinetic energy to run the bicycle.
Does the transfer of energy take place when you push a huge rock with all your might and fail to move it? Where is the energy you spend going?
When we push the rock and fail to move it. Some of our energy is absorbed by the rock in the form of potential energy and the rest of our energy is goes to environment through our muscles and the surface between the rock and out hand.
What is the work done by the force of gravity on a satellite moving round the Earth? Justify your answer.
When a satellite moves around the Earth, the displacement in short interval is along the tangential direction and the force (gravitational force) is towards the centre of the Earth. Since, the force and displacement are perpendicular to each other, the work done by gravitational force is zero.
A person holds a bundle of hay over his head for 30 minutes and gets tired. Has he done some work or not? Justify your answer.
The person holding a bundle of hay get tired because his muscular energy is converting into thermal energy. There is no displacement at all, so he had no work. As Work done = Force × displacement.
A freely falling object eventually stops on reaching the ground. What happens to its kinetic energy?
When a freely falling body eventually stops on reaching the ground, its kinetic energy gets converted into heat energy (as the body and ground become warm due to collision), sound energy and into potential energy (due to change of shape or deformation).
Question 1:
A bullet of mass 5 g travels with a speed of 500 m/s. if it penetrates a fixed target which offers a constant resistive force of 1000 N to the motion of the bullet, find (a) the initial kinetic energy of the bullet (b) the distance through which the bullet has penetrated.
Answer 1:
(a) 625 J (b) 0.625 m
Question 2:
A ball of mass 1 kg is dropped from a height of 5 m. (a) Find the kinetic energy of the ball just before it reaches the ground (b) what is the speed at this instant?
Answer 2:
(a) 50 J (b) 10 m/s
Question 3:
A man does 200 J of work in 10 s and a boy does 100 J of work in 4 s. (a) who is delivering more power? (b) Find the ratio of the power delivered by the man to that delivered by the man to that delivered by the boy.
Answer 3:
(a) The boy delivers more power
(b) 4/5 J