NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Exercise 4.3 Practical Geometry in Hindi and English Medium updated for CBSE new session. Access updated Tiwari Academy’s free NCERT solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4, Exercise 4.3 on Practical Geometry. Available in both Hindi and English for students following CBSE and state board guidelines. Simplify your geometry learning with our expert resources.
8th Maths Exercise 4.3 Solution in Hindi and English Medium
Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Exercise 4.3 Solution
Class VIII Maths Ex. 4.3 of chapter 4 Practical Geometry free to download in PDF file format updated for CBSE session 2025-26. In this exercise, we will construct quadrilaterals with two given sides and three given angles. Class 8 NCERT Textbook Maths ex. 4.3 is easy to solve as compared to other exercises of chapter 4 class 8th Maths. Videos with complete explanation and step by step solving are given with the solutions.
| Class: 8 | Mathematics |
| Chapter: 4 | Exercise: 4.3 |
| Topic Name: | Practical Geometry |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
| Content: | Online Text and Videso |
Class 8 Maths Exercise 4.3 Extra Questions for Practice
How do you write an adjacent side?
Adjacent side is the side next to the angle in question. (The one other than the hypotenuse). For example: Here, the side A is adjacent to the angle x.
What are adjacent sides and angles?
Two angles are Adjacent when they have a common side and a common vertex (corner point) and don’t overlap. They have a common side (line CB) they have a common vertex (point B).
Can 2 adjacent angles be complementary?
Two adjacent angles can be complimentary, if they add up to 90∘, i.e. the sum of two angles formed should be 90∘. They are also complementary as the sum of the angles is 90∘, i.e. ∠ABD+∠CBD=30∘+60∘=90∘.
When two adjacent sides and three angles are given
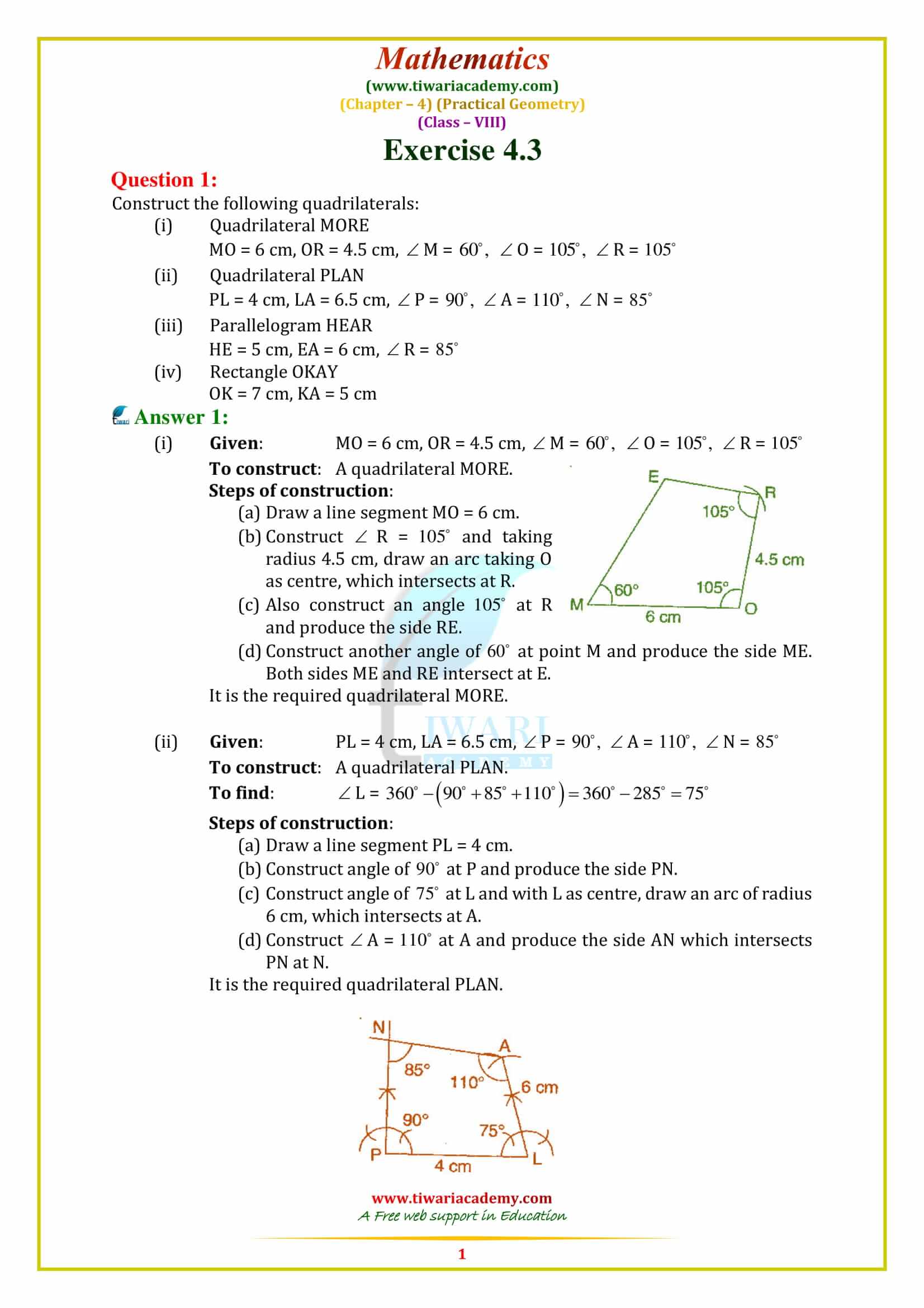
Construct a quadrilateral PQRS in which PQ = 4.5 cm, ∠PQR = 120°, QR = 3.8 cm, ∠QRS = 100° and ∠QPS = 60°.
First we draw a rough sketch of quad. PQRS and write down its dimensions, as given.
Steps of construction:
Step 1. Draw PQ = 4.5 cm.
Step 2. Make ∠PQX = 120°.
Step 3. With Q as centre and radius 3.8 cm, draw an arc, cutting QX at R.
Step 4. Make ∠QRY = 100°.
Step 5. Make ∠QPZ = 60°
So that PZ and RY intersect each other at the point S.
Then, PQRS is the required quadrilateral.
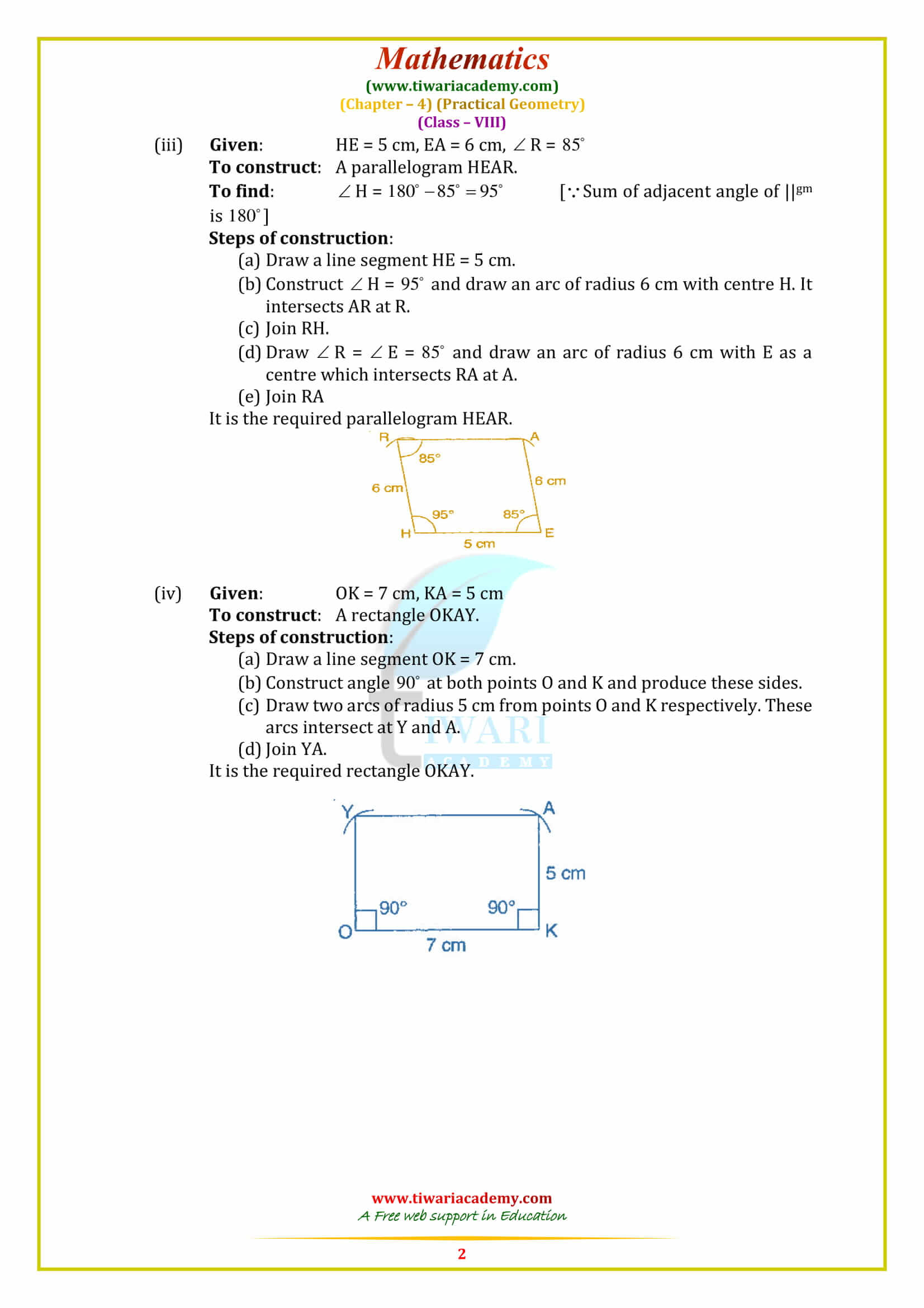
Question:
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD in which AB = 5.6 cm, BC = 4 cm, ∠A = 50°, ∠B = 105° and ∠D = 80°.
Solution:
First we draw a rough sketch of quad. ABCD and write down its dimensions, as given.
Steps of construction:
Step 1. Draw AB = 5.6 cm.
Step 2. Make ∠ABE = 105°
Step 3. With B as centre and radius 4 cm, draw an arc, cutting BE at C.
Step 4. Make ∠BAF = 50° (∠A + ∠B + ∠D = 50° + 105° + 80° = 2350, so, ∠C = 3600 – 2350 = 1250)
Step 5. Make ∠BCD = 125°
So that AF and CG intersect each other at the point D.
Then, ABCD is the required quadrilateral.