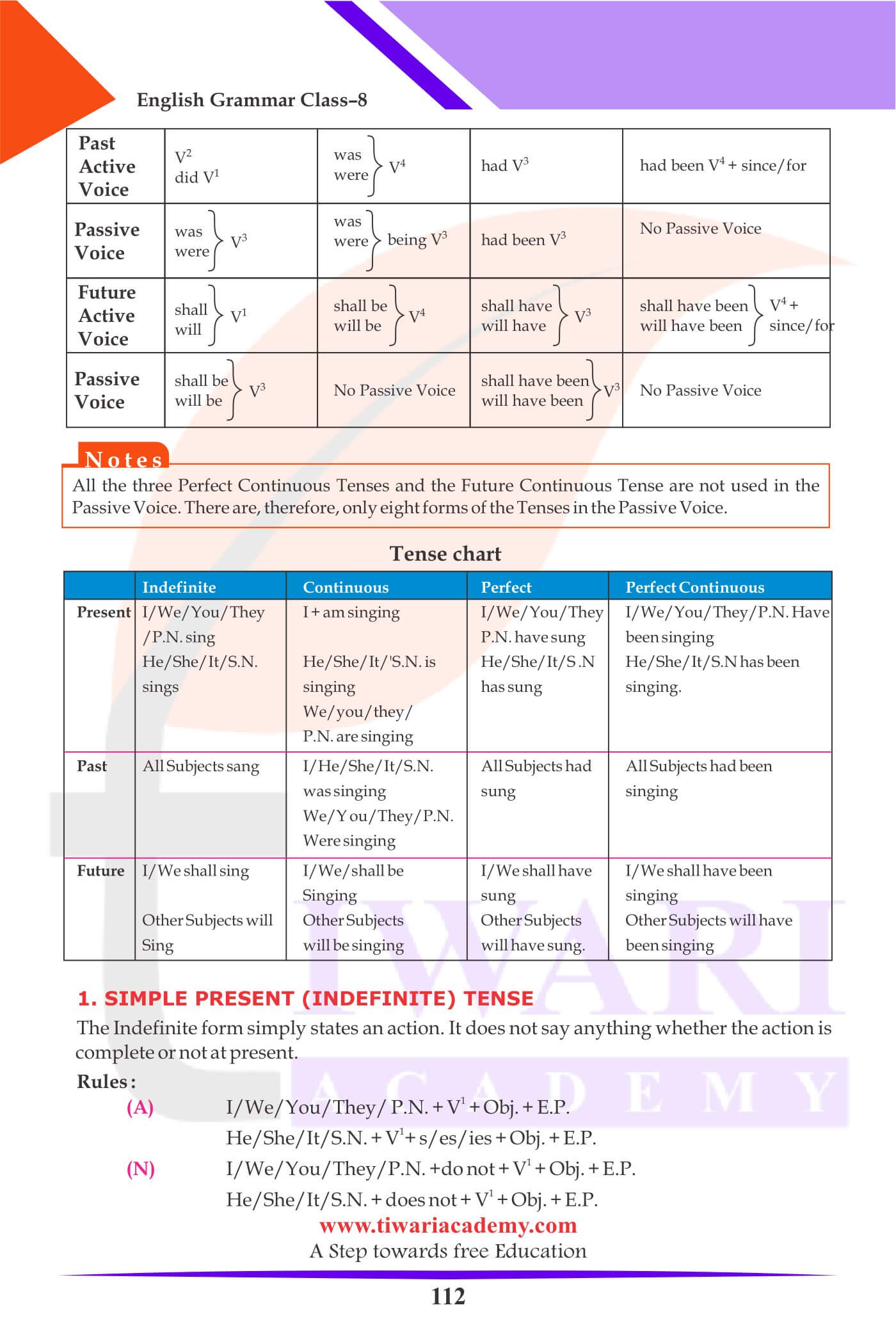
Class 8 English Grammar Chapter 9 The Tense. Tense is the form of a verb which shows the time of action or event and the degree of completeness and also the state of action. The word Tense means time. There are three tenses Present, Past and Future. A verb that refers to present time is said to be in the Present Tense. A verb that refers to past time is said to be in the Past Tense. A verb that refers to future time is said to be in the Future Tense.
A foundational aspect of mastering any language, particularly English, is grasping its tenses. Class 8 English Grammar Chapter 9 focuses precisely on ‘The Tense.’ The concept of tense is intrinsic to English, influencing the way actions or events are conveyed concerning their occurrence in time. In the digital age, online platforms like Tiwari Academy provide invaluable resources and NCERT Solutions for students to delve deeper into this topic, enabling a thorough understanding.
At its essence, tense refers to the form of a verb that highlights the time of an action or event. But it doesn’t stop there; tense also delineates the degree of completeness of that action or event. Simplifying it further, the term ‘tense’ is derived from the Latin word for ‘time,’ which is central to its definition in grammar.
| Class: 8 | English Grammar |
| Chapter: 9 | The Tense |
| Study Material: | Textbook and Revision Book |
| Academic Session: | 2025-26 |
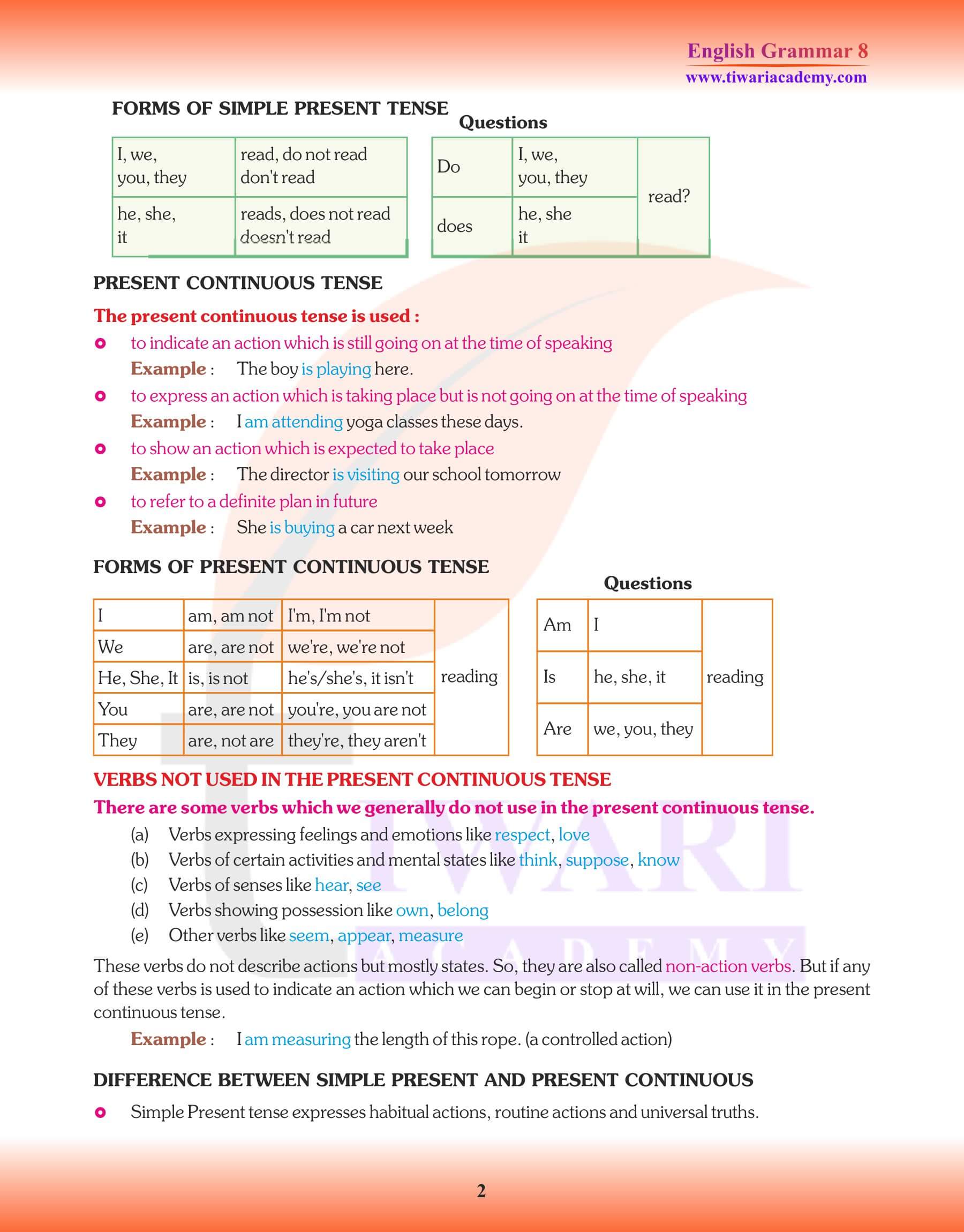
Simple Present (Indefinite) Tense
The Indefinite form simply states an action. It does not say anything whether the action is The Indefinite form simply states an action. It does not say anything whether the action is complete or not at present.
Let’s break down the tenses:
- Present Tense: As the name suggests, the Present Tense is utilized when the action or event is happening now or holds relevance in the current context. For instance, “She reads a book” indicates an ongoing or habitual action. It’s the verb form that points to the present time.
- Past Tense: This tense takes the reader or listener back in time. When an action or event has already occurred, the verb is structured in the Past Tense. An example would be, “He played football,” suggesting the action was completed in the past.
- Future Tense: Indicative of actions or events that haven’t occurred yet but are expected to take place in the future, this tense employs verbs that signal anticipation. “They will travel tomorrow” showcases a plan or intention set for a future time.
| Affirmative | Negative | Interrogative |
|---|---|---|
| I write a letter. | I do not write a letter. | Do I write a letter? |
| We play football. | We do not play football. | Do we play football? |
| They take tea. | They do not take tea. | Do they take tea? |
| The boys take exercise. | The boys do not take exercise. | Do the boys take exercise? |
| He writes a letter. | He does not write a Letter. | Does he not write a letter? |
Uses Of the Simple Present (indefinite) Tense
The sun rises in the east and sets in the west.
The rose smells sweet.
Present Continuous (progressive) Tense: The Present Continuous Tense indicates an action going on at the time of speaking.
| Affirmative | Negative | Interrogative |
|---|---|---|
| I am writing a letter. | I am not writing a letter. | Am I writing a letter? |
| We are playing chess. | We are not playing chess. | Are we not playing chess? |
| You are running a race. | You are not running a race. | Are you not running a race? |
| They are crossing the river. | They are not crossing the river. | Are they crossing the river? |
To flourish in English, having a firm grip on tenses is paramount. These grammatical classifications offer clarity, ensuring that the timeline of events in a sentence is transparent to its reader or listener. Renowned educational resources emphasize the importance of tenses, given their role in crafting precise and coherent narratives.
In conclusion, Chapter 9 of Class 8 English Grammar is a pivotal step in a student’s journey to linguistic proficiency. By mastering tenses, students equip themselves with the tools to articulate thoughts with accuracy and context, making their communication more effective and nuanced.
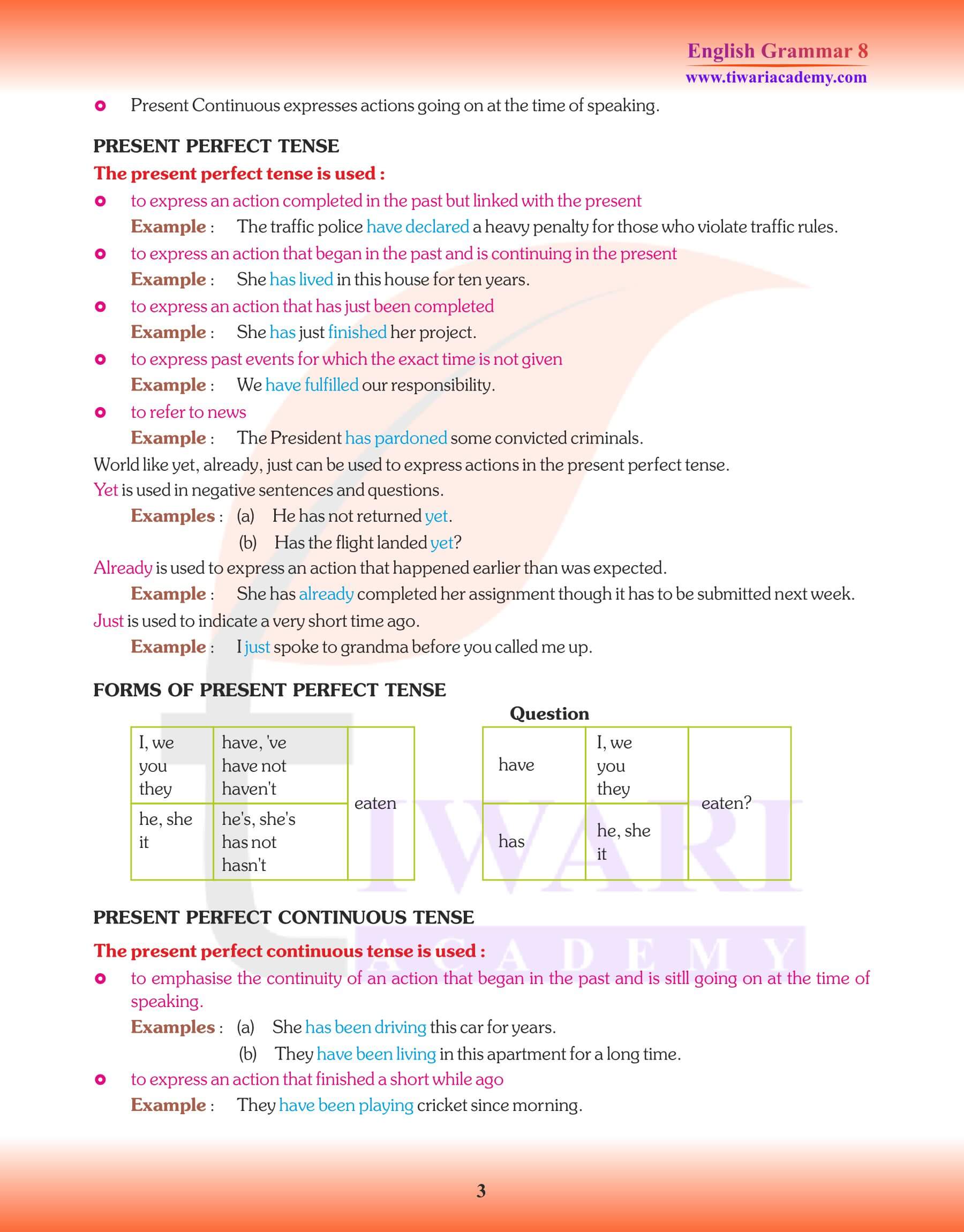
Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect Tense indicates that the action is complete and in perfect state at present.
| Assertive | Negative | Interrogative |
|---|---|---|
| I have lost my pen. | We have not made a noise. | Have we got his permission? |
| You have told a lie. | You have not done your duty. | Have you not got well? |
| They have honored me. | They have not yet taken lunch. | Have they missed the train? |
| We have learnt our lesson. | I have not beaten him. | Have I cheated you? |
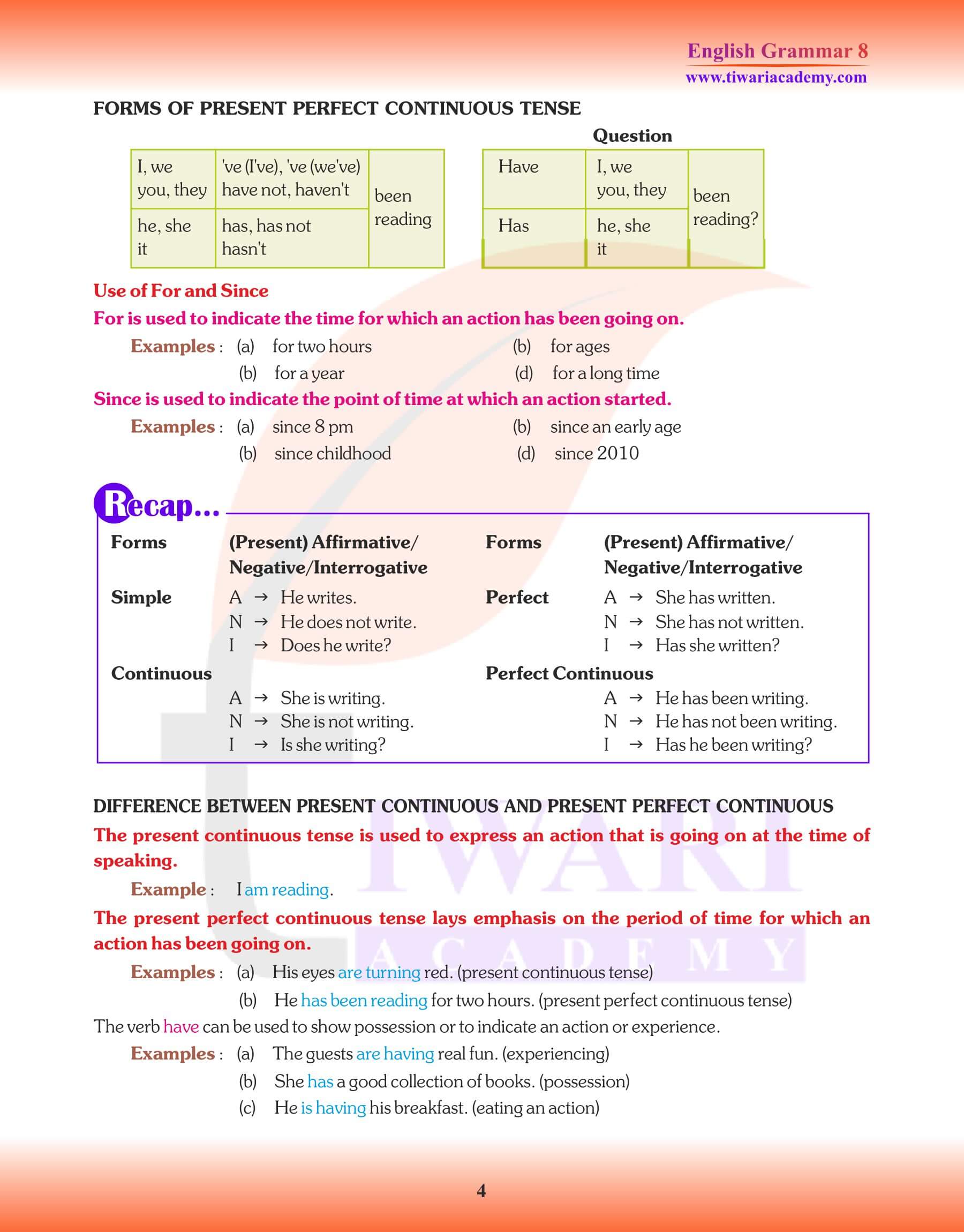
Use of Since and For
Point of time – Since
Period of time – For
Names of the days and months-since
Number of days and months-for two
Monday, Friday, June, May etc.
days/one day/five months/two weeks etc.
Fixed dates and years-since 25th
For five years.
March, since 1990.
four hours
Present Perfect Continuous Tense: The Present Perfect Continuous Tense indicates an action which began in the past and is still going on.
| Simple | Negative | Interrogative |
|---|---|---|
| We have been wandering. | We have not been playing | Have we been learning? |
| I have been writing a letter since two o’clock. | I have not been waiting for you for two hours. | Have I not been studying? in this school for ten years? |
| They have been watching T.V. for three hours. | They have not been swimming in the river since 10 o’clock. | Have they been ironing? their clothes since morning ? |
Uses of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The laborers have been repairing the road since Sunday.
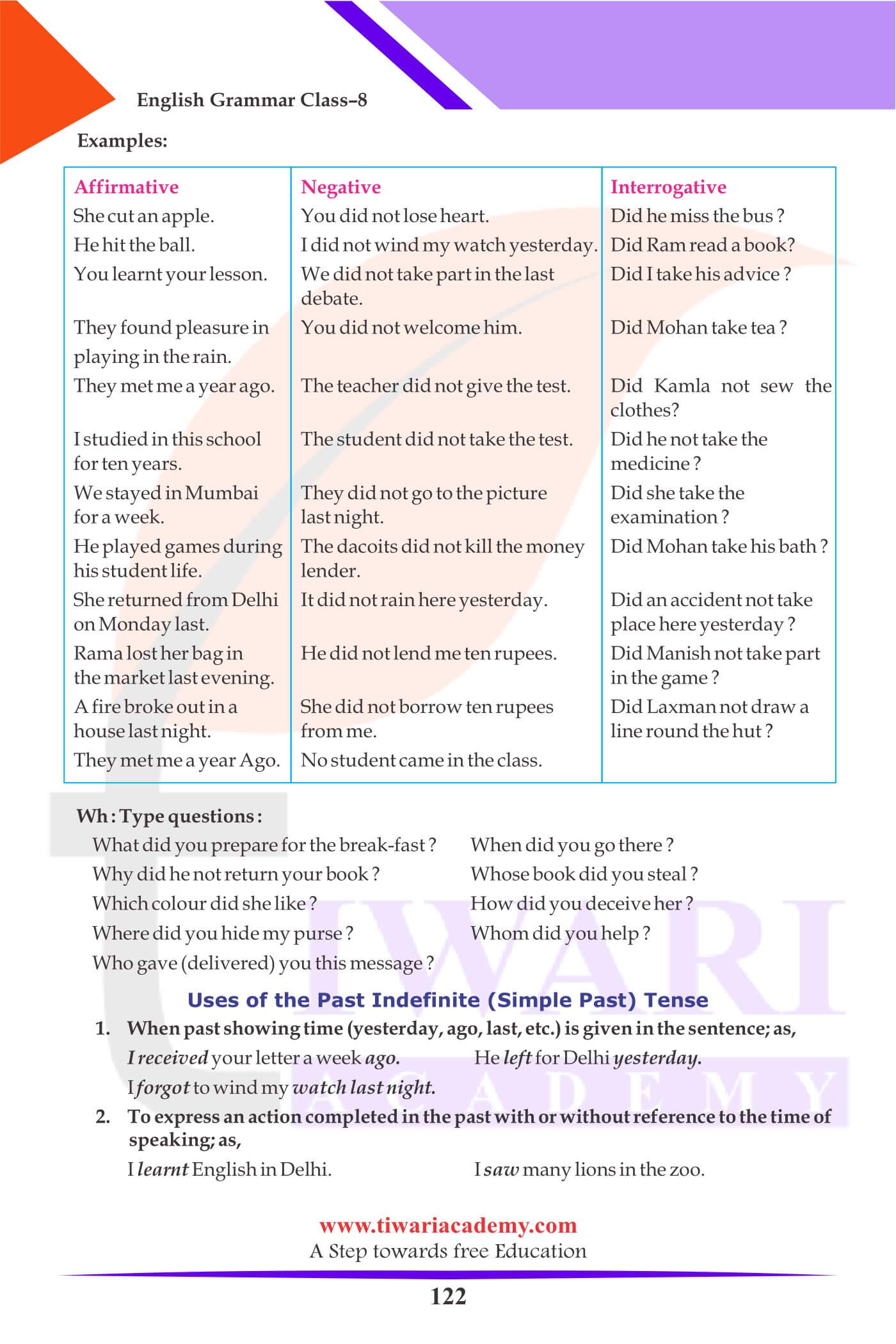
Simple Past (Indefinite) Tense
| Affirmative | Negative | Interrogative |
|---|---|---|
| She cut an apple. | You did not lose heart. | Did he miss the bus? |
| He hit the ball. | I did not wind my watch yesterday. | Did Ram read a book? |
| You learnt your lesson. | We did not take part in the last debate. | Did I take his advice? |
| They found pleasure in You | did not welcome him. | Did Mohan take tea? |
Uses of the Past Indefinite (Simple Past) Tense
I received your letter a week ago.
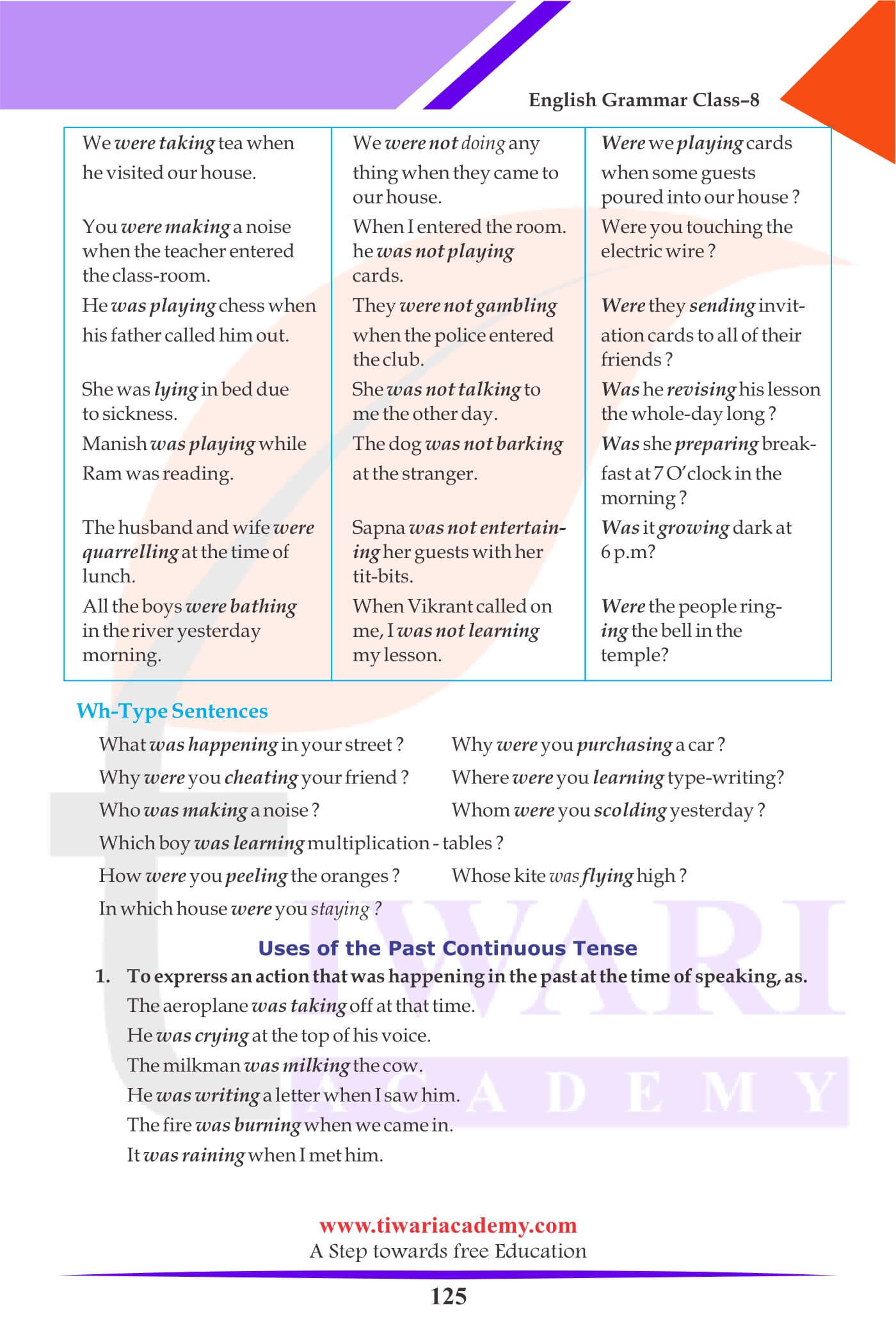
Past Continuous Tense:
1. He was crying at the top of his voice.
2. The milkman was milking the cow.
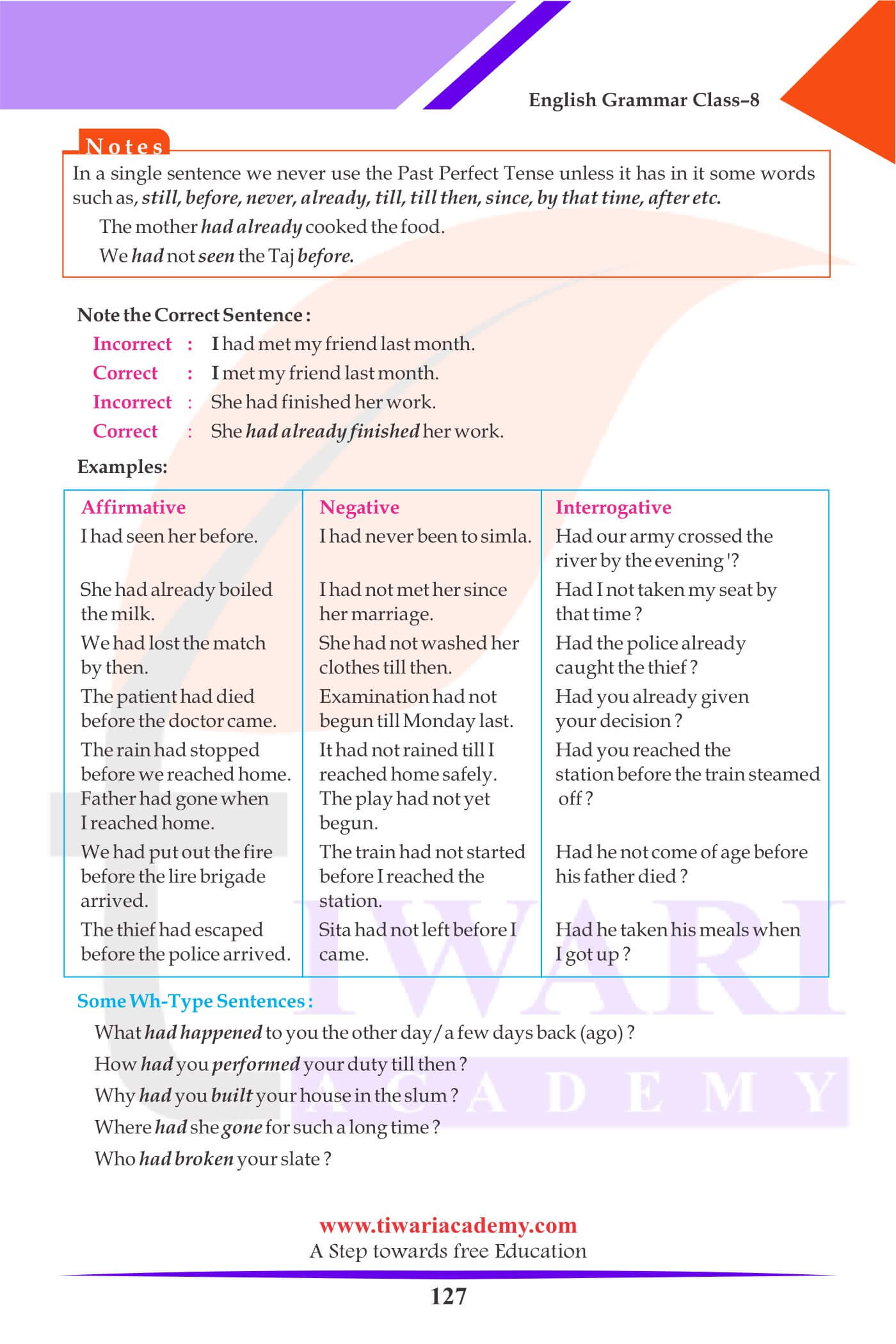
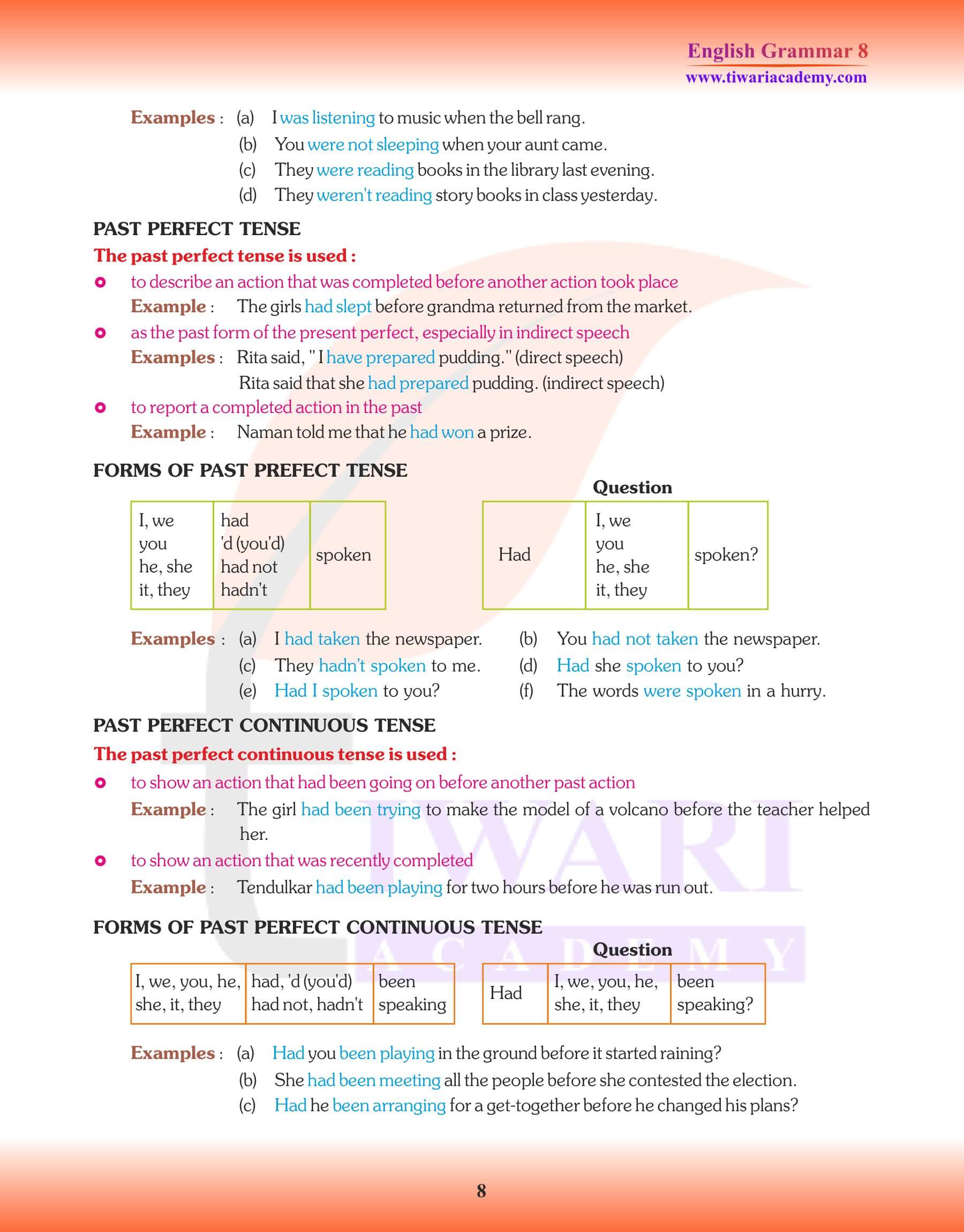
Past Perfect Tense:
1. I had seen her before.
2. I had never been to Shimla.
3. Had you already given your decision?