Class 8 English Grammar Chapter 4 The Noun and Kinds of Noun. We know that a Noun is the name of a person, place or a thing. A noun is further divided in four kinds as Proper Noun, Common Noun, Collective Noun, Material Noun and Abstract Noun. A Collective Noun takes a singular verb. For example, Our army is strong. The class is in the room.
Grade 8 English Grammar Chapter 4 The Noun and its Kinds
One of the foundational chapters in Class 8 English Grammar is Chapter 4, titled ‘The Noun and Kinds of Noun.’ This pivotal segment introduces students to the dynamic realm of nouns, those indispensable components of language that name people, places, or things. As they venture further, learners discover the multifaceted nature of nouns, each kind with its distinct attributes and usage.
At its core, a noun represents a label, a descriptor that offers identity. However, a mere definition doesn’t do justice to its diversity. To truly appreciate the nuances of nouns, one must explore its various kinds: Proper Noun, Common Noun, Collective Noun, Material Noun, and Abstract Noun. Each category lends a unique dimension to how we perceive and communicate about the world around us.
Class 8 English Grammar Chapter 4 The Noun
Proper Nouns offer specificity, pinpointing particular entities, like ‘London’ or ‘Shakespeare’. Common Nouns, on the other hand, provide general names for items, people, or places, such as ‘city’ or ‘writer’. The realm of Collective Nouns takes a fascinating turn, representing groups or collections. Interestingly, they usually take a singular verb. Sentences like “Our army is strong” or “The class is in the room” exemplify this rule, guiding students in their grammatical correctness.
Material Nouns delve into the domain of substances or materials like ‘gold’ or ‘water’, whereas Abstract Nouns touch on intangible concepts or qualities, such as ‘love’ or ‘freedom’. Each kind plays a vital role, enriching our linguistic expressions.
| Class: 8 | English Grammar |
| Chapter: 4 | Noun and kinds of Noun |
| Contents: | Revision Books and Study Material |
| Academic Session: | 2025-26 |
Common Noun
A Common Noun is the name that can be given to every person, animal, place or thing of the same class or kind as,
Persons: Man, woman, boy, girl, teacher, doctor, peon etc.
Animals: Bull, cow, horse, cat, lion, mouse, elephant etc.
Places: School, temple, church, farm, park, zoo, roof, street etc.
Things: Pen, book, bag, bat, needle, table, spoon etc.
Top educational platforms, including the likes of Tiwari Academy, emphasize the significance of mastering nouns. Their curated resources, practice exercises, and NCERT Solutions related to ‘The Noun and Kinds of Noun’ reinforce its importance, ensuring students grasp its intricacies.
In conclusion, Chapter 4 is more than a lesson; it’s a linguistic exploration. By immersing in the diverse world of nouns, Class 8 students fortify their English foundations, poised to tackle more advanced linguistic challenges in their academic journey.
Collective Noun
A Collective Noun is the name of a group or collection of persons, animals or things of the same kind taken together and described as one whole; as, team, mob, jury, committee, family, party, group, regiment, dozen, score, heap, bundle, packet, library, fleet, herd, band, bouquet etc.
Note: A Collective Noun takes a singular verb, as:
1. Our army is strong.
2. The class is in the room.
Class 8 English Grammar The Noun Numbers
Material Noun
A Material Noun is the name of the matter or substance of which things are made as, Gold, silver, cotton, wood, iron, steel, milk, honey, water, butter, oil, ice, bread, wheat, sugar, ink, paper, glass, china, leather, nylon, cloth, clay, salt etc.
1. Our clothes are made of cotton.
2. Iron is a very useful metal.
3. This ring is made of gold.
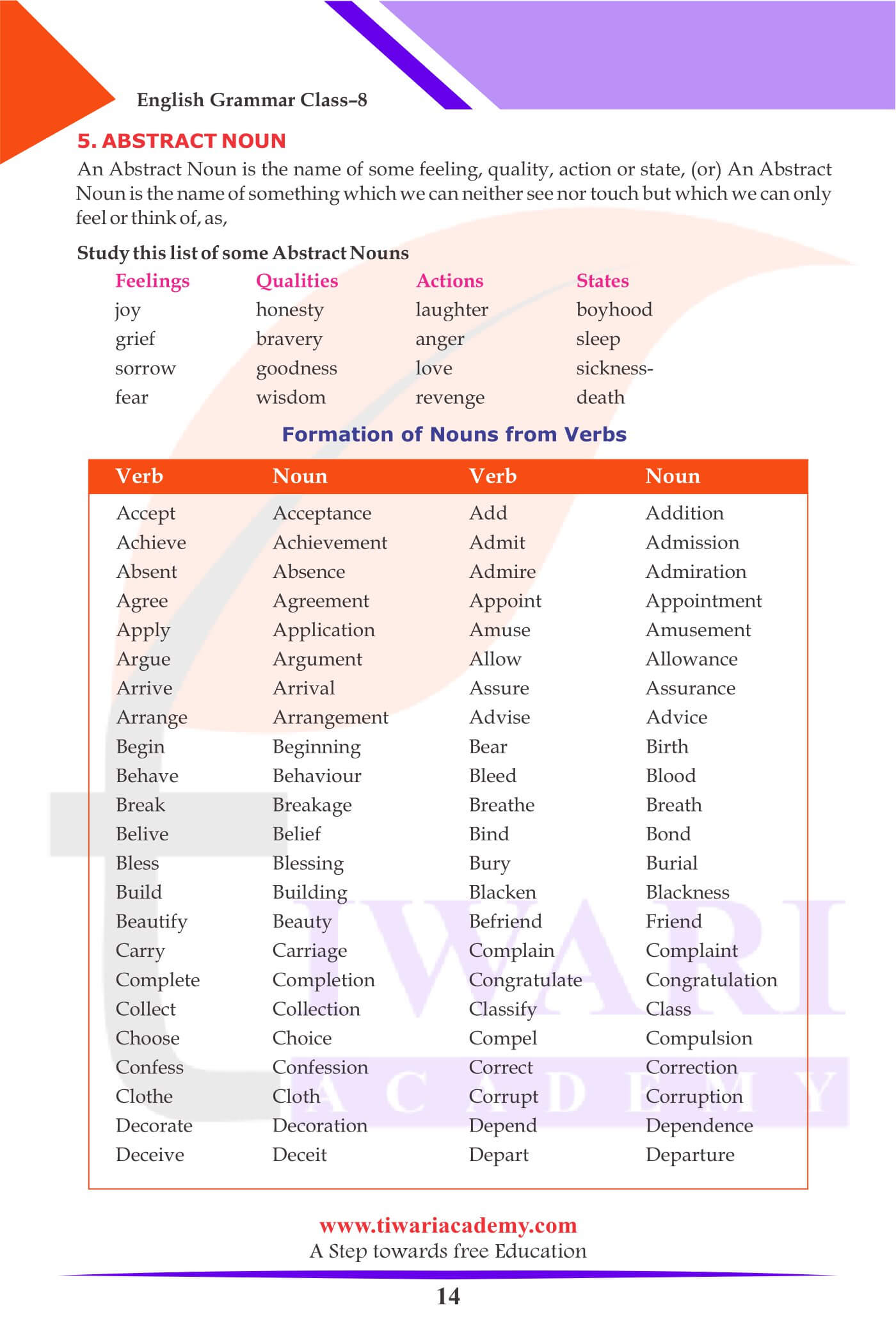
Abstract Noun
An Abstract Noun is the name of some feeling, quality, action or state, (or) An Abstract Noun is the name of something which we can neither see nor touch but which we can only feel or think of as, Study this list of some Abstract Nouns
| Feelings | Actions | States |
|---|---|---|
| Joy | laughter | boyhood |
| Grief | anger | sleep |
| sorrow | love | sickness |
| fear | revenge | death |
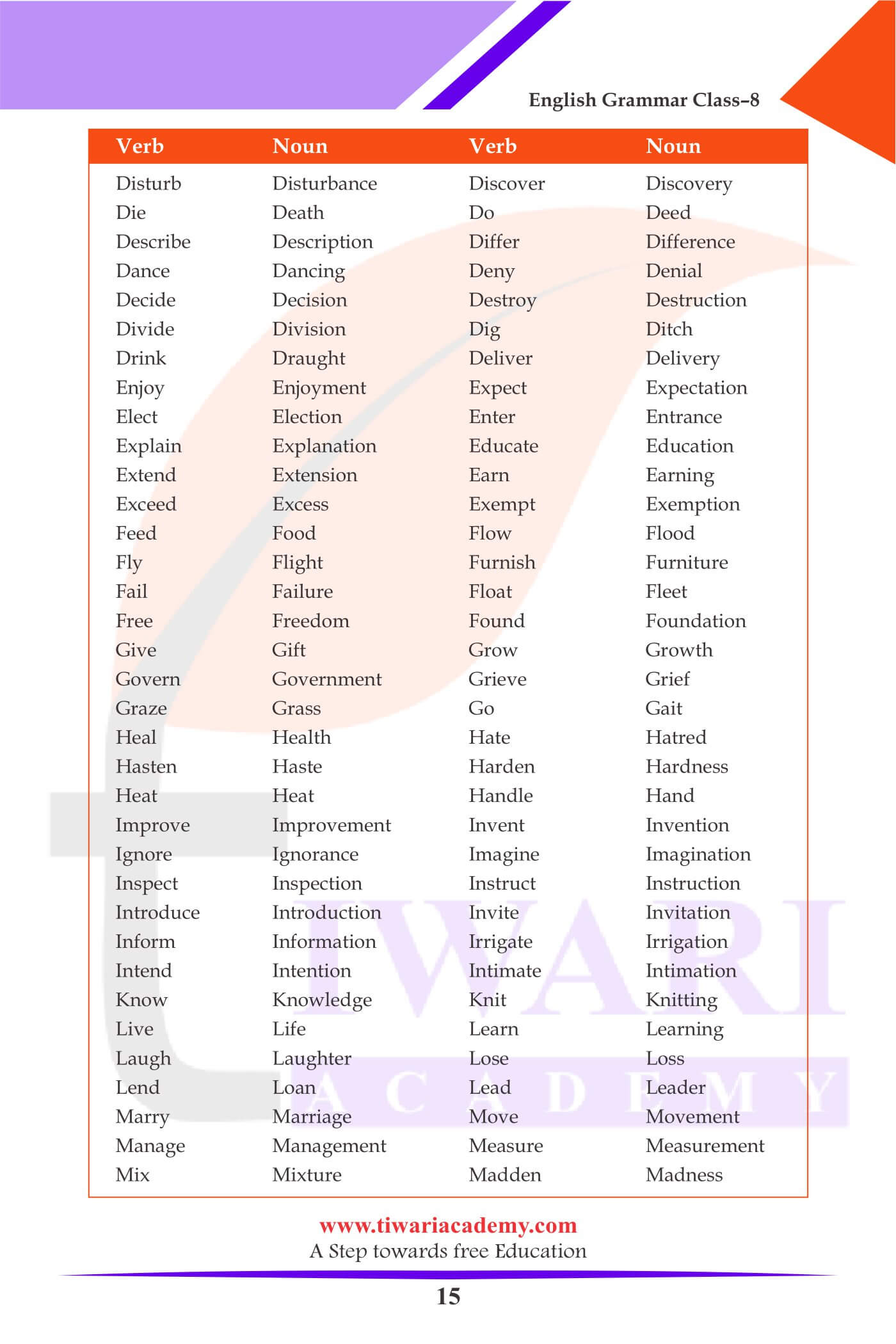
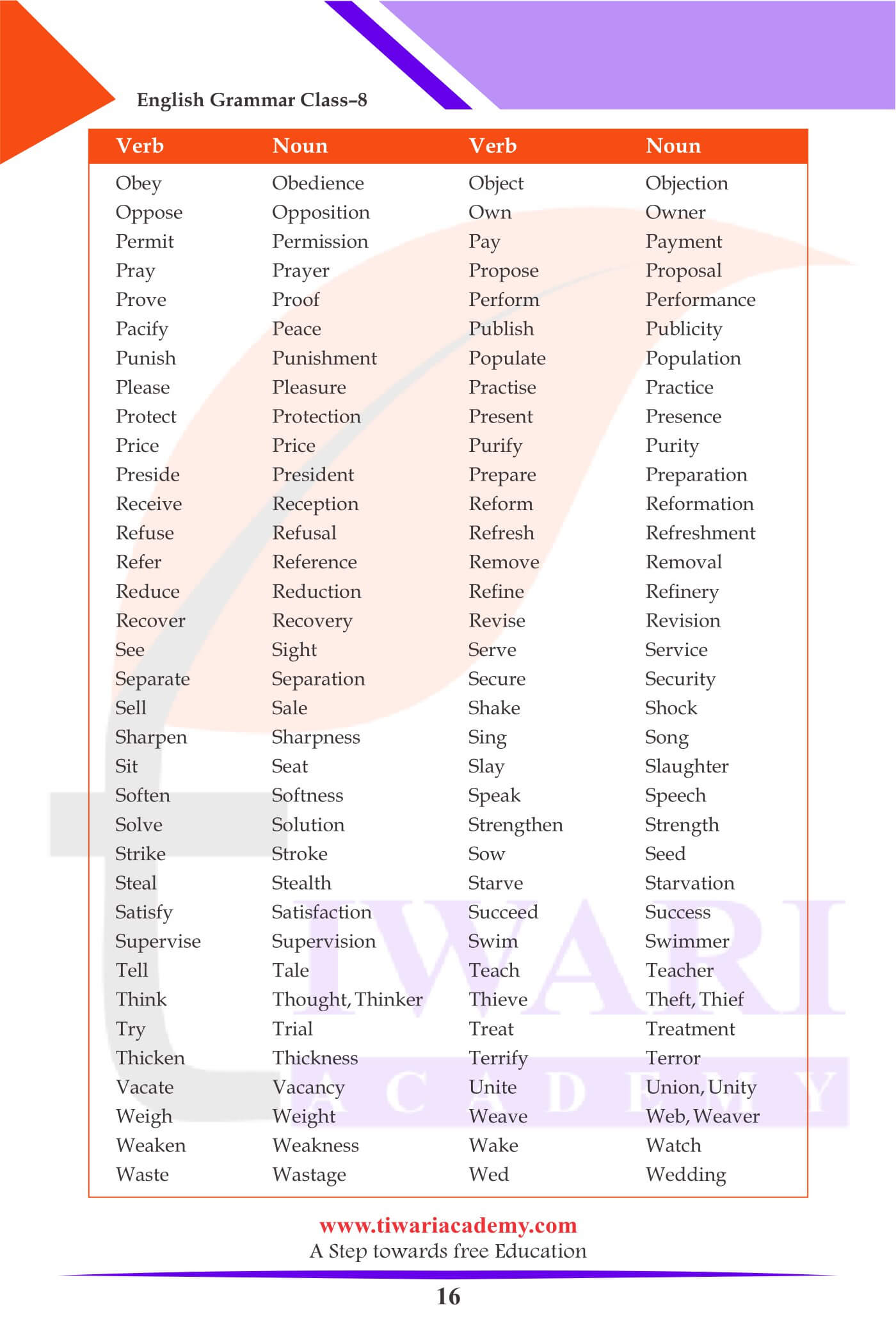
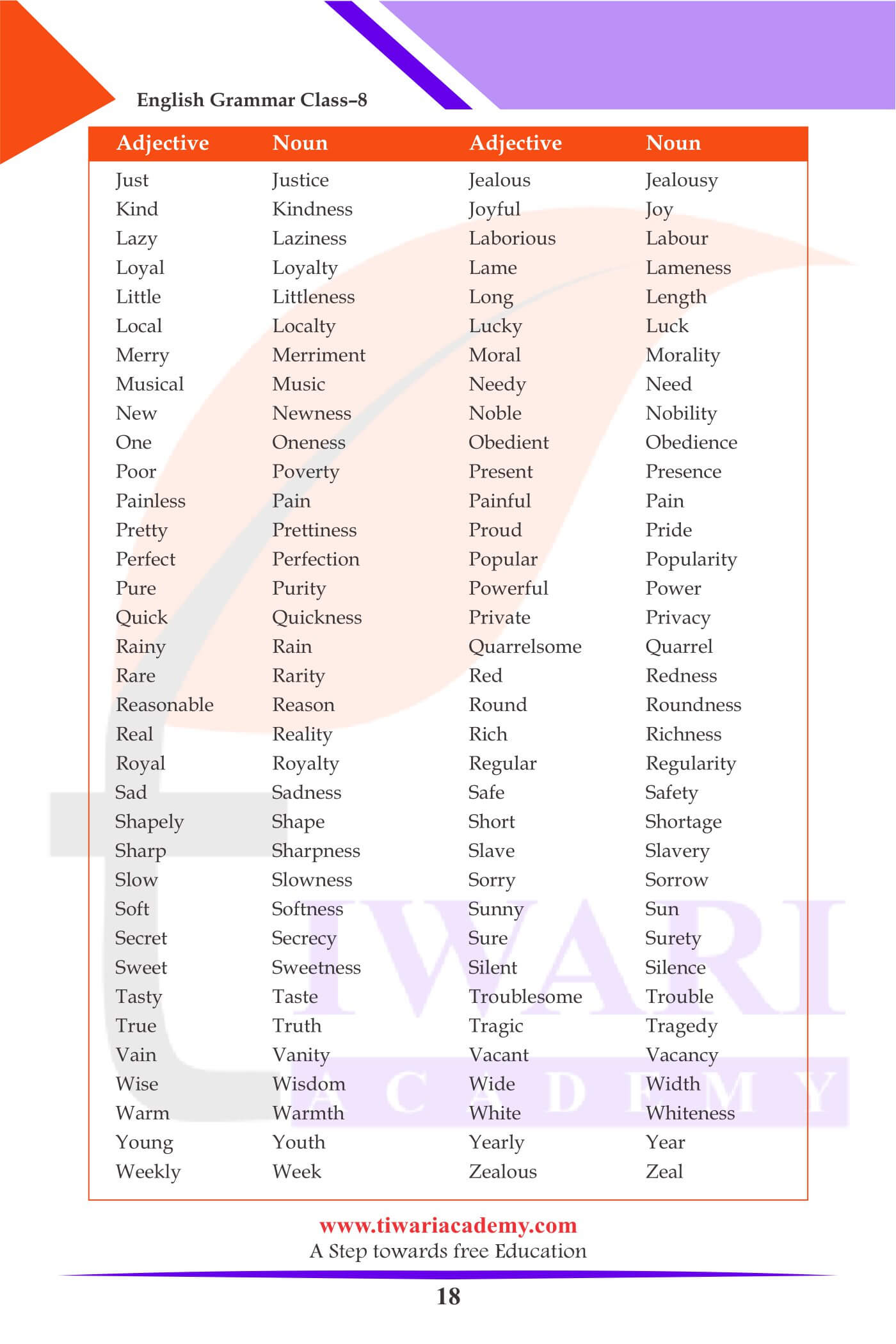
Formation of Nouns from Verbs
| Verb | Noun |
|---|---|
| Accept | Acceptance |
| Add | Addition |
| Achieve | Achievement |
| Admit | Admission |
| Absent | Absence |
| Admire | Admirations |
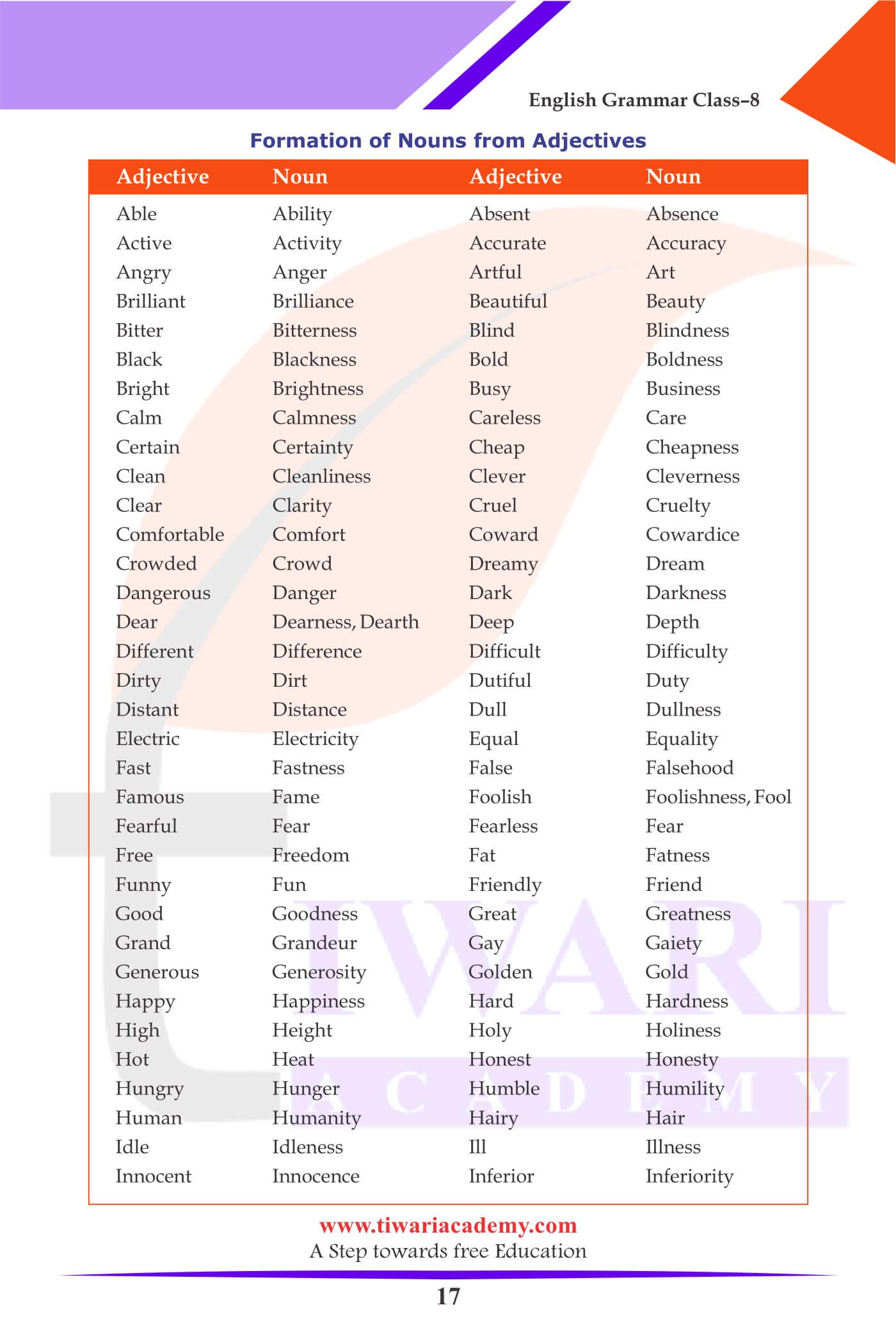
Formation of Nouns from Adjectives
| Adjective | Noun |
|---|---|
| Able | Ability |
| Absent | Absence |
| Active | Activity |
| Accurate | Accuracy |
| Angry | Anger |
| Artful | Art |
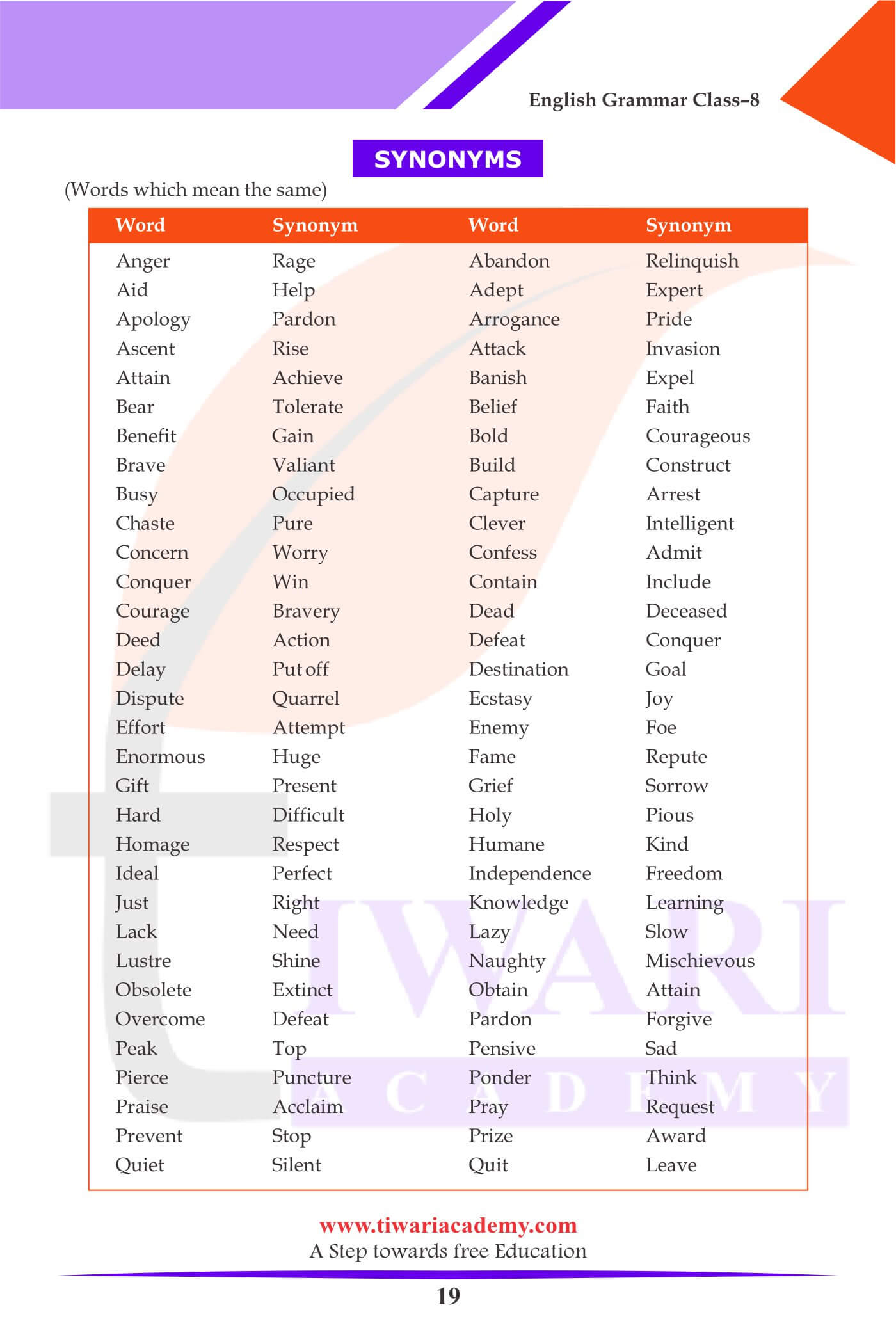
Synonyms: (Words which mean the same)
| Word | Synonym |
|---|---|
| Anger | Rage |
| Abandon | Relinquish |
| Aid | Help |
| Adept | Expert |
| Apology | Pardon |
| Arrogance | Pride |
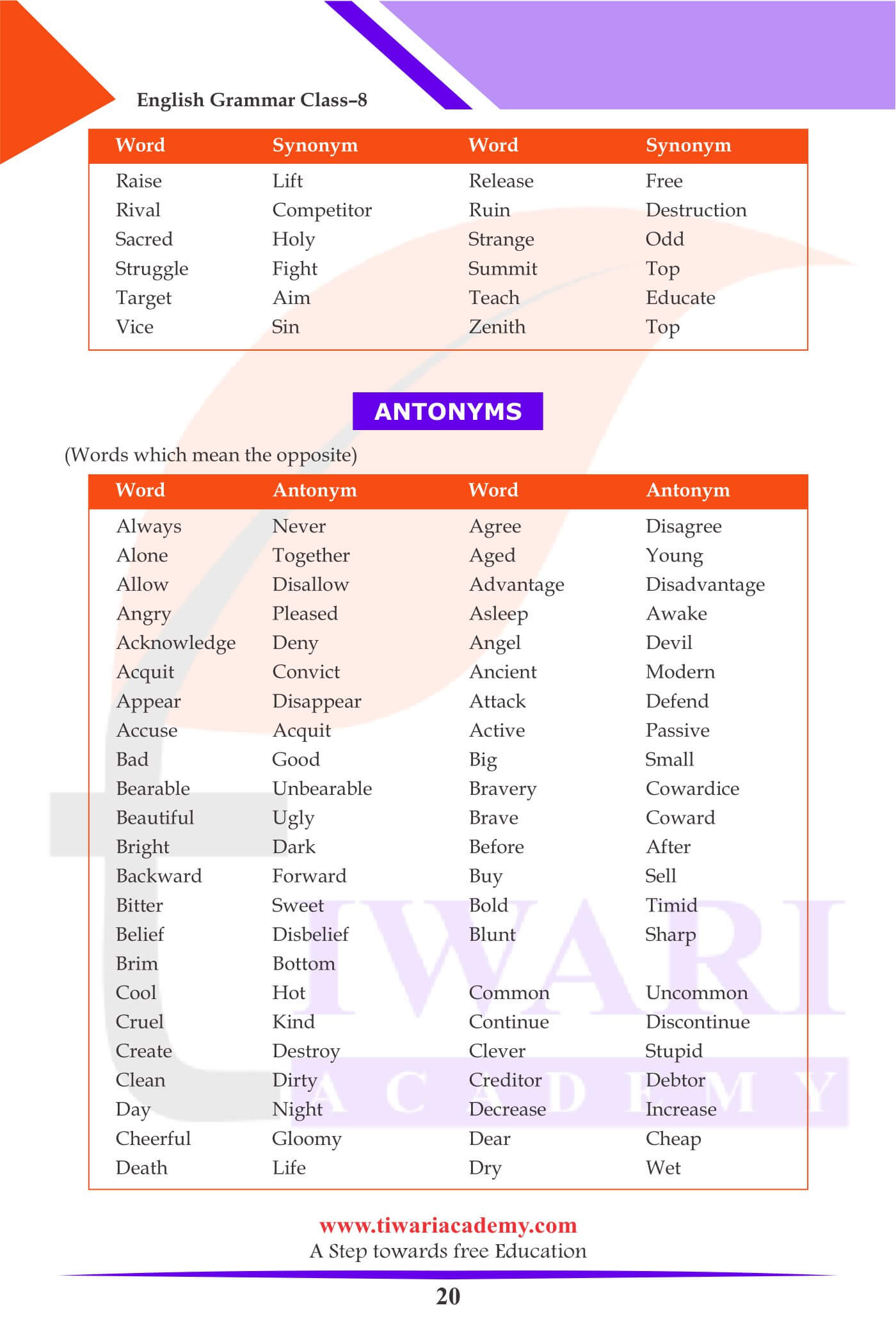
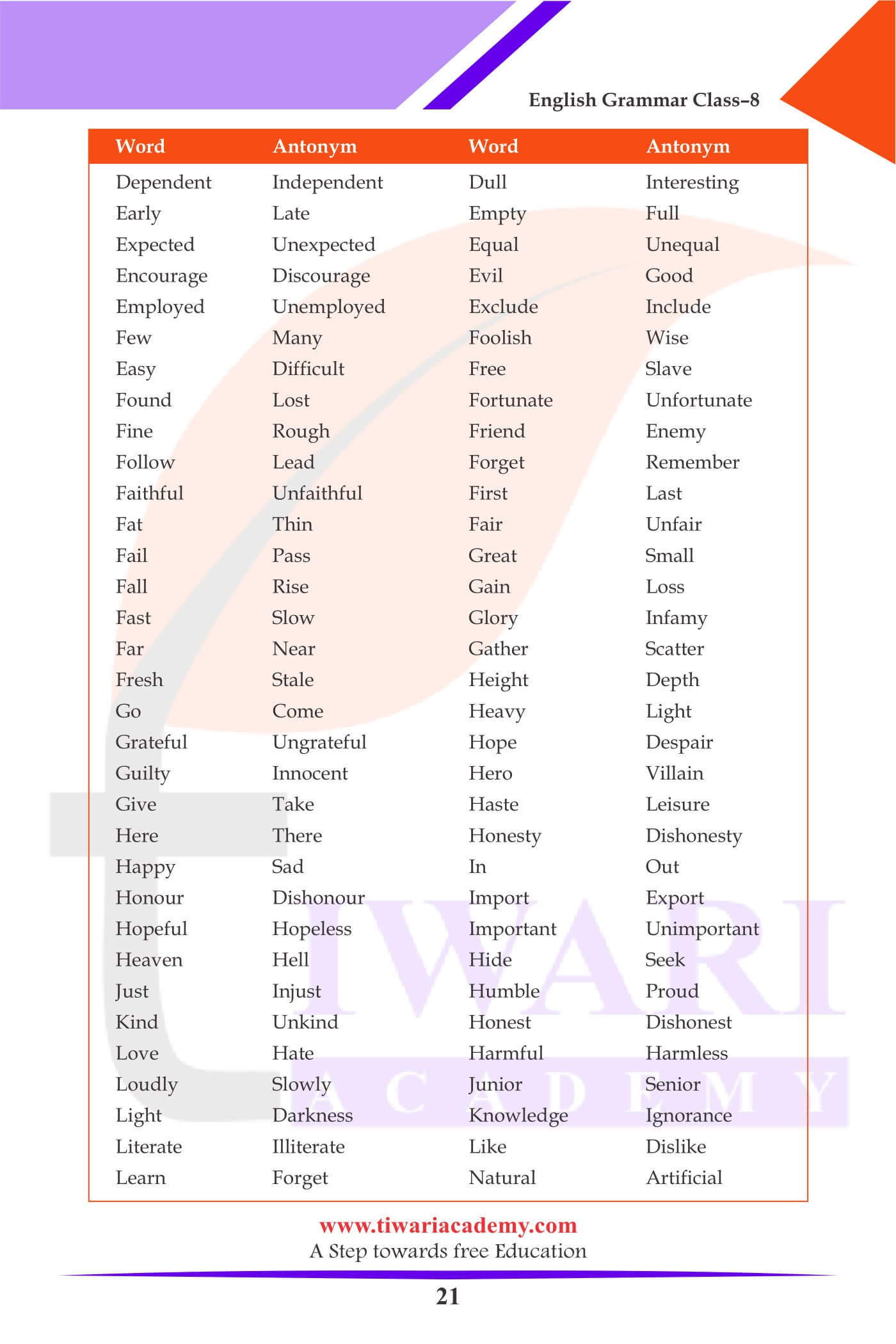
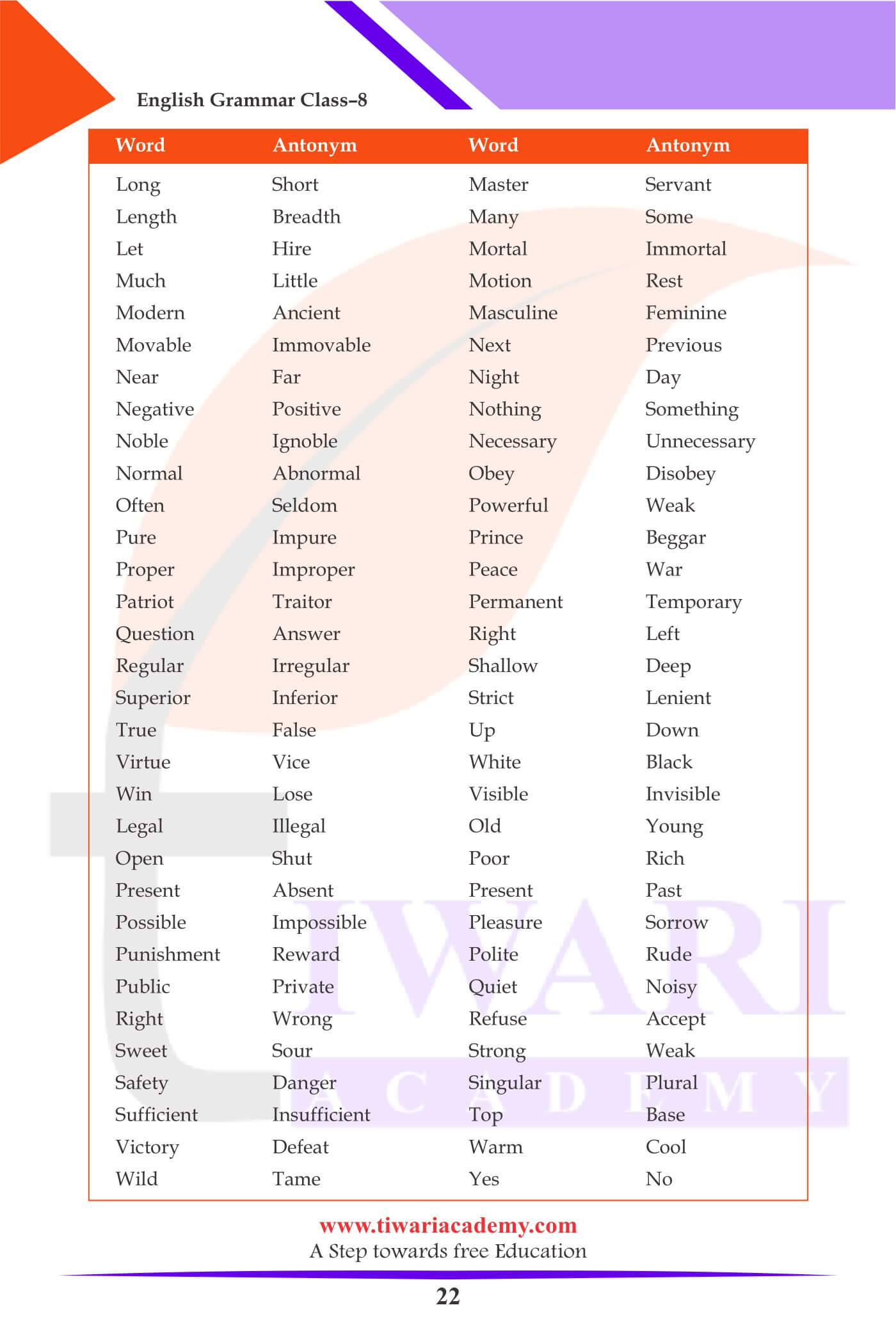
Antonyms: (Words which mean the opposite)
| Word | antonym |
|---|---|
| Always | Never |
| Agree | Disagree |
| Alone | Together |
| Aged | Young |
| Allow | Disallow |
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
The Number
There are two numbers in English:
1. Singular Number
2. Plural Number
- Singular Number: A Noun or Pronoun that denotes one person or thing is said to be in the Singular Number as, Boy, Pen, Child, Tree, Book, etc.
- Plural Number: A Noun or Pronoun that denotes more than one persons or things is said to be in the Plural Number; as, Boys, Pens, Children, Trees, Books etc.
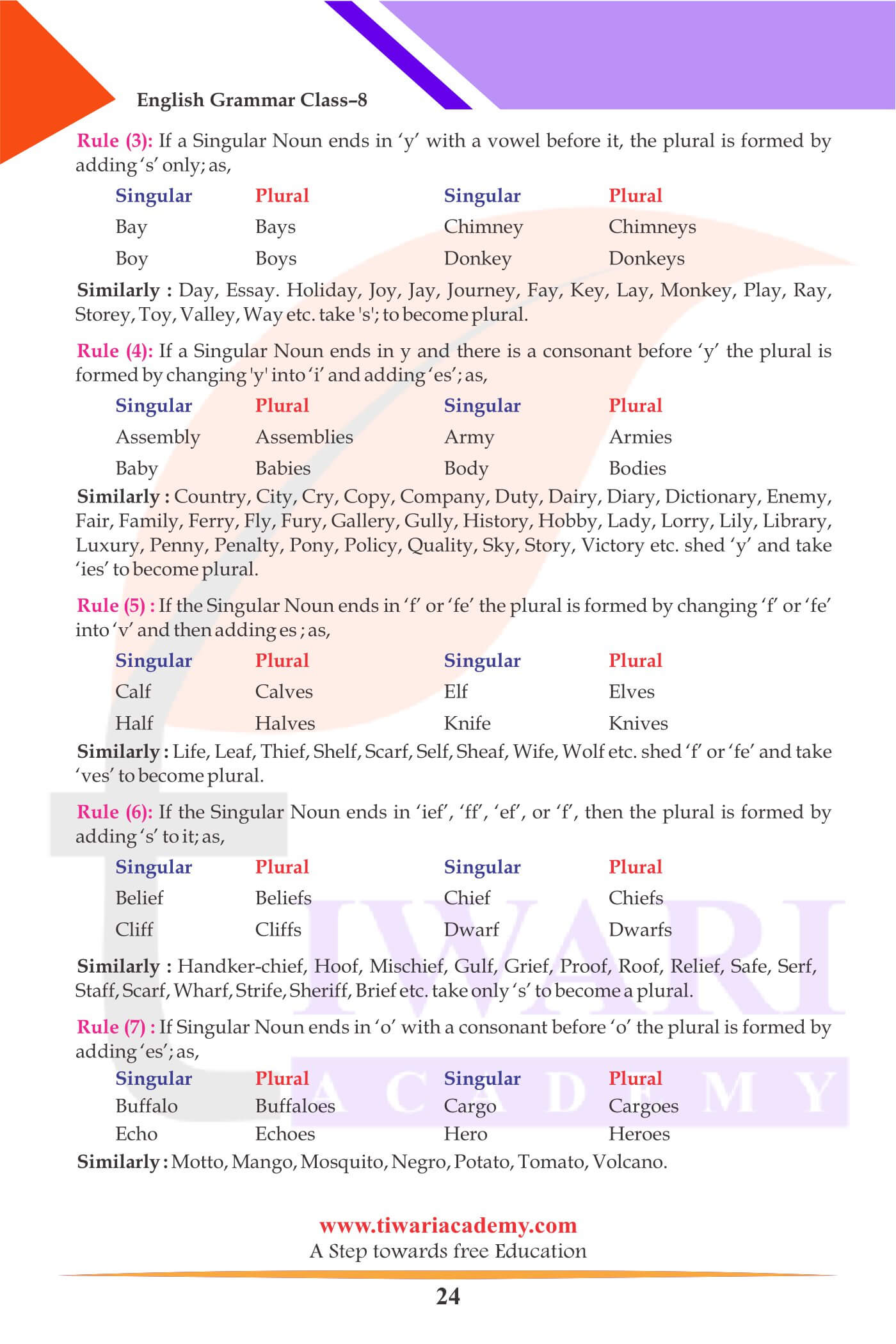
- Rules for Change of Number
Rule (1): The Plural of a Noun is generally formed by adding ‘s’ to the Singular form as,
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Apple | Apples |
| Act | Acts |
| Actor | Actors |
| Article | Articles |
Rule (2): Singular Nouns ending in s, ss, sh, ch, x or z become plural by adding “es” to them, as,
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Address | Addresses |
| Ass | Asses |
| Arch | Arches |
| Ash | Ashes |
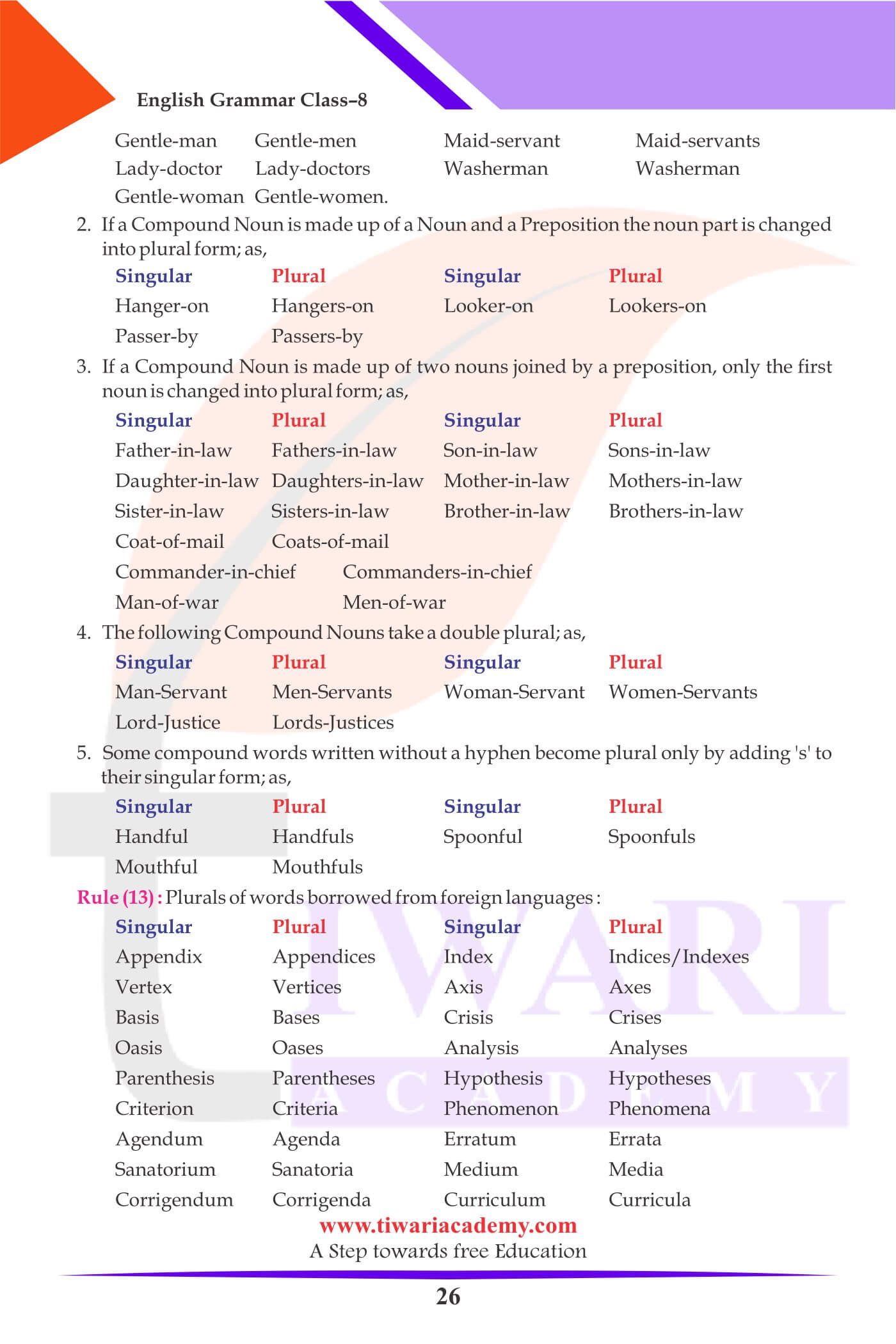
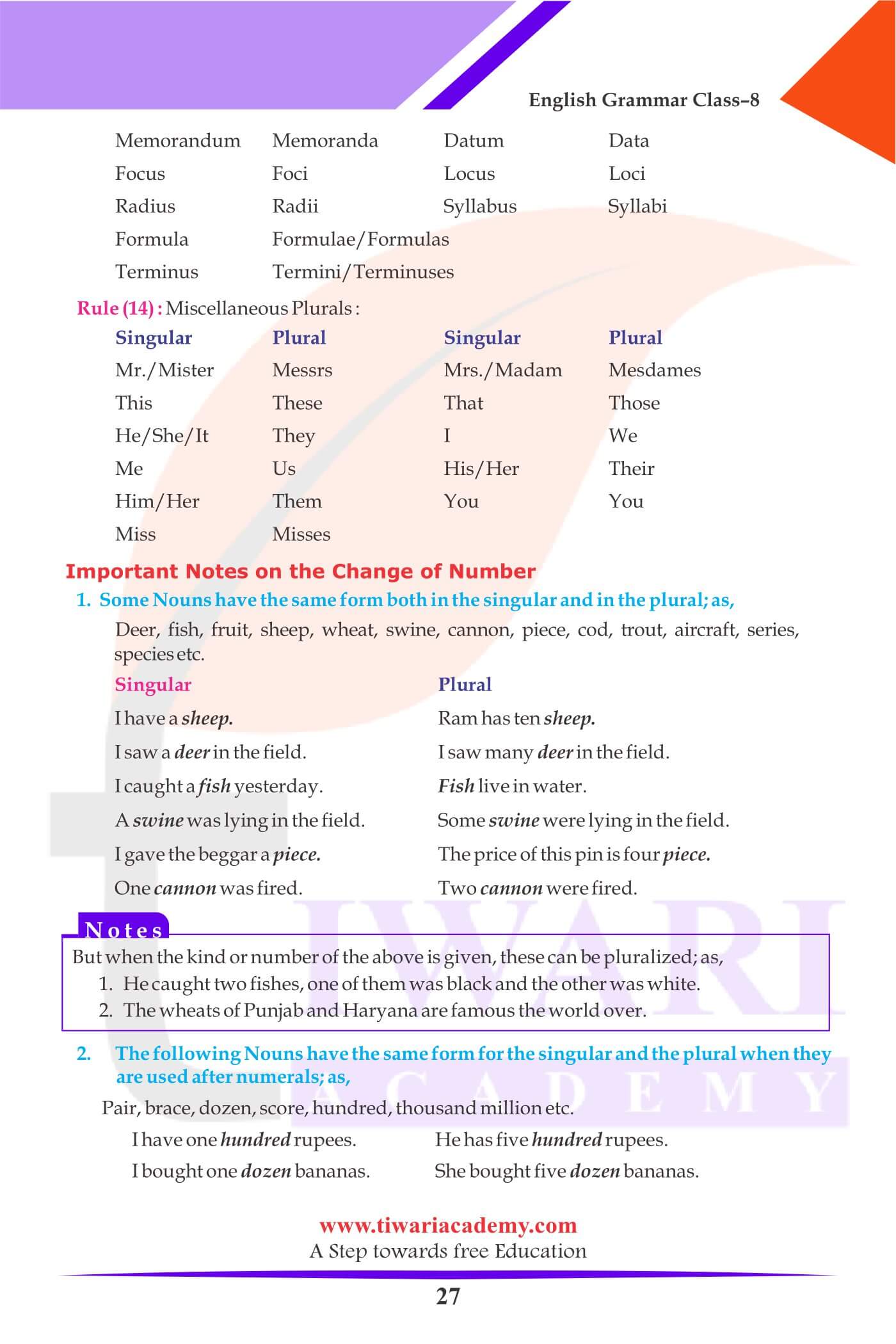
Important Notes on the Change of Number:
1. Some Nouns have the same form both in the singular and in the plural as,
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| I have a sheep. | Ram has ten sheep. |
| I saw a deer in the field. | I saw many deer in the field. |
| I caught a fish yesterday. | Fish live in water. |
2. The following Nouns are always used as plural:
The cattle are grazing in the field.
3. Some Nouns are plural in appearance but singular in use:
Mathematics is an interesting subject.
Genders of Noun: Genders tell us whether a noun belongs to the male sex, female sex or to neither of the two:
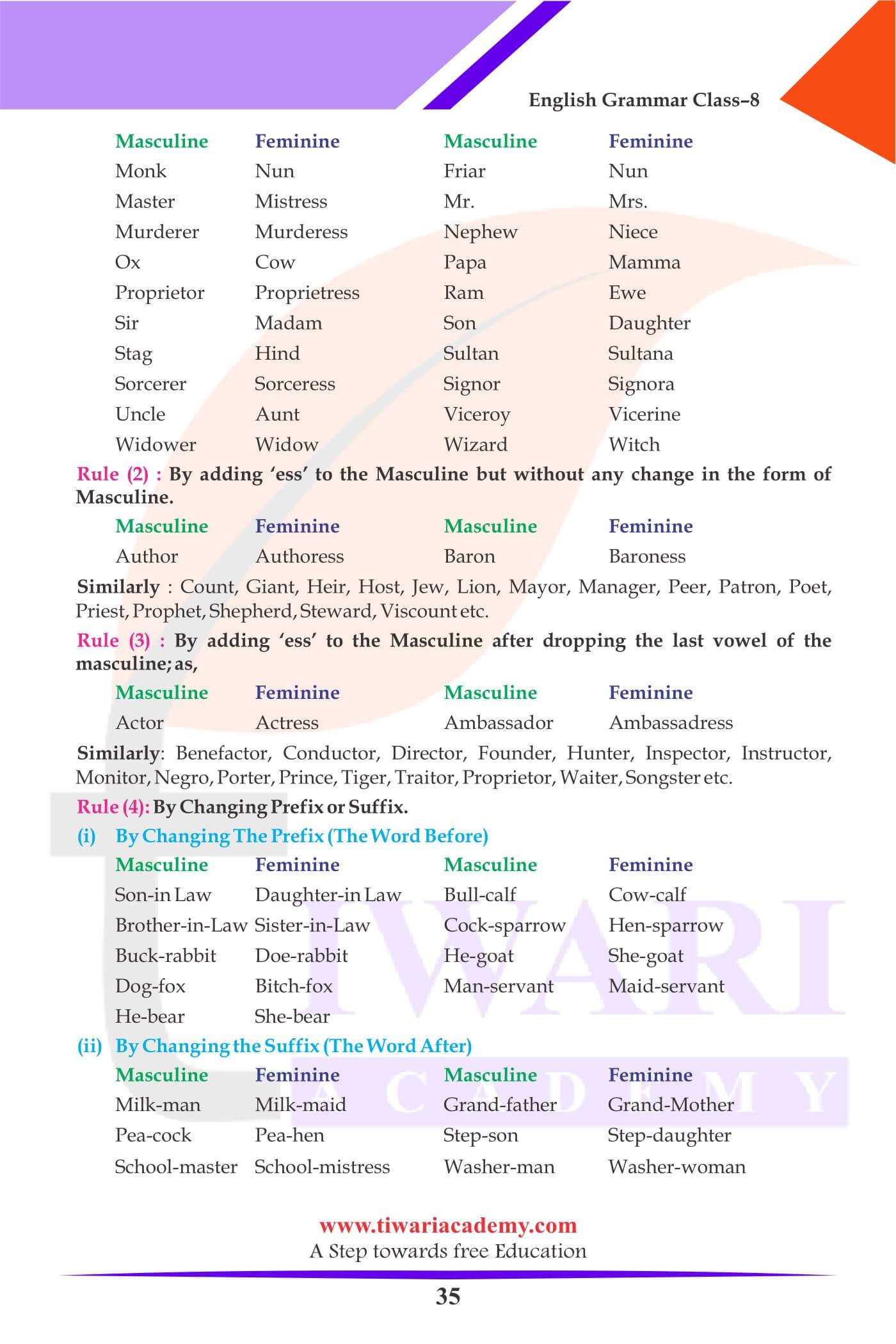
1. Masculine Gender
2. Feminine Gender
3. Common Gender
4. Neuter Gender
1. Men, boys and male animals are Masculine.
2. Women, girls and female animals are Feminine.
3. A noun which has the same form for masculine and feminine is of the Common Gender (Baby, Child)
4 A lifeless thing is of the Neuter Gender. (Book, Chair)
Case of The Nouns: There are four cases in English:
1. Nominative Case
2. Objective or Accusative Case
3. Dative Case
4. Possessive Case
1. Nominative: Dogs bark.
2. Objective Case or Accusative Case: We serve our country.
3. Dative Case: I bought Sita a doll.
4. Possessive or Genitive Case: Manish’s father is a doctor.