NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 Symmetry in Hindi and English Medium for CBSE session 2025-26. Students of class VII can get the revised solutions of ex. 12.2 mathematics here based on new syllabus and latest textbooks issued for academic year 2025-26.
Class 7 Maths Exercise 12.2 Solution in Hindi and English Medium
| Class: 7 | Mathematics |
| Chapter: 12 | Exercise: 12.2 |
| Chapter Name: | Symmetry |
| Content Mode: | Images, Text and Videos |
| Academic Session: | CBSE 2025-26 |
| Medium: | English and Hindi Medium |
Class 7 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 Solution
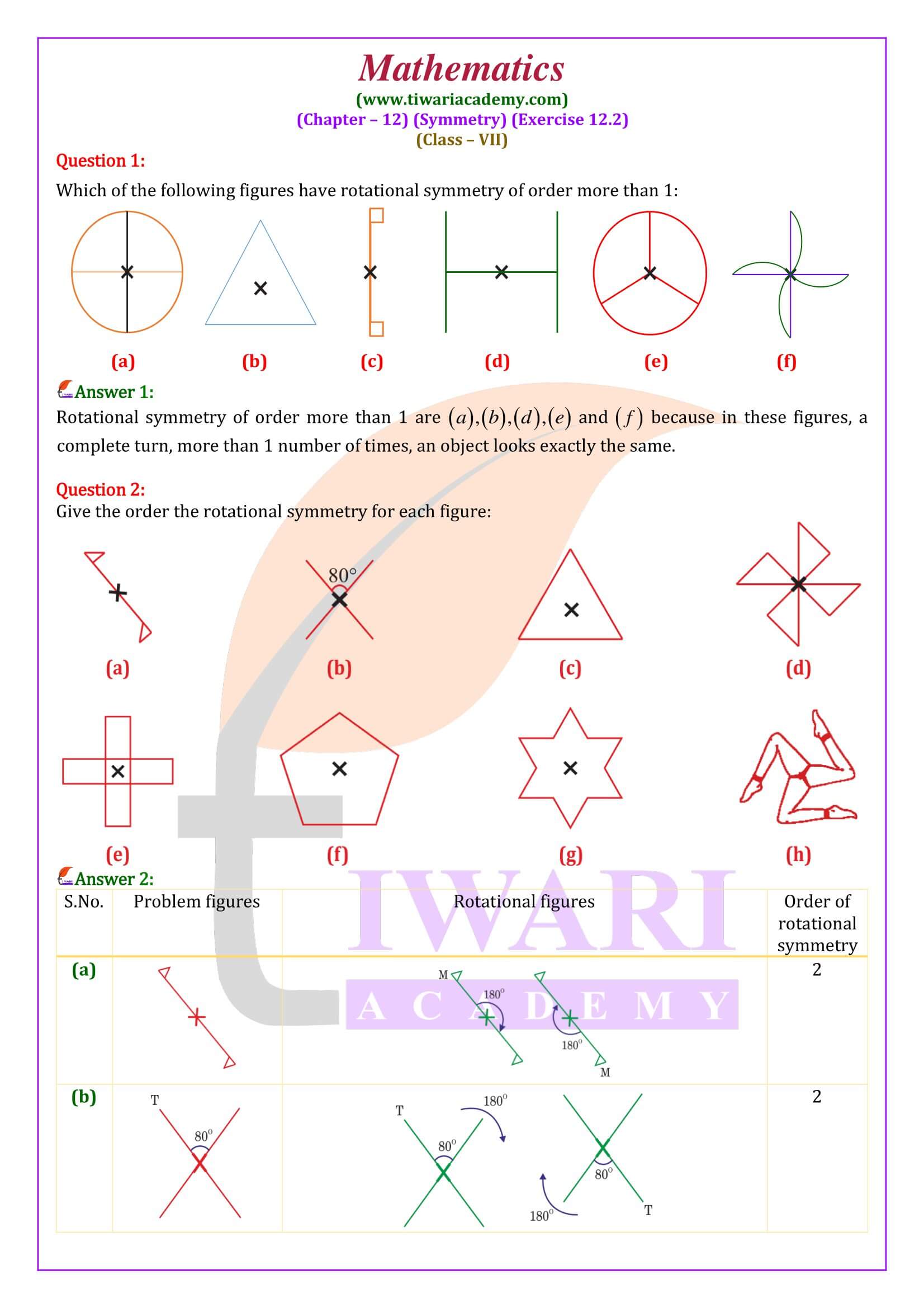
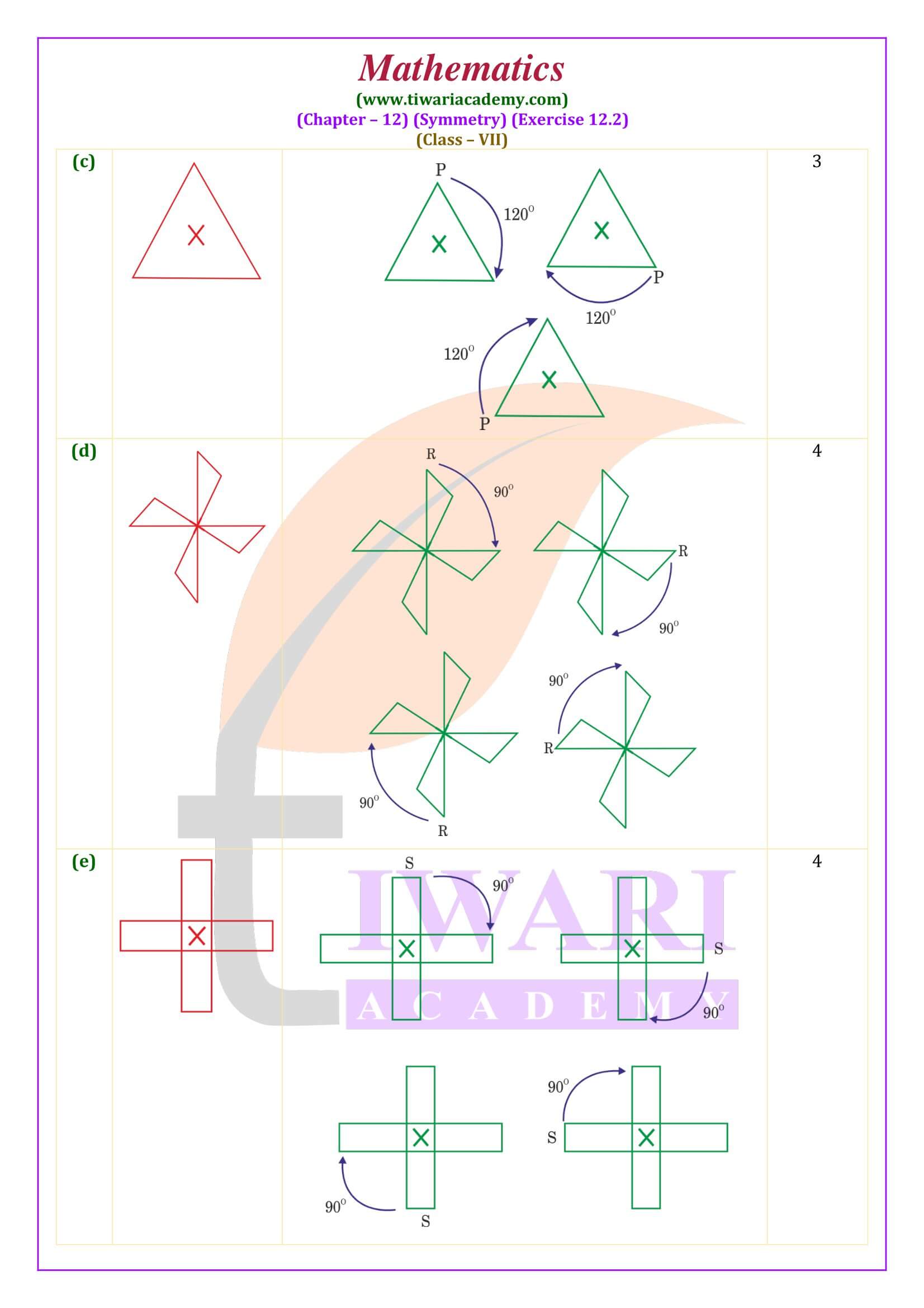
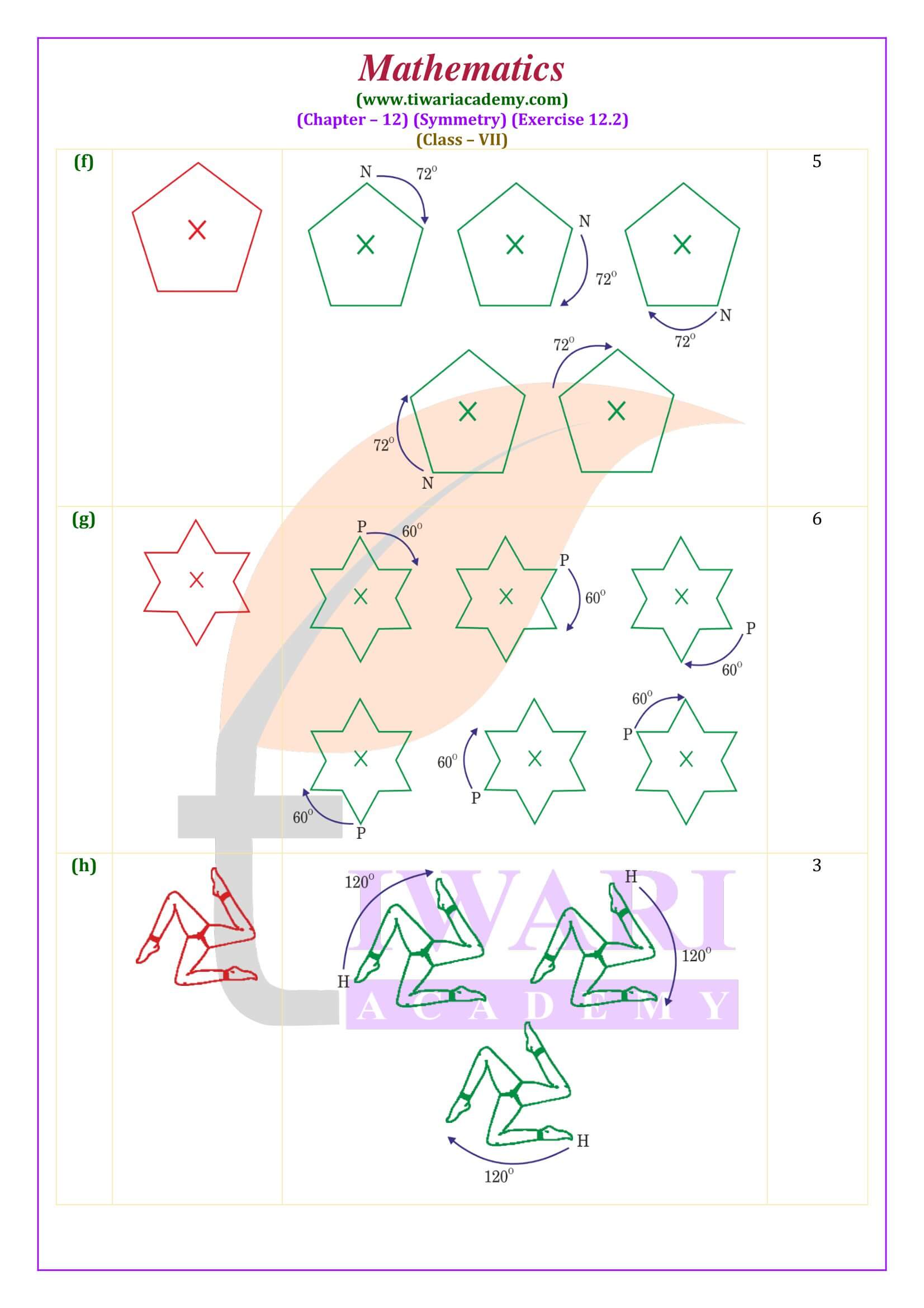
All the contents are updated according to latest CBSE syllabus 2025-26. In class 7 math NCERT exercise 12.2 the concepts are given based on rotational symmetry. Here the questions are simple but somehow tricky. Student need more attention to do these questions.
Class 7 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 Solution in Videos
Rotational Symmetry
Rotation means the circular movement of an object around a center. It is possible to rotate different shapes by an angle around the center point.
Examples:
If you spin the wheel of a bicycle, it rotates. It can rotate in either way: both clockwise and anticlockwise.
(i) a clockwise rotation and
(ii) anticlockwise rotation.
Class 7 Maths Exercise 12.2 Important Questions
How do you know if a shape has rotational symmetry?
A figure has rotational symmetry if it can be rotated by an angle between 0° and 360° so that the image coincides with the pre-image. The angle of rotational symmetry is the smallest angle for which the figure can be rotated to coincide with itself.
Which figure has only rotational symmetry?
Common figures with only rotational symmetry are the recycling sign and fan blades. If a figure coincides with the original twice in one full turn, it has two-fold rotational symmetry, or rotational symmetry order two.
What are the 4 types of symmetry?
The four main types of this symmetry are:
(i) Translation
(ii) Rotation
(iii) Reflection
(iv) Glide reflection.
Do parallelograms have rotational symmetry?
Parallelogram. A parallelogram has no lines of symmetry. It has rotational symmetry of order two.
Centre of Rotation
When an object rotates, its shape and size do not change. The rotation turns an object about a fixed point. This fixed point is the centre of rotation.
Angle of Rotation
The angle of turning during rotation is called the angle of rotation. A full turn, you know, means a rotation of 360°.
Example:
The degree measure of the angle of rotation for
(i) a half-turn is 180⁰
(ii) a quarter-turn is 90⁰
Order of Rotational Symmetry
Consider a square with P as one of its corners
Let us perform quarter-turns about the centre of the square marked x. Rotation by 90° about the centre. In this way, when you complete four quarter-turns, the square reaches its original position.
Thus a square has a rotational symmetry of order 4 about its centre. Observe that in this case,
(i) The centre of rotation is the centre of the square.
(ii) The angle of rotation is 90°.
(iii) The direction of rotation is clockwise.
(iv) The order of rotational symmetry is 4.