Class 7 English Grammar Chapter 3 The Noun Numbers. There are two numbers in English: Singular Number and Plural Number. A Noun or Pronoun that denotes one person or thing is said to be in the Singular Number; Boy, Pen, Child, Tree, Book etc. A Noun or Pronoun that denotes more than one persons or things is said to be in the Plural Number; Boys, Pens, Children. Trees, Books etc.
Class 7 English Grammar Chapter 3 The Noun Numbers – Singular and Plural
In Chapter 3 of Class 7 English Grammar, students embark on a journey to explore the intriguing concept of ‘Noun Numbers’. English, like many languages, categorizes nouns based on quantity. Singular and Plural are the two primary classifications or ‘numbers’. The Singular Number represents a singular entity, denoting just one person, animal, place, thing, or idea. Common examples include ‘boy’, ‘pen’, ‘child’, ‘tree’, and ‘book’. Such nouns are fundamental in everyday communication, emphasizing individuality.
Class 7 English Grammar Chapter 3 Tne Noun Numbers
| Class: 7 | English Grammar |
| Chapter: 3 | The Noun Numbers – Singular and Plural |
| Study Material: | Textbook and Revision Book |
| Academic Session: | 2025-26 |
Class 7 English Grammar The Noun- Singular and Plural
Points to be Remembered
Only countable nouns have plural forms. Singular countable nouns can be made plural usually by adding the suffix–s or es.
Nouns that are made plural by adding–s or es are called regular nouns. For example: table –tables, glass–glasses.
However the plural form of some nouns are made differently. Such nouns are called irregular nouns
The Plural of a Noun formed by adding s to the Singular
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Article | Articles |
| Act | Acts |
| Apple | Apples |
| Actor | Actors |
Singular to Plural using es
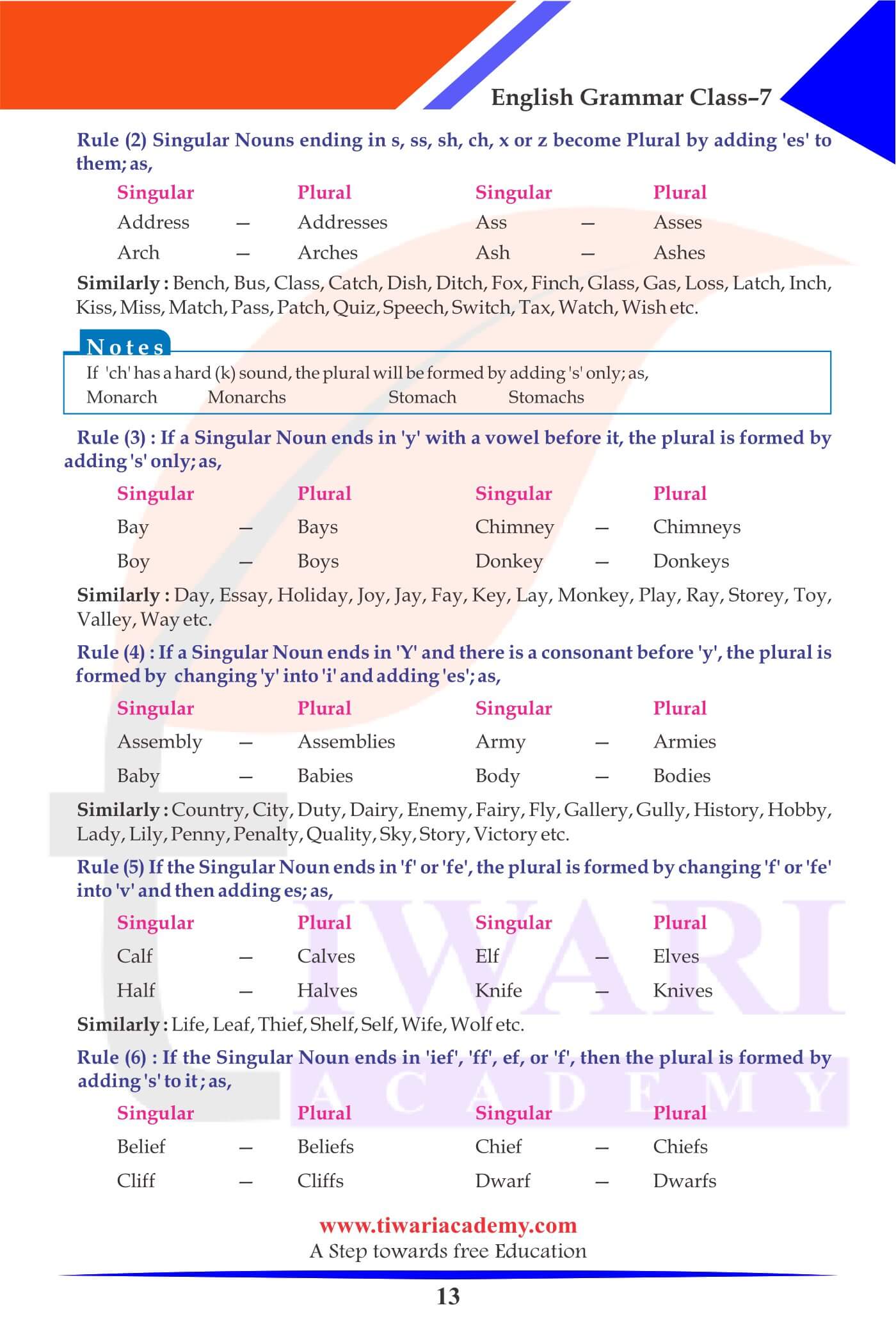
Singular Nouns ending in s, ss, sh, ch, x or z become Plural by adding es to them.
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Ash | Ashes |
| Address | Addresses |
| Arch | Arches |
| Ass | Asses |
Conversely, the Plural Number extends beyond singularity, encompassing multiple entities. Nouns in this category denote more than one person, place, thing, or concept. For instance, ‘boys’, ‘pens’, and ‘books’ signify multiples of their singular counterparts. Interestingly, some nouns, like ‘children’, undergo more intricate transformations from their singular form ‘child’. This chapter provides a deep understanding of these variations, enhancing students’ ability to construct and comprehend diverse sentences, further solidifying their grasp on English grammar.
If a Singular Noun ends in y with a vowel before it, the plural is formed by adding s only.
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Chimney | Chimneys |
| Boy | Boys |
| Donkey | Donkeys |
| Bay | Bays |
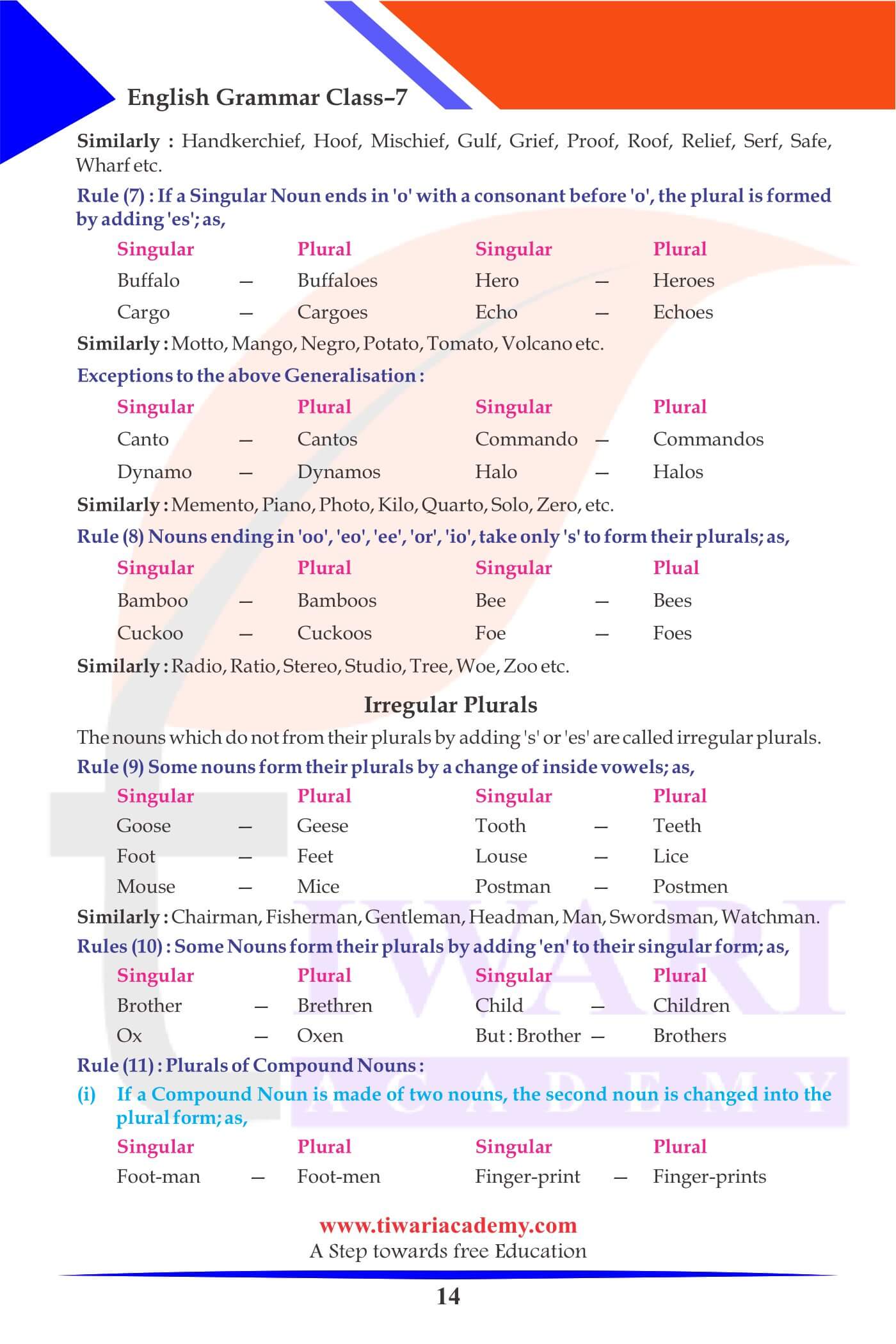
If a Singular Noun ends in o with a consonant before o, the plural is formed by adding es.
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Hero | Heroes |
| Cargo | Cargoes |
| Echo | Echoes |
| Buffalo | Buffaloes |
Plural of Noun by a change of inside vowels
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Foot | Feet |
| Postman | Postmen |
| Mouse | Mice |
| Goose | Geese |
| Louse | Lice |
| Tooth | Teeth |
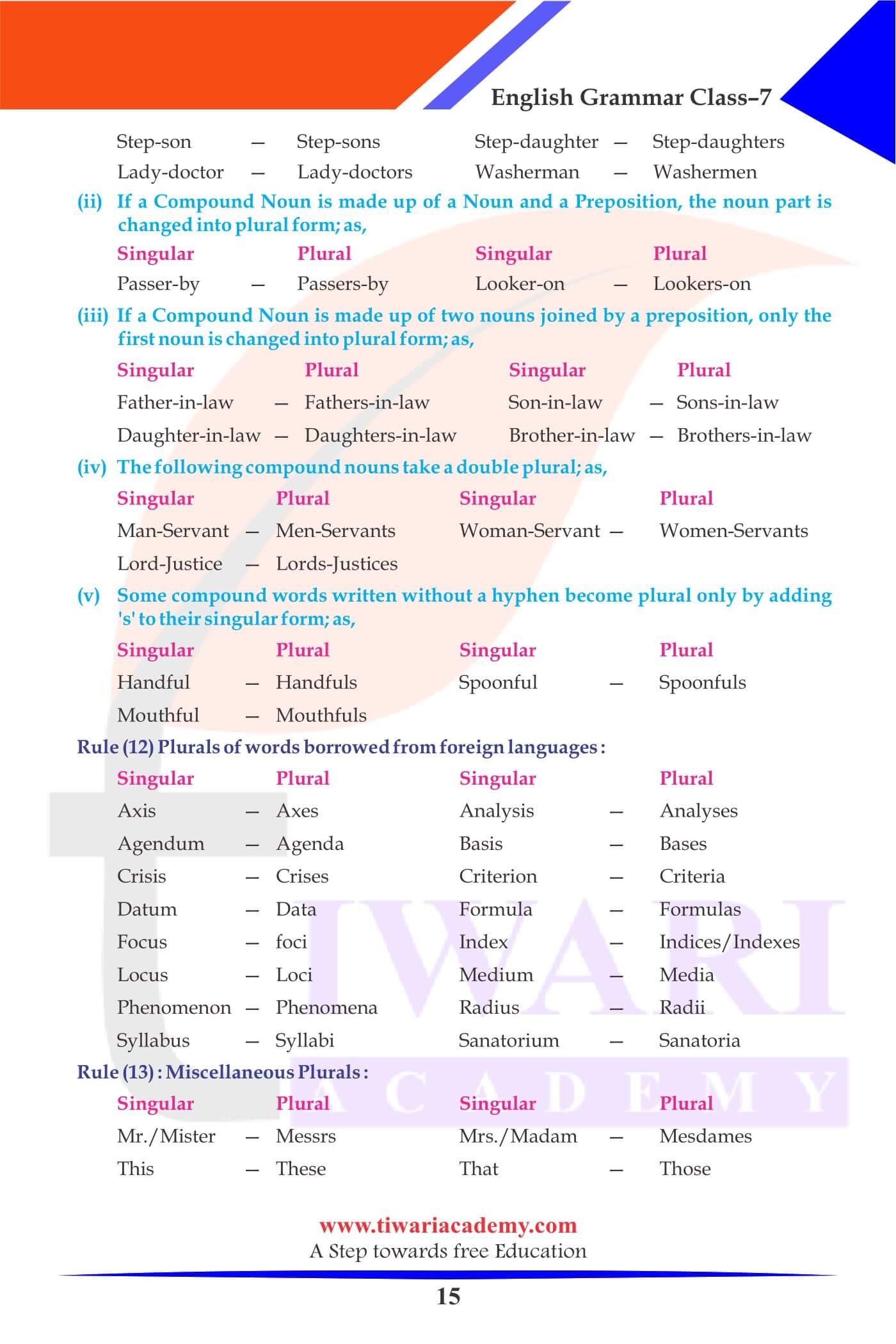
Nouns used only in singular
abuse, advice, luggage, machinery, money, poetry, jewellery, scenery, vacation, word, furniture, fruit, meal, fun, freedom, music, joy, permission, progress, rice, wheat, bread, milk, butter, glass, silver, gold, education, homework, employment, etc.
Nouns used as both the numbers, the singular and the plural
Committee, govt, police, wages, jury, means, politics, pains, publics etc.
The jury was unanimous in its opinion.
The jury were divided in their opinion.
The committee has agreed on this issue.
The committee are divided on this issue.