Class 7 English Grammar Chapter 11 The Tense or Tenses. Tense is the format of a verb which shows the time of action or event and the degree of completeness and also the state of action. Here, you will learn about the kinds of tenses and their application in different sentences. Explanation wit examples of Present, Past and Future tense.
Navigating the intricacies of the English language requires a clear understanding of ‘Tense.’ As delved into in Chapter 11 of Class 7 English Grammar, tense is the form of a verb that illuminates when an action or event occurs, its degree of completion, and the ongoing state of that action. Tense is paramount in painting a clear picture of events, placing them in the right temporal frame, be it the past, present, or future.
| Class: 7 | English Grammar |
| Chapter: 11 | The Tense or Tenses |
| Session: | 2025-26 |
| Study Material: | Textbook and Revision Notes |
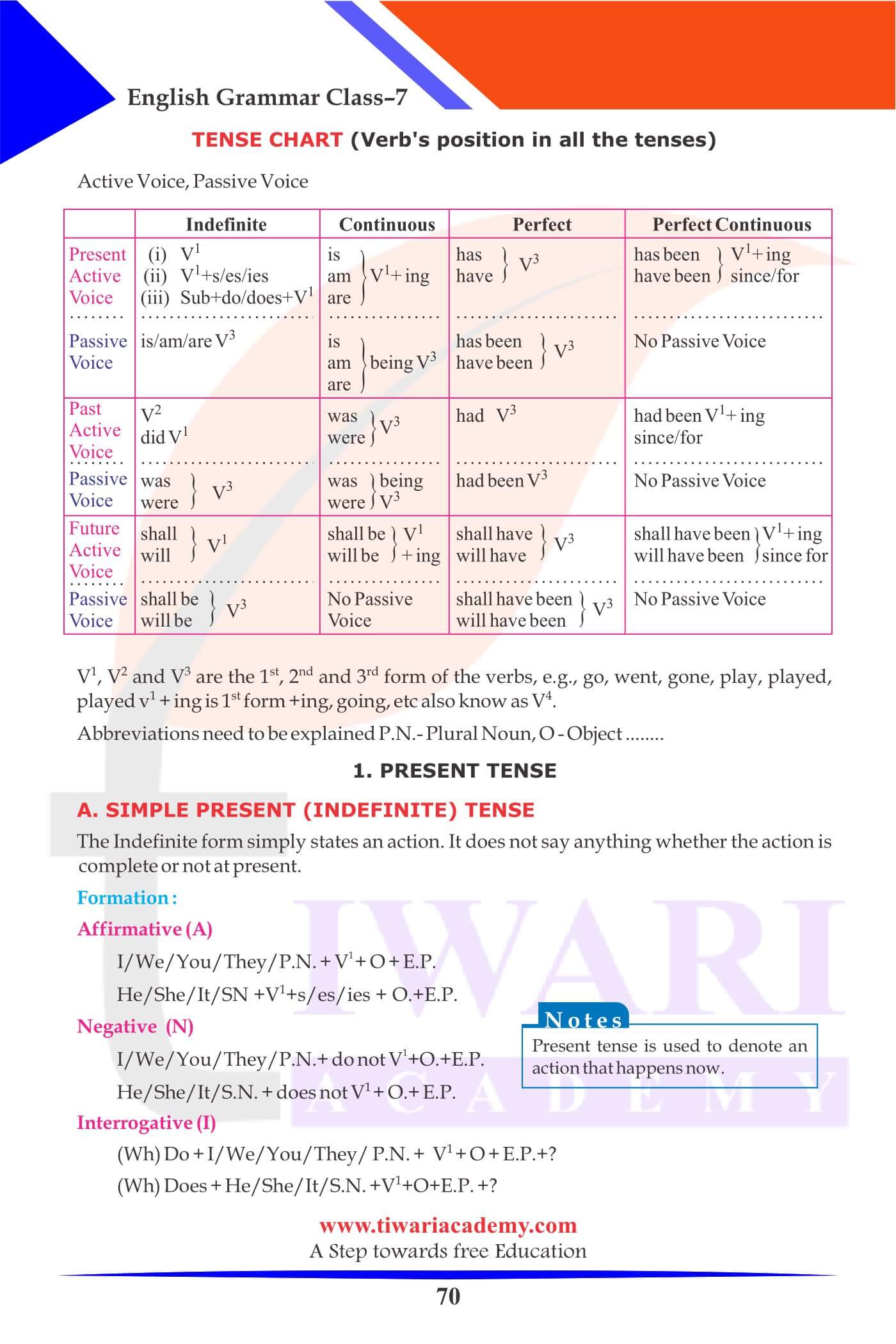
Kinds of Tenses
The word Tense means time. There are three tenses: Present, Past and Future.
(a) A verb that refers to present time is said to be in the Present Tense as,
1. I play.
2. I write.
(b) A verb that refers to past time is said to be in the Past Tense as,
1. I played.
2. I wrote.
(c) A verb that refers to future time is said to be in the Future Tense as,
1. I shall play.
2. I shall write.
This chapter offers learners a deep dive into the multifaceted world of tenses, detailing their diverse types and precise applications. With an array of examples, students will gain insights into the nuances of Present, Past, and Future tenses. These examples, rooted in everyday scenarios, make it straightforward for students to grasp and apply these crucial grammatical components, paving the way for impeccable English communication.
Thus there are three main tenses:
1. The Present
2. The Past
3. The Future
Each of the three main tenses has four forms:
A. Simple (Indefinite): It simply states an action.
B. Continuous (Progressive): It indicates an action going on at the time of speaking.
C. Perfect: It indicates that the action is complete just now.
D. Perfect Continuous: It shows that the action has been continuous.
PRESENT TENSE
SIMPLE PRESENT (INDEFINITE) TENSE
The Indefinite form simply states an action. It does not say anything whether the action is complete or not at present.
The earth is round.
The sun rises in the east.
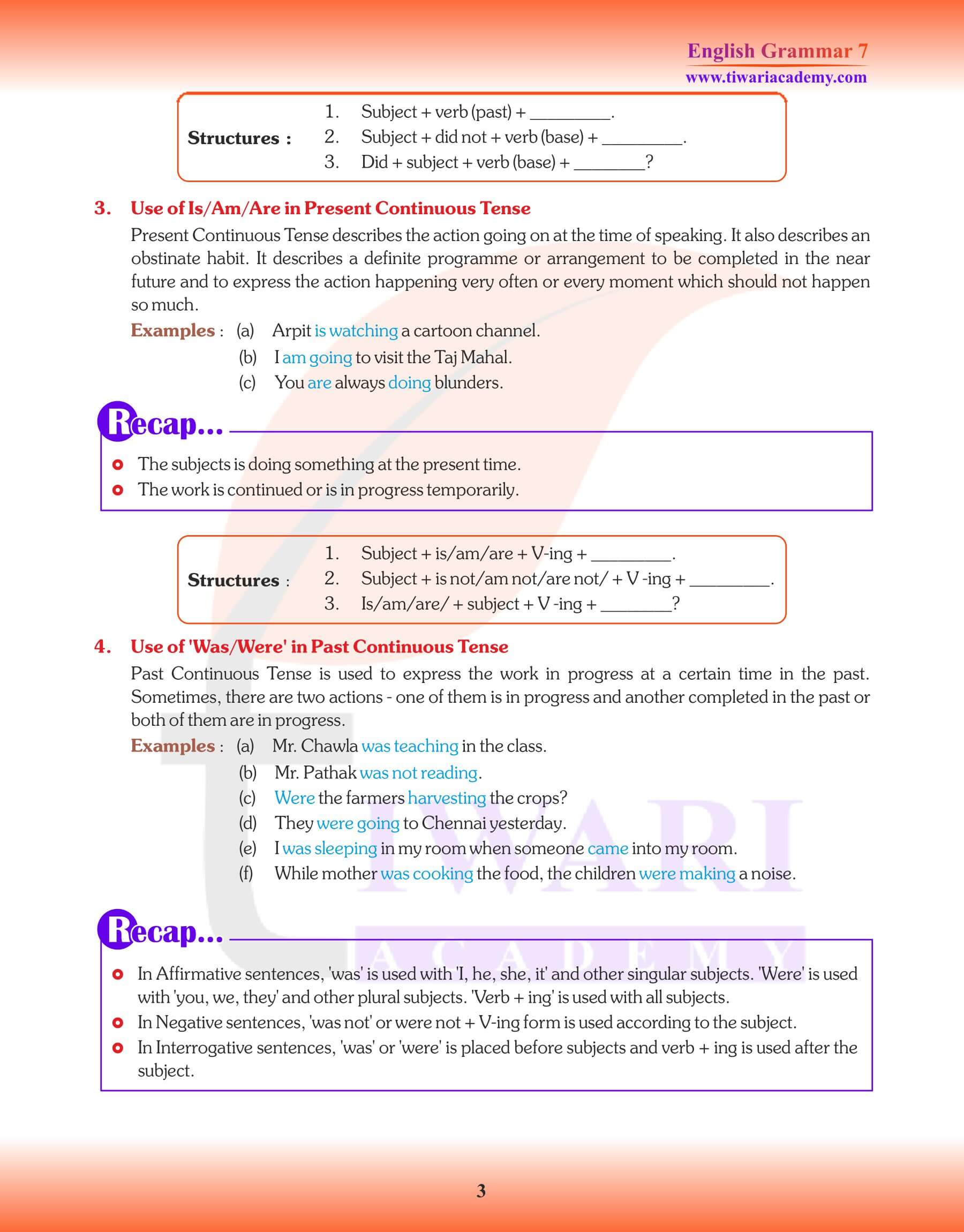
PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE
The baby is sleeping.
Mother is telling a story.
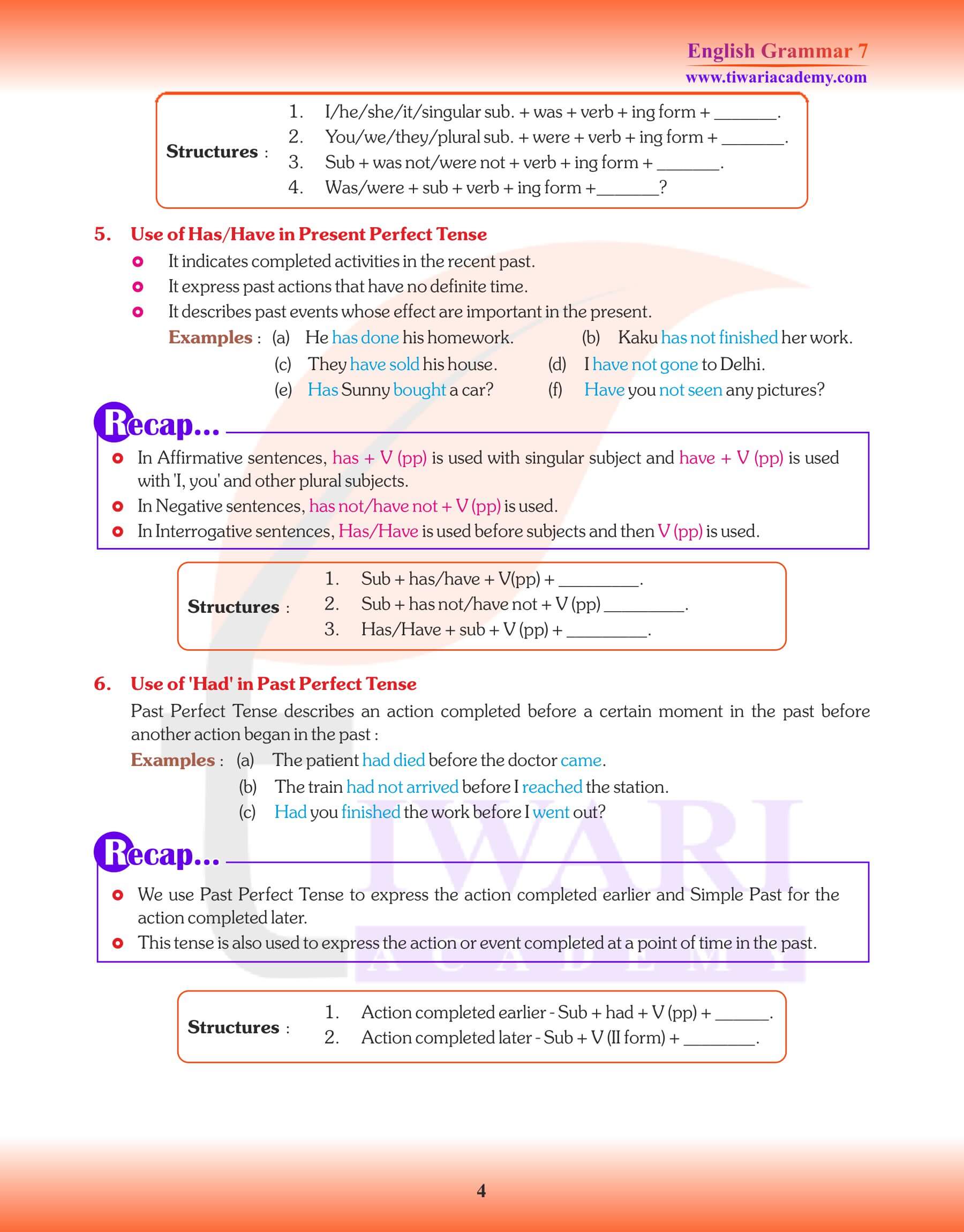
PRESENT PERFECT TENSE
Santosh has just gone out.
We have just been informed of the matter.
We use Past Indefinite Tense, as
He lived at Aurangabad for ten years. (but he does not live there now)
Workers have gone on strike.
Use of since and for:
| Since – Point of Time | For – Period of time |
|---|---|
| since Monday | for two day |
| Since 8 o’clock, since 5 p.m. | for two hours |
SIMPLE PAST/PAST INDEFINITE TENSE
We saw the Prime Minister last month.
I received your letter a week ago.
PAST CONTINUOUS/PROGRESSIVE TENSE
1. To express an action that was happening in the past at the time of speaking, as
Babali was writing a letter when Neeraj called on her.
2. For repeated actions in the past, as
Jyoti was always telling lies.
3. To denote an action which is related to the past, as
She was always asking me for help.
PAST PERFECT TENSE
1. To indicate an action in the past that had been completed before another action the past happened, as
The match had started before we reached the stadium.
2. To express an action or event that happened earlier than a point of time in the past (Time Phrase), as
By 5 p.m., they had scored 250 runs.
3. To express an unfulfilled wish in the past, as
I wish I had worked hard.
PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE:
To denote an action that had been going on for some time before another action took place in the past as,
We had been solving the sums for one hour when you joined us.
He had been sleeping for four hours when the thief broke into his house.
THE FUTURE TENSE
FUTURE INDEFINITE TENSE/SIMPLE FUTURE TENSE
1. To express an action which will take place in the future, as
Ritesh will come here tomorrow.
2. To talk about things which we cannot control. It expresses the future as fact, as
It will be Diwali in a week.
FUTURE CONTINUOUS / PROGRESSIVE TENSE
1. To show an action that will be going on in the future, as
Kush will be studying in 7th Class from next April.
2. To denote an action as going on at some point of time in future, as
I shall be waiting for her here at six p.m.
FUTURE PERFECT TENSE
1. To show an action that will be completed before a certain time in future, as
I shall have completed all the lessons before the end of February.
2. To show speaker’s inference or conclusion, as
Deepak will have reached Delhi by now.
FUTURE PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
1. To show an action that will begin in the future but may continue for some time, as
We shall have been revising our courses since February.
The team will have been practicing for an hour before the match begins.