Study here about Class 6 English Grammar Chapter 7: A Pronoun, in which you will learn about Pronoun and its seven kinds. We know that Pronoun is a word used for a noun. It is of the same person: gender and number as the Noun for which it is used. In NCERT Solutions for class 6 English Grammar Chapter 7, we will learn that Pronouns are substitutes for Nouns to avoid repetition. In English language, Pronoun help us making a perfect meaningful sentence with easy words. Here we have to learn about seven kinds of Pronouns, which are as 1. Personal Pronouns, 2. Demonstrative Pronouns, 3. Indefinite Pronouns, 4. Relative Pronouns, 5. Distributive Pronouns, 6. Reflexive and Emphatic Pronouns, 7. Interrogative Pronouns. Pronoun can be used as subject, object or sometime it shows a possession.
Explanation of Pronoun and its Kinds
| Class: 6 | English Grammar |
| Chapter: 7 | A Pronoun |
| Textbooks: | Course Book and Revision Notes |
| Academic Session: | 2025-26 |
6th English Grammar: Pronoun and its uses
Class 6 English Grammar Chapter 7: A Pronoun with its types are described below with suitable examples. The description of seven kinds of pronoun with examples are given in simplified format.
Personal Pronoun
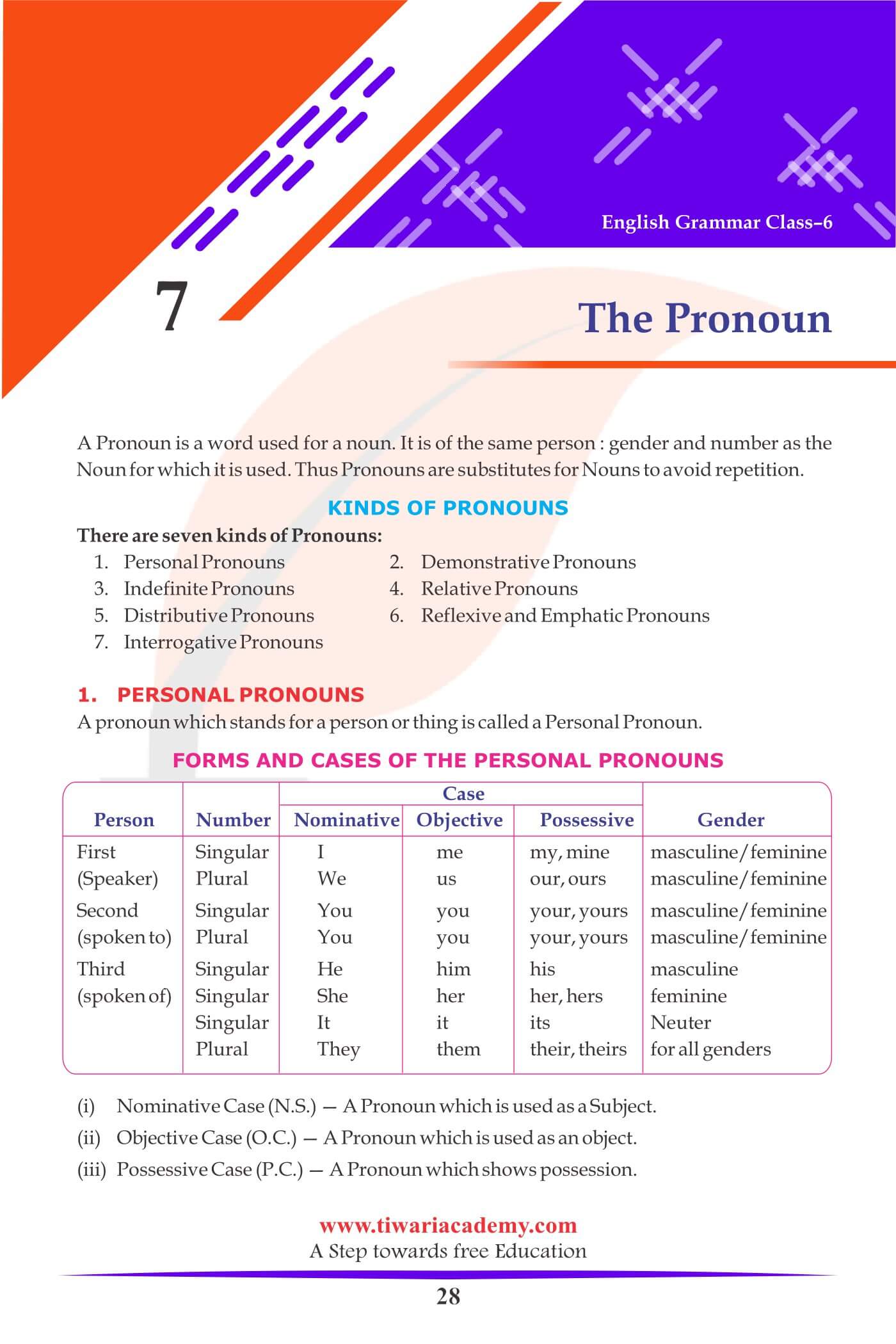
A pronoun which stands for a person or thing is called a Personal Pronoun. For example, he, she, they, I, her, etc.
- Nominative Case (N.S.) — A Pronoun which is used as a Subject.
- Objective Case (O.C.) — A Pronoun which is used as an object.
- Possessive Case (P.C.) — A Pronoun which shows possession.
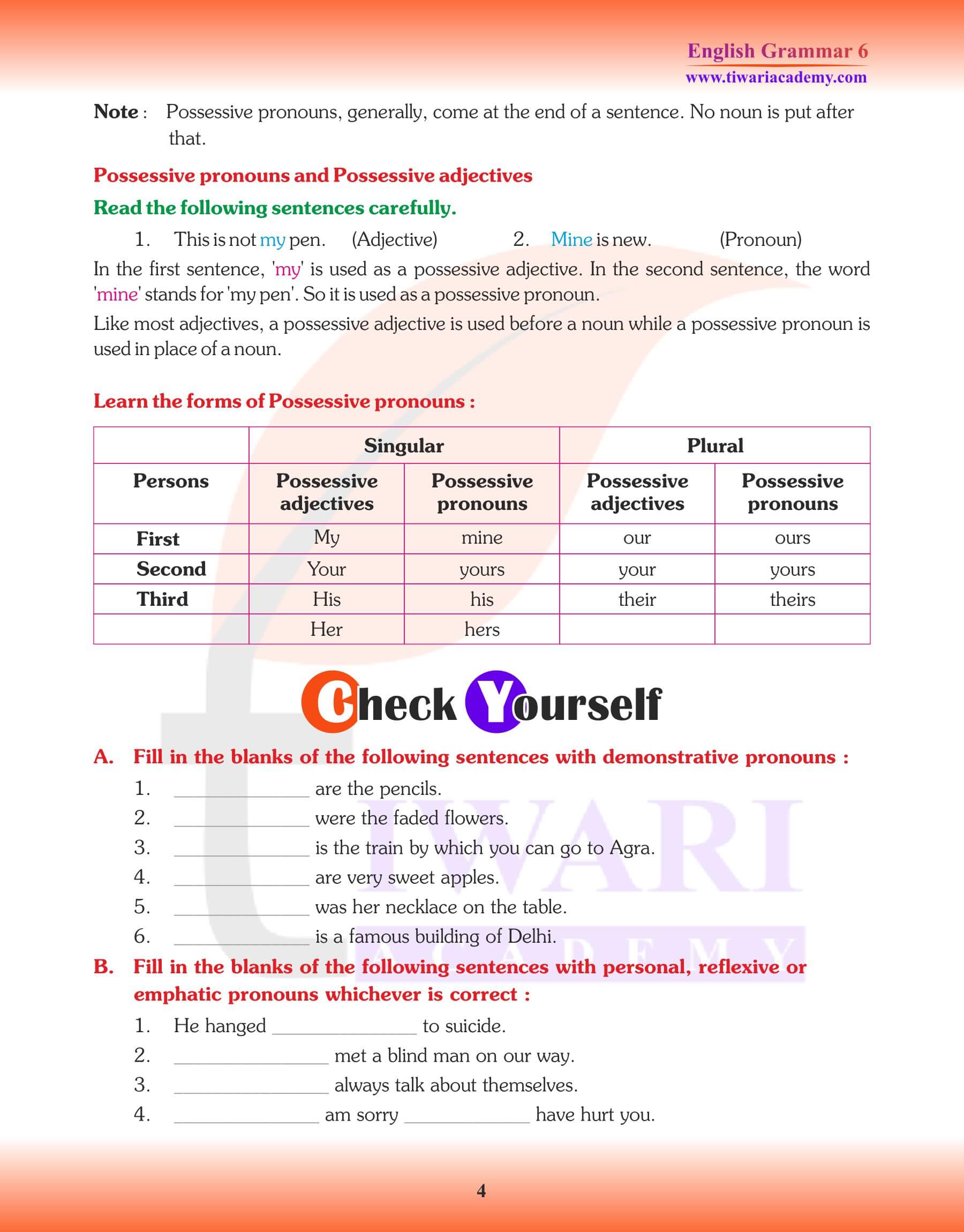
(a) The forms mine, ours, yours, his, hers, theirs are called possessive pronouns.
(b) The forms my, our, your, his, her, their and its are called possessive determiners.
(Remember) that determiners are always followed by nouns but pronouns are never followed by nouns.
Demonstrative Pronoun
A Demonstrative Pronoun is used to point the object or objects to which it refers; as,
This is my purse.
That is your cycle.
These are her dolls.
Those are our friends.
Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite Pronouns do not refer to any particular person or thing, but they refer to Nouns in a general way; as,
- Some are born great.
- Many of these eggs are rotten.
- Few escaped unhurt.
- One should keep one’s promise.
- Do good to others.
- None of these apples are ripe.
- All are quite upto the mark.
- Somebody has stolen my book.
Interrogative Pronoun
An Interrogative Pronoun is used to ask a question; as,
- Who teaches you English?
- Whose is this pen?
- Whom do you want to see?
- Which is your house?
- What are you doing?
Relative Pronouns
All five Interrogative Pronouns become Relative Pronouns when they relate a noun or pronoun in a sentence.
- I met Khushi. Khushi stood first in the class.
I met Khushi who stood first in the class. - We met a girl. Her brother was given a reward.
We met a girl whose brother was given a reward. - This is the girl. All praise her.
This the girl whom all praise. - Sagun has found the purse. She had lost the purse.
Sagun has found the purse which she had lost. - What had happened? I do not know.
I do not know what had happened. - I know the hostel. He lives in the hostel.
I know the hostel that he lives in.
Distributive Pronouns
Distributive Pronouns are those which show that persons or things are taken one at a time or in separate groups.
Each refers to two or more persons taken one by one. Either means one or the other. Neither is of course, the negative of either.
- Each of them got a prize.
- Neither of them came to see me.
- Either of the two roads leads to Delhi.
Reflexive Pronouns
Pronoun in which the action of the subject reflects or turns back on the Subject itself are called Reflexive Pronouns. The various forms of Reflexive/Emphatic Pronouns are—myself, ourselves, yourself, yourselves, himself, herself, itself, themselves.
- I injured myself.
You hurt yourself. - She killed herself.
They will enjoy themselves.
A Pronoun used to convey emphasis is called an Emphatic Pronoun.
- I myself locked the door.
You yourself ask for money. - He himself insulted her.
The wall itself fell.