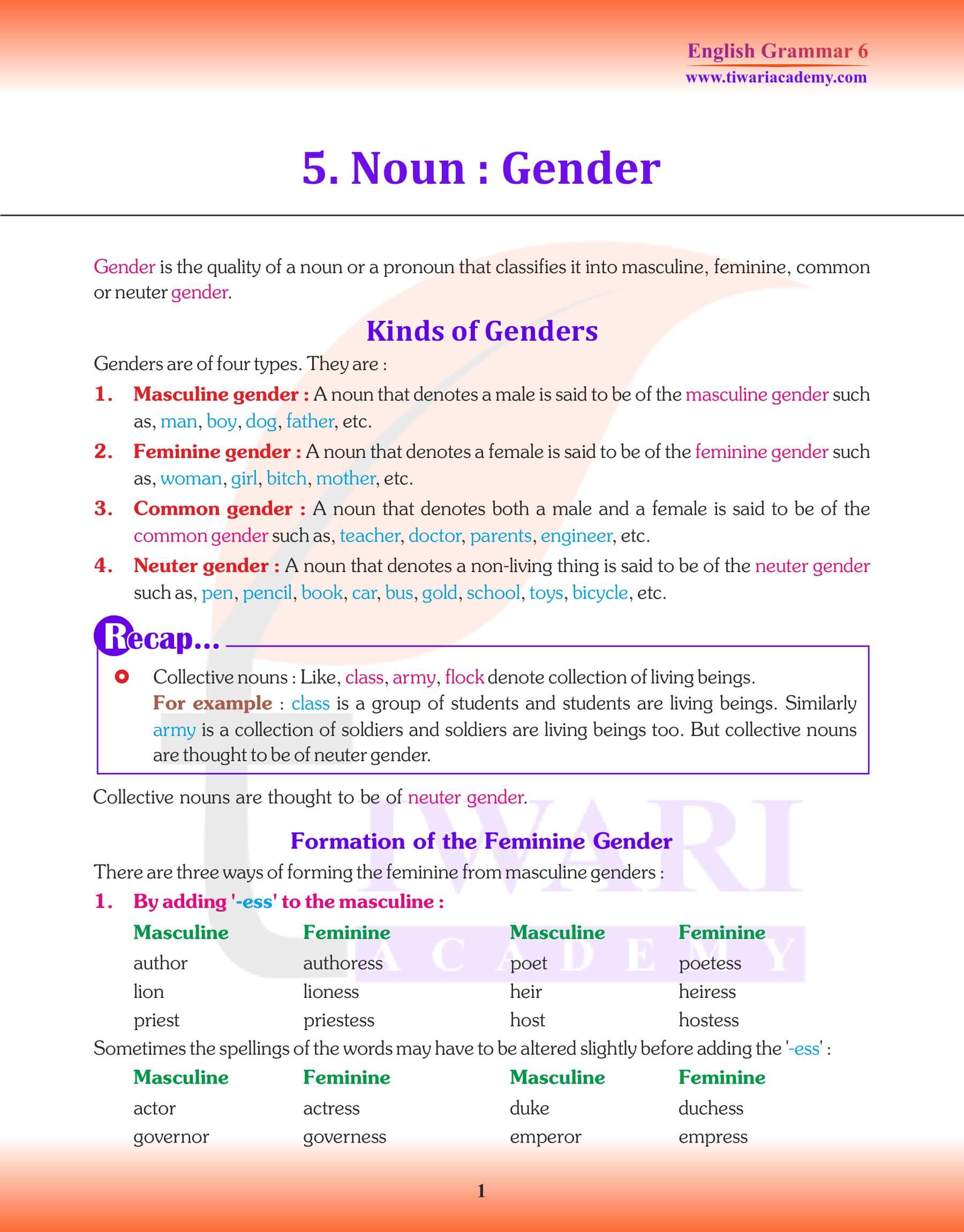
Class 6 English Grammar Chapter 5: Noun Genders, which tell us whether a noun belongs to the male sex, female sex or to neither of the two. There are four genders in the English language: (a) Masculine Gender (b) Feminine Gender (c) Common Gender (d) Neuter Gender. For example, Man, boy and the male animals are masculine. Women, girls and female animals are feminine. A noun which has the same form for masculine and feminine is of the Common Gender; as, parent, baby, child, cousin, author, painter, artist, etc. A lifeless thing is of the Neuter Gender; as, book, table, knife, pen, etc.
Class 6 English Grammar Chapter 5 Noun Genders Notes
Deciphering Noun Genders in English Grammar
Chapter 5 of Class 6 English Grammar offers insights into the intriguing world of Noun Genders. Gender in grammar provides context regarding whether a noun pertains to the male category, the female category, or neither. English stands out with its classification of nouns into four distinct genders: Masculine, Feminine, Common, and Neuter. The way nouns are categorized based on gender enhances the richness of language, helping users describe and understand relationships, characteristics, and distinctions between entities more accurately.
Noun Genders Explanation Video
Distinguishing Masculine and Feminine Genders
In the realm of English grammar, the Masculine Gender is designated for nouns that refer to male beings, such as “man” or “boy,” and even extends to male animals. Conversely, the Feminine Gender encompasses nouns that signify female entities, including “woman,” “girl,” and names of female animals. Being able to distinguish between these two genders is fundamental in conveying accurate descriptions and relationships in both spoken and written forms, ensuring clear communication.
| Class: 6 | English Grammar |
| Chapter: 5 | Noun Genders |
| Content: | Study Material and Textbook for Revision |
| Academic Session: | 2025-26 |
English Grammar for 6th about Noun Genders
Class 6 English Grammar Chapter 5: Noun Genders with examples of Masculine Gender, Feminine Gender, Common Gender and Neuter Gender are given below. All the contents are updated for new academic session 2025-26.
Exploring Common and Neuter Genders
Moving beyond the realms of masculinity and femininity, we encounter the Common Gender and Neuter Gender. Nouns of the Common Gender are versatile; they have a consistent form irrespective of whether they’re referring to a male or female. Examples include terms like “parent,” “child,” “author,” and “artist.” These nouns are especially valuable in contexts where gender specificity is unnecessary or unknown. Meanwhile, the Neuter Gender is reserved for lifeless objects, entities devoid of a gender association. Common examples include “book,” “table,” “knife,” and “pen.” Recognizing these distinctions enhances language precision and helps readers and speakers navigate the multifaceted landscape of English grammar.
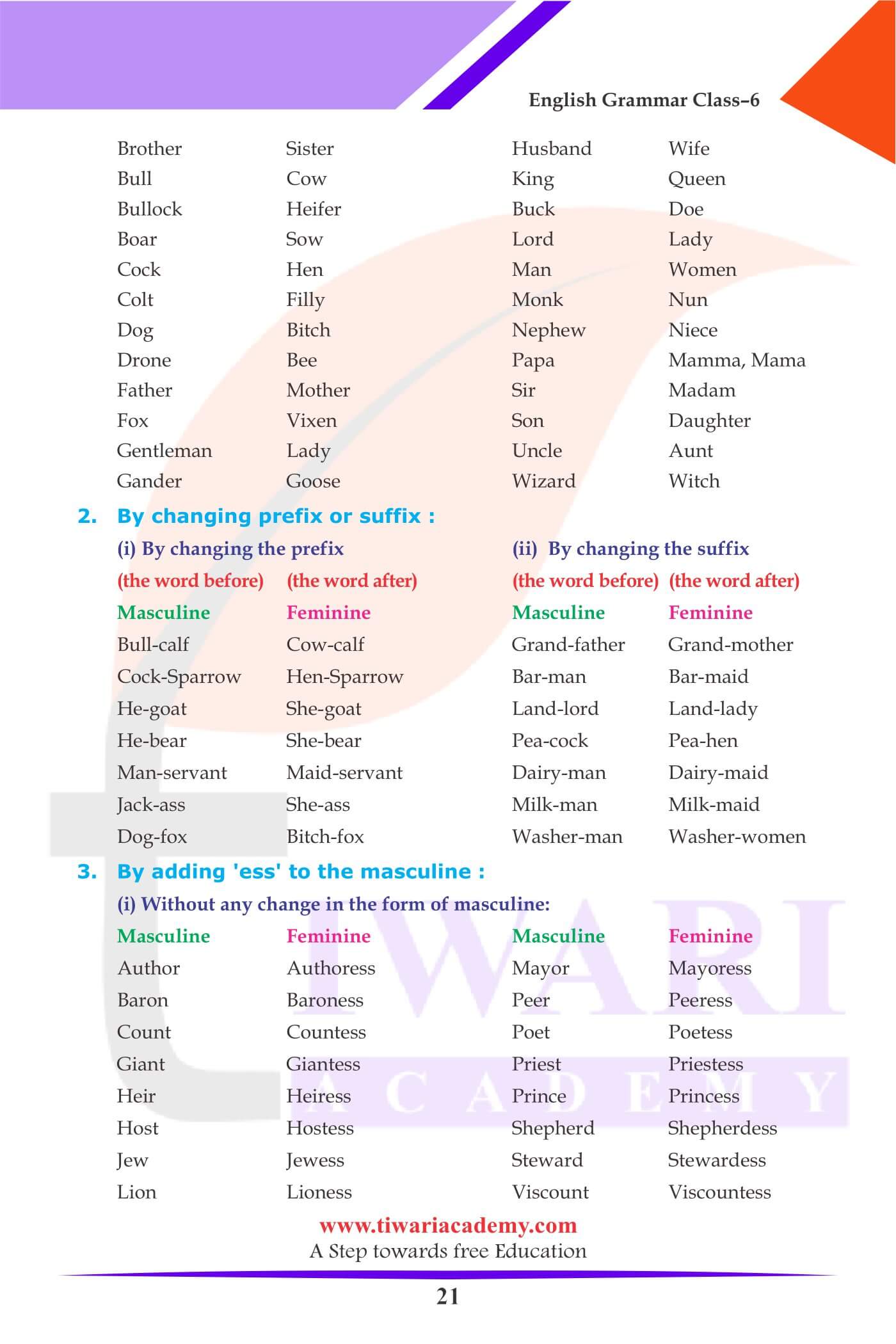
WAYS OF CHANGING GENDER
- Words change from masculine to feminine by adding a suffix: For example, author: authoress and heir: heiress.
- Words change from feminine by adding–ess with some changes to the masculine. For example, Waiter: Waitress, duke: duchess.
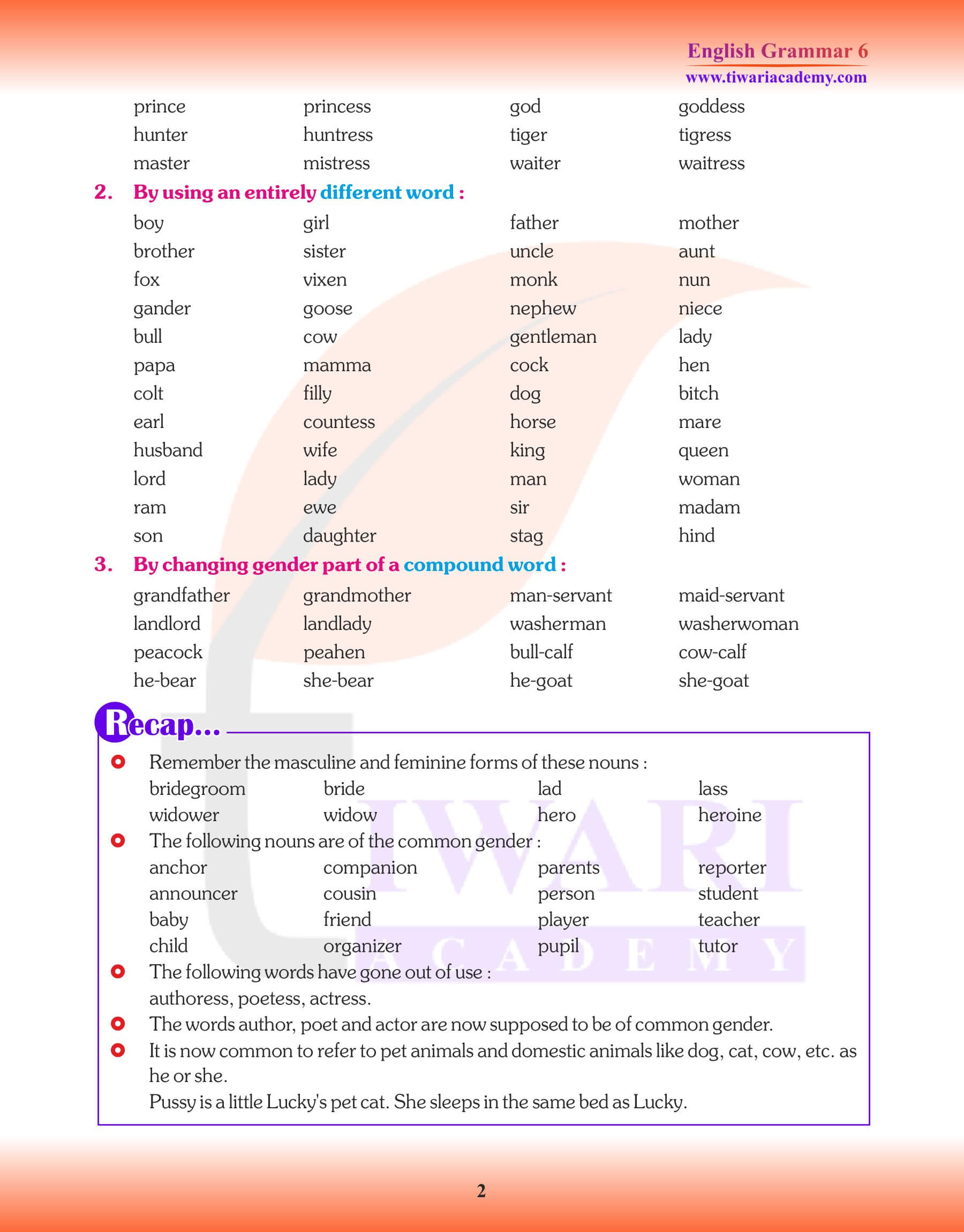
- Some masculine words change entirely as they become feminine words. For example, king: queen, bride: groom.
- Some masculine words change party when they become feminine words. For example, Landlord: landlady, milkman: milkmaid
| Masculine | Feminine |
| Boy | Girl |
| Horse | Mare |
| Brother | Sister |
| Husband | Wife |
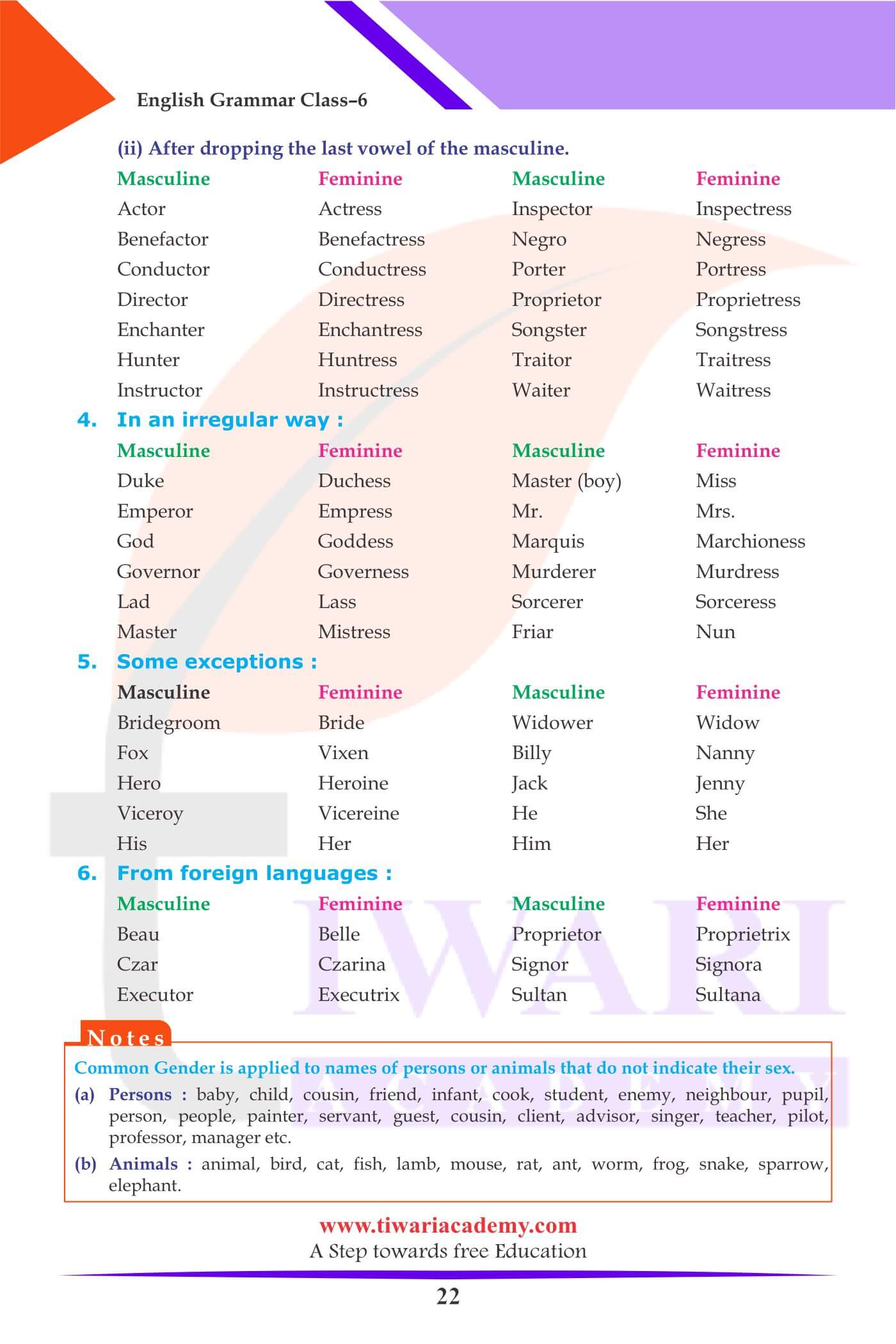
Name of Person
Common Gender is applied to names of persons that do not indicate their sex.
Persons: Baby, child, cousin, friend, infant, cook, student, enemy, neighbour, pupil, person, people, painter, servant, guest, cousin, client, advisor, singer, teacher, pilot, professor, manager etc.
| Masculine | Feminine |
| Actor | Actress |
| Inspector | Inspectress |
| Benefactor | Benefactress |
| Negro | Negress |
| Conductor | Conductress |
| Porter | Portress |
| Director | Directress |
| Proprietor | Proprietress |
Name of Animals
Common Gender is applied to names of animals that do not indicate their sex.
Animals: Animal, bird, cat, fish, lamb, mouse, rat, ant, worm, frog, snake, sparrow, elephant.
| Masculine | Feminine |
| God | Goddess |
| Marquis | Marchioness |
| Governor | Governess |
| Murderer | Murdress |
| Lad | Lass |
| Sorcerer | Sorceress |
| Master | Mistress |
Feedback and Suggestions
Ask your doubts related to your course in CBSE Board 2025-26 and share your knowledge with your friends and other users through Discussion Forum. Download the latest CBSE NCERT Books and Offline Apps of Tiwari Academy.