Class 6 English Grammar Chapter 23 Active and Passive Voice. Transitive Verb has two voices, the Active Voice and the Passive Voice. Voices show whether the Subject of the Verb acts or is acted upon. There is no difference in the meanings of these two sentences. There are simply two different ways of saying the same thing. But sometime, subject performs the action, otherwise the subject of the verb is acted upon. Thus the voice shows whether the subject of a verb acts or is acted upon.
Class 6 English Grammar Chapter 23 Active and Passive Voice
| Class: 6 | English Grammar |
| Chapter: 23 | Active and Passive Voice |
| Textbooks: | Course Book and Revision Notes |
| Academic Session: | 2025-26 |
Active Voice
When the subject of a verb acts or the subject is the doer of the action, the verb is said to be in the Active Voice; as,
- Kanta writes a letter.
- Rama helped Sita.
Passive Voice
When the Subject of a Verb is acted upon, or the Subject is the receiver of the action, the verb is said to be in the Passive Voice; as,
- A letter is written by Kanta.
- Sita was helped by Rama.
Active Voice to Passive Voice
To change a sentence from its Active Voice to its Passive Voice:
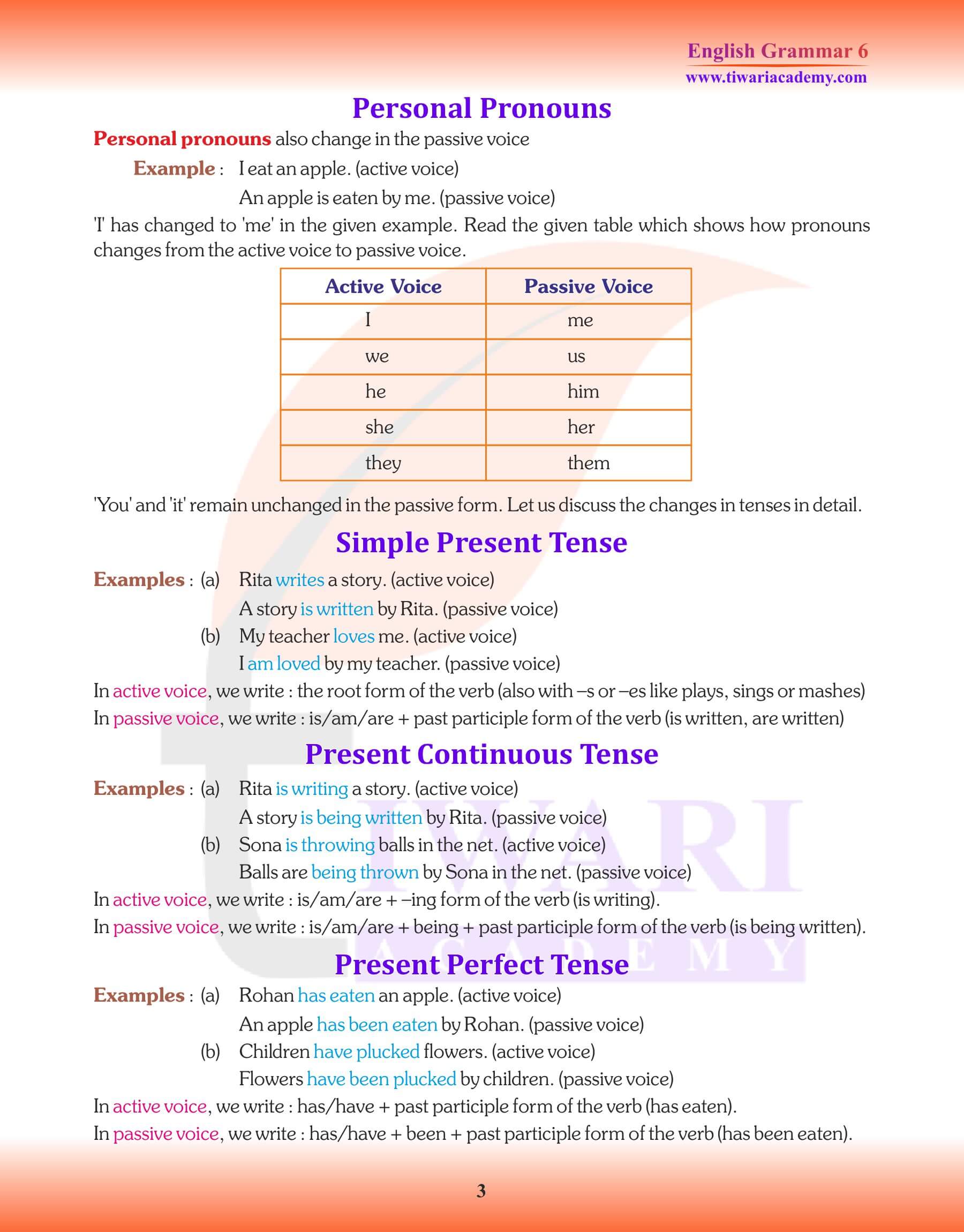
1. Subject in the Active Voice takes the place of Object in the Passive Voice.
2. Object in the Active Voice takes the place of the Subject in the Passive Voice.
3. “By” is used before object in the Passive Voice.
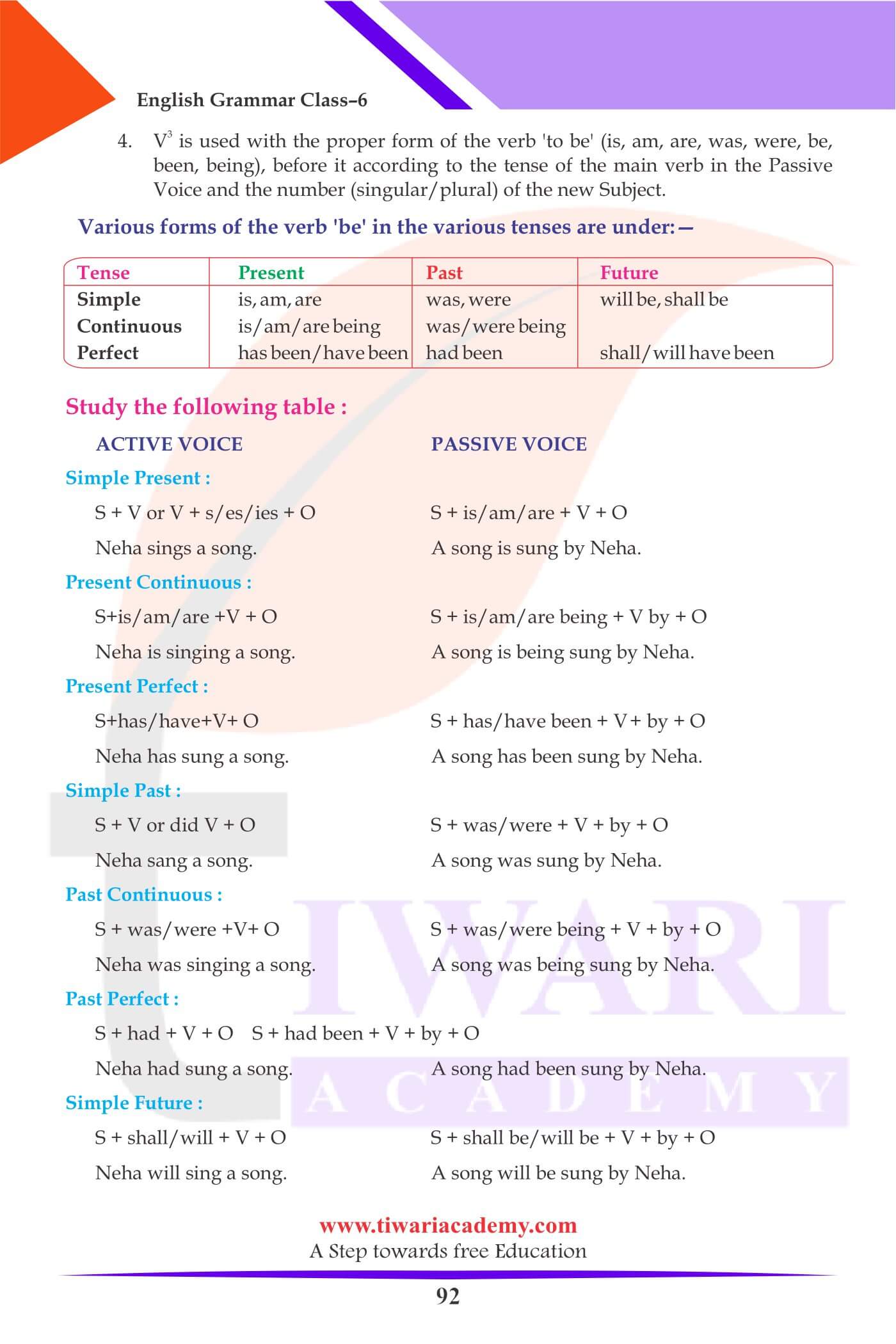
4. Verb third form is used with the proper form of the verb “to be” (is, am, are, was, were, be, been, being), before it according to the tense of the main verb in the Passive Voice and the number (singular/plural) of the new Subject. Various forms of the verb “be” in the various tenses are under:—
| Present | Past | Future |
|---|---|---|
| is, am, are | was, were | will be, shall be |
| is/am/are being | was/were being | – |
| has been/have been | had been | shall/will have been |
| Type of senteence | Active Voice | Passive Voice |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Present | Neha sings a song. | A song is sung by Neha. |
| Present Continuou | Neha is singing a song. | A song is being sung by Neha. |
| Simple Past | Neha sang a song. | A song was sung by Neha. |
| Past Continuous | Neha was singing a song. | A song was being sung by Neha. |
| Past Perfect | Neha had sung a song. | A song had been sung by Neha. |
| Simple Future | Neha will sing a song. | A song will be sung by Neha. |
| Future Perfect | Neha will have sung a song. | A song will have been sung by Neha. |
Remember:
1. In sentences having verb + preposition in Active Voice, remember to retain the preposition with the verb.
A: The nurse looked after the child.
P: The child was looked after by the nurse.
2. In Questions:
Remember that in Interrogative sentences, Interrogative form of the sentence is always unchanged, i.e. use helping verb before subject in Passive Voice. (according to its subject) as,
A: Is he taking tea? P: Is tea being taken by him?
A: Do you eat mangoes? P: Are mangoes eaten by you?
A: Does he hurt you? P: Are you hurt by him?
3. IMPERATIVE SENTENCES
A: Help the poor. P: Let the poor be helped. (or) The poor should be helped.
A: Open the door. P: Let the door be opened. (or) The door should be opened.
Notes:
1. Future Continuous tense has no passive voice.
2. All Perfect Continuous tenses also have no passive voice.