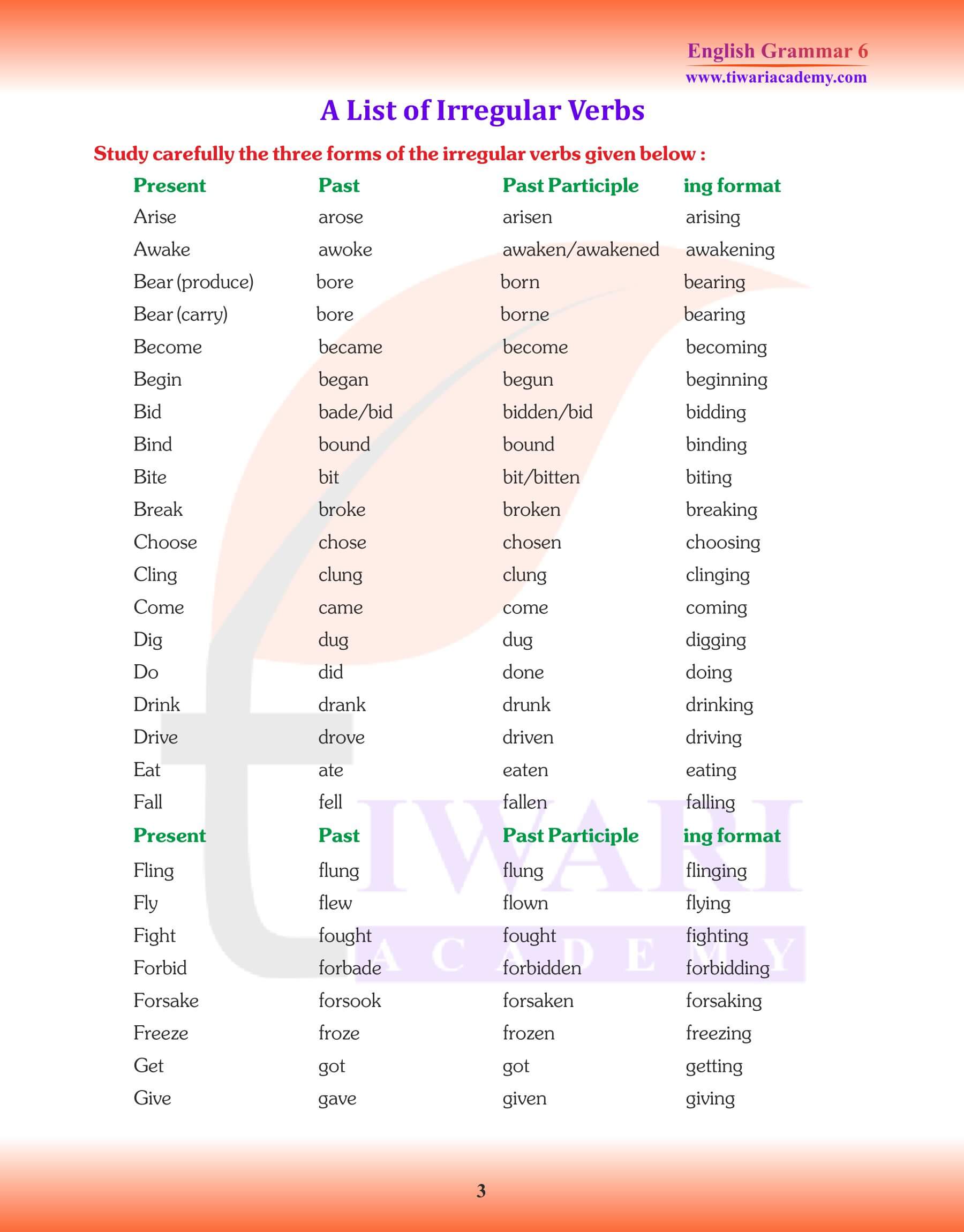
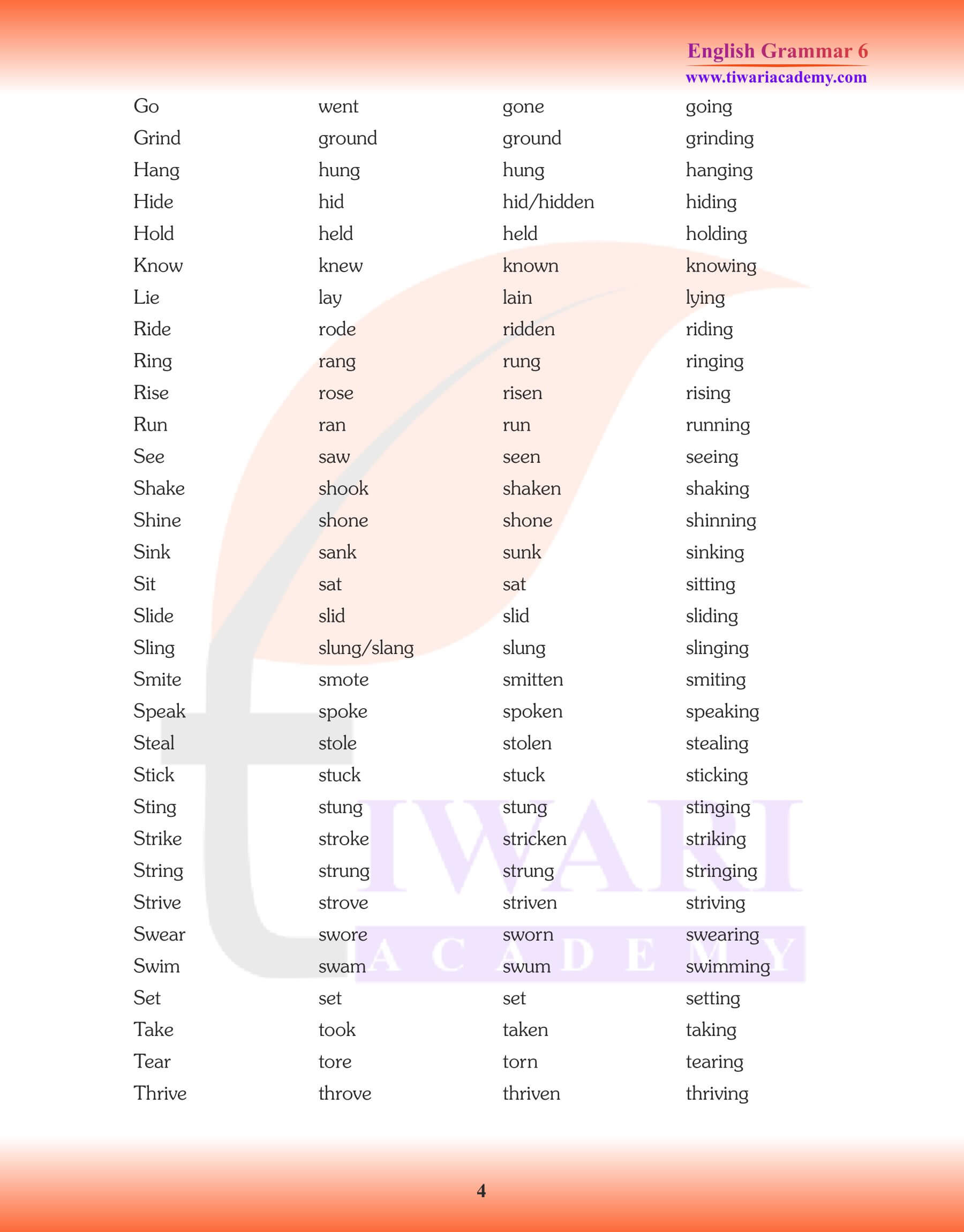
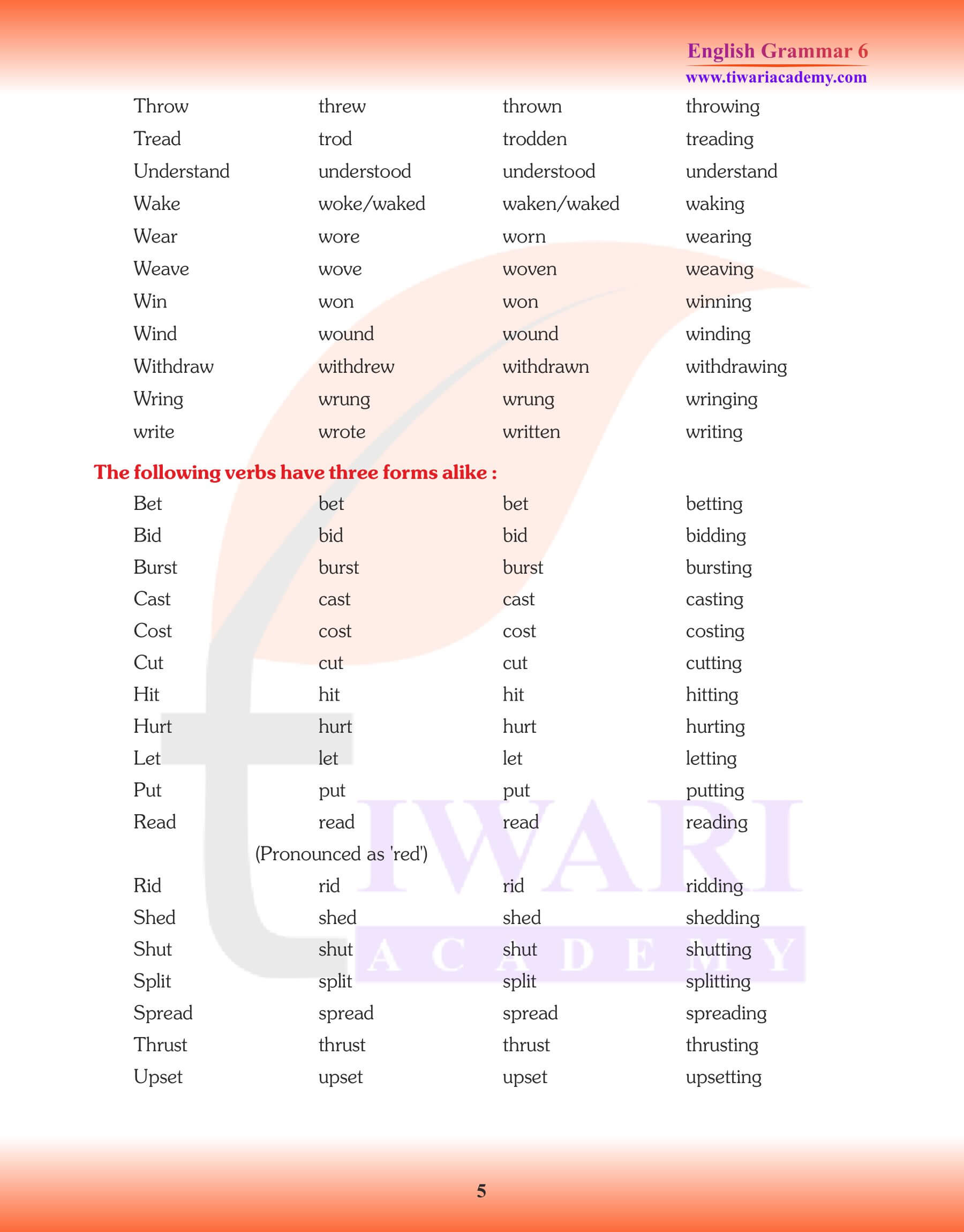
In Class 6 English Grammar, we use four forms of verbs in various tenses, voices and moods. Class 6 English Grammar Chapter 11: Verbs and Their Forms, is very important that we should know here these forms to be able to speak and write English correctly. On the basis of manner in which verbs form their past, past participle and present participle, they are classified into two groups. 1. Weak Verbs or Regular Verbs 2. Strong or Irregular Verbs. Verb forms are also useful to understand all the chapters of NCERT Textbook Honeysuckle and supplementary reader – A pact with the Sun. Forms of verb make sentences easy to understand and helps in the formation of new sentences. This English Grammar is useful for the students of CBSE, UP Board, MP Board, Uttarakhand, Rajasthan and Punjab Board, who are using NCERT Textbooks are a course books.
Class 6 English Grammar Chapter 11 Verbs and their Forms
Noun and their Forms Explanation
| Class: 6 | English Grammar |
| Chapter: 11 | Verbs and Their Forms |
| Content Source: | Textbook and Revision book |
| Academic session: | 2025-26 |
6th English Grammar Chapter 11: Verbs and Their Forms
Get here the complete solutions of Class 6 English Grammar Chapter 11: Verbs and Their Forms in PDF form updated for new academic session 2025-26. Kinds of verb with examples and assignment for practice are given.
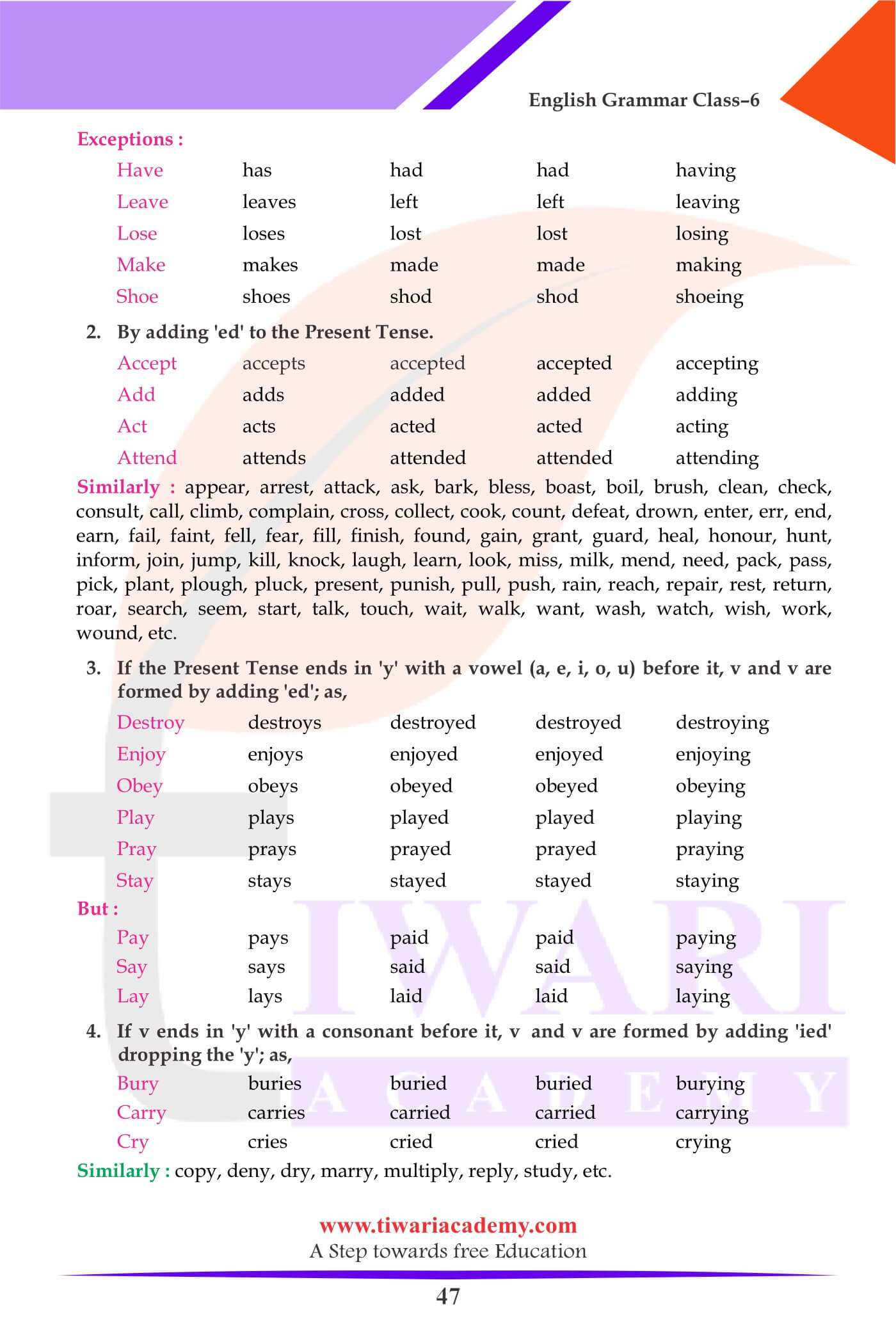
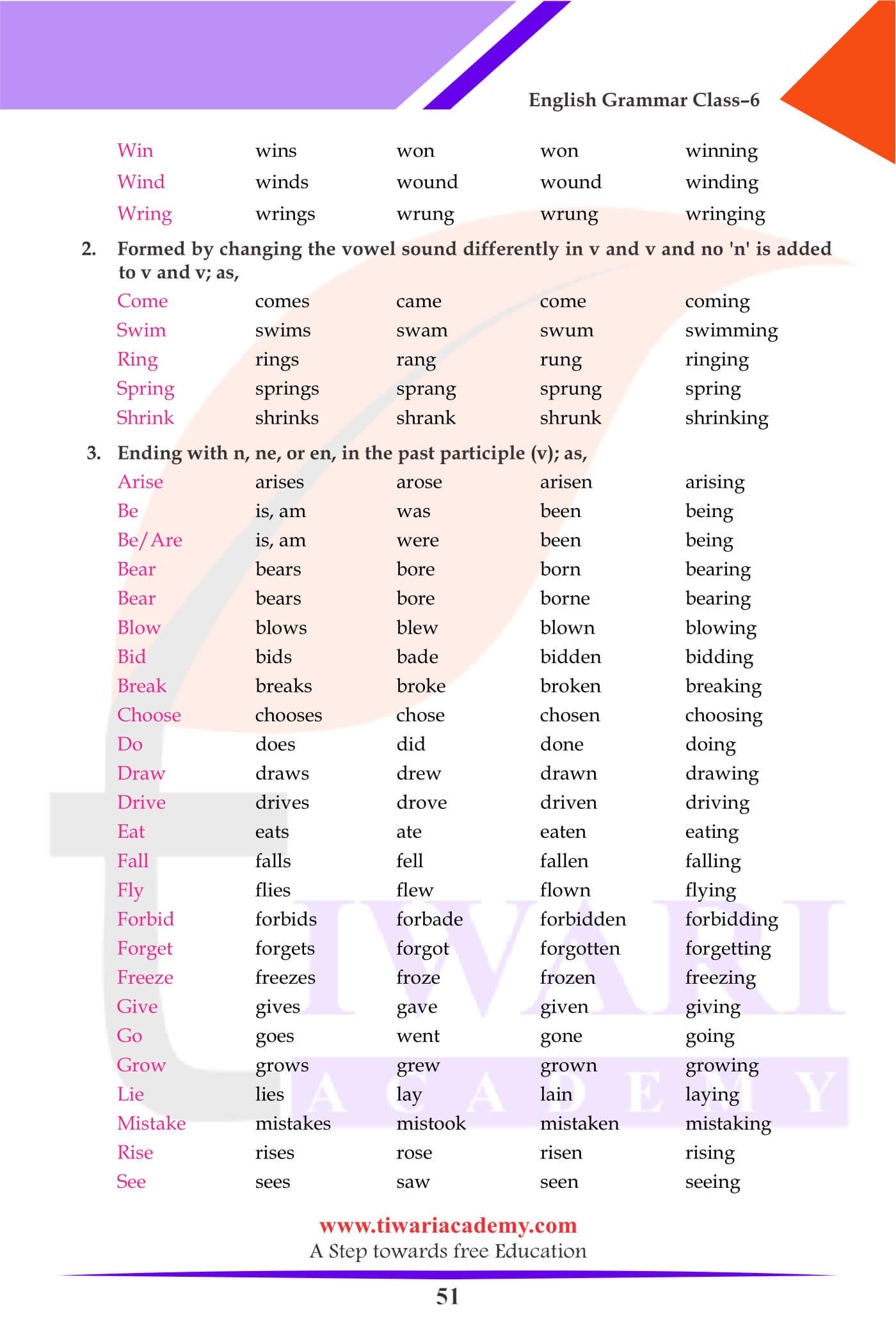
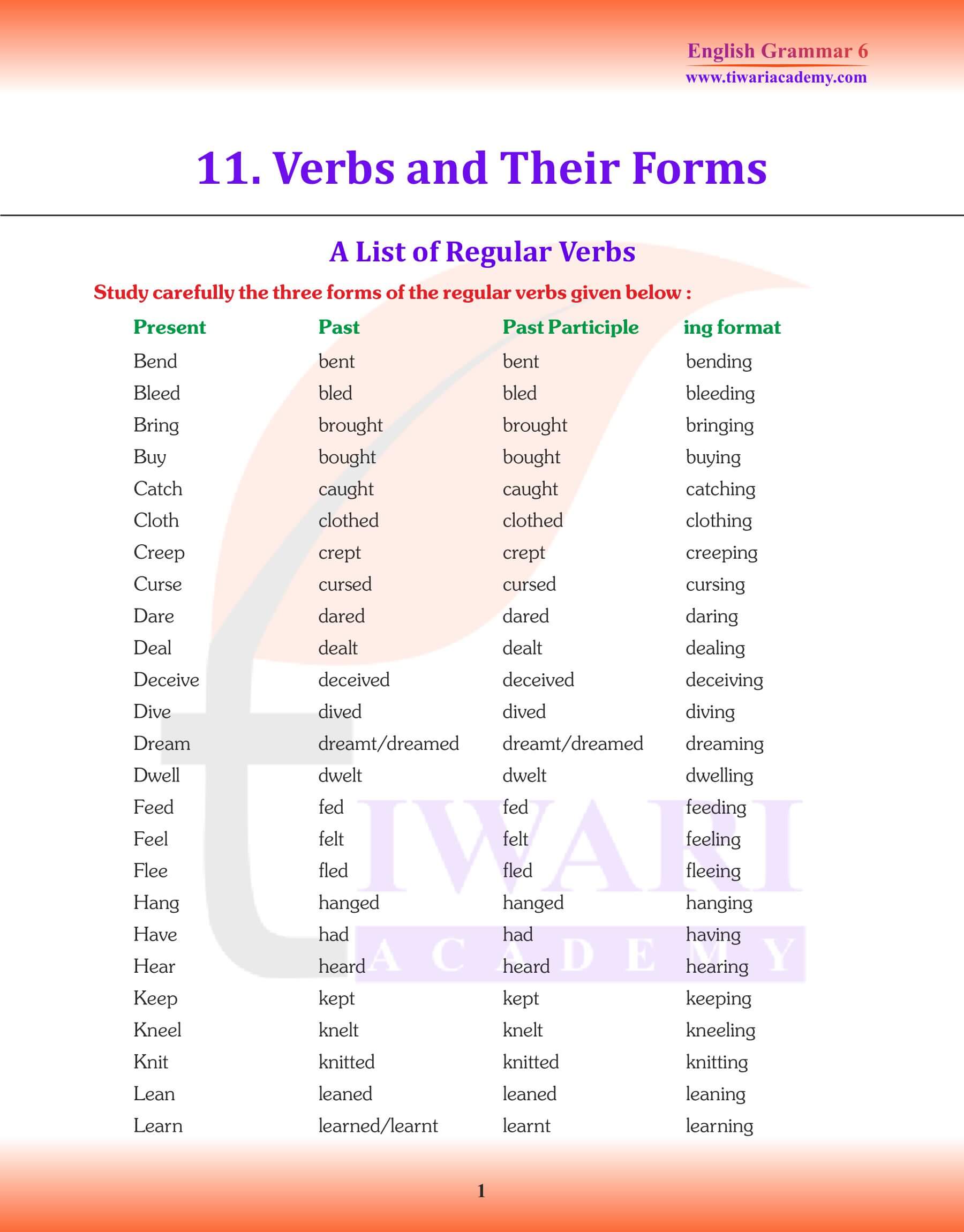
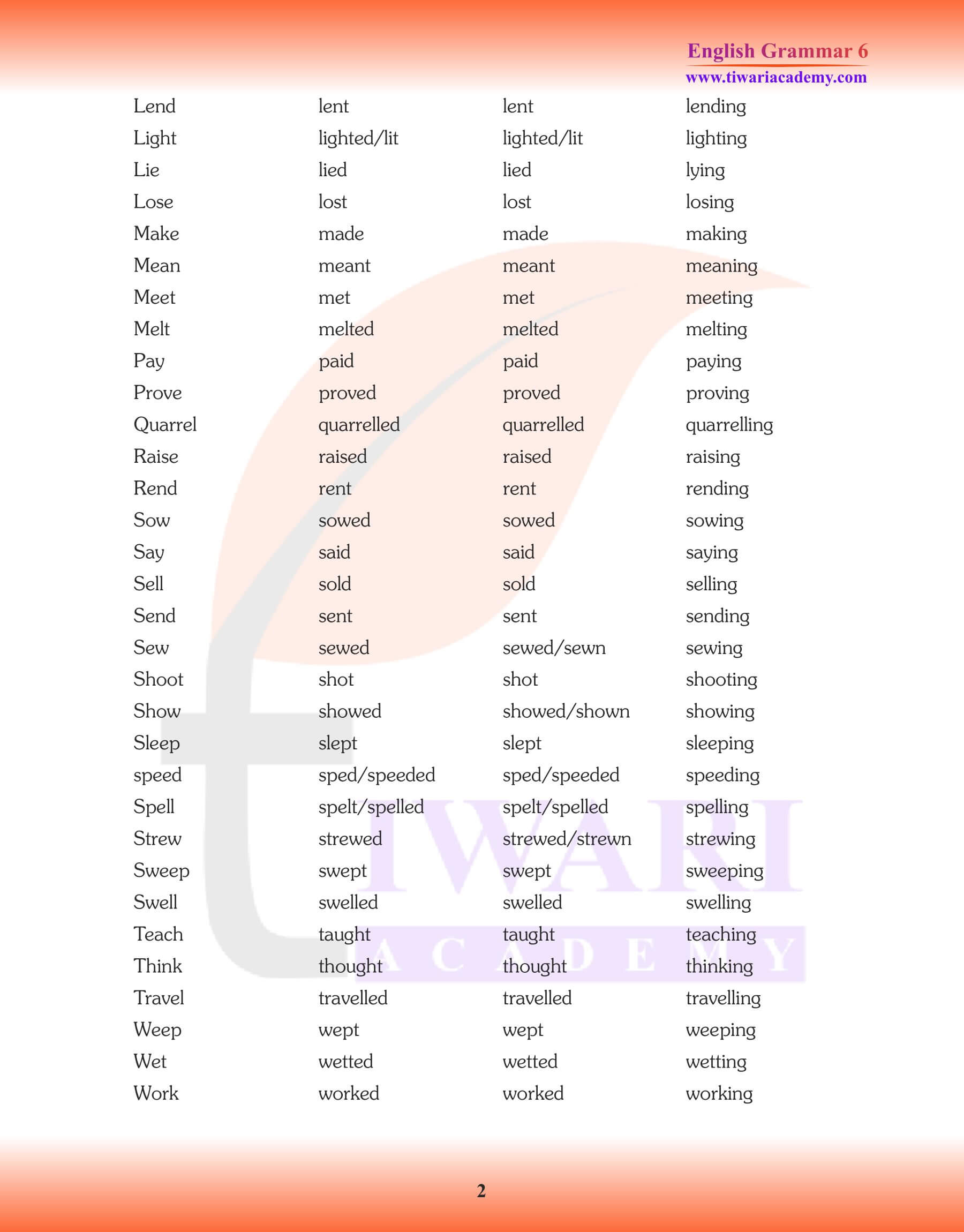
Weak Verbs
- Regular verbs are those verbs which require, -ed, -d or -t to form their past tense. They are also called weak because they take the help of these extra letters.
- All verbs whose past tense is the same as the present are also called weak verbs.
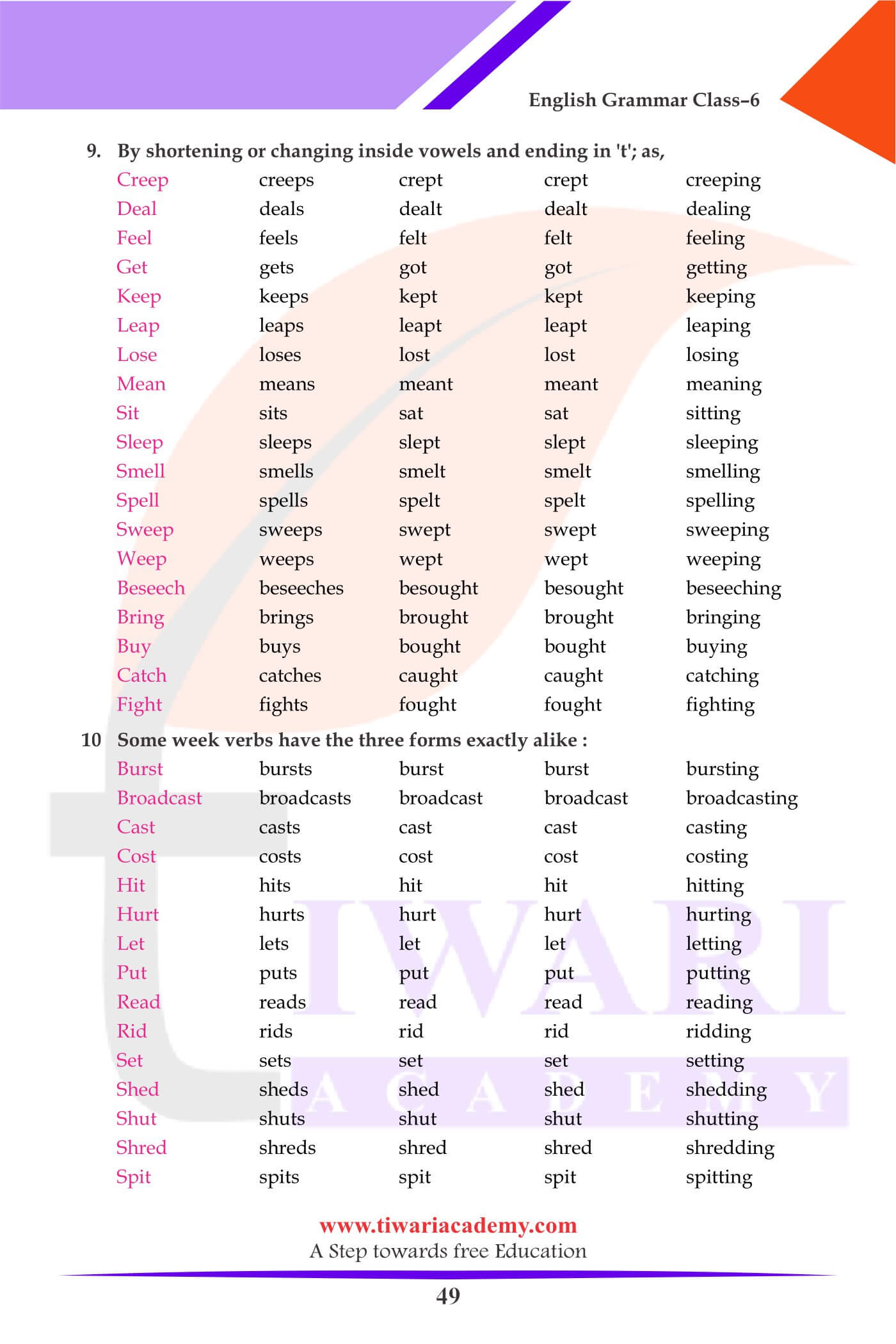
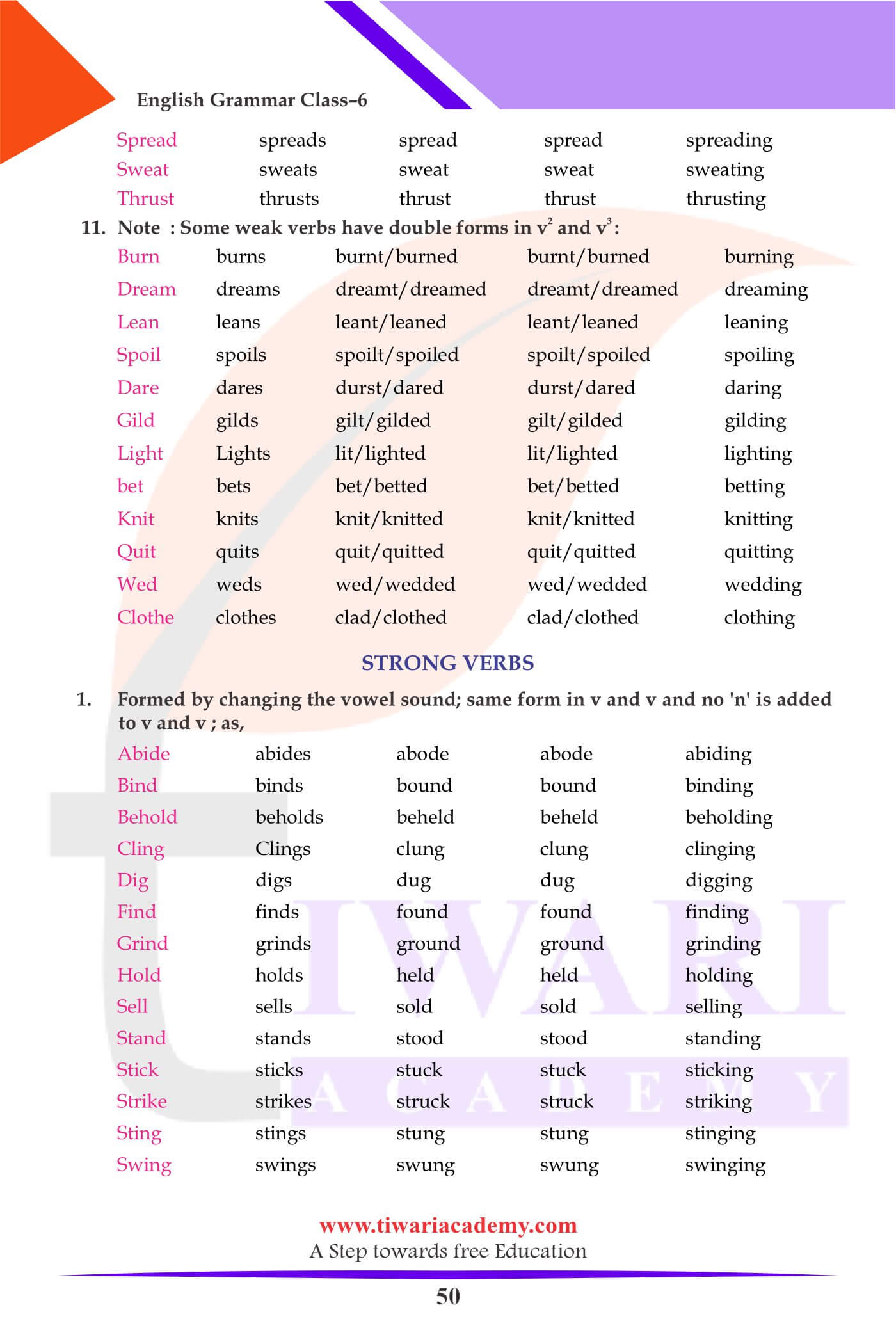
Strong Verbs
- Strong verbs are those which form their past (v) and past participle (v) by merely changing the inside vowels without ending in d, ed or t.
- Verbs form their past tense by changing a vowel and the past participle by addition of n, ne or en.
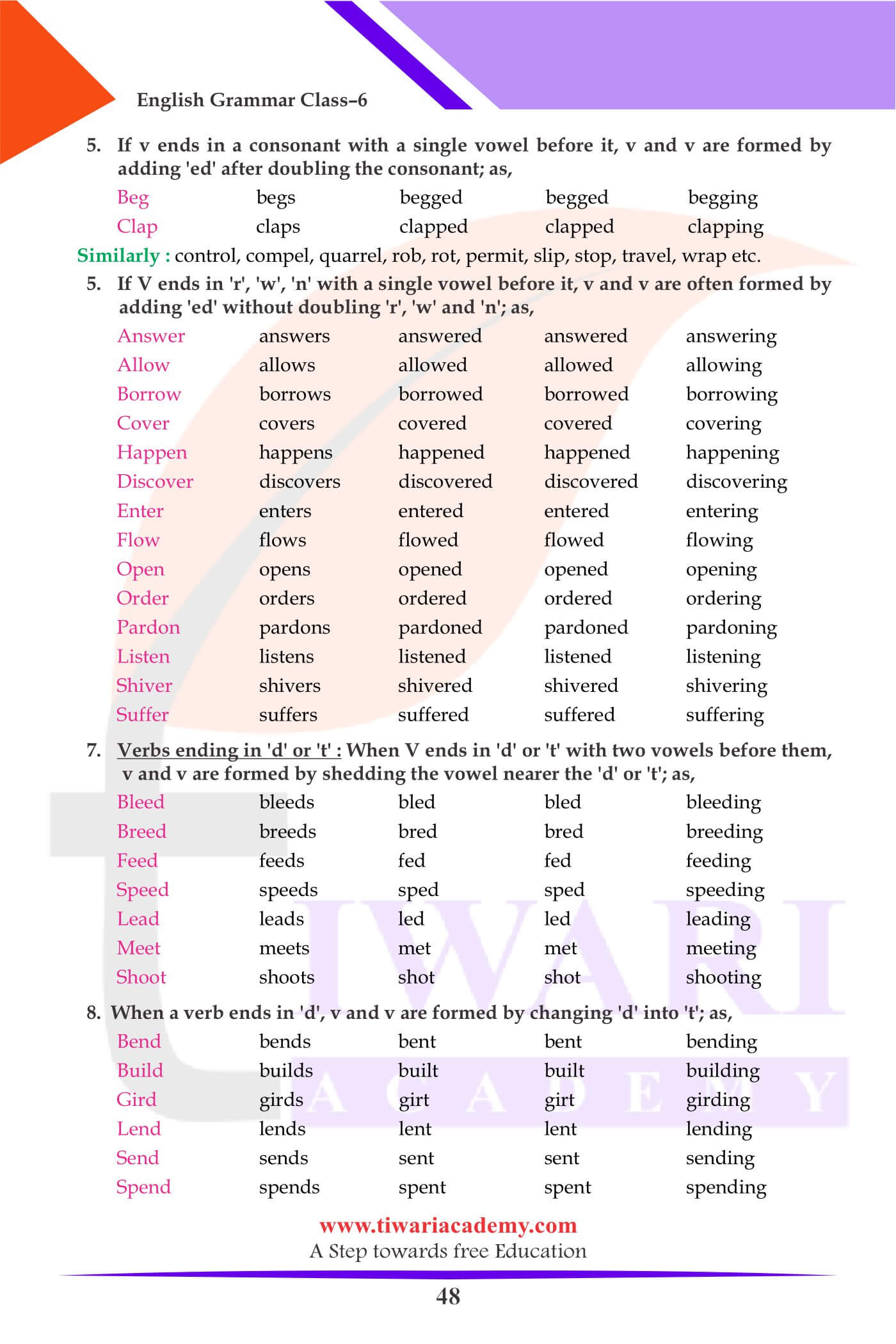
Rules for Making the Present Participle
- Generally the present participle (v) is formed by adding ing after v.
For example: act-acting, bark-barking, call-calling etc. - If the V ends in e, then ing is added after dropping e.
For example: abuse-abusing, take-taking, come-coming etc.
Exception : dye-dyeing, eye-eyeing etc. - If the V ends in ee or vowel+e then ing is added without dropping e.
For example: agree-agreeing, see-seeing, shoe-shoeing etc. - When the V ends in a single consonant preceded by a vowel, then ing is added after doubling the consonant.
For example: beg – begging, clap-clapping, sit-sitting, stop-stoping, cut-cutting etc. - But if the V ends in r, w, n and y with a single vowel before it, v is formed by adding ing.
For example: answer-answering, allow-allowing, happen-happening, play-playing etc. - When the V ends in a single consonant preceded by double vowel then ing is added without doubling the consonant.
For example: beat-beating, meet-meeting, eat-eating, clean-cleaning etc. - If the V ends in ie, then ing is added after dropping ie and putting y in place of ie.
For example: die-dying, lie-lying, tie-tying, vie-vying etc.
Rules for Making Singular Present Form
- If the subject is of the third person and singular in number, we add s to the V.
For example: take-takes, change-changes, like-likes, use-uses etc. - We add es to the verbs which end in ss, sh, ch, and o.
For example: cross, crosses, push-pushes, catch-catches, fix-fixes, go-goes etc. - When verbs end in y following a consonant, change the y into i and add es.
For example: cry-cries, copy-copies, marry-marries, study-studies etc.
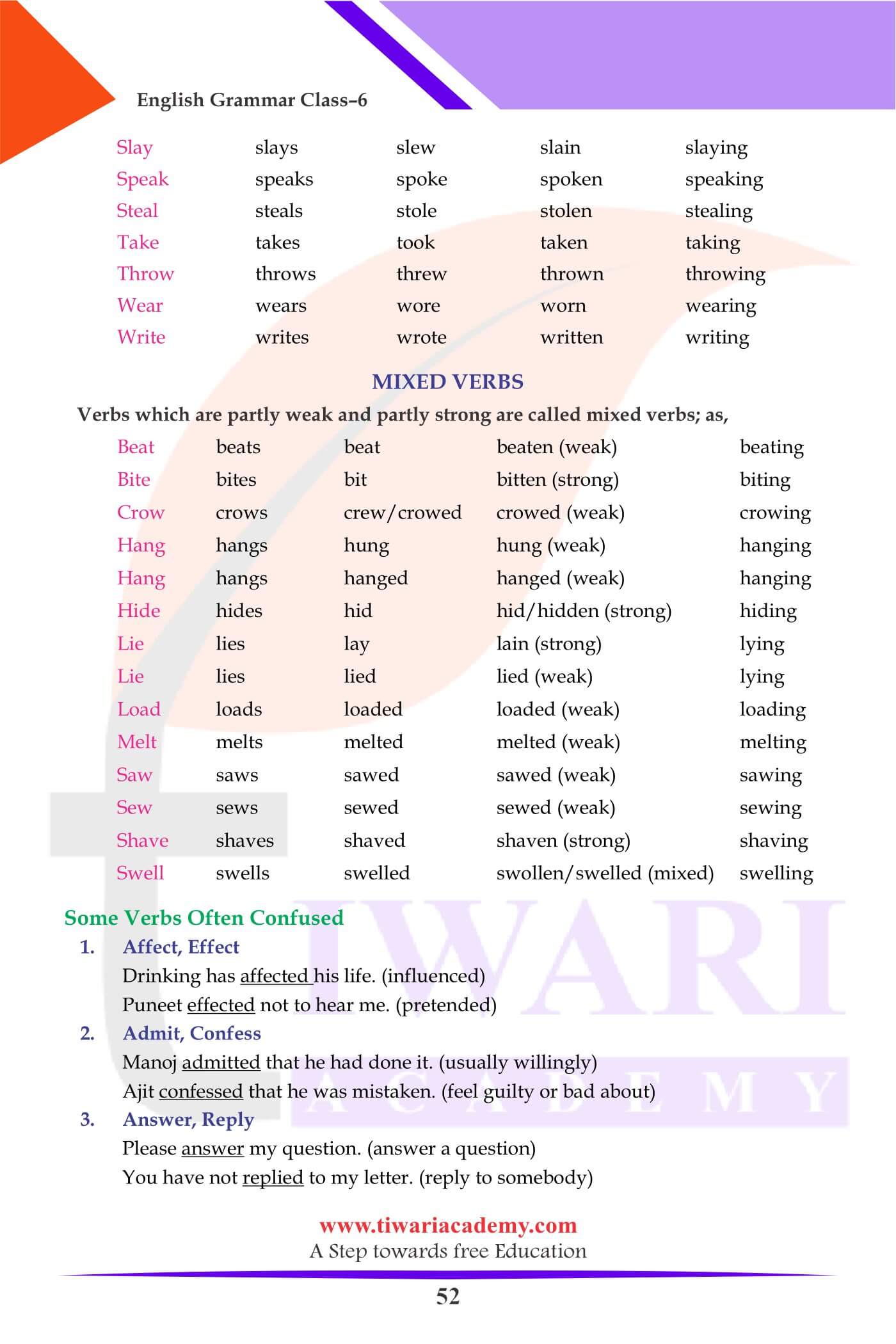
Some Verbs Often Confused
- Look, See, Watch
I see many people on the beach. (does not imply attention)
Look at the black-board, boys. (seeing attentively)
They were watching T.V. (look with interest) - Die, Dye
We would die without air and water. (cease being alive)
She has dyed her hair purple. (to colour) - Doubt, Suspect
I doubt she is speaking the truth. (not to be sure)
I suspect she is telling a lie. (I think she is not speaking the truth) - Rob, Steal
The robbers robbed the passengers. (take away things by force)
Someone stole my purse. (without force or threat) - Rise, Raise
We are all feeling the effects of the price rise. (increase)
The Sun rises in the east. (come out)
She rises at 5 a.m. these days. (get up)
Raise your hands if you know the answer. (lift) - Lie, lay
Please lie down quietly. (rest)
She told a lie. (falsehood)
She lied to me. (saying untrue)
Lay these book on the table. (place)
Lay the table. (serve)
Hens lay eggs. (produce eggs) - Fly, Flow
Birds fly.
Plane flew over the river. (Move through the air)
The parrots have just flown by our house.
She tried to stop the flow of blood from the wound. (Continuous movement)
The stream flowed rapidly down the mountains.
Verbs which create Confusion
- Affect, Effect
Drinking has affected his life. (influenced)
Puneet effected not to hear me. (pretended) - Admit, Confess
Manoj admitted that he had done it. (usually willingly)
Ajit confessed that he was mistaken. (feel guilty or bad about) - Bare, Bear
John decided to bare his heart to the priest. (to reveal)
I cannot bear such an insult. (tolerate) - Born, Borne
Khushi was born in 2003. (come into the world by birth)
At last, his effects have borne fruit. (bring forth) - Defer, Differ
Father has deferred his decision. (to postpone)
I differ with you on this point. (do not agree with) - Deny, Refuse
He denied that he was guilty. (is not true)
Hans refused to go to school. (not agree)
Feedback and Suggestion
We are here to help you and respect your suggestions and feedback. The overall improvement of Tiwari Academy website is the result of suggestions received by the users. Download NCERT Textbook Solutions for Standard 6 all subjects without any login or password.