NCERT Solutions for Class 2 Joyful Maths Chapter 2 Shapes Around Us (3D Shapes) in Hindi and English Medium based on NEP 2020. Class 2 Maths chapter 2 solutions are updated for new academic session 2025-26 CBSE and State Board. Class 2 Math NCERT Chapter 2, Shapes Around Us, introduces young learners to the fascinating world of 3D shapes, helping them identify and understand solid geometric structures in their environment. This chapter explores common 3D shapes such as cubes, spheres, cylinders and cones, linking them to everyday objects like dice, balls, cans and ice cream cones.
Class 2 Joyful Maths Chapter 2 Shapes Around Us Solutions
Activities such as identifying 3D shapes in daily life examples and solving shapes worksheets make learning fun and interactive. The lesson plan encourages students to observe their surroundings and recognize shapes around them, bridging theoretical knowledge with practical understanding. By focusing on 3D shapes properties for kids, the chapter builds a strong foundation in geometry while enhancing visual and spatial skills.
Study Plan for Class 2 Math Exam
Study Plan for Class 2 all Exams
To make learning engaging, teachers can use creative shapes activities and solutions to simplify the concepts of 3D geometric shapes for Class 2 students. These NCERT Math exercises include sorting objects based on their shapes, understanding the properties of solid shapes and solving shapes questions tailored to their level. Students can practice identifying 3D shapes through fun exercises like matching objects to their corresponding shapes and creating 3D models. With a mix of practical examples and theoretical understanding, the chapter ensures students grasp the significance of shapes in their daily lives. The solutions and practice worksheets provided in Joyful Mathematics make it easy for parents and educators to teach the topic effectively, ensuring students develop a deep appreciation for the shapes around us.
Class 2 Maths Chapter 2 Shapes Around Us (3D Shapes)
In Class 2 Maths Chapter 2 Shapes Around Us, students embark on an exploratory journey to understand and recognize three-dimensional shapes in their environment. This chapter introduces the concept of 3D shapes, distinguishing them from 2D shapes by highlighting their depth, in addition to length and width. Through various interactive activities and visual aids, children learn to identify common 3D shapes such as cubes, cylinders, cones, spheres, and rectangular prisms. This foundational knowledge helps students develop spatial awareness and recognize these shapes in different objects and settings around them, from the packaging of their snacks to the design of playground equipment.
Characteristics of 3D Shapes
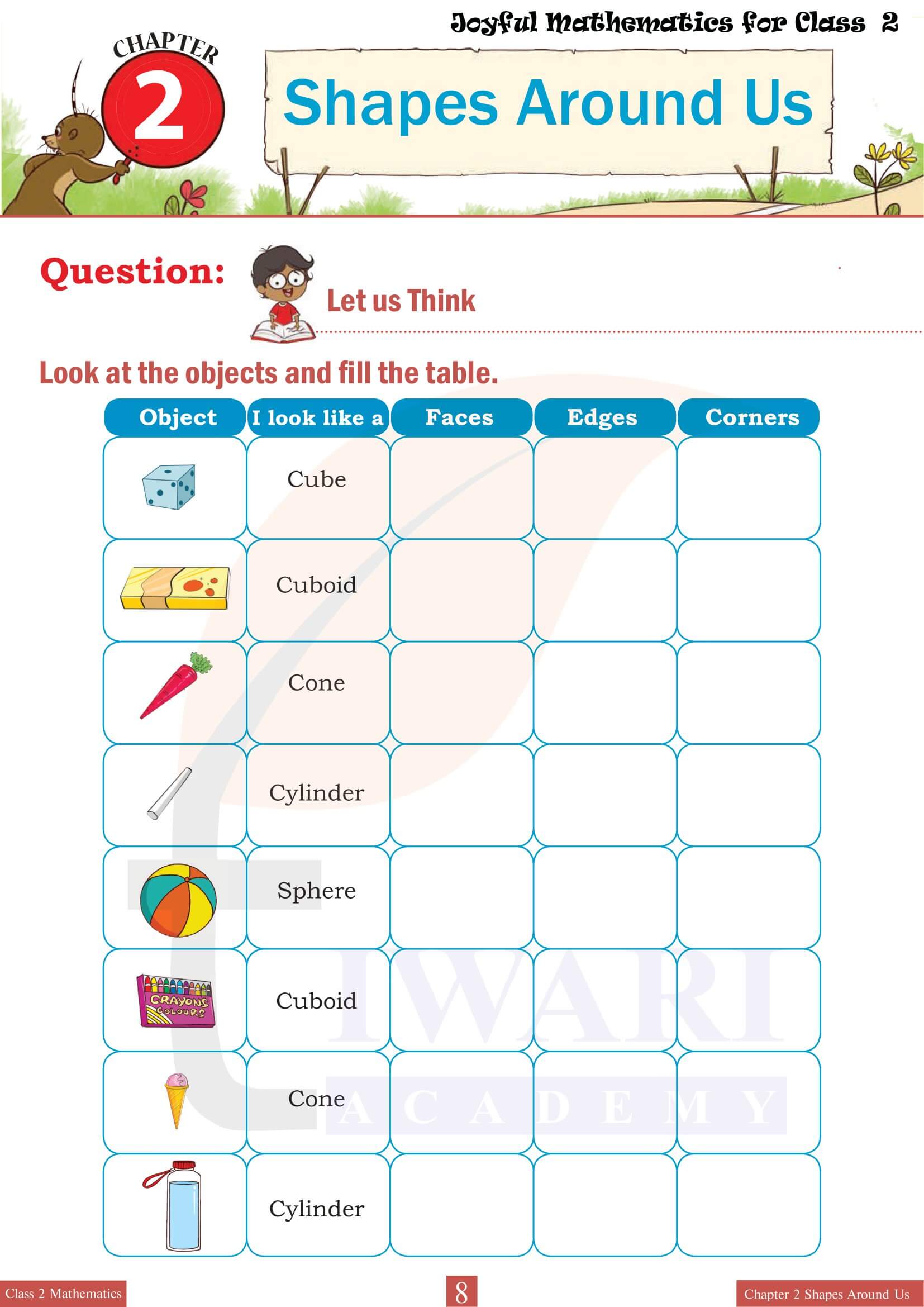
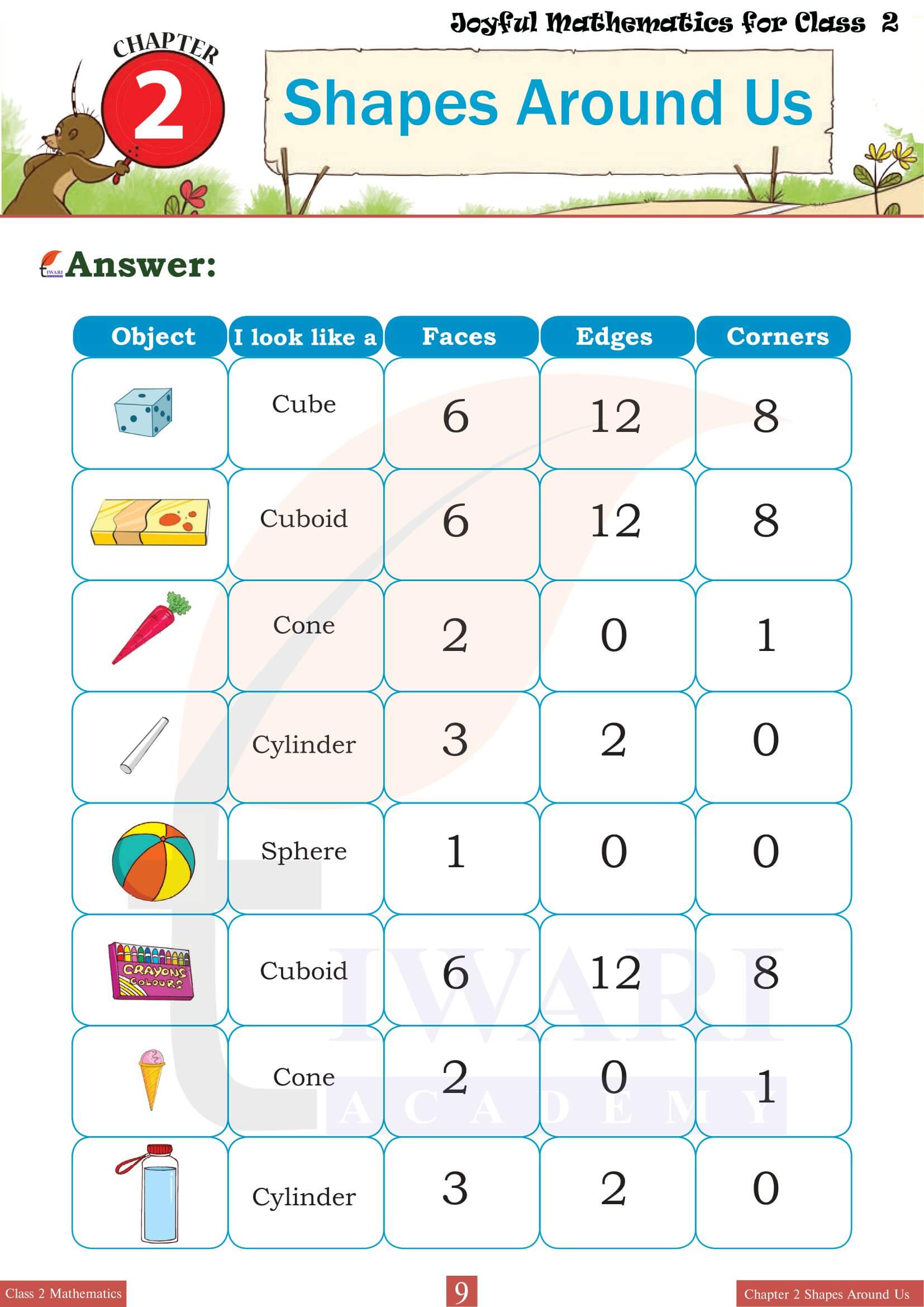
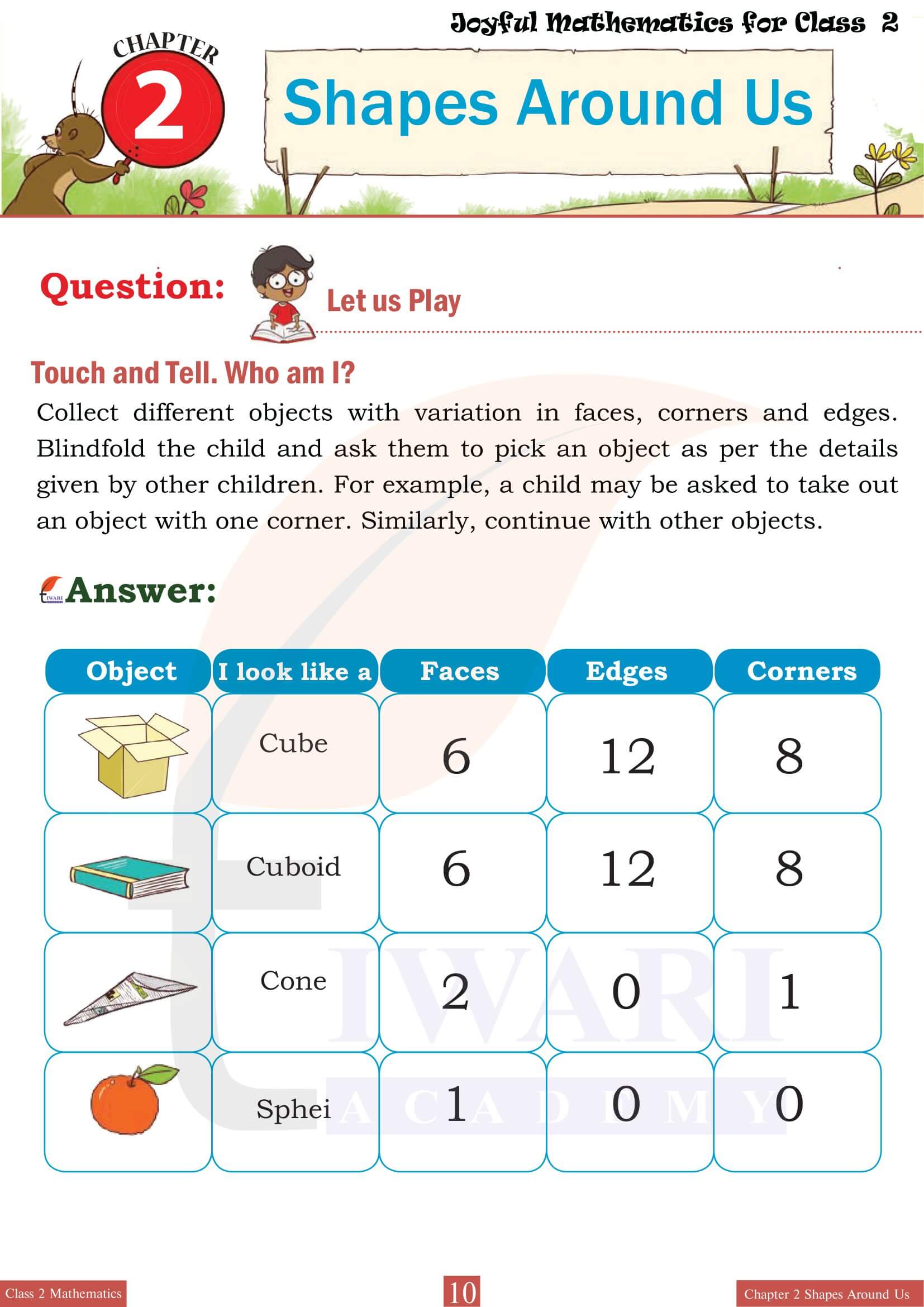
Class 2 Mathematics Chapter 2 delves into the specific characteristics that define 3D shapes, such as edges, vertices and faces. Each shape is examined in detail to illustrate these features. For example, students learn that a cube has six faces, all of which are squares and that it has twelve edges and eight vertices. Engaging exercises encourage students to count and record these attributes for various shapes, reinforcing their understanding through hands-on learning. By interacting with physical models or 3D representations, students become adept at distinguishing between different types of 3D shapes based on their unique characteristics.
Visualizing 3D Shapes in the Environment
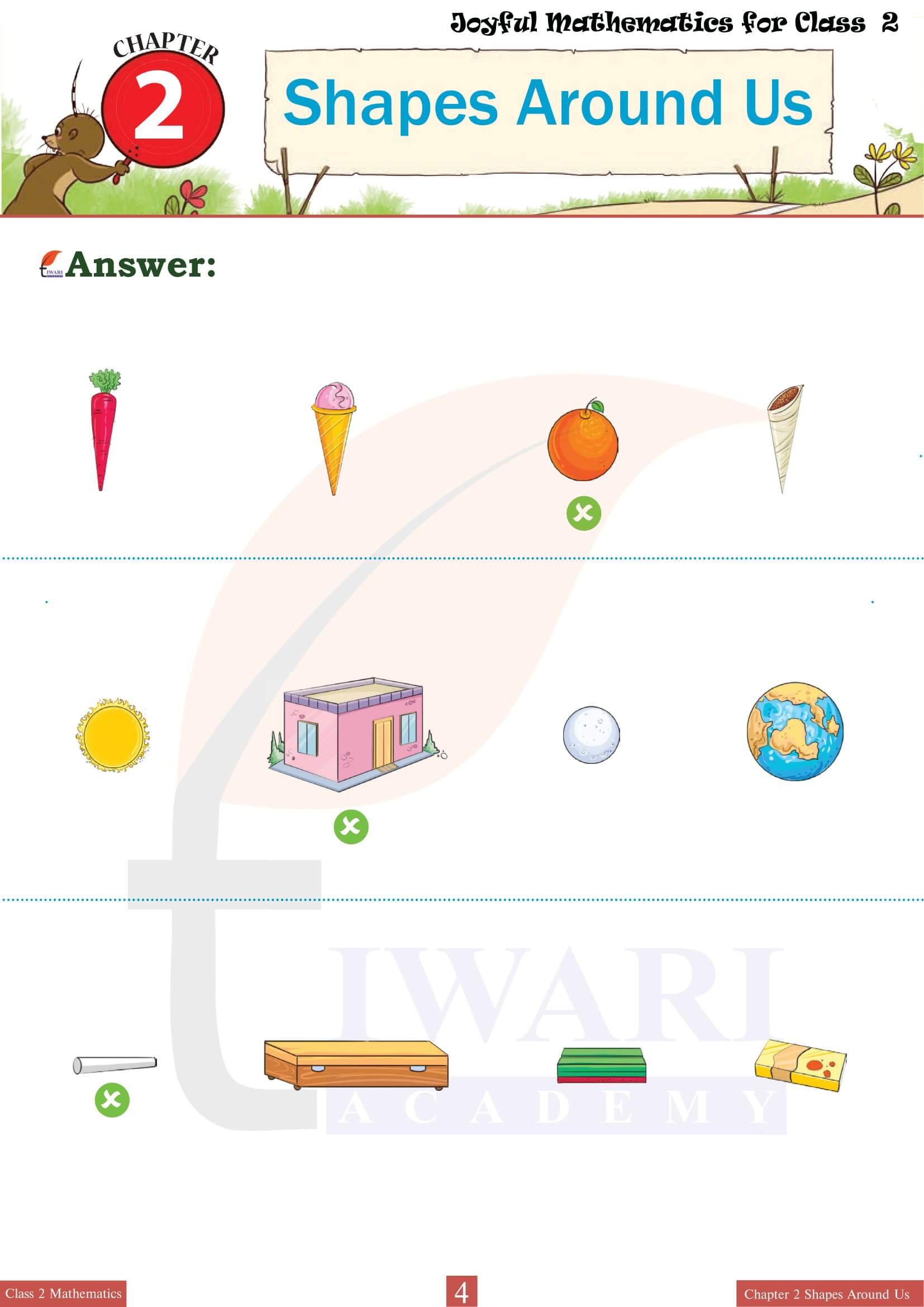
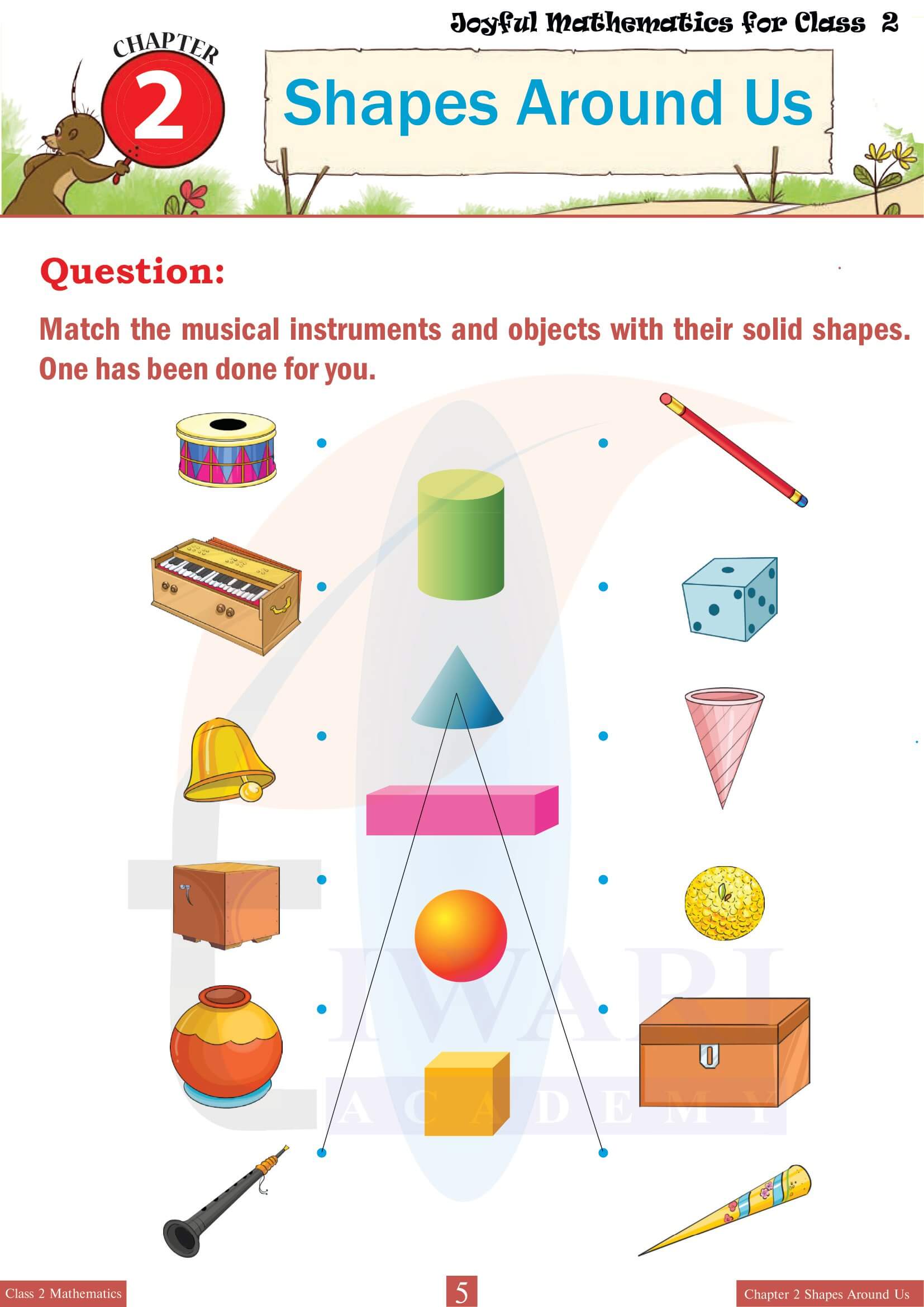
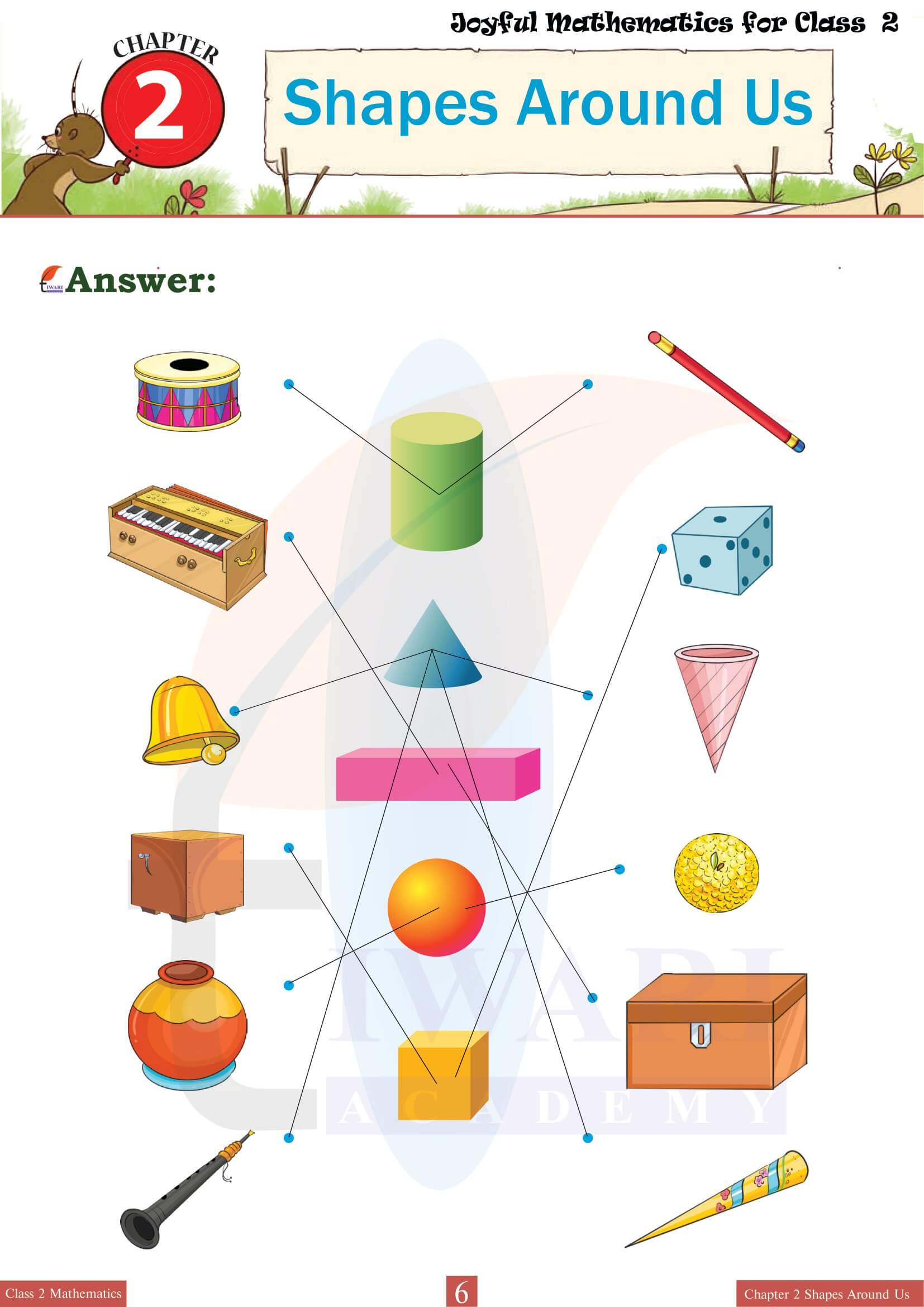
Shapes Around Us emphasizes the relevance of 3D shapes in everyday life by encouraging students to identify these forms in their surroundings. This practical application of the chapter’s concepts helps students connect classroom learning with the real world. For instance, they might recognize cylinders in water bottles, cones in traffic cones, spheres in balls, and cubes in dice. This segment of the chapter often includes activities like shape scavenger hunts or matching exercises where students pair everyday objects with their corresponding 3D shapes, enhancing both their observational skills and their ability to categorize shapes effectively.
Constructing 3D Shapes
In chapter 2 of class 2 mathematics, students get the opportunity to create 3D shapes using various materials such as clay, play-dough, or construction paper. This activity not only solidifies their understanding of the shapes’ properties but also enhances their motor skills and creativity. As they mold a sphere or assemble a cube, children grasp the tangible aspects of these shapes. Instructions guide them through the process of constructing each shape step by step, reinforcing the relationship between 2D faces and their assembly into 3D forms. This experiential learning segment is crucial for deepening students’ comprehension and retention of the subject matter.
Comparison Between 2D and 3D Shapes
To further cement their understanding, students are taught to compare and contrast 2D and 3D shapes. Through illustrative examples, they come to understand that 2D shapes are flat and have only length and width, whereas 3D shapes have an additional dimension—depth. This chapter typically includes side-by-side comparisons of shapes like circles to spheres and squares to cubes, helping students grasp the concept of dimensionality. Activities might involve classifying a mix of 2D and 3D shapes, thereby reinforcing the differences and encouraging critical thinking about how shapes occupy space.
Applications of 3D Shapes
The chapter also explores the applications of 3D shapes in various fields and everyday life, aiming to inspire curiosity and a deeper understanding of geometry’s role in the world. For example, students might learn how architects use 3D shapes in designing buildings or how product designers think about these shapes when creating toys, furniture, or gadgets.
By showcasing the practical utility of 3D shapes, this part of the chapter not only consolidates students’ knowledge but also broadens their perspective on how math intersects with creativity and innovation in various industries. Through this exploration, students appreciate the importance of geometry in both artistic and scientific contexts.
What are some examples of 3D shapes taught in Class 2 Maths Chapter 2: Shapes Around Us?
In Class 2 Maths Chapter 2, students learn about common 3D shapes like cubes, spheres, cylinders, and cones. These shapes are linked to real-life objects, such as dice for cubes, balls for spheres, cans for cylinders and ice cream cones for cones. The chapter encourages children to identify these shapes in their surroundings and understand their properties through fun activities and worksheets, helping them connect theoretical concepts to practical examples in their daily lives.
How does Chapter 2: Shapes Around Us make learning about 3D shapes engaging?
The chapter 2 of class 2 math engages students through interactive activities, like identifying 3D shapes in their environment and matching objects to shapes. Worksheets, practice questions, and creative tasks, such as building models of 3D shapes, make learning hands-on and enjoyable. Teachers and parents can use these exercises to simplify complex concepts, like the properties of solid shapes, ensuring that young learners grasp them easily. By relating shapes to everyday objects, the chapter fosters curiosity and helps students understand the relevance of geometry in real life.
What skills do class 2 students develop by learning about 3D shapes in Math chapter 2?
Learning about 3D shapes helps students develop spatial awareness and visual recognition skills. By identifying shapes in their surroundings, they improve observational abilities. Understanding the properties of shapes enhances critical thinking and analytical skills. Activities like sorting and matching shapes encourage problem-solving and logical reasoning. Additionally, creative tasks, such as building or drawing 3D models, foster imagination and motor skills. These foundational skills are essential for advanced topics in geometry and practical applications in real-world scenarios.
How do the exercises in Chapter 2 help students connect shapes to real life?
The exercises in Chapter 2 use real-life examples to make geometry relatable. For example, students match objects like boxes, balls and traffic cones to their respective shapes—cubes, spheres and cones. Activities such as identifying shapes in their home or classroom encourage observation and application. Practice questions and creative worksheets help them understand the properties of solid shapes while solving real-world problems. These exercises not only simplify geometry concepts but also show students how 3D shapes are part of their everyday lives, making learning meaningful and fun.