NCERT Exercise Solutions for Class 12 Mathematics Chapter 10 Vector Algebra in Hindi and English Medium for Session 2025-26 Maths Exams. Vector Algebra in Mathematics forms a crucial part of the NCERT Class 12 Maths syllabus, especially in Chapter 10. NCERT Class 12th Mathematics chapter 10 introduces concepts like vectors, their magnitudes and directions, which are vital for solving various mathematical and real-world problems. For students tending to grasp these topics, NCERT Textbook solutions for Vector Algebra provide step-by-step guidance.
NCERT Textbook Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Vector Algebra
Whether you’re working on NCERT exercise 10.1 solutions or trying to solve Book exercise 10.2, these solutions simplify complex ideas into manageable steps. Class 12 Maths NCERT Chapter 10 notes are an excellent resource to understand the application of vectors in geometry, physics and engineering. By reviewing the solved examples and important questions included in the chapter, you can strengthen your problem-solving skills and ace the exams confidently. Get here the chapter 10 Class 12 Math updated according to new NCERT textbooks released for CBSE 2025-26 exams.
Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Solution in English Medium
Comprehensive Mathematics Exercise Solutions for Vector Algebra
Exercises in NCERT Class 12 Mathematics Chapter 10, ranging from exercise 10.1 to the miscellaneous exercise, are designed to test your understanding of vector addition, scalar multiplication and their applications. NCERT Exercise solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Vector Algebra break these exercises into easy-to-follow steps, making it simpler for students to comprehend and apply the principles. For example, NCERT Math Book exercise 10.3 solutions focus on dot and cross products of vectors, which are critical in physics.
Class 12th Mathematics Vector Algebra important questions highlight key problems frequently asked in CBSE board exams. The detailed explanations in the NCERT Class 12 Math Textbook solutions ensure that students can solve problems efficiently and without confusion. Reviewing the Vector Algebra Class 12 Maths solved examples is an effective way to enhance your understanding of complex calculations.
Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Solution in Hindi Medium
Preparing for CBSE Board Exams with Class 12 Vector Algebra
Scoring well in Class 12 NCERT Mathematics requires a strong command of topics like Vector Algebra and NCERT textbook solutions are your best resource for this. NCERT Class 12th Mathematics Exercise solutions cover all questions from Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 and provide clarity on challenging topics like vector projections and co-planar vectors.
NCERT Class 12 Math Book Exercise Chapter 10 PDF makes it convenient to study any moment. Practicing with the Class 12th Mathematics Book Chapter 10 exercise solutions ensures you understand the core concepts and can handle diverse problems during exams. Solving the NCERT Complete miscellaneous exercise solutions will further prepare you for tricky, real-world applications of vector principles. The comprehensive study materials, including Vector Algebra examples and explanations, not only enhance your mathematical skills but also help you approach board exams with confidence.
| Class: 12 | Maths |
| Chapter: 10 | Vector Algebra |
| Number of Exercises: | 4 + Miscellaneous |
| Contents: | NCERT Exercises Solution |
| Content Mode: | Online Text, Videos and PDF |
| Session: | CBSE 2025-26 |
| Medium: | English and Hindi Medium |
Important Points for Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Vector Algebra
1. Definition of vectors, magnitude and direction.
2. Vector addition and scalar multiplication.
3. Dot product and cross product of vectors.
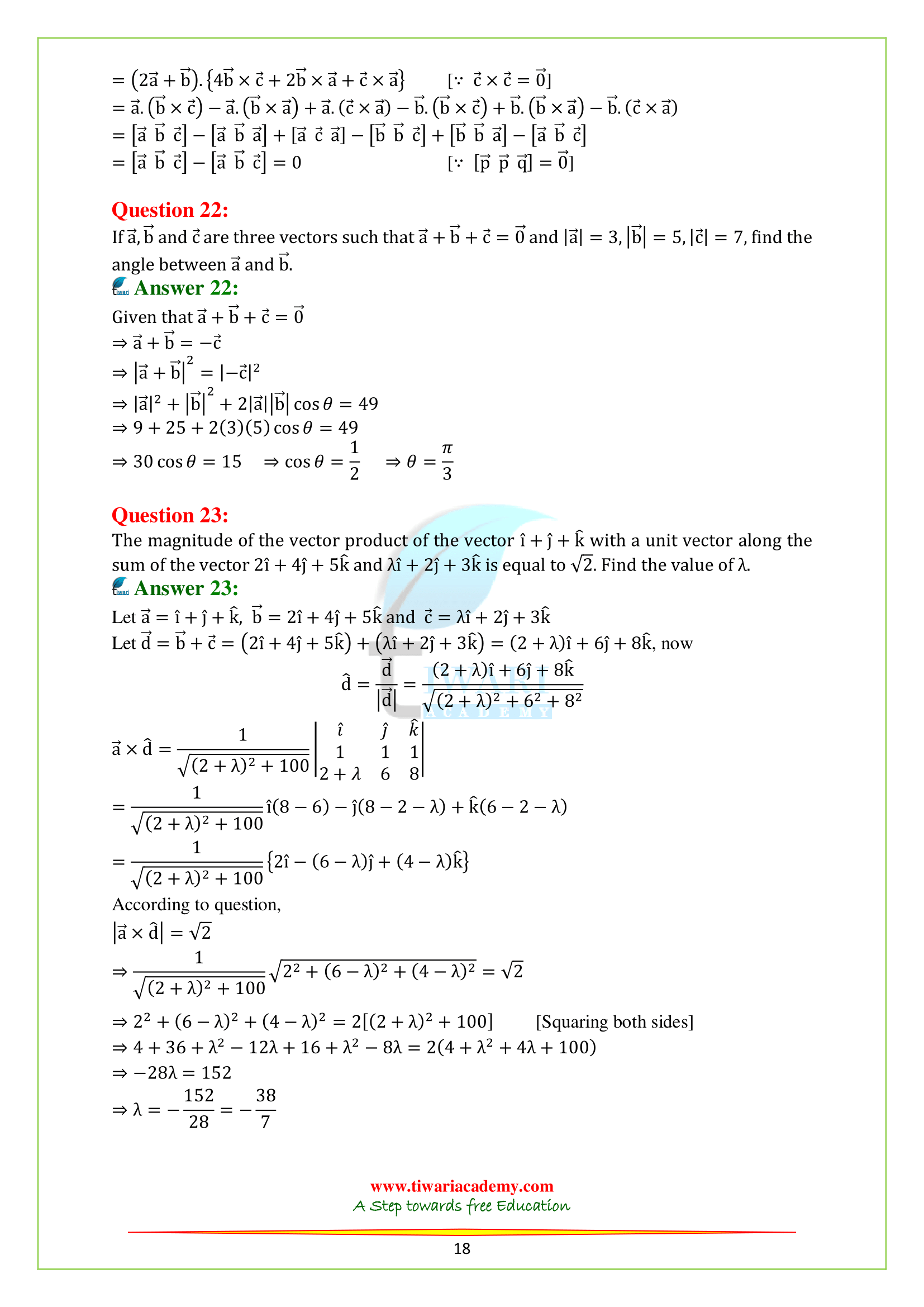
4. Conditions for coplanar vectors.
5. Applications of vector projections.
6. Focus on solved examples and NCERT miscellaneous exercises for board exams.
| Day | Topics to Cover | Resources | Practice Exercises |
|---|---|---|---|
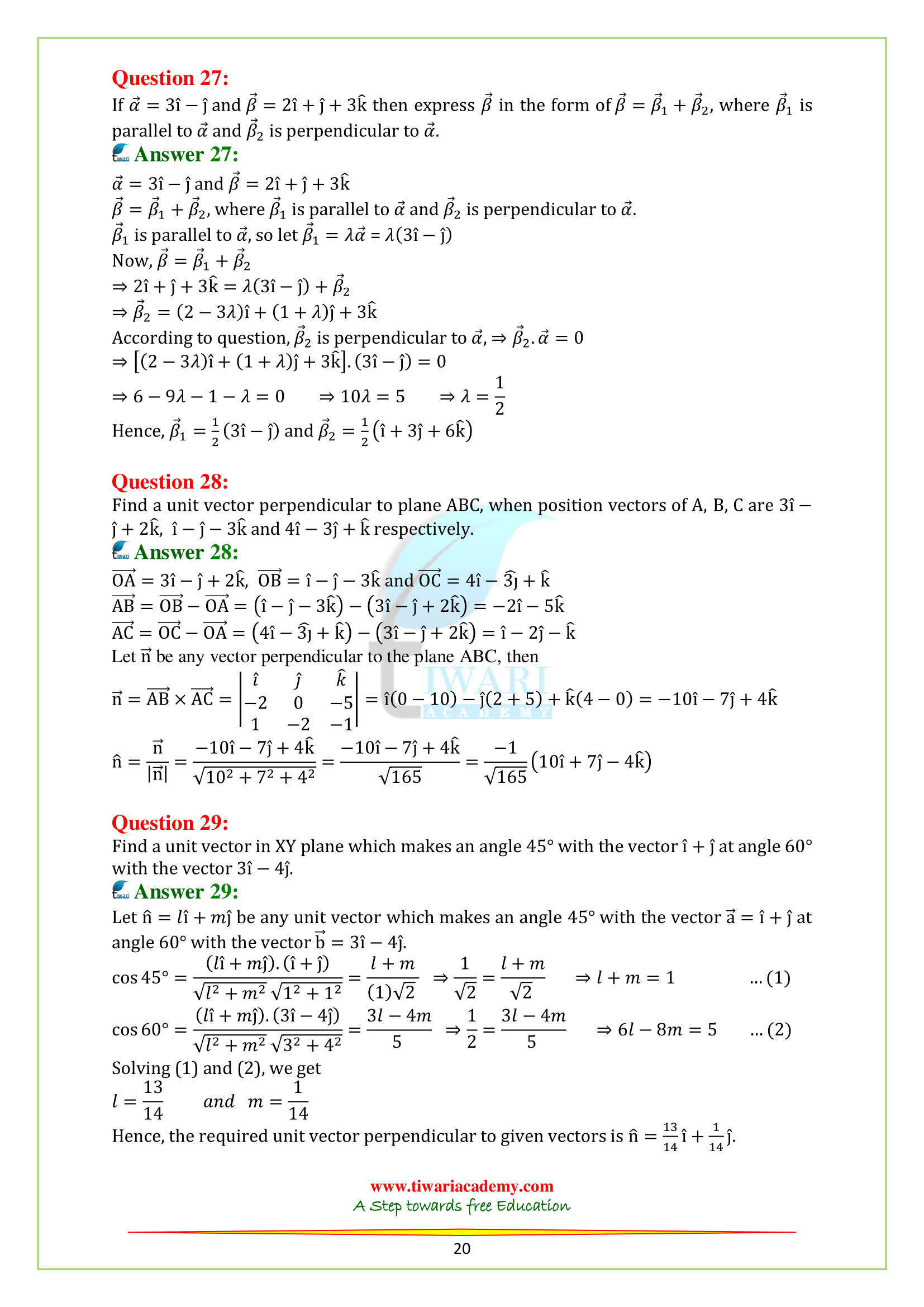
| Day 1 | Introduction to Vectors, Magnitude and Direction | NCERT Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 PDF | Exercise 10.1 |
| Day 2 | Vector Addition and Scalar Multiplication | NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths | Exercise 10.2 |
| Day 3 | Dot Product and Cross Product | Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Notes | Exercise 10.3 |
| Day 4 | Applications of Vector Algebra | Important Questions and Examples | Miscellaneous Exercise |
| Day 5 | Revision of Key Topics | NCERT Class 12 Maths Solutions PDF | Full Chapter Revision |
NCERT solutions for class 12 Maths Chapter 10
Class XII Mathematics Chapter 10 exercise 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.4 and miscellaneous exercises in Hindi and English Medium for UP Board and CBSE Board students. Download Class 12 solutions all subjects, Solutions are prepared according to CBSE Syllabus for 2025-26. Solutions are prepared as per the CBSE guidelines and are easy to understand. Videos of solutions in Hindi and English are also given here to explore each exercise.
Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Study Material
- NCERT Book Class 12 Maths Chapter 10
- Revision Book Class 12 Maths Chapter 10
- Revision Book Class 12 Maths Answers
- Download Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Assignment 1
- Download Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Assignment 2
- Download Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Assignment 2 Answers
- Download Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Assignment 3
- Download Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Assignment 4
- Class 12 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Class 12 all Subject NCERT Solutions
12th Maths Chapter 10 Solutions
NCERT solutions for class 12 Maths Chapter 10 in PDF format to free download for current academic session. If you doubt to asked, please join the discussion forum to express your opinion and ask questions related to NIOS and CBSE Board. Here you can reply to the questions asked by others.
Assignments with Solution on Chapter 12
Important Questions Assignment with Solutions
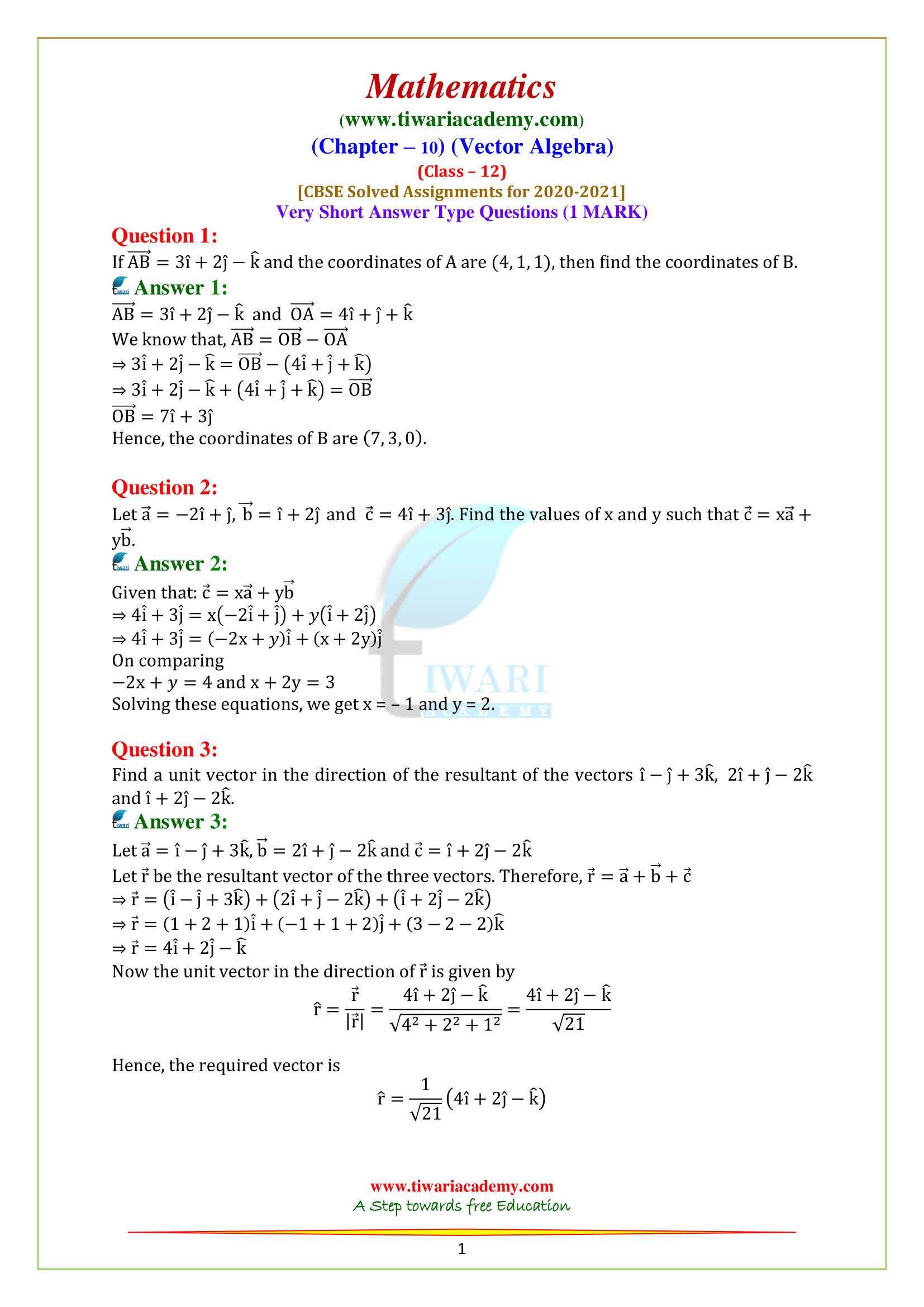
Q.1. If AB = 3i + 2j – k and the coordinates of A are (4, 1, 1), then find the coordinates of B.
Q.2. Let a = -2i + j, b = i + 2j and c = 4i + 3j. Find the values of x and y such that c = xa + yb.
Q.3. Find a unit vector in the direction of the resultant of the vectors i – j+ 3k, 2i + j – 2k and i + 2j – 2k.
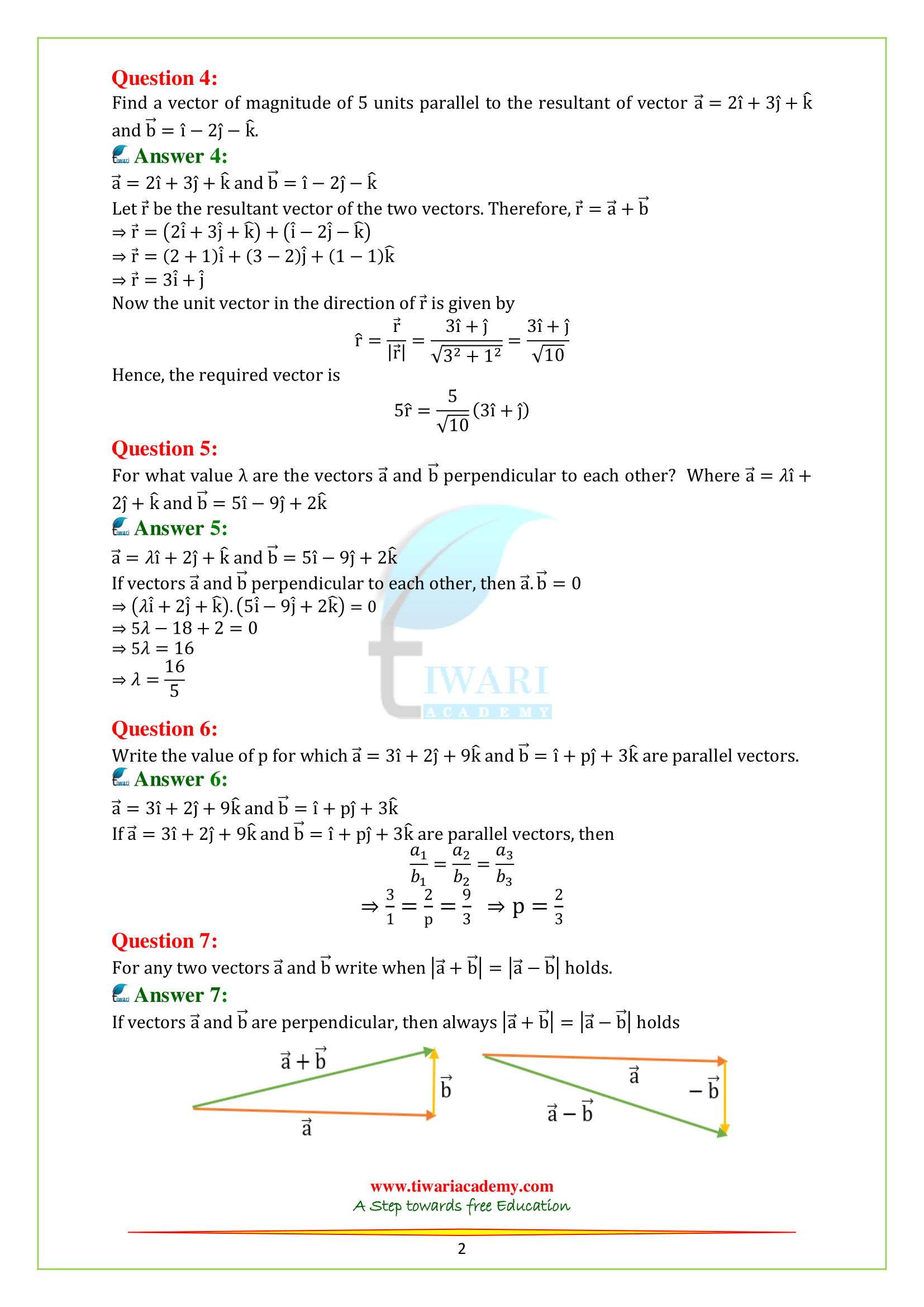
Q.4. Find a vector of magnitude of 5 units parallel to the resultant of vector a = 2i + 3j + k and b = i – 2j – k.
Q.5. For what value λ are the vectors a and b perpendicular to each other? Where a = λi + 2j + k and b = 5i – 9j + 2k.
Q.6. Write the value of p for which a = 3i + 2j + 9k and b = i + pj + 3k are parallel vectors.
Q.7. For any two vectors a and b, write when |a + b|=|a – b| holds.
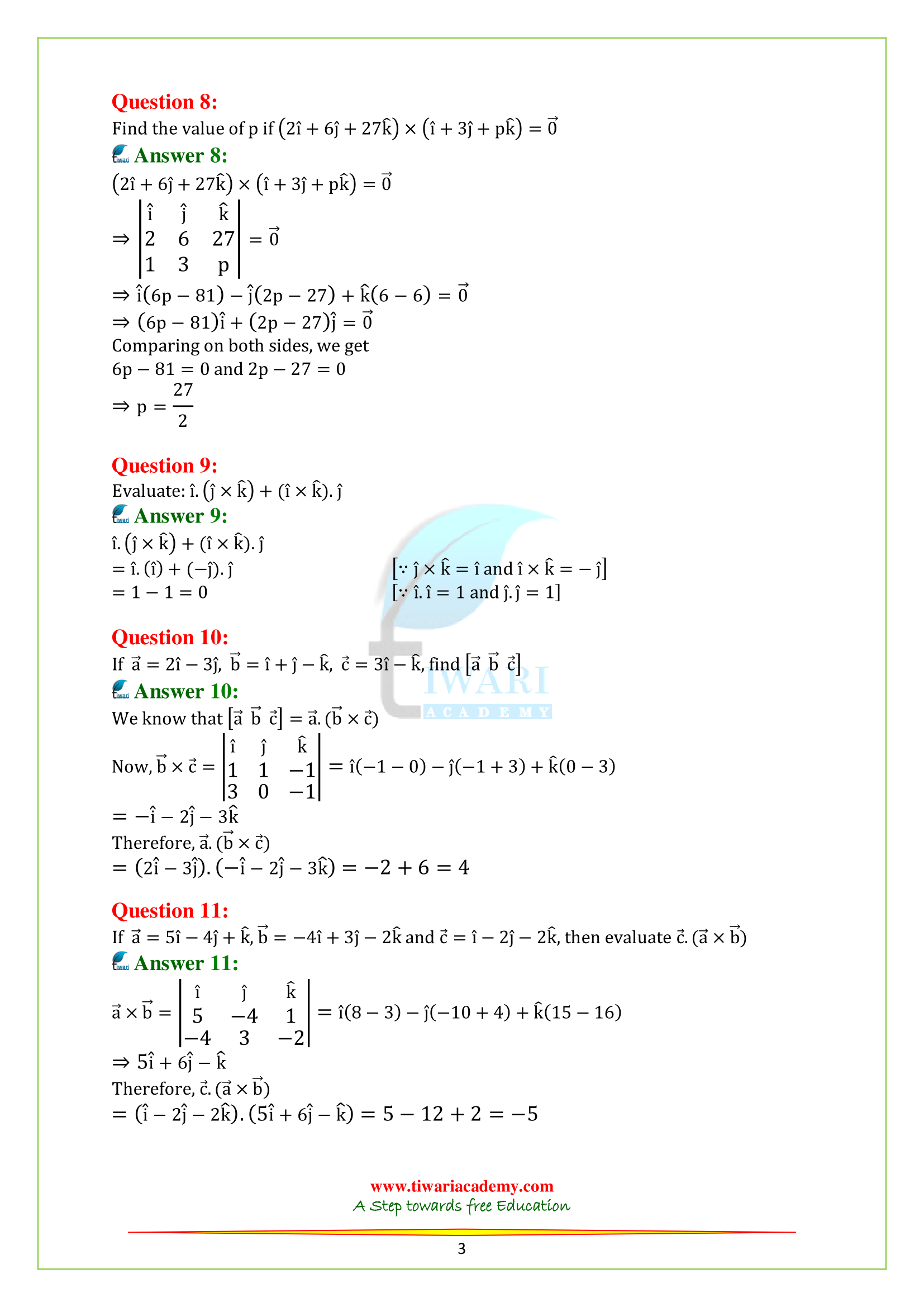
Q.8. Find the value of p if (2i + 6j + 27k)×(i + 3j + pk) = 0.
Q.9. Evaluate: i.(j × k) + (i × k).j.
Q.10. If a = 2i – 3j, b = i + j – k, c = 3i – k, find [a b c].
Q.11. If a = 5i – 4j + k, b = -4i + 3j – 2k and c = i – 2j – 2k, then evaluate c.(a × b).
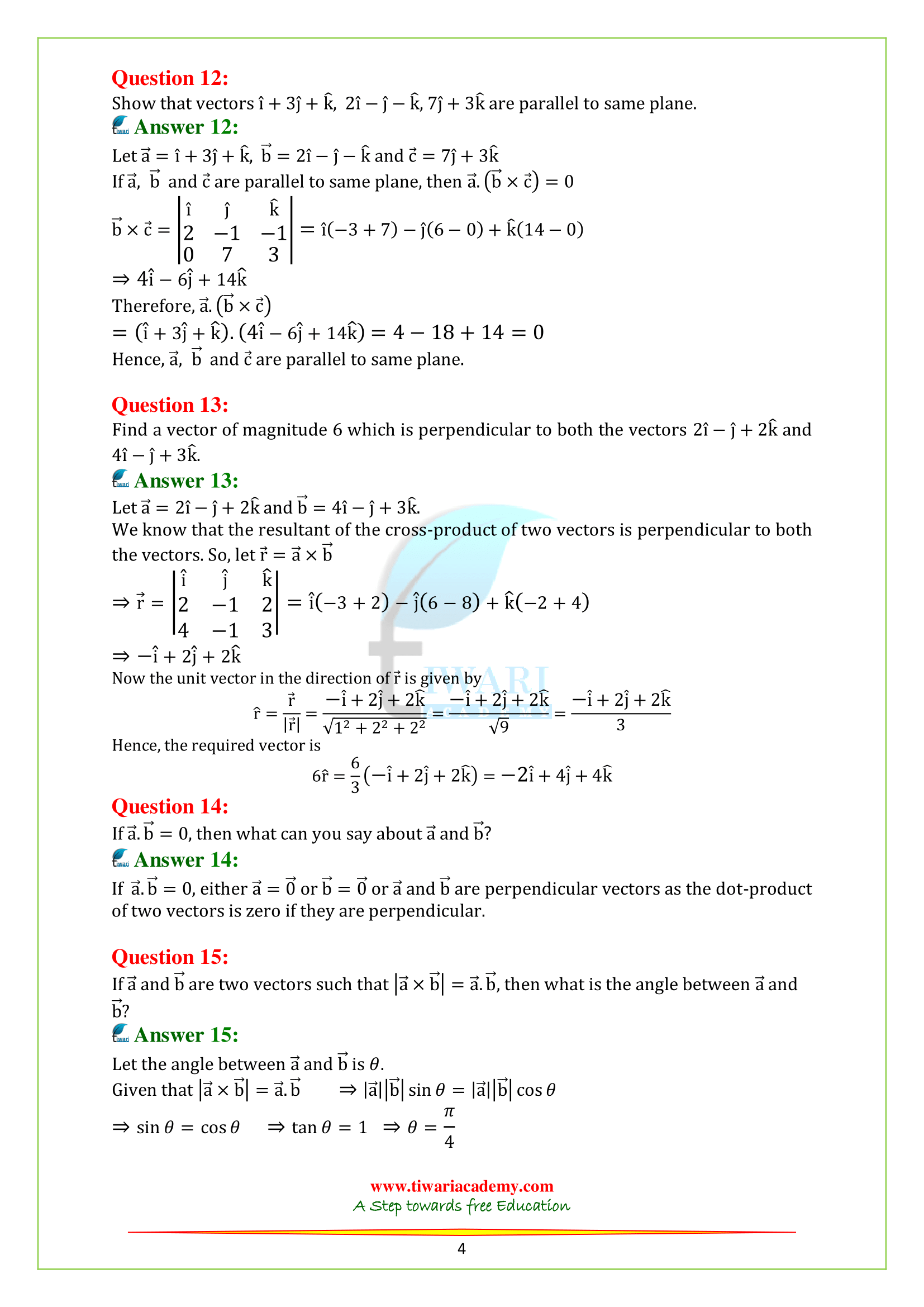
Q.12. Show that vectors i + 3j + k, 2i – j – k, 7j + 3k are parallel to same plane.
Q.13. Find a vector of magnitude 6 which is perpendicular to both the vectors 2i – j + 2k and 4i – j + 3k.
Q.14. If a.b = 0, then what can you say about a and b?
Q.15. If a and b are two vectors such that |a × b| = a.b, then what is the angle between a and b?
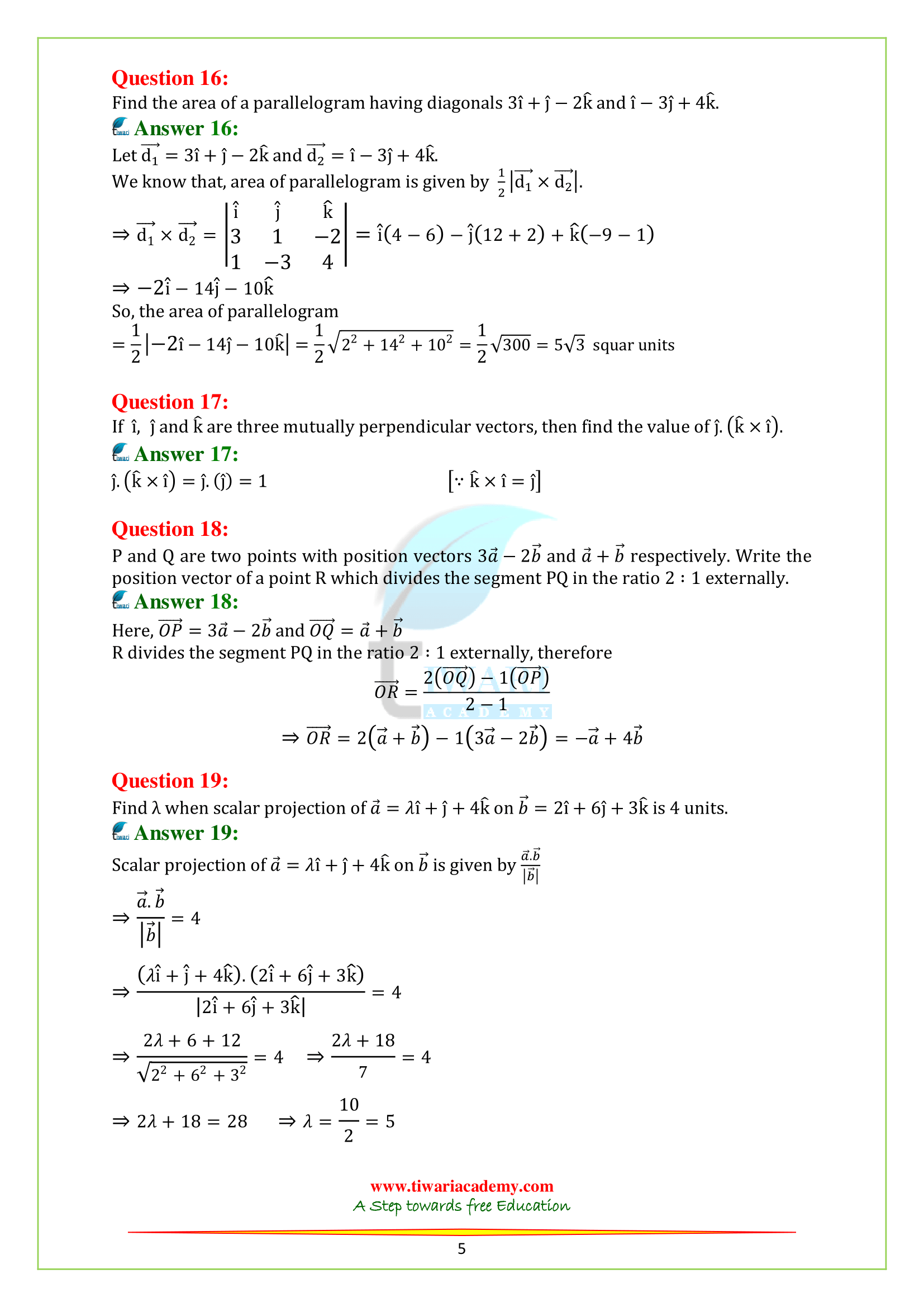
Q.16. Find the area of a parallelogram having diagonals 3i + j – 2k and i – 3j + 4k.
Q.17. If i, j and k are three mutually perpendicular vectors, then find the value of j.(k × i).
Q.18. P and Q are two points with position vectors 3a – 2b and a + b respectively. Write the position vector of a point R which divides the segment PQ in the ratio 2∶1 externally.
Q.19. Find λ when scalar projection of a = λi + j + 4k on b = 2i + 6j + 3k is 4 units.
Q.20. Find “a” so that the vectors p = 3i – 2j and q = 2i – aj be orthogonal.
Q.21. If a = i – j + k, b = 2i + j – k and c = λi – j + λk are co-planar, find the value of λ.
Q.22. What is the point of trisection of PQ nearer to P if positions of P and Q are 3i + 3j – 4k and 9i + 8j – 10k respectively?
Q.23. What is the angle between a and b, if a.b = 3 and |a × b| = 3√3.
Important Questions on 12th Maths Chapter 10
What do you mean by a vector?
A quantity that has magnitude as well as direction is called a vector.
What are the scalar components of vectors?
The scalar components of a vector are its direction ratios, and represent its projections along the respective axes.
What is the triangle law of vector addition?
The triangle law of vector addition states that “If two vectors are represented by two sides of a triangle taken in order, then their sum or resultant is given by the third side taken in opposite order”.
How do you find the dot product of two vectors a and b?
The scalar or dot product of two given vectors a and b having an angle θ between them is defined as a.b = |a||b|cos θ.
How do you find the cross product of two vectors a and b?
The vector or cross product of two given vectors a and b having an angle θ between them is defined as axb = |a||b|sin θ.
Short Answer type Questions (2 Marks)
Q.1. A vector r is inclined to x- axis at 45° and y- axis at 60° if |r| = 8 units find r.
Q.2. If |a + b|= 60, |a – b| = 40 and b = 46 find |a|.
Q.3. Write the projection of b + c on a where a = 2i – 2j + k, b = i + 2j – 2k and c = 2i – j + 4k.
Q.4. If the points (-1, -1, 2), (2, m, 5) and (3, 11, 6) are co-linear, find the value of m.
Q.5. For any three vectors a, b and c write value of the following. a × ( b + c ) + b × (c + a ) + c × (a + b).
Q.6. If (a + b)² + (a . b)² = 144 and |a|, then find the value of |b|.
Q.7. If for any two vectors a and b, (a + b)² + (a – b)² = λ[a² + b²] then write the value of λ.
Q.8. If a, b are two vectors such that |a + b| = |a| then prove that 2a + b is perpendicular to b.
Q.9. Show that vectors a = 3i – 2j + k, b = i – 3j + 5k, c = 2i + j – 4k form a right angle triangle.
Q.10. If a, b, c are three vectors such that a + b + c = 0 and |a| = 5, |b| = 12, |c| = 13, then find a.b + b.c + c.a
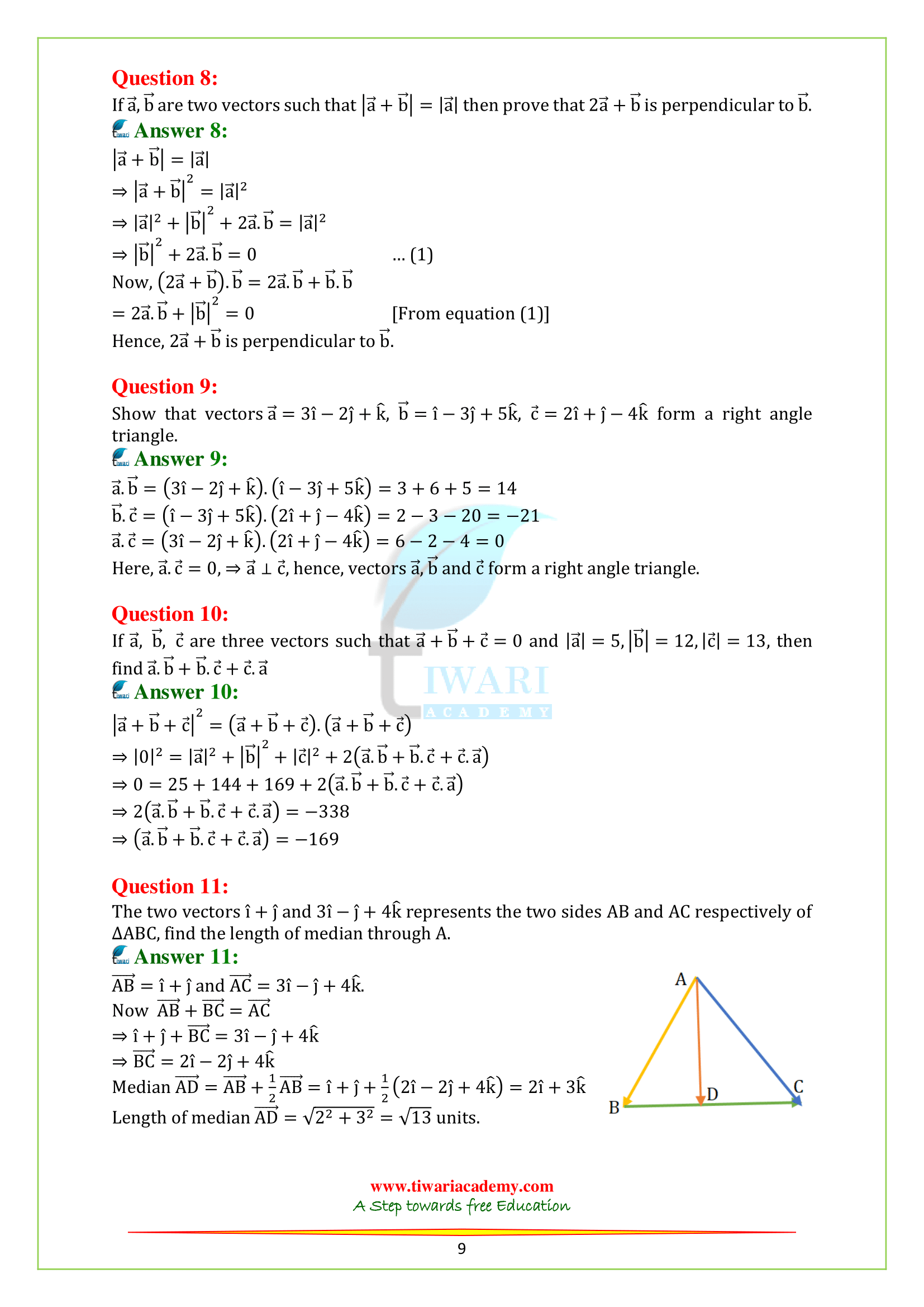
Q.11. The two vectors i + j and 3i – j + 4k represents the two sides AB and AC respectively of ΔABC, find the length of median through A.
Short Answer type Questions (4 Marks)
Q.1. The points A, B and C with position vectors 3i – yj + 2k, 5i – j + k and 3xi + 3j – k are collinear. Find the values of x and y and also the ratio in which the point B divides AC.
Q.2. If the sum of two unit vector is a unit vector, prove that the magnitude of their difference is √3.
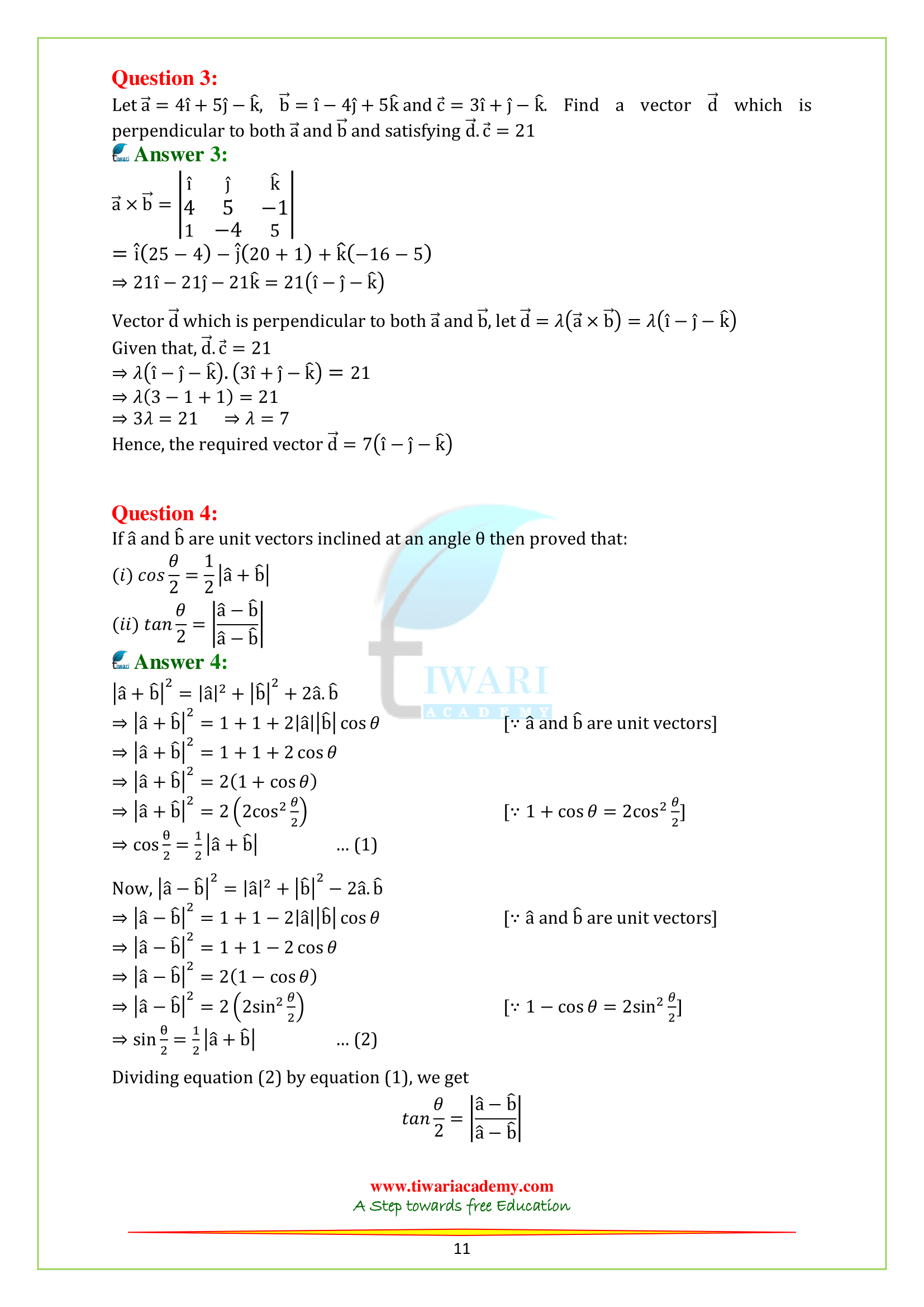
Q.3. Let a = 4i + 5j – k , b = i – 4j + 5k and c = 3i + j – k. Find a vector d which is perpendicular to both a and b and satisfying d.c = 21.
Q.4. If a and b are unit vectors inclined at an angle θ then proved that: (i) cos θ/2 = ½|a + b| (ii) tan θ/2=|(a – b)/(a – b)|.
Q.5. If a, b, c are three mutually perpendicular vectors of equal magnitude. Prove that a + b + c is equally inclined with vectors a, b, and c. Also find angles.
Q.6. For any vector a prove that |a × i|² + |a × j|² + |a × k|² = 2|a|².
Q.7. Show that (a × b)² = |a|² |b|² – (a.b)².
Q.8. If a, b, and c are the position vectors of vertices A, B, C of a ΔABC, show that the area of a triangle ABC is ½|a × b + b × c + c × a|. Deduce the condition for points a, b, and c to be collinear.
Q.9. Let a, b and c be unit vectors such that a.b = a.c = 0 and the angle between b and c is π⁄6, prove that a = ±2(b × c ).
Q.10. If a, b and c are three vectors such that a + b + c = 0 , then prove that a × b = b × c = c × a.
Q.11. If a = i + j + k, c = j – k are given vectors, then find a vector b satisfying the equations a × b = c and a.b = 3.
Q.12. Let a, b and c be three non zero vectors such that c is a unit vector perpendicular to both a and b. if the angle between a and b is π⁄6, prove that [a b c]² = ¼|a|²|b|².
Q.13. If the vectors α = ai + j + k, β = i + bj + k and γ = i + j + ck are coplanar, than prove that 1/(1-a)+1/(1-b)+1/(1-c)=1 where a ≠ 1, b ≠ 1 and c ≠ 1.
Q.14. Find the altitude of a parallelepiped determined by the vectors a, b and c if the base taken as parallelogram determined by a and b and if a = i + j + k, b = 2i + 4j – k and c = i + j + 3k.
Q.15. Show that four points whose position vectors are 6i – 7j, 16i – 19j – 4k, 3i – 6k, 2i – 5j + 10k are coplanar.
Q.16. If |a| = 3, |b| = 4 and |c| = 5 such that each is perpendicular to sum of the other two, find |a + b + c|
Q.17. Decompose the vector 6i – 3j – 6k into vectors which are parallel and perpendicular to the vector i + j + k.
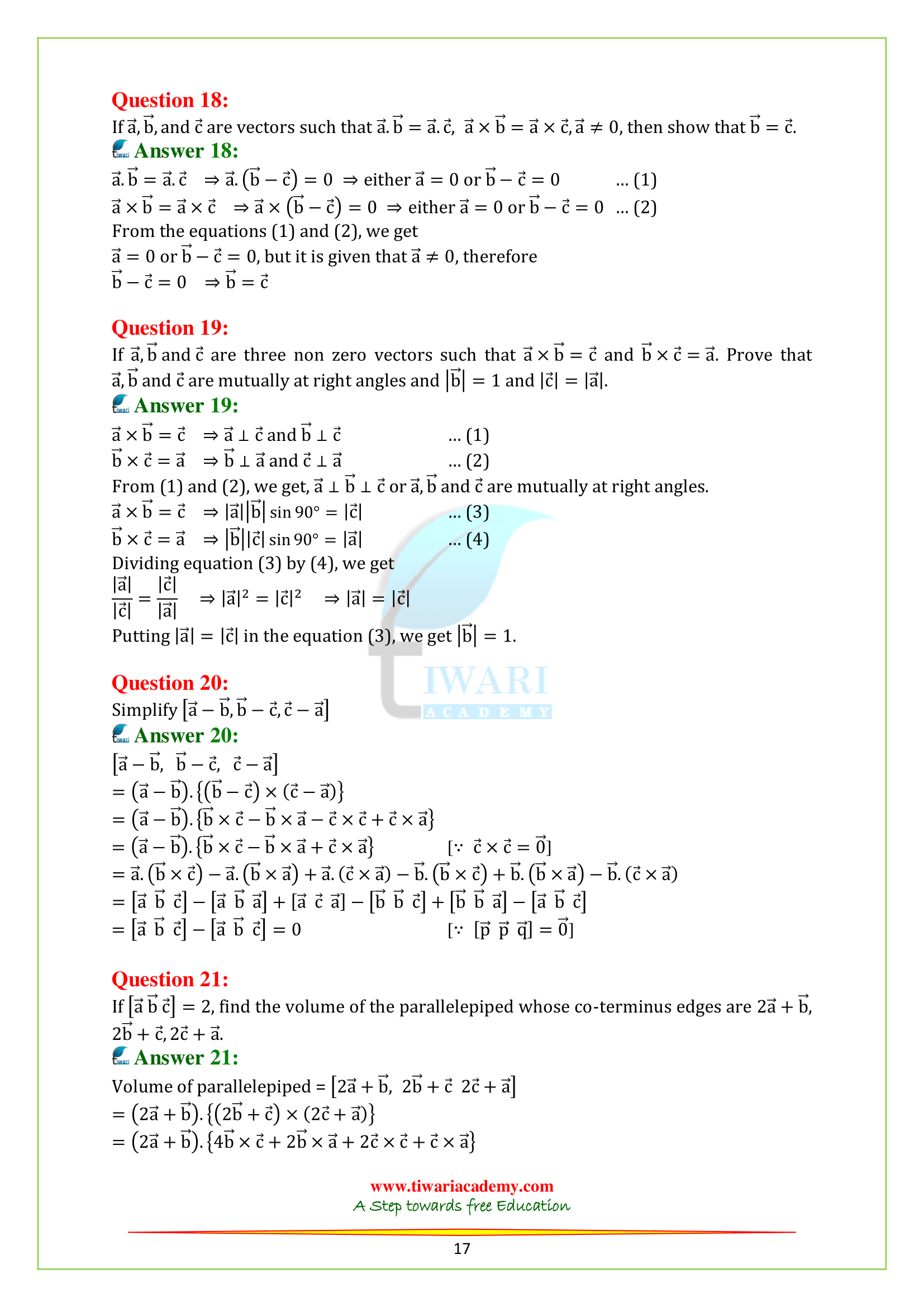
Q.18. If a, b and c are vectors such that a.b = a.c, a × b = a × c, a ≠ 0, then show that b = c.
Q.19. If a, b and c are three non zero vectors such that a × b = c and b × c = a. Prove that a, b and c are mutually at right angles and |b| = 1 and |c| = |a|.
Q.20. Simplify [a – b, b – c, c – a].
Q.21. If [abc] = 2, find the volume of the parallelepiped whose co-terminus edges are 2a + b, 2b + c, 2c + a.
Q.22. If a,b and c are three vectors such that a + b + c = 0 and |a| = 3, |b| = 5, |c| = 7, find the angle between a and b.
Q.23. The magnitude of the vector product of the vector i + j + k with a unit vector along the sum of the vector 2i + 4j + 5k and λi + 2j + 3k is equal to √2. Find the value of λ.
Q.24. If a × b = c × d and a × c = b × d, prove that (a – d) is parallel to (b – c), where a ≠ d and b ≠ c.
Q.25. Find a vector of magnitude √51 which makes equal angles with the vector a = 1/3 (i – (2j) + 2k), b = 1/5 (-4i – 3k) and c = j.
Q.26. If a,b and c are perpendicular to each other, then prove that [a b c] = a²b²c²
Q.27. If α = 3i – j and β = 3i + j + 3k then express β in the form of β = β1 + β2, where β1 is parallel to α and β2 is perpendicular to α.
Q.28. Find a unit vector perpendicular to plane ABC, when position vectors of A,B,C are (3i) – j + 2k, i – j – 3k and 4i – (3j) + k respectively.
Q.29. Find a unit vector in XY plane which makes an angle 45° with the vector i + j at angle 60° with the vector 3i – 4j.
Q.30. Find the altitude of a parallelepiped determined by the vectors a, b and c if the base taken as parallelogram determined by a and b and if a = i + j + k, b = 2i + 4j – k and c = i + j + 3k.
Q.31. Let v = (2i) + j – k and w = i + 3k. If u is a unit vector, then find the maximum value of the scalar triple product u, v, w.
Q.32. If a = i – k, b = xi + j + (1-x)k and c = yi + x j + (1 + x – y)k then prove that [a b c] depends upon neither x nor y.
Q.33. A, b and c are distinct non negative numbers, if the vectors ai + aj + ck and ci + cj + bk lie in a plane, then prove that c is the geometric mean of a and b.
Q.34. If |(a & a2 & 1+a3 @ b & b2 & 1+b3 @ c & c2 & 1+c3)| = 0 and vectors (1, a, a²), (1, b, b²) and (1, c, c²) are non-coplanar, then find the value of abc.
Previous Years CBSE Important Questions
1. Find the magnitude of each of the two vectors a and b, having the same magnitude such that the angle between them is 60º and their scalar product is 9/2. [CBSE Exam 2018]
2. If θ is the angle between two vectors i – 2j + 3k and 3i – 2j + k, find sin θ. [CBSE Exam 2018]
3. Let a = 4i + 5j – k , b = i – 4j + 5k and c = 3i + j – k. Find a vector d which is perpendicular to both a and b and satisfying d.c = 21.
4. What is the distance of the point (p, q, r) from the x-axis? [CBSE Sample Paper 2017]
5. If a line makes angles 90° and 60° respectively with the positive directions of x and y axes, find the angle which it makes with the positive direction of z-axis. [Delhi 2017]
6. If a, b and c are mutually perpendicular vectors of equal magnitudes, show that the vector a + b + c is equally inclined to a, b and c. Also, find the angle which a + b + c makes with a or b or c. [Delhi 2017]
7. Find the position vector of a point which divides the join of points with position vectors a – 2b and 2a + b externally in the ratio 2:1. [Delhi 2016]
8. The two vectors j + k and 3i – j + 4k represent the two sides AB and AC, respectively of a triangle ABC. Find the length of the median through A. [Delhi 2016]
9. Find a vector in the direction of a = i – 2j that has magnitude 7 units. [Delhi 2015C]
10. If a and b are unit vectors, then what is the angle between a and b so that √2 a – b is a unit vector? [Delhi 2015C]
11. If a = 7i + j – 4k and b = 2i + 6j + 3k, then find the projection of a on b. [Delhi 2015]
12. If a line makes angles 90°, 60° and θ with x, y and z-axis respectively, where θ is acute, then find θ. [Delhi 2015]
13. If r = xi + yj + zk, find (r × i).(r × j) + xy. [Delhi 2015]
How can NCERT solutions help with Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Vector Algebra?
NCERT Complete solutions for Class 12 Mathematics Chapter 10 Vector Algebra simplify the learning process by offering step-by-step explanations for all exercises, including exercise 10.1, 10.2, 10.3 and the miscellaneous exercise. These solutions focus on essential concepts like vector addition, scalar multiplication and vector projections, which are crucial for solving board exam problems. By studying the Class 12 Math Chapter 10 solved examples and important questions, students gain confidence in applying mathematical principles to real-world problems. NCERT Class 12 Maths solutions PDF is an accessible resource for preparing effectively, ensuring a clear understanding of key topics.
What topics are covered in NCERT Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 Vector Algebra?
NCERT Class 12 Mathematics Chapter 10 Vector Algebra covers a wide range of topics, including the definition of vectors, their magnitude and direction, addition, scalar multiplication and vector products like dot and cross products. These concepts are explored through exercises such as exercise 10.3 solutions, which focus on vector products and exercise 10.2 solutions, which delve into scalar multiplication. The chapter also includes important questions frequently asked in board exams. By referring to the NCERT solutions for Class 12 Math, students can strengthen their conceptual understanding and improve their problem-solving abilities, especially for challenging miscellaneous exercises.
How can I prepare effectively for Vector Algebra in Class 12 board exams?
To prepare effectively for Vector Algebra Class 12, start by reviewing the NCERT Class 12 Maths solutions for Chapter 10. Focus on understanding the solved examples and practicing exercises like NCERT exercise 10.1 solutions and the miscellaneous exercise solutions, as they cover a wide range of problems. Utilize the NCERT Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 PDF to study on the go. Practicing important questions helps you identify topics commonly asked in exams. Regularly revisiting Class 12 Maths Chapter 10 notes ensures you have a clear grasp of fundamental concepts, enabling you to perform well on exam day.