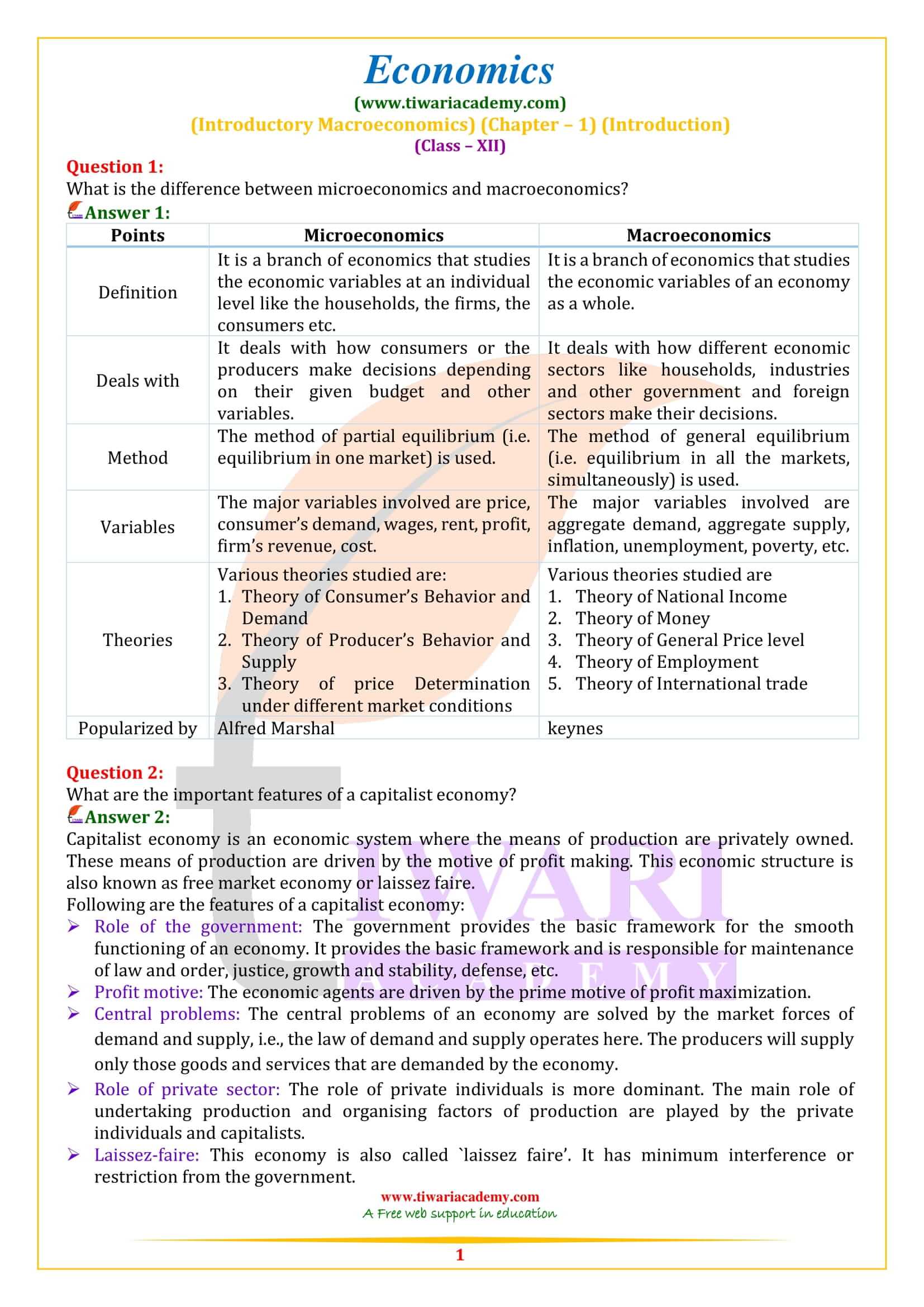
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics Chapter 1 Introduction – Macroeconomics in English Medium updated for CBSE session 2025-26. Get here class 12 Macroeconomics chapter 1 important questions, Case Studies and MCQ with answers and explanation.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics Chapter 1
Class 12 Economics Macroeconomics Chapter 1 Introduction Question Answers
Simple description of Economy
In our daily life we use different-different types of goods and services. We are using these goods and services even while sleeping. For example: From the time when you wake up in the morning and till you go to sleep, you utilise many goods and services such as: Toothpaste, Toothbrush, Tea, Sugar, Bread, Electricity, Fan, Bulb, Mixer, Transportation, etc. Every human being uses different set of goods and services as per their need and liking. A family farm may own a land, farming tools and equipment, labour services of family members, grains, etc. A teacher in the school can earn money by educating the children and fulfil his need of goods and services using that money.
Some others in the society may not have any resource excepting their own labour services. Each of these decision-making units can produce some goods or services by using the resources they have, they can use a part of the produce for their consumption and by the rest of the produce they can procure clothing, housing, and various services or goods of their need. It goes without saying that no individual has unlimited resources compared to his need. The amount of corn a family can produce is limited by the amount of resources it has, and hence, the amount of different goods and services that it can procure in exchange of corn is also limited.
Effect of Economic Betterment
As a result, the family is forced to make a choice between the goods and services that are available. This means that if the family is opting for some new or better goods or services which will cost them more than usual, they will have to cut down the expenses on other things. Like, if they want more and better education for their children, they may have to give up some of the luxuries of life. The same is the case with other individuals in the society. Everyone faces scarcity of resources, and therefore, has to use the limited resources in the best possible way to fulfil their needs.
The Economic fulfil in needs and Demand
Everyone in the society is engaged in producing some goods or services but the problem is that everyone needs many different goods and services in their daily life. Sadly, all of them cannot be produced by a single individual. We don’t have to tell this that the amount of the goods produced must have some compatibility between what the people of the society collectively wants. For example, the total amount of corn produced by a family farm along with other farming units in a society must match the total amount of corn that people in the society collectively wants to consume.
If the total production of the corn exceeds the consuming capacity of the society, then the extra corn is used to produce some other high demand goods or services. Just as the resources of an individual are scarce, the same thing goes with the society as well. The scarce resources of the society have to be allocated properly in the production of different goods and services in keeping with the likes and dislikes of the society members.
Allocation of resources of the society would result in the production of different sets of goods and services. So, after the production, these goods and services has to be distributed among the individuals as per the demand. The allocation of the limited resources and distribution of the final mix of products are two of the basic problems of an economy.
Central Problems of an Economy
Production, exchange and consumption of goods and services e among the basic economic activities of life. While performing these basic activities, every society has to face scarcity of resources and it is the scarcity of resources that gives rise to the problem of choice. The scarce resources of an economy have competing usage. In simpler words, every society has to decide on how to use its scarce resources.
Class 12 Economics Macroeconomics Chapter 1 Important Question Answers
What is produced and in what quantities?
The first problem is to decide that what goods or services should be produced and how much should be the quantity. There are countless goods and services present and every society has to choose from them. They have to choose whether to produce more food, clothing, housing or to have more of luxurious goods. Whether to use more resources in education and health or to use more resources in building military service. Whether to have more of basic education or more of higher education.
How are these goods produced?
In the production of different goods and services, how much of what resources should be implemented, has to be decided by the society. They have to decide that what or which available technology to adopt in the production of each of the goods? Should they use more manpower or should they use more of machines?
For whom are these goods produced?
Once the goods are produced, it has to be distributed among the individuals in the economy. How should the produce of the economy be distributed? Who gets how much of the goods that is produced in the economy? Who gets more and who gets less? Whether the basic education and health services should be freely available for everyone in the society or not.
Thus, every economy faces the problem of scarce resources to the production of different goods and services and of distributing the produced goods and services to everyone in the economy. These problems are the central problems of an economy.
What are the main topics in Class 12 Macroeconomics Chapter 1?
Students will be studying macroeconomics for the first time in detail in class 12. The first topic in macroeconomics is about National income and related aggregates like- GDP, Per Capita income etc. In this topic we study the three main formulae for calculating national income. These three are (i) The value added method, (ii) The income method, (iii) The expenditure method.
In an examination question where we are asked to find the national income/ GDP/ some other aggregate, theoretically the answer arrived at will be the same by both methods asked. However, Twice in the last decade the answer to the aggregate asked were different.
We also study how growth in GDP is related to welfare of the people in the economy.
What are the Important Concepts in 12th Macroeconomics chapter 1 to prepare?
The following are some of the important concepts involve in the study of national income:
Stocks and flows, circular flow in a two sector economy, domestic territory, normal resident, factor income and transfer income, final goods and intermediate goods, COE, operating surplus and mixed income of self- employed, Private final consumption expenditure, Government final consumptions expenditure and Capital formation.
In order to arrive at national income we have to learn three important equations and also learn about consumption of its capital (Depreciation), Net factor income from abroad and net indirect taxes.
We also study, National income at constant prices (which is required to measure growth) and National income at current prices. The concept of personal income and personal disposable income have been deleted from CBSE syllabus but they may be relevant for other Boards.
What are the class 12 Economics chapter 1 Important Questions from examination perspective?
(i) What is double counting? How can it be avoided? (4 marks)
(ii) What are the steps and precautions for calculating the national income by all the three methods? (6 marks)
(iii) What are the limitations of GDP as a indicator of Welfare? (4- 6 marks)
(iv) Numericals on calculating National income, operating surplus and COE. (3 – 6 marks)
(v) Whether the given items will be included in National Income/ domestic income (with reasons). (2 marks each)
What are the Important Abbreviations in chapter 1 of 12th Macroeconomics?
GDP (MP) = Gross domestic product at Market Price
NDPFC = Net domestic product at Factor cost (Domestic income)
NNPFC = Net National product at Factor cost (National Income)
NFIA = net factor income received from Abroad
GDCF = Gross Domestic Capital Formation