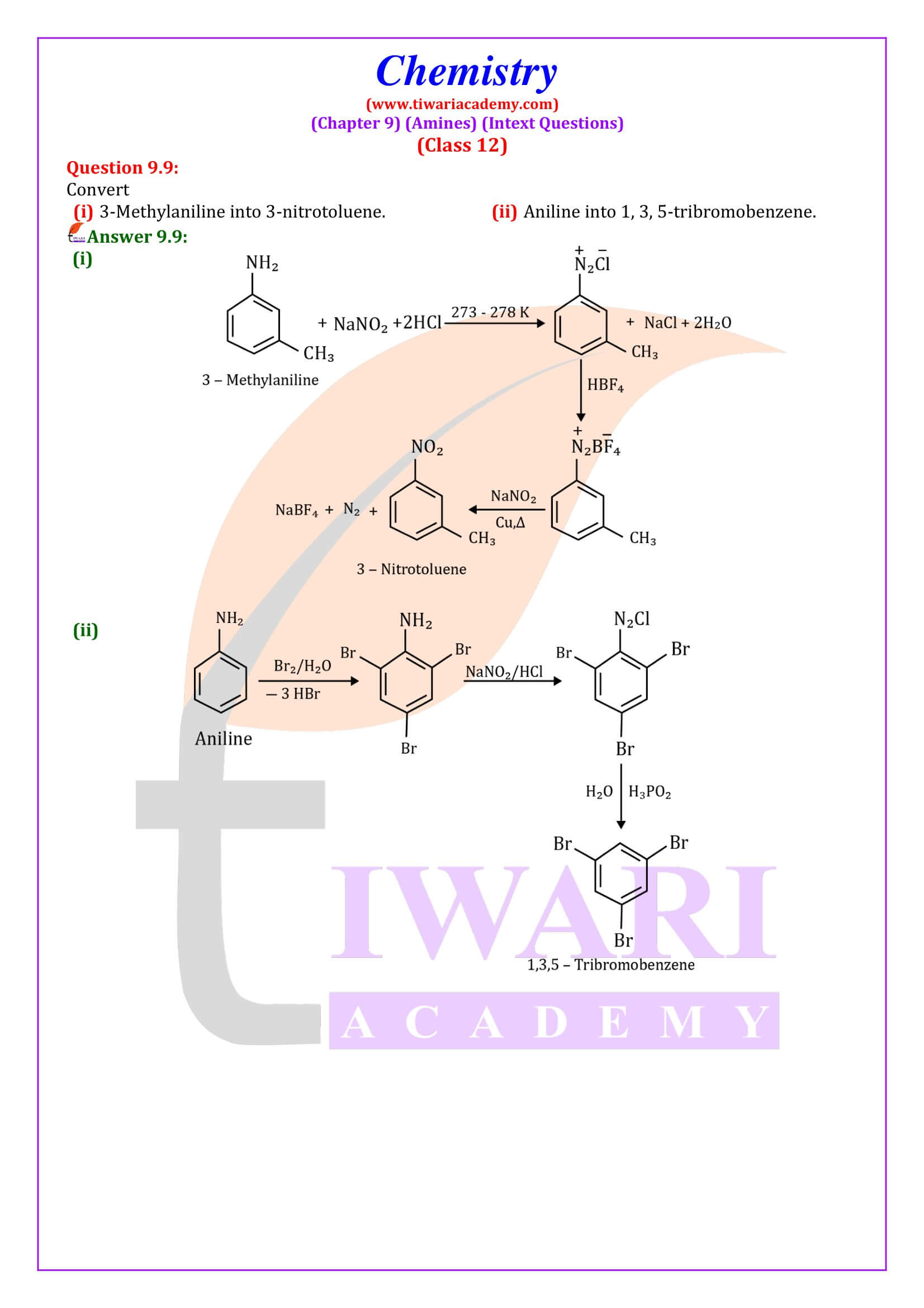
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Amines exercises and extra questions answers with intext questions updated for new academic session 2025-26. Class 12 Chemistry unit 9 solutions are given here in Hindi and English Medium free to use.
Viva Questions for 12th Chemistry
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9
| Class: 12 | Chemistry |
| Chapter: 9 | Amines |
| Content: | Exercises and Intext Question Answers |
| Mode of Content: | Images, PDF and Videos |
| Academic Session: | 2025-26 |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
Amines
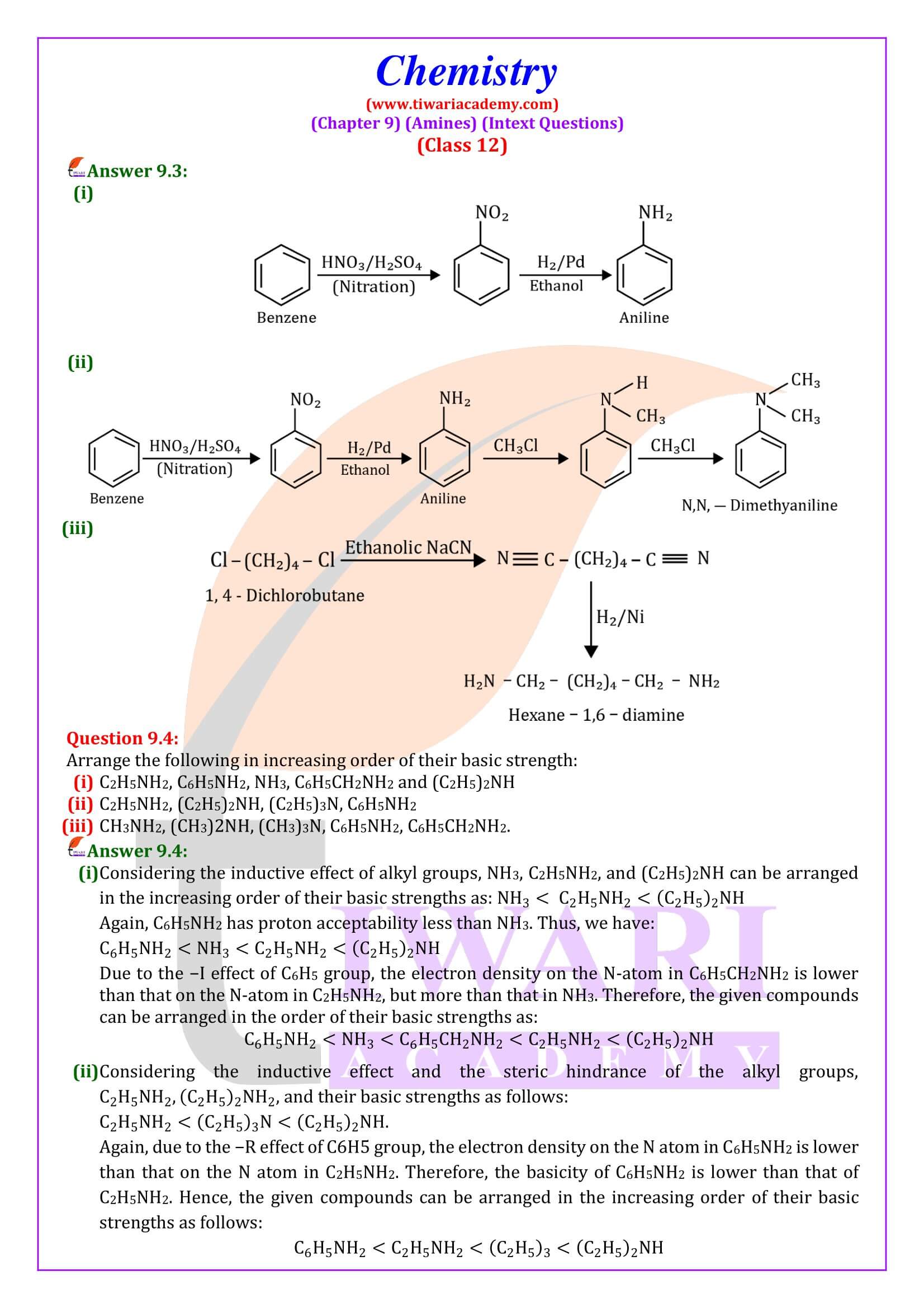
Amines can be considered as derivatives of ammonia, obtained by replacement of one, two or all the three hydrogen atoms by alkyl and/or aryl groups.
For example:
CH₃NH₂, C₆H₅ -NH₂, CH₃ -NH-CH₃, CH₃ -N-(CH₃)₂, etc.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 MCQ
Which of the following amines can exhibit enantiomerism?
Nitrogen atom of amino group is ______ hybridised.
Amine that cannot be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is
Which of the following is most basic?
Structure of Amines
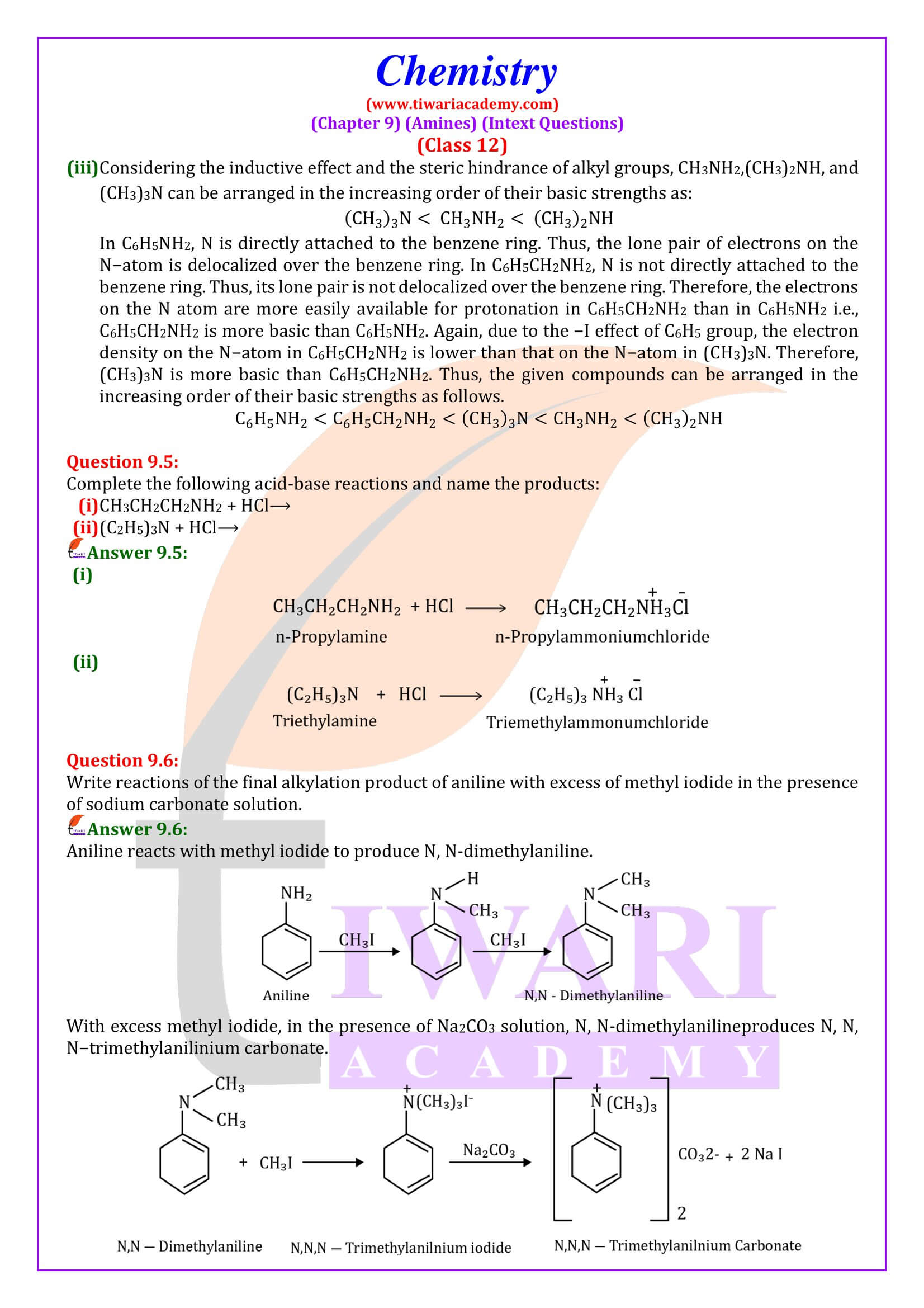
Like ammonia, nitrogen atom of amines is trivalent and carries an unshared pair of electrons. Nitrogen orbitals in amines are therefore, sp³ hybridised and the geometry of amines is pyramidal.
Classification
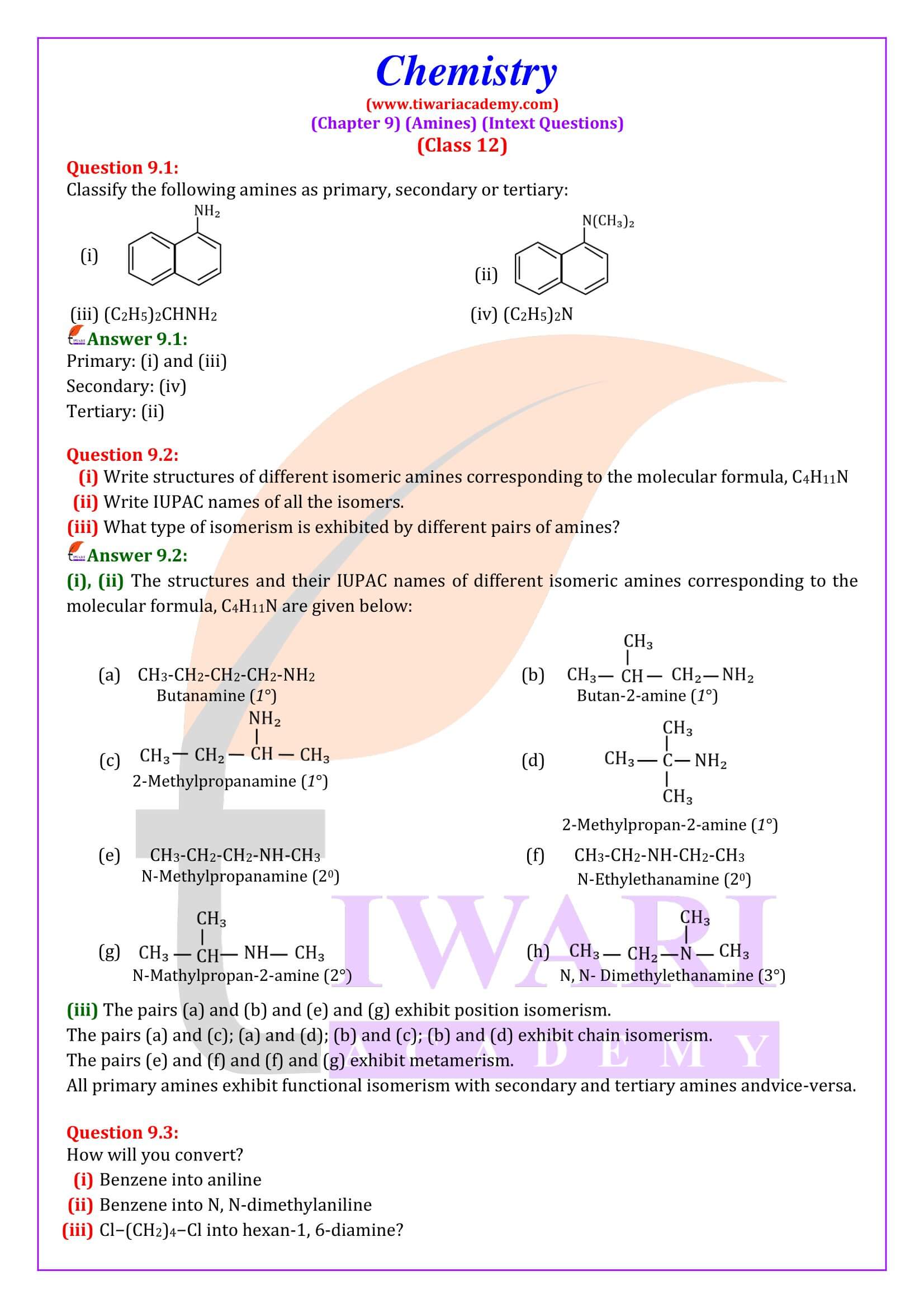
Amines are classified as primary (1⁰), secondary (2⁰) and tertiary (3⁰) depending upon the number of hydrogen atoms replaced by alkyl or aryl groups in ammonia molecule.
CH₃NH₂ (Primary), CH₃ -NH-CH₃ (Secondary), CH₃ -N-(CH₃)₂ (Tertiary)
Physical Properties
The lower aliphatic amines are gases with fishy odour. Primary amines with three or more carbon atoms are liquid and still higher ones are solid. Aniline and other arylamines are usually colourless but get coloured on storage due to atmospheric oxidation.
Lower aliphatic amines are soluble in water because they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. However, solubility decreases with increase in molar mass of amines due to increase in size of the hydrophobic alkyl part. Higher amines are essentially insoluble in water.
12th Chemistry Unit 9 Multiple Choice Questions
When excess of ethyl iodide is treated with ammonia, the product is
The reaction of aniline with benzoyl chloride gives
Amines behave as
Secondary amines can be prepared by
Chemical Reactions
Some of the reactions of amines are described below:
- Basic character of amines
Amines, being basic in nature, react with acids to form salts. - Alkylation
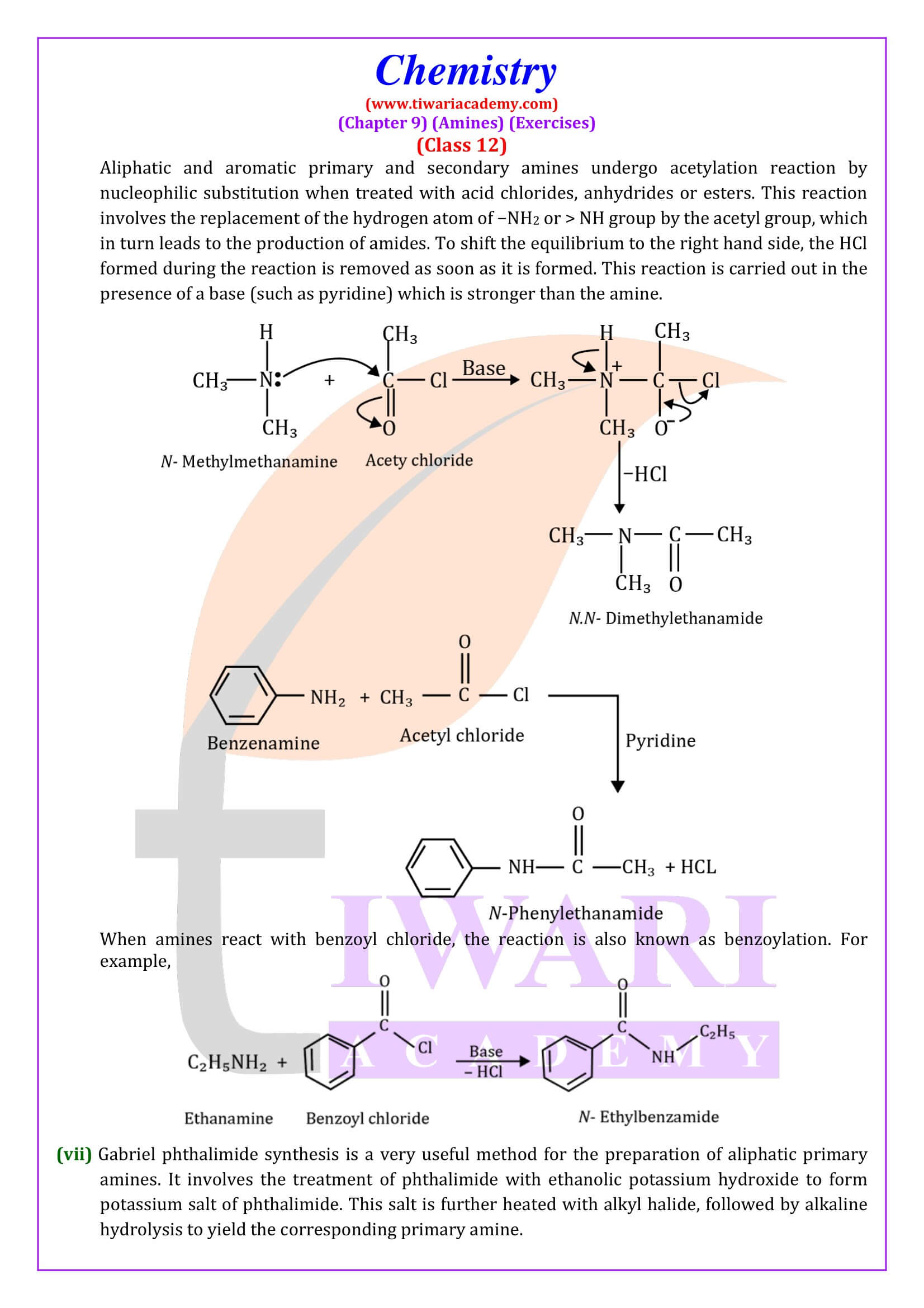
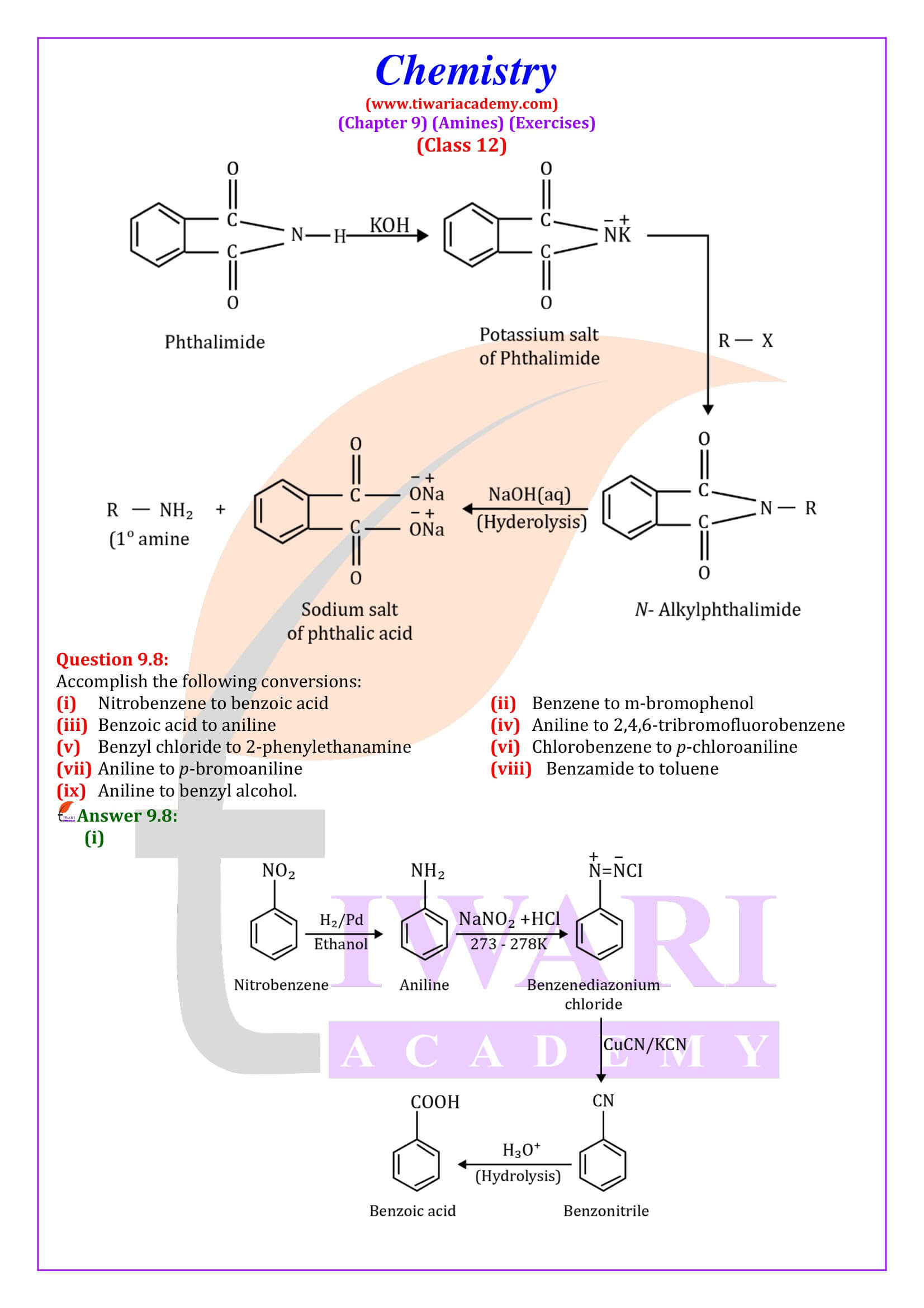
Amines undergo alkylation on reaction with alkyl halides. - Acylation
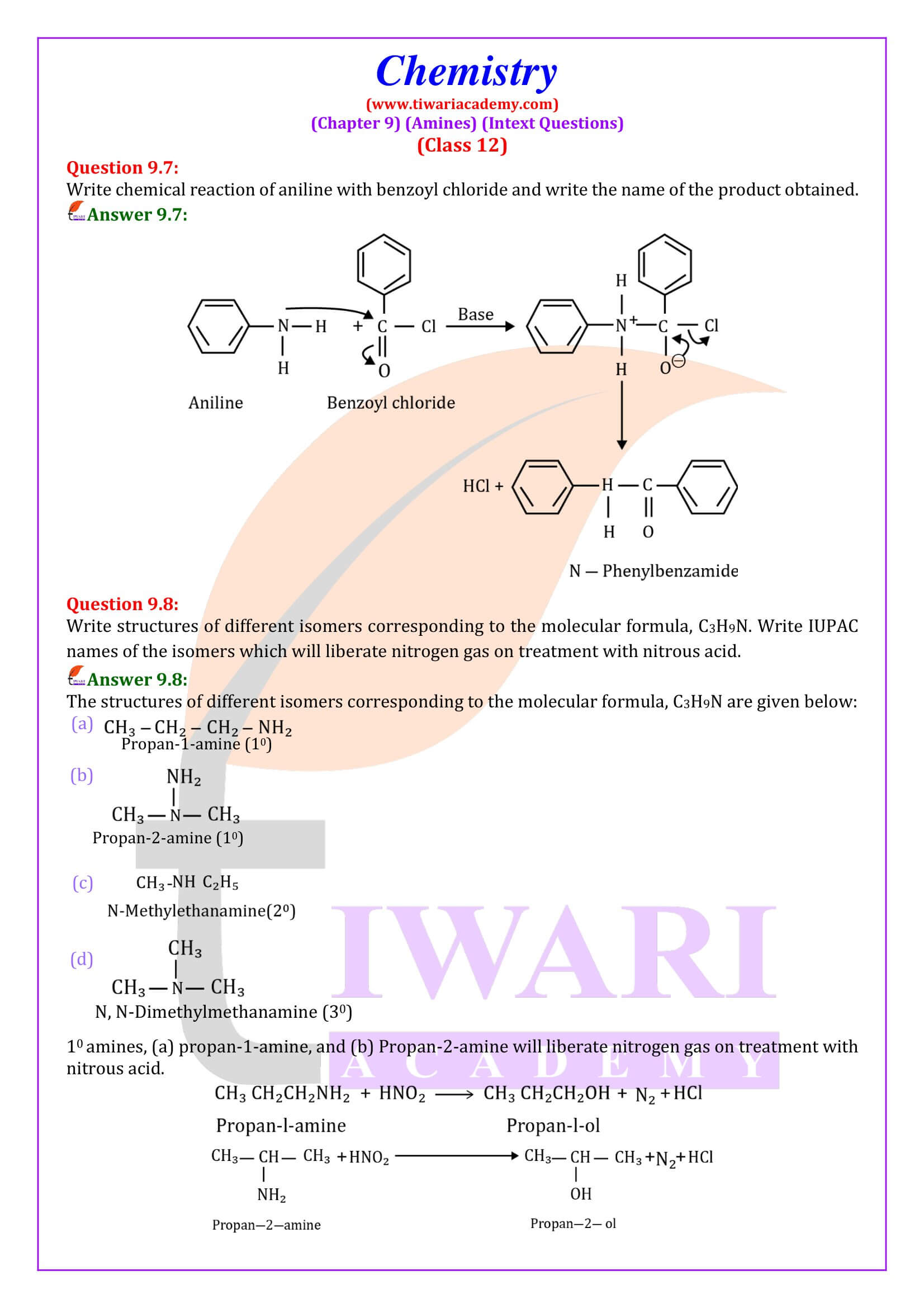
Aliphatic and aromatic primary and secondary amines react with acid chlorides, anhydrides and esters by nucleophilic substitution reaction. This reaction is known as acylation.
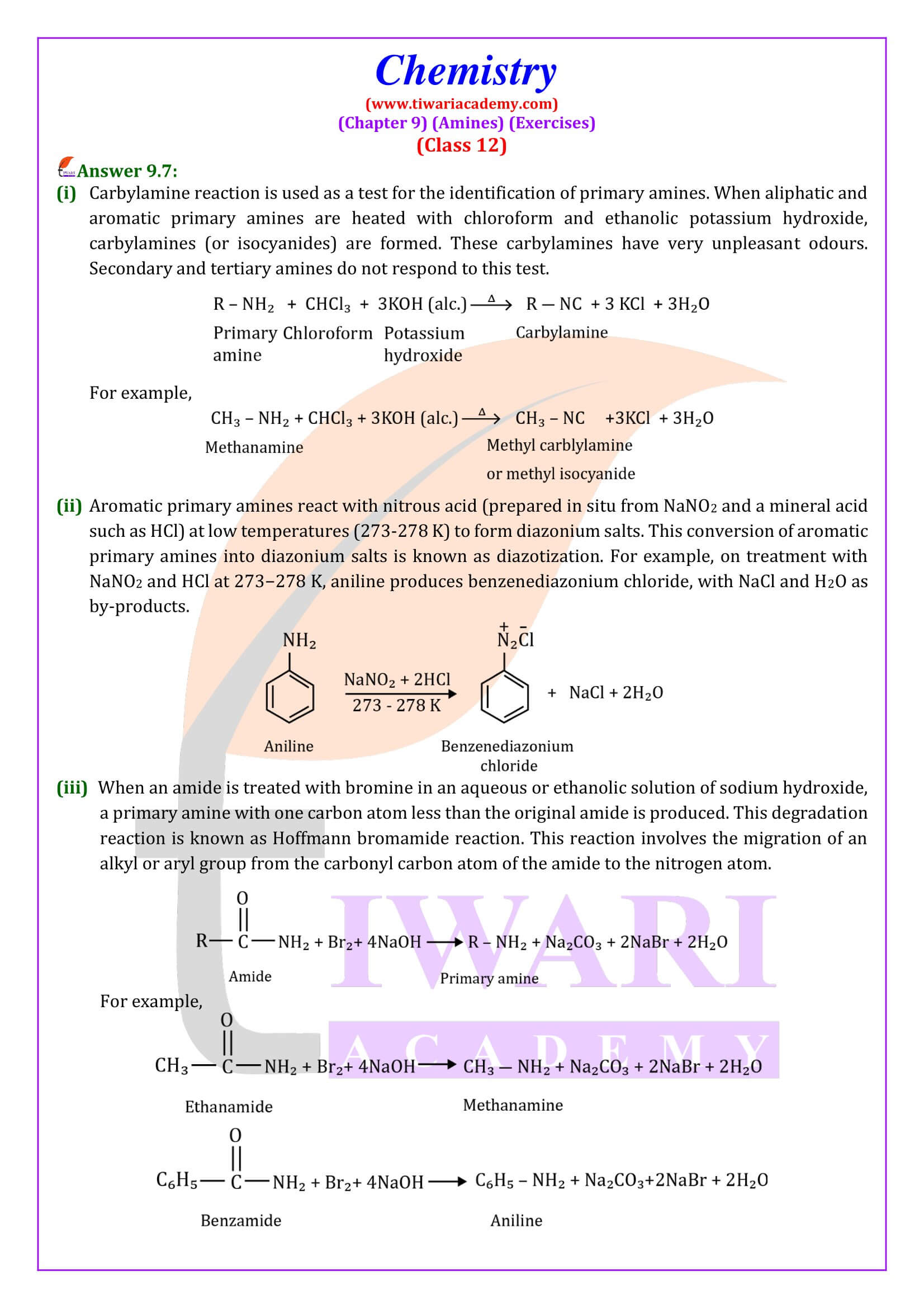
Carbylamines reaction
Aliphatic and aromatic primary amines on heating with chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide form isocyanides or carbylamines which are foul smelling substances. Secondary and tertiary amines do not show this reaction. This reaction is known as carbylamines reaction or isocyanide test and is used as a test for primary amines.
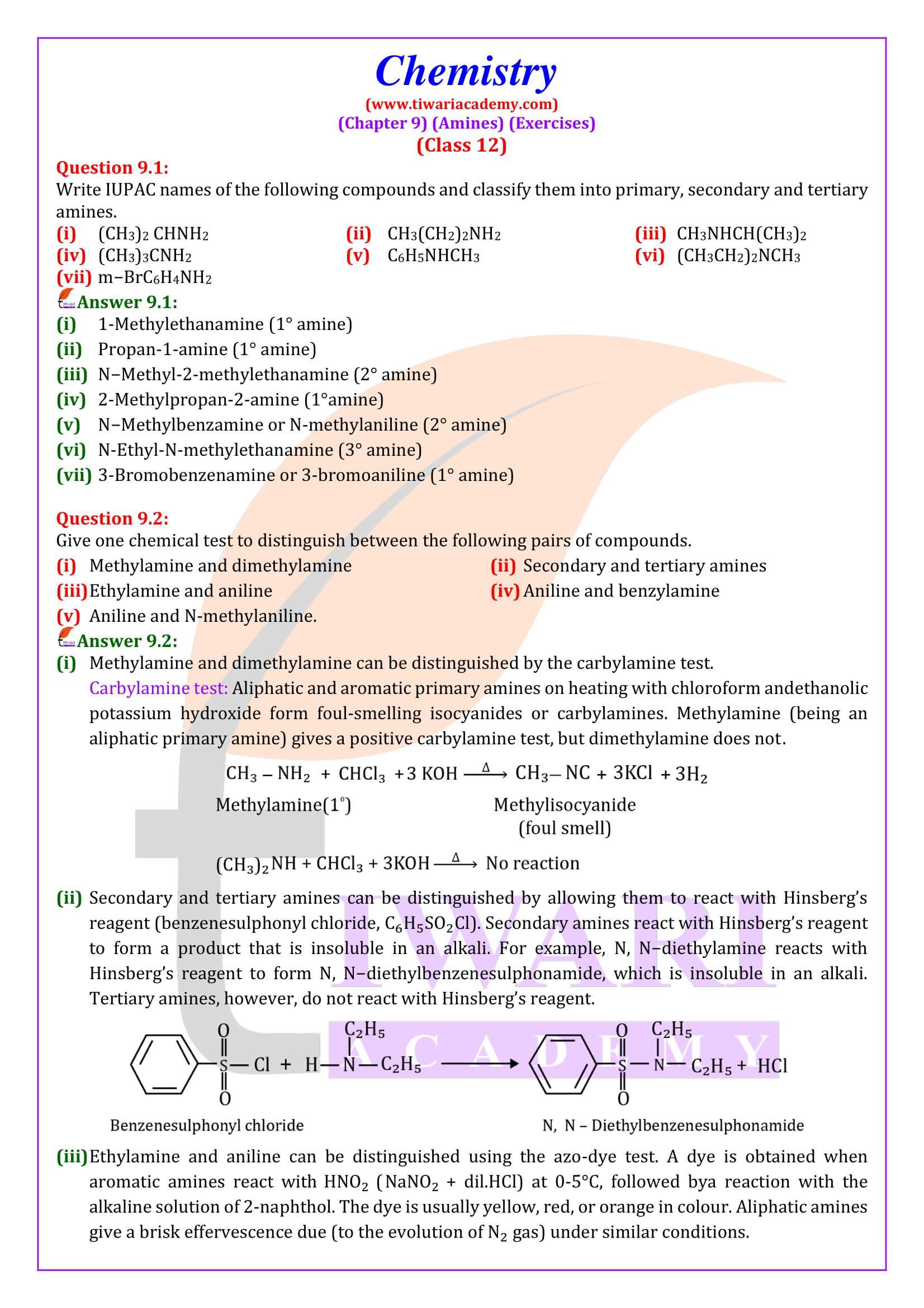
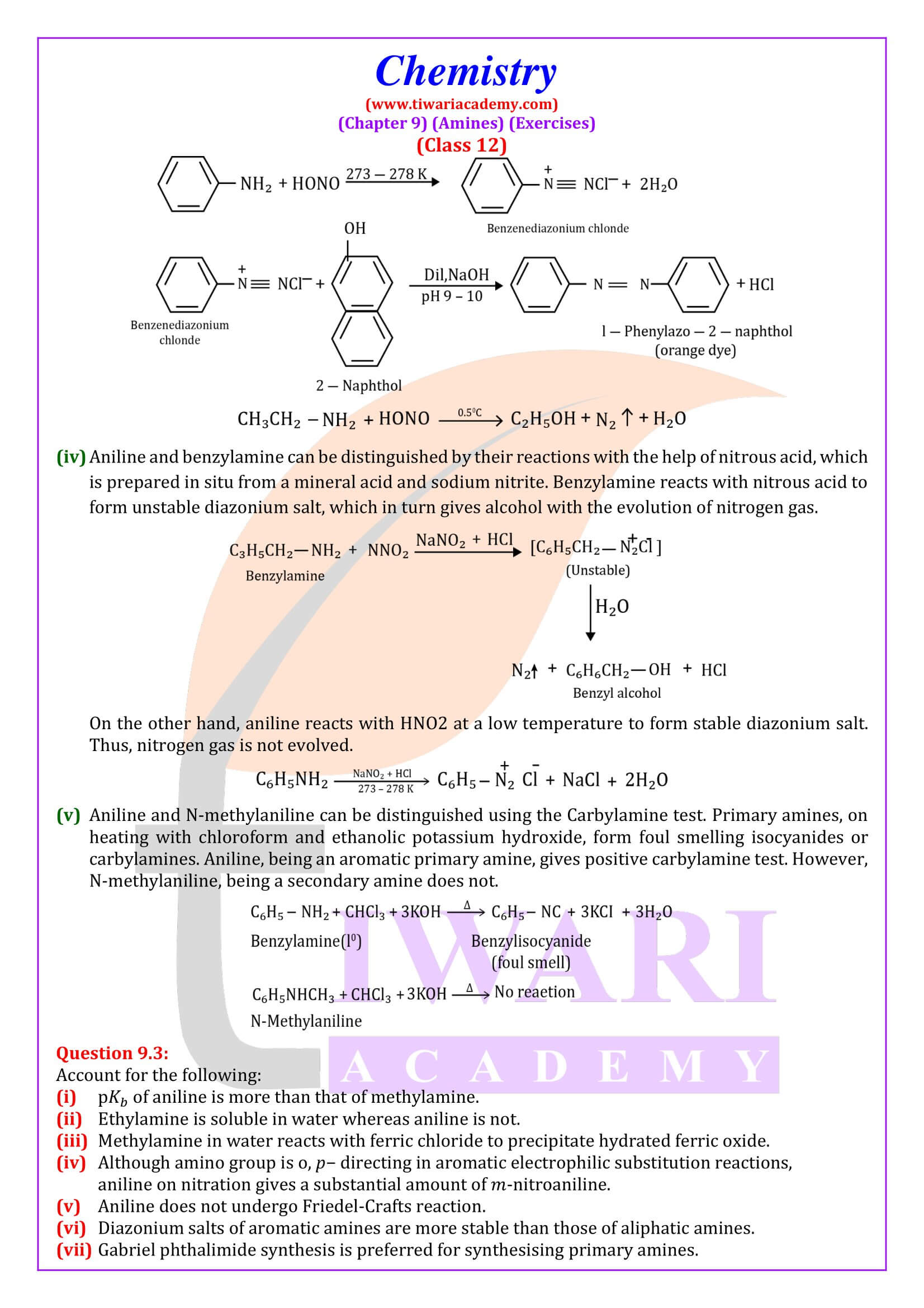
Reaction with nitrous acid Three classes of amines react differently with nitrous acid which is prepared in situ from a mineral acid and sodium nitrite.
Reaction with arylsulphonyl chloride Benzenesulphonyl chloride (C₆H₅SO₂Cl), which is also known as Hinsberg’s reagent, reacts with primary and secondary amines to form sulphonamides.
Electrophilic substitution
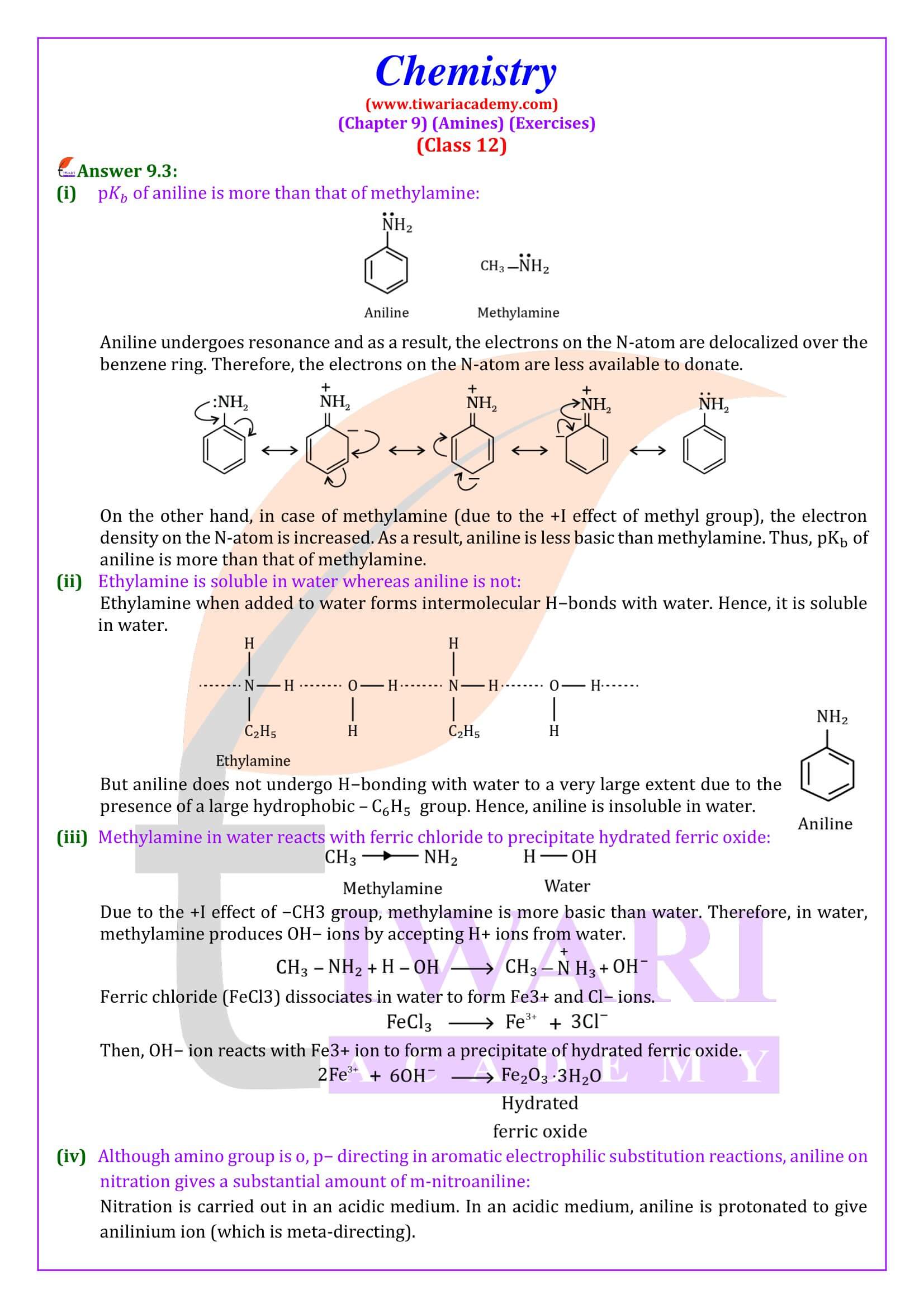
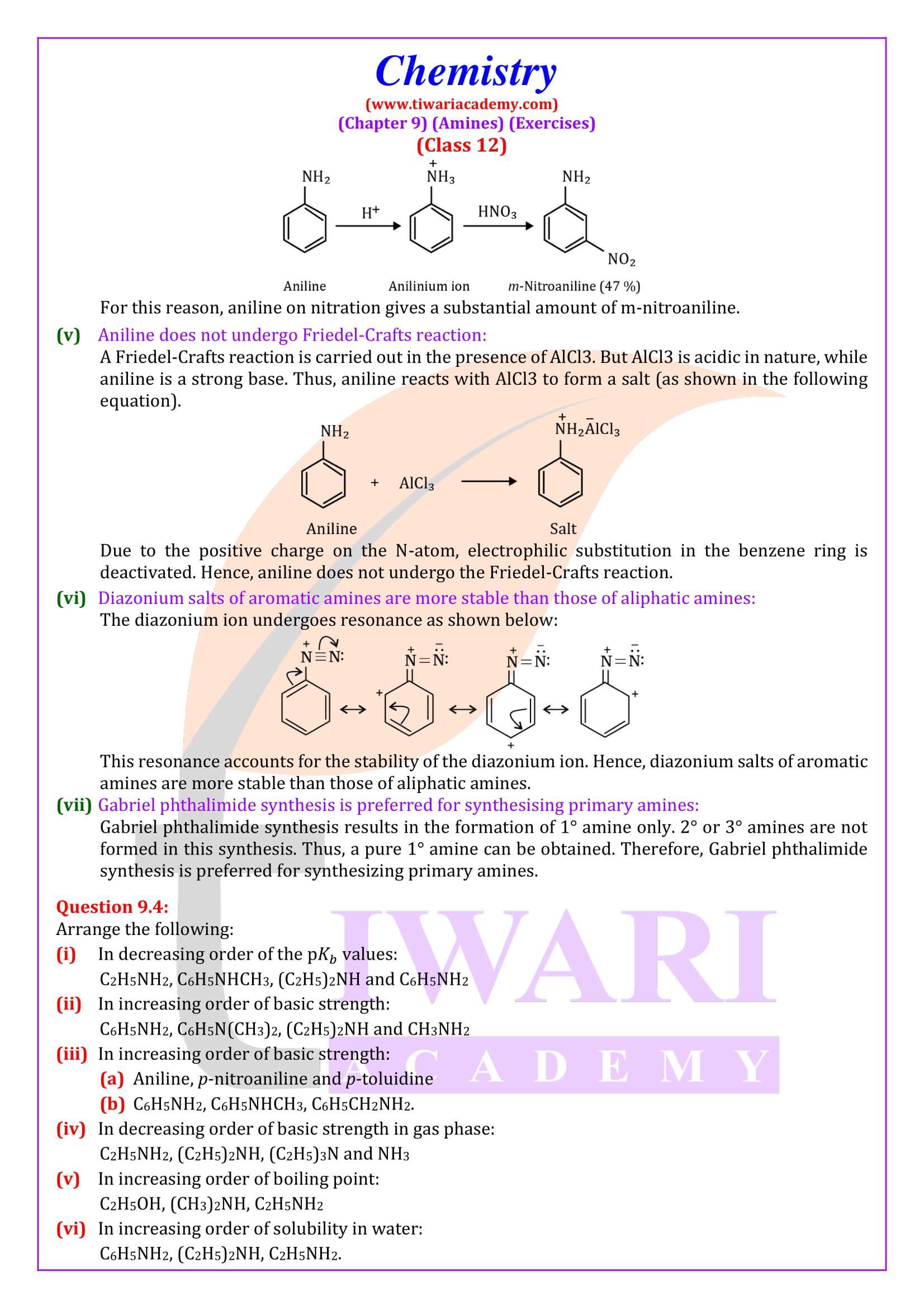
Ortho- and para-positions to the –NH₂ group become centres of high electron density. Thus –NH₂ group is ortho and para directing and a powerful activating group.
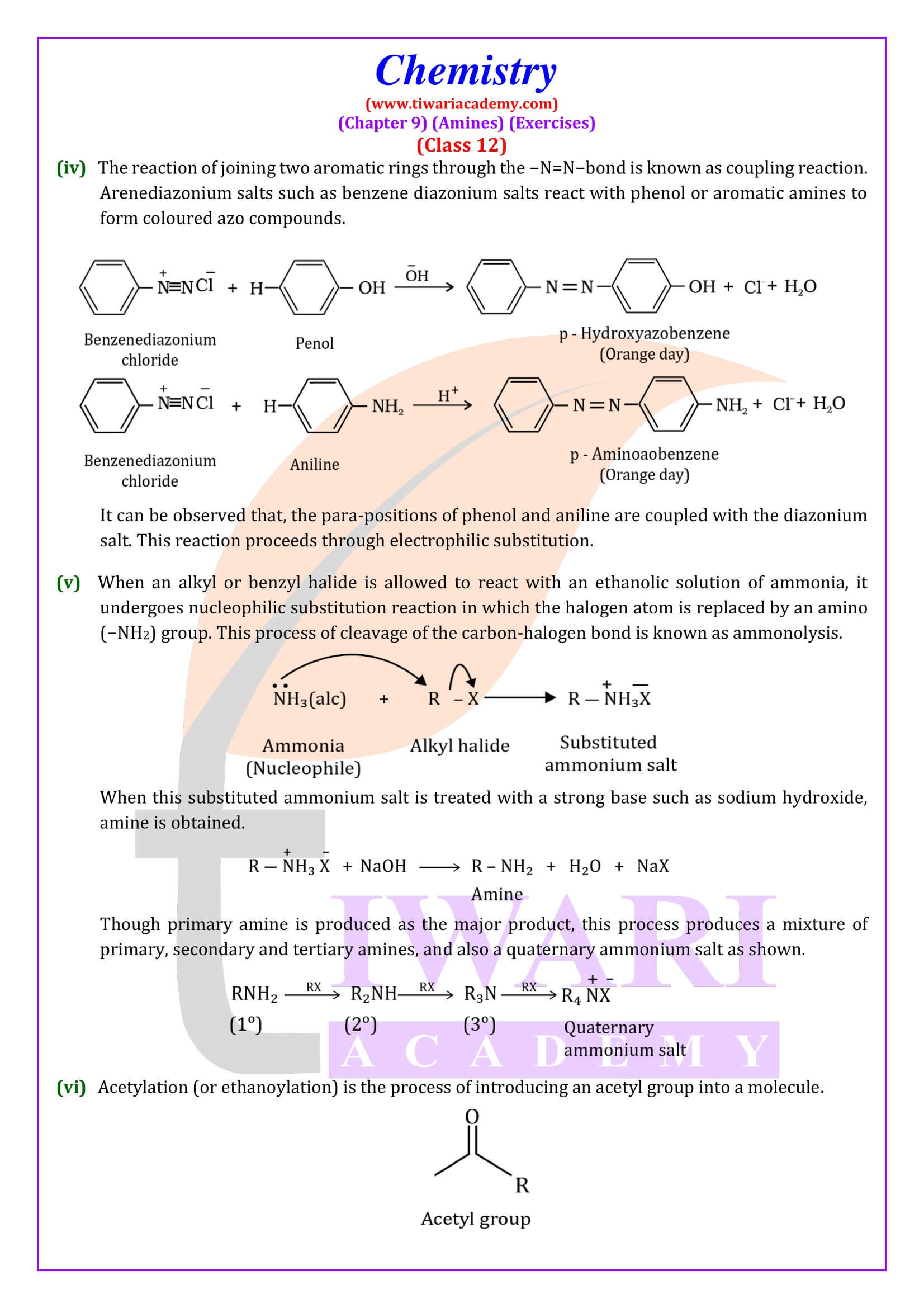
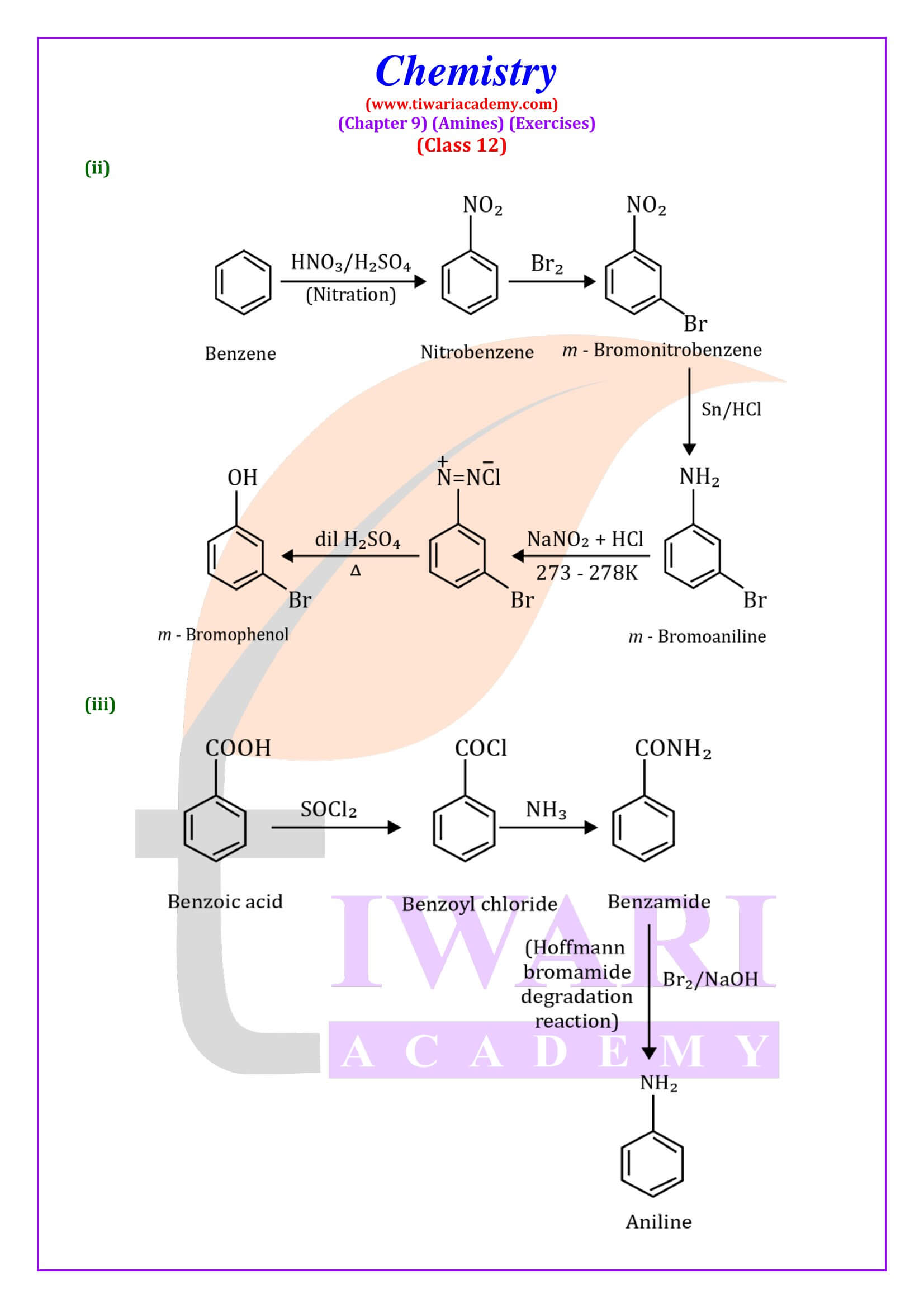
Diazonium Salts
General formula of diazonium salts is RN₂ + X⁻ where R = aryl group and X⁻ ion can be Cl⁻, Br⁻, HSO₄⁻ and BF₄⁻. Diazonium salts are named by suffixing diazonium to the name of the parent hydrocarbon from which they are formed, followed by the name of anion such as chloride, hydrogensulphate, etc.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Important Questions
How are amines produced?
Large quantities of aliphatic amines are made synthetically. The most widely used industrial method is the reaction of alcohols with ammonia at a high temperature, catalyzed by metals or metal oxide catalysts (e.g., nickel or copper). Mixtures of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines are thereby produced.
What is the importance of amines?
Amines play an important role in the survival of life. They are involved in the creation of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins in living beings. Many vitamins are also built from amino acids. Serotonin is an important amine that functions as one of the primary neurotransmitters for the brain.
What are amines in food?
Amines in food are chemicals that occur naturally, caused by bacteria that breaks down amino acids. They are related to the inorganic compound ammonia. Higher levels of amines are found in fermented, charred, grilled, over ripe, over cooked or decomposing foods.