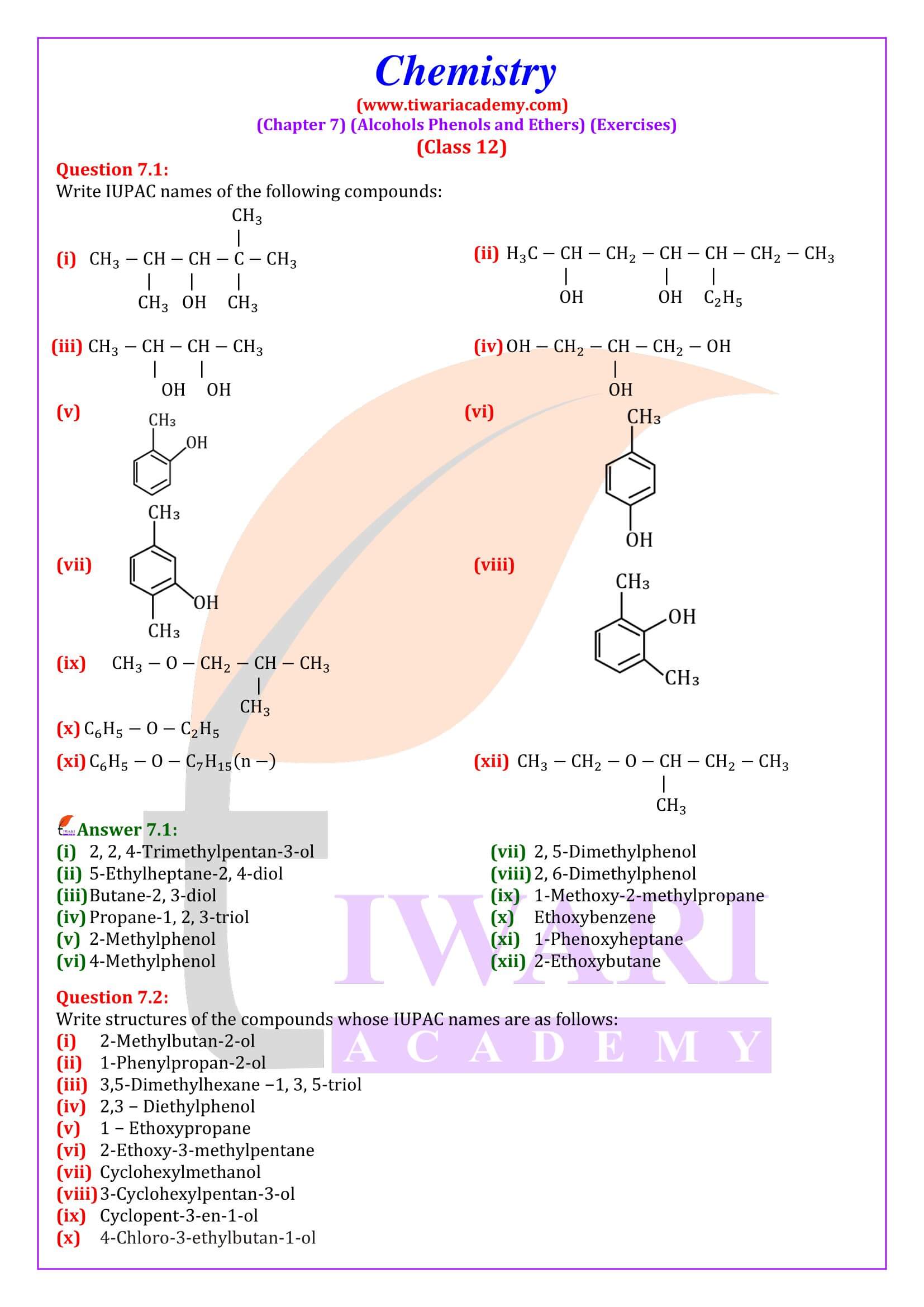
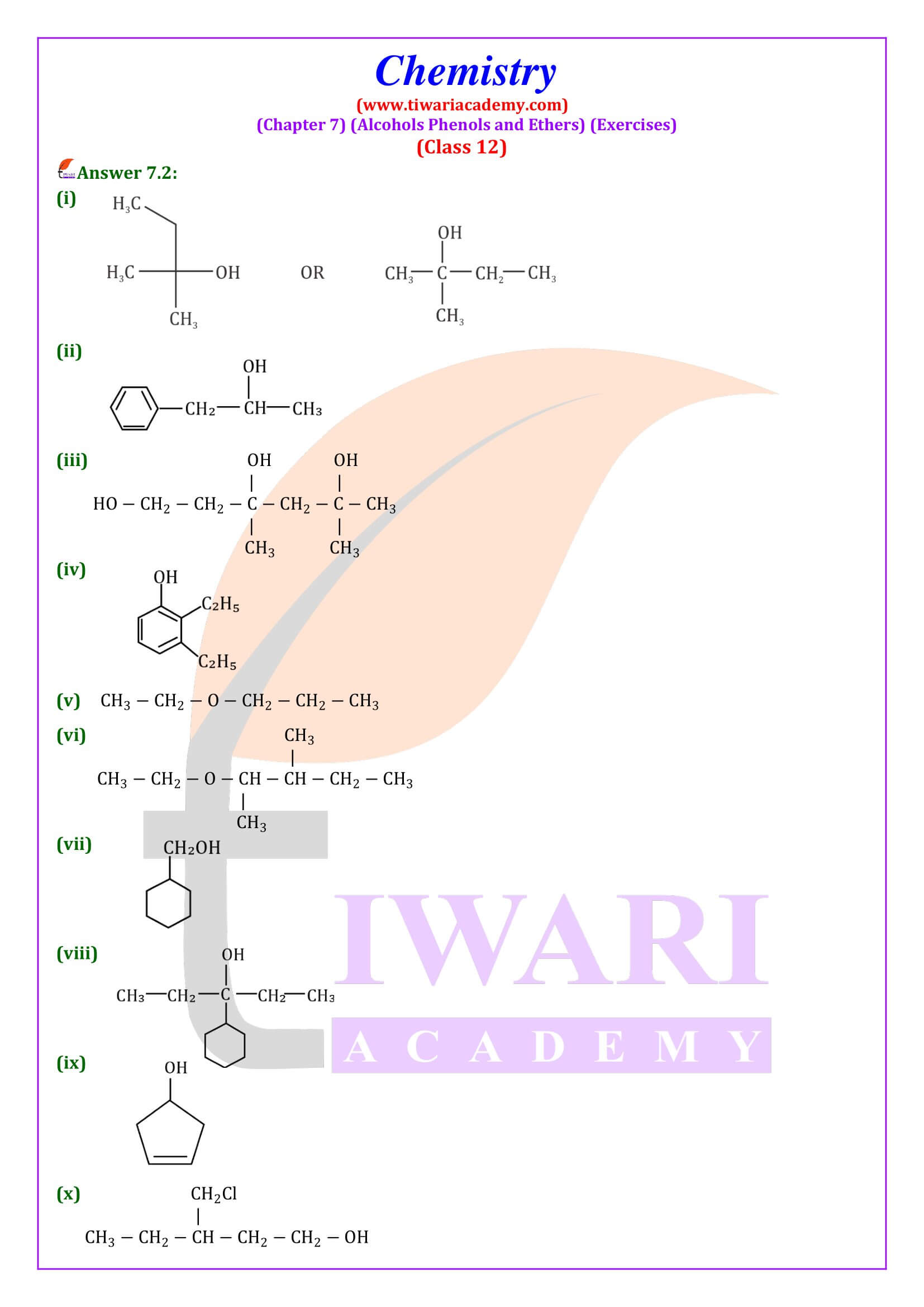
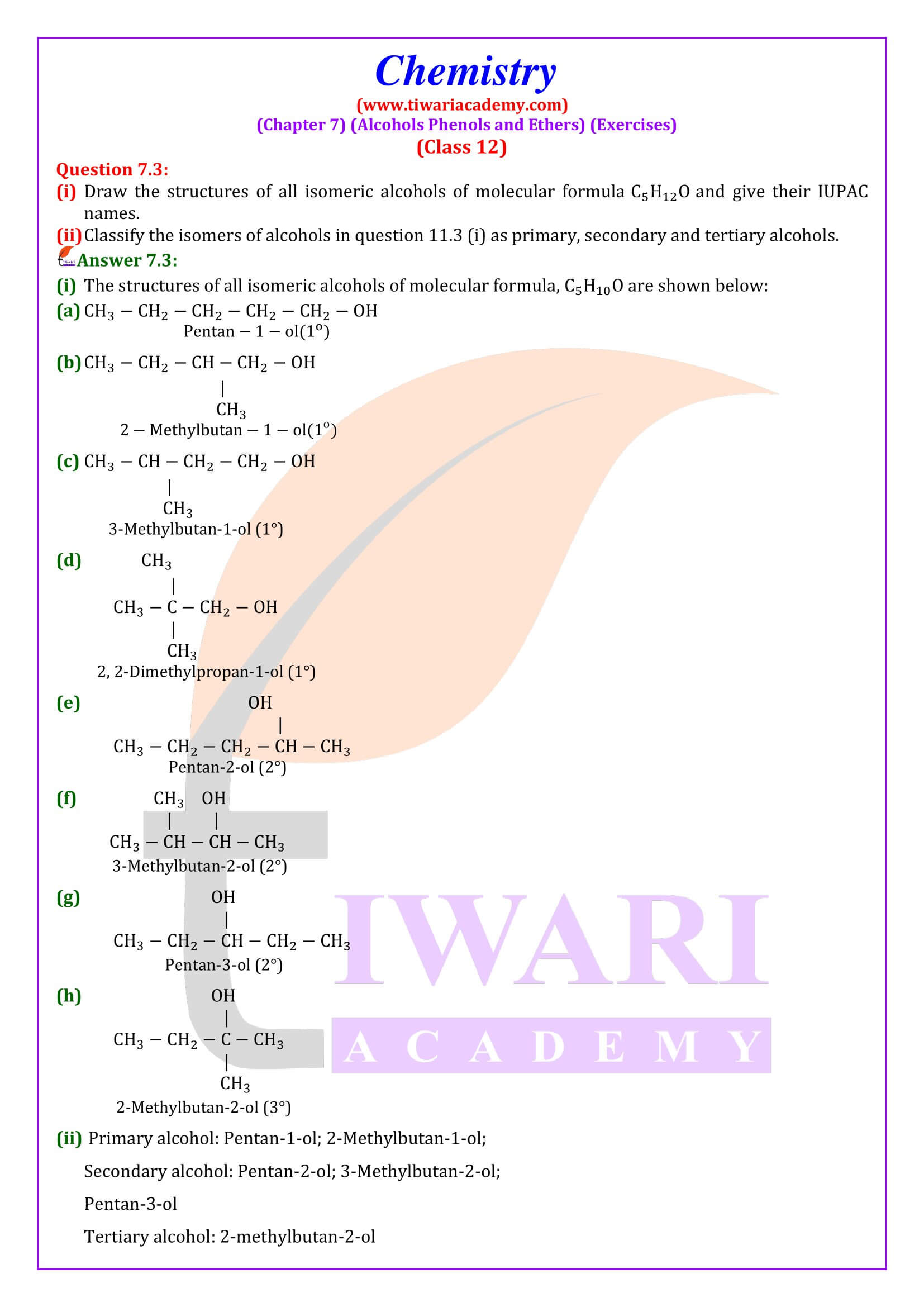
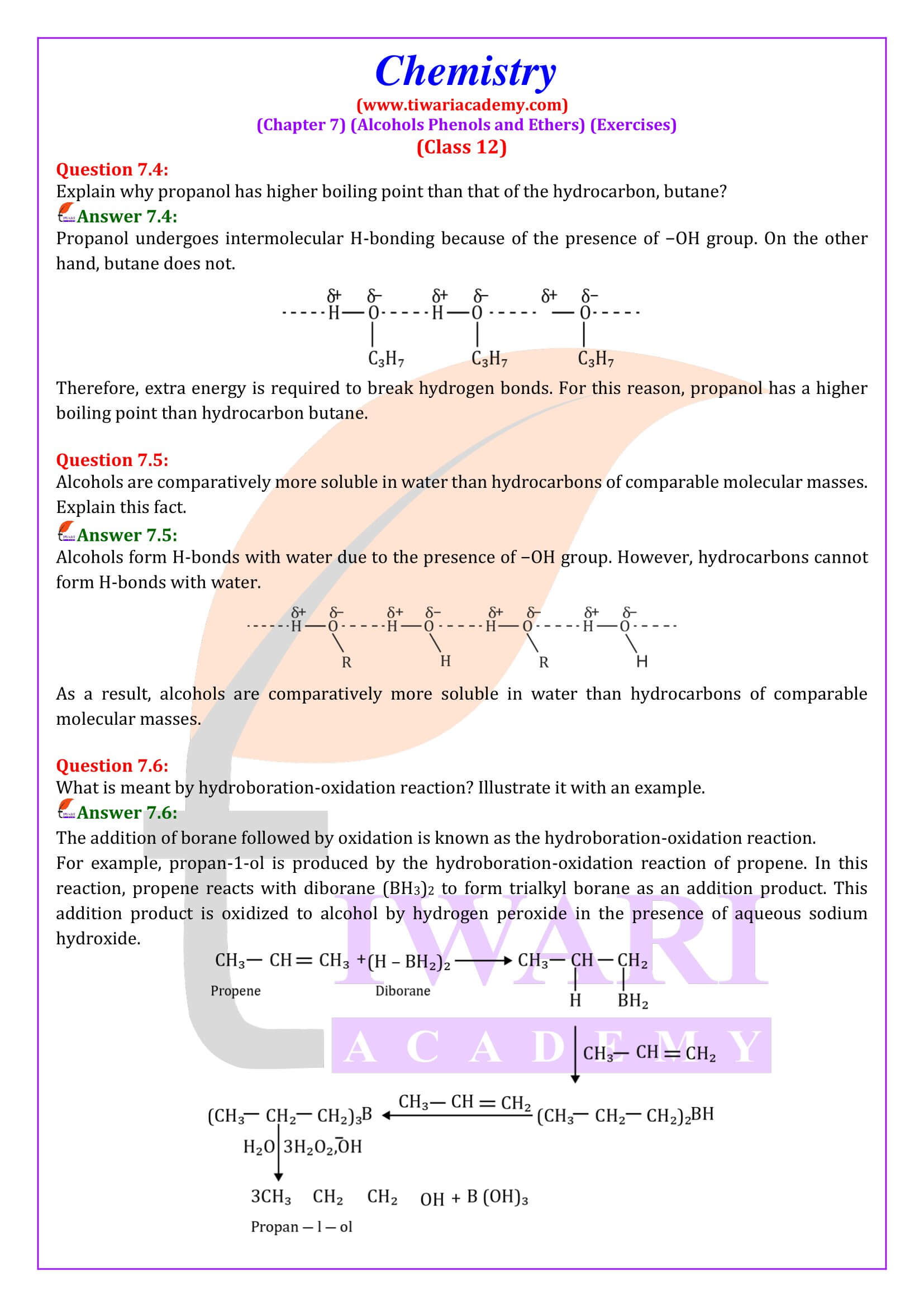
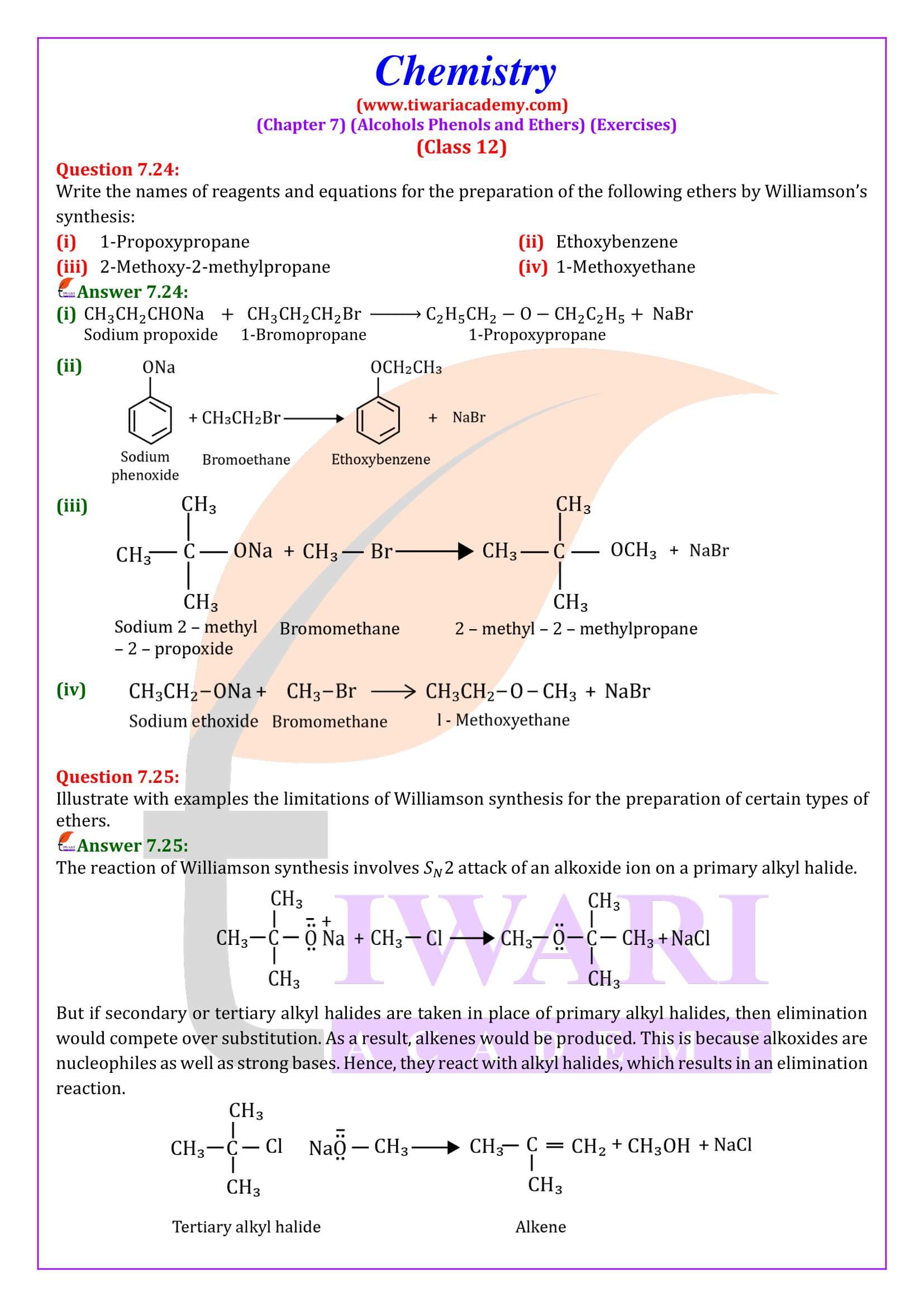
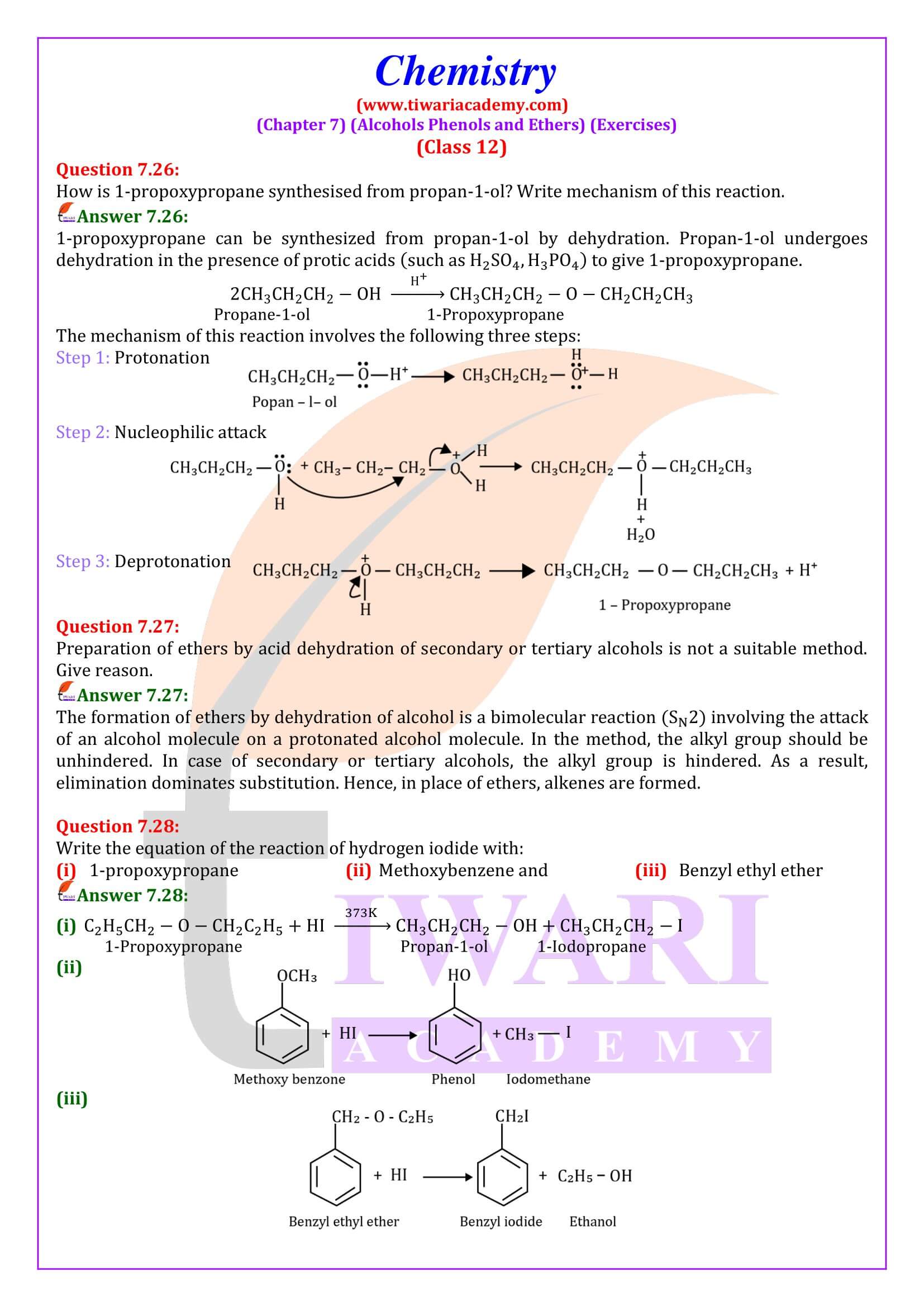
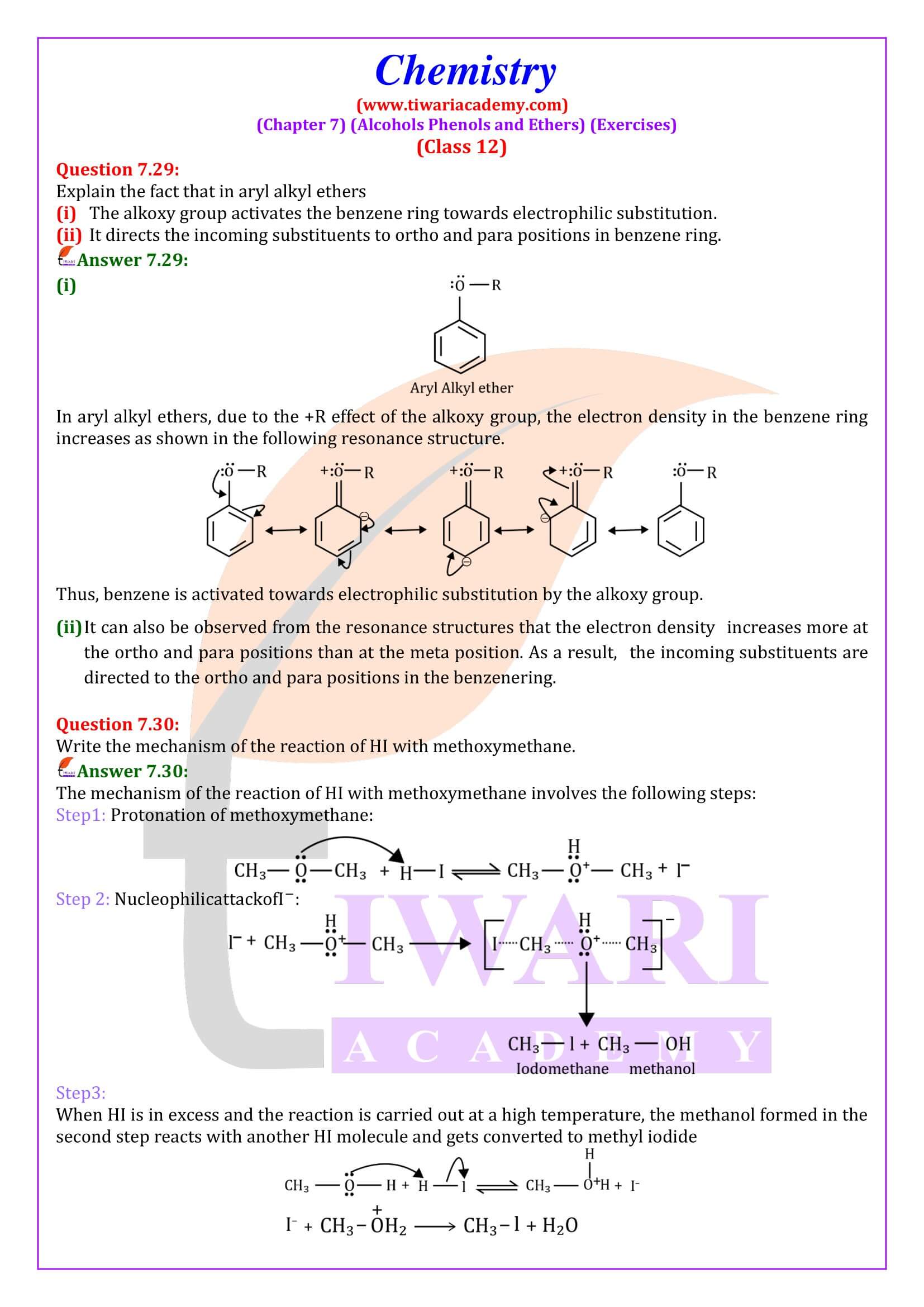
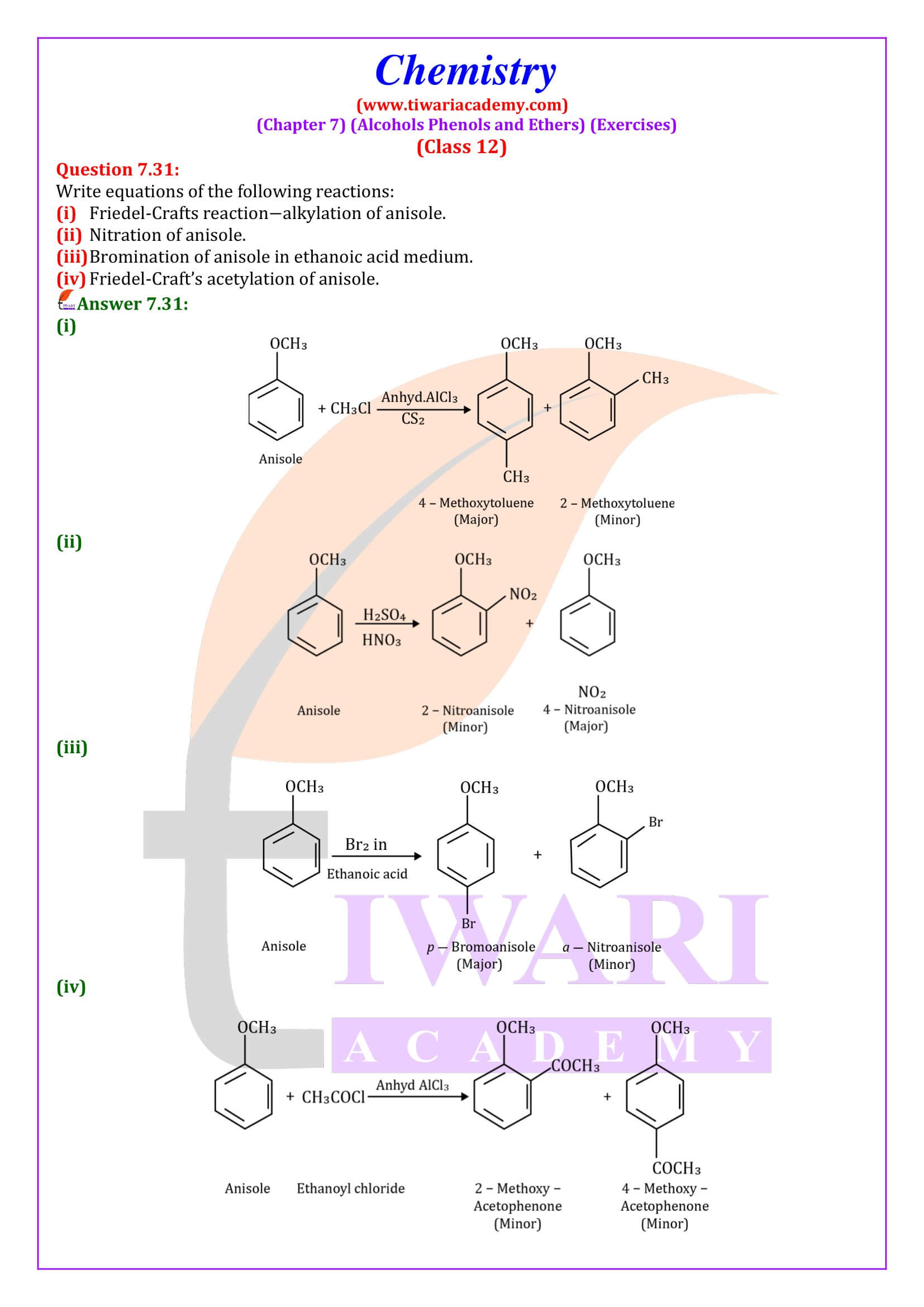
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers updated for new academic session 2025-26. Question answers and intext questions of class 12 Chemistry unit 7 are given here in English and Hindi Medium free to use.
Important Viva Question for Class 12 Chemistry
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Question Answers
| Class: 12 | Chemistry |
| Chapter: 7 | Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers |
| Content: | Exercises and Intext Solutions |
| Format of Content: | PDF, Images, Text and Videos |
| Session: | Academic Year 2025-26 |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Alcohols
Alcohols are produced by the reaction of Grignard reagents with aldehydes and ketones. The first step of the reaction is the nucleophilic addition of Grignard reagent to the carbonyl group to form an adduct. Hydrolysis of the adduct yields an alcohol.
Phenols
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula C₆H₅OH. It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group (−C₆H₅) bonded to a hydroxy group (−OH). Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns.
Ethers
Ethers are the organic compounds in which an oxygen atom is connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. These are represented by the general formula R-O-R’ where R and R’ may be alkyl or aryl groups.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 MCQ
Which of the following reagents cannot, be used to oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes?
Among the following compounds, strongest acid is
The compound which reacts fastest with Lucas reagent at room temperature is
Ethyl alcohol is industrially prepared from ethylene by
Classification of Alcohols
Alcohols may be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary, according to which carbon of the alkyl group is bonded to the hydroxyl group. Most alcohols are colourless liquids or solids at room temperature.
Examples: Ethyl alcohol, methyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, etc.
Phenols— Mono, Di and Trihydric Phenols
Depending on the number of hydroxyl groups attached, phenols can be classified into three types.
- (i) Monohydric phenols: They contain one -OH group.
- (ii) Dihydric phenols: They contain two -OH groups. They may be ortho-, meta- or para- derivative.
- (iii) Trihydric phenols: They contain three -OH groups.
12th Chemistry Unit 7 Multiple Choice Questions
What happens when tertiary butyl alcohol is passed over heated copper at 300°C?
When Phenol is distilled with zinc dust, it gives
Ethylene reacts with Baeyer’s reagent to give
Classification of Ethers
Ethers are classified as simple or symmetrical, if the alkyl or aryl groups attached to the oxygen atom are the same, and mixed or unsymmetrical, if the two groups are different. Diethyl ether, C₂H₅OC₂H₅, is a symmetrical ether whereas C₂H₅OCH₃ and C₂H₅OC₆H₅ are unsymmetrical ethers.
Physical Properties
Alcohols and phenols consist of two parts, an alkyl/aryl group and a hydroxyl group. The properties of alcohols and phenols are chiefly due to the hydroxyl group. The nature of alkyl and aryl groups simply modify these properties.
Boiling Points
The boiling points of alcohols and phenols increase with increase in the number of carbon atoms (increase in van der Waals forces). In alcohols, the boiling points decrease with increase of branching in carbon chain (because of decrease in van der Waals forces with decrease in surface area).
Solubility
Solubility of alcohols and phenols in water is due to their ability to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules as shown. The solubility decreases with increase in size of alkyl/aryl (hydrophobic) groups. Several of the lower molecular mass alcohols are miscible with water in all proportions.
Chemical Reactions
Alcohols are versatile compounds. They react both as nucleophiles and electrophiles. The bond between O–H is broken when alcohols react as nucleophiles.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 Important Questions
What is acetone used for?
Acetone is a chemical used to make products like nail polish remover and paint remover. Your body also makes this chemical when it breaks down fat.
An alkoxide is a stronger base than a hydroxide ion. Justify.
Due to the presence of electron-donating alkyl group, there is high electron density in alkoxide ion as compared to hydroxide ion. Therefore, the alkoxide ion is more basic than the hydroxide ion.
What is the difference between methanol and ethanol?
Methanol and ethanol are alcohol variants. Methanol contains only one carbon and ethanol contains two carbons in each molecule. Both substances can be used as energy sources, but methanol primarily serves as a research subject, and its use as a motor fuel.