NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 5 Organising in English Medium updated for session 2025-26. Class 12 B St Chapter 5 answers carry the latest questions given in NCERT textbook. Answers are given in easy to learn format.
What are Viva Questions for Class 12 Business Studies
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 5
Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 5 NCERT Solutions
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Identify the network of social relationships which arises spontaneously due to interaction at work.
The network of social relationship which arises spontaneously due to interaction at work is called Informal organization.
What does the term ‘Span of management’ refer to?
Span of management refers to the number of subordinates that can be effectively managed by a superior. This determines the levels of management in the structure.
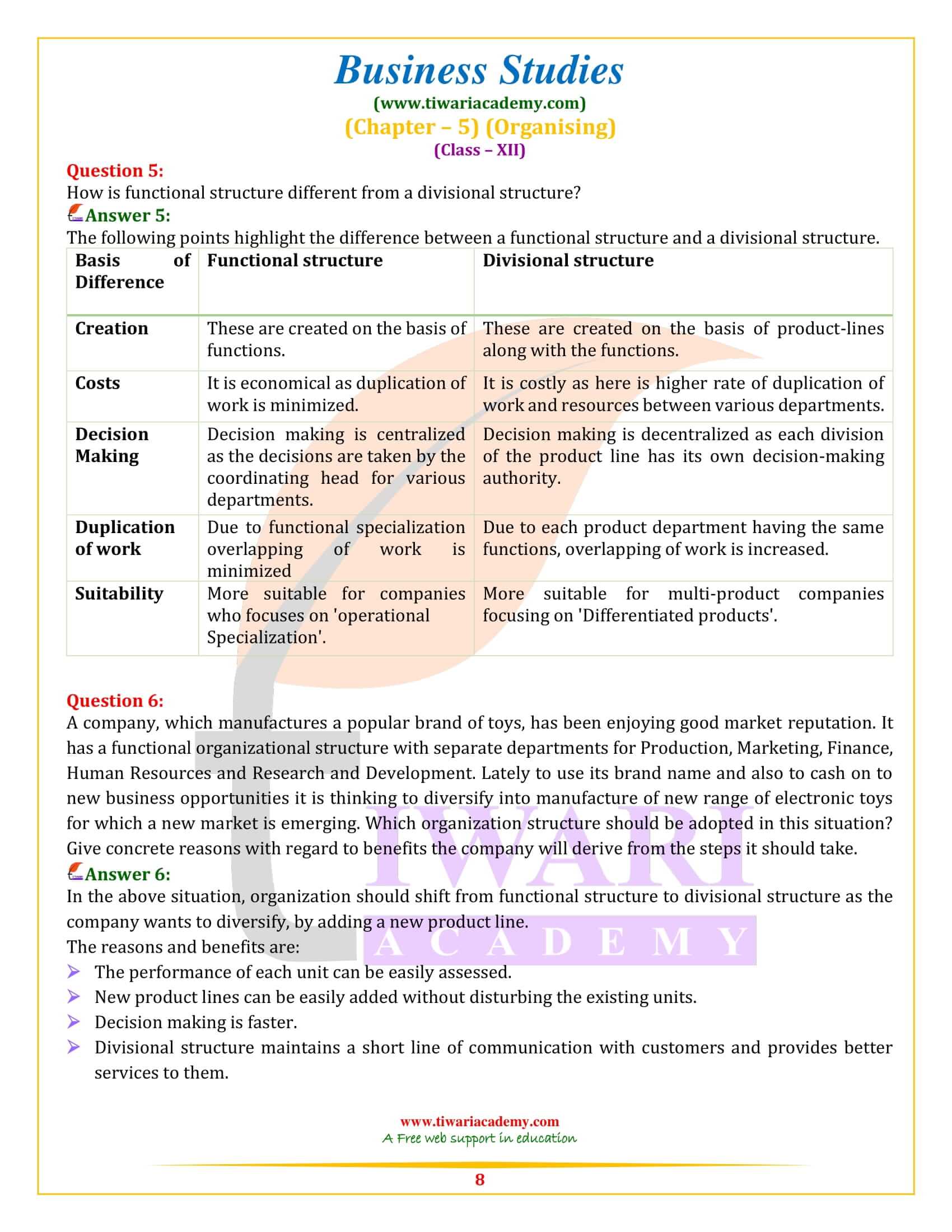
State any two circumstances under which the functional structure will prove to be an appropriate choice.
The two circumstances under which the functional structure will be an appropriate choice are:
1. Size of the organizationis large.
2. Operations require a high degree of specialization.
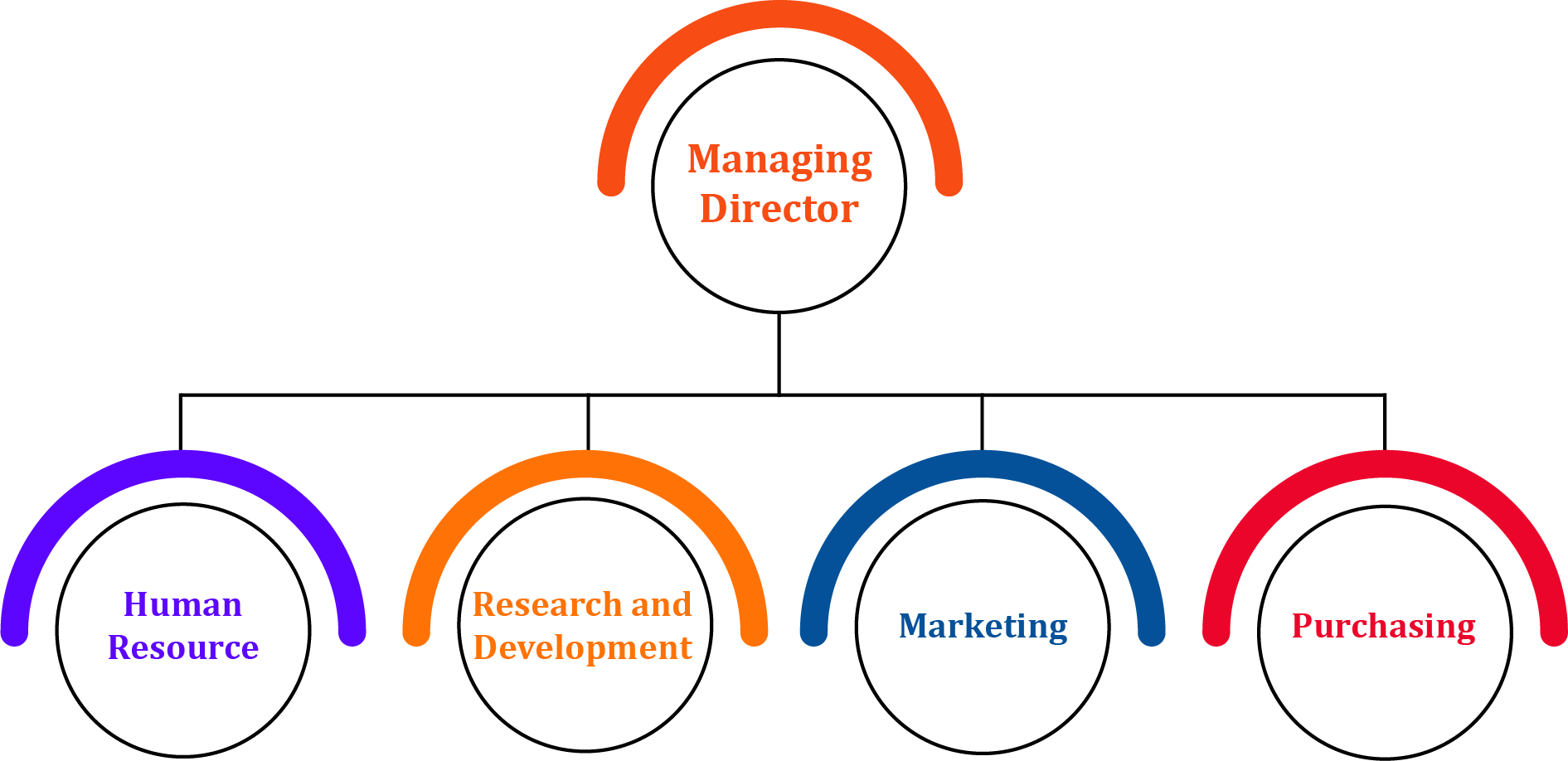
Draw a diagram depicting a functional structure.
Company has its registered office in Delhi, manufacturing unit at Gurgaon and marketing and sales department at Faridabad. The company manufactures the consumer products. Which type of organizational structure should it adopt to achieve its target?
They should adapt the Functional organization structure to achieve their target.
Short Answer Type Questions
What are the steps in the process of organizing?
The following are the steps involved in a successful process of organizing:
- Identification and division of work: The work that has been to be done in accordance with previously determined plans. The work is divided into manageable activities so that duplication can be avoided and the burden of work can be shared among the employees.
- Departmentalization: Once work has been divided into small and manageable activities then those activities which are similar in nature are grouped together. Such process of creating departments is called departmentalization. Departments can be created using several criteria as a basis.
- Assignment of duties: Jobs are then allocated to the members of each department in accordance with their skills and competencies. Proper match is made between the nature of a job and the ability of an individual.
- Establishing reporting relationships: Each individual should know who he has to take orders from and to whom he is accountable. It helps in coordination amongst various departments.
Discuss the elements of delegation.
Delegation refers to the transfer of authority and responsibility to the subordinates. The following are the basic elements of delegation.
Authority: It refers to the power given to an individual to command and direct the subordinates. It implies the right to take decisions regarding what is to be done and by whom.
Scalar chain in a formal organization gives rise to authority as it entails the link between various jobs and determines the relation of who is to report to whom. It is a downward flowing channel, i.e. superior commands authority over the subordinates.
The extent of authority at the top level management is the highest and it becomes lesser at the middle level and the lowest at the lower level management. However, the quantum of authority delegated, depends on the rules and regulations of the organization. Assigning authority helps in maintaining obedience and compliance.
Responsibility: Responsibility refers to the adherence and answerability of the subordinate to complete the given task. That is, once a duty has been assigned to a subordinate, it is his responsibility to perform the task properly. A subordinate should be obedient and loyal towards the duty assigned to him. The superior- subordinate relationship gives rise to a sense of responsibility.
As against authority, responsibility flows upward i.e. the subordinate is responsible to his superior. However, care should be taken that while assigning responsibility to a subordinate, he must also be given a certain degree of authority. On the other hand, an individual who is given authority must also have some responsibility. This is because authority without responsibility may lead to the injudicious use of power. On the other hand, responsibility without authority may lead to inefficiency.
Accountability: Accountability implies the answerability of the superior for the final outcome of the work he assigned. Though the superior delegates the work to his subordinate but he still will be responsible for the final outcome. For this the superior, through regular feedbacks and supervision ensures that the subordinate performs the tasks properly and satisfactorily. The concept of being accountable arises out of responsibility itself. We may say that while responsibility is assumed, accountability is imposed.
How does informal organization support the formal organization?
Informal organization supports formal organizations in many ways; some of them are as follows:
- Quick feedback: Prescribed lines of communication are not followed. Thus, the informal organization leads to faster spread of information as well as quick feedback.
- Social needs: It helps to fulfill social needs of the members. This enhances their job satisfaction, since it gives them a sense of belongingness in the organization.
- Flexibility: In formal organization, rules and policies are fixed, thus it is rigid in nature. On the other hand, in informal organizations, no such rules are there, thus it leads to flexibility.
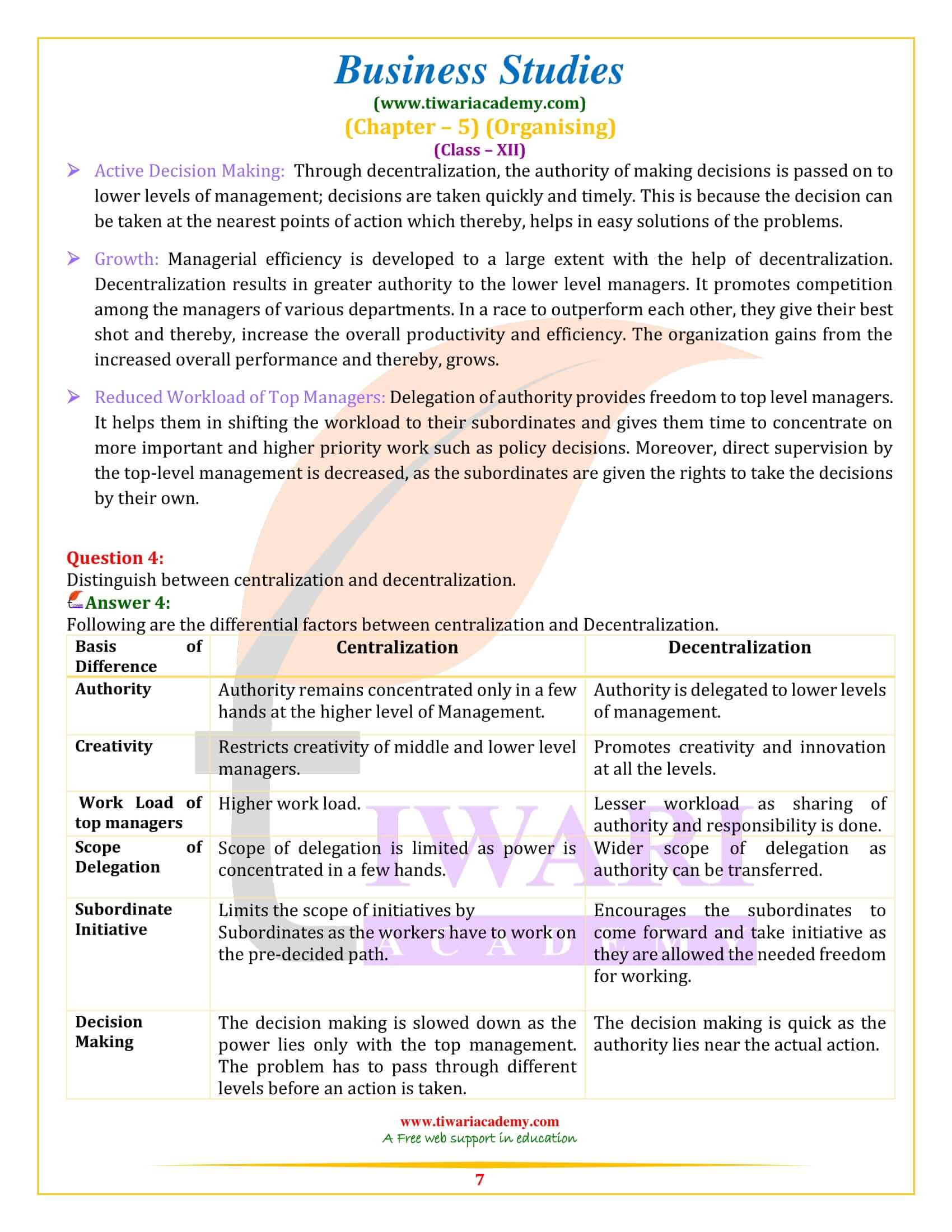
Can a large sized organization be totally centralized of decentralized? Give your opinion.
No, a large sized organisation cannot be totally centralized or decentralized because every organization must have a blend of centralization and decentralization. While complete centralization means concentration of authority in a few hands and complete decentralization means greater autonomy to the lower levels of management. Therefore, an organisation cannot be completely centralized or decentralized. As an organisation grows, there is a tendency to move towards decentralization. At the same time, decisions need to be centralized in priority and key result areas.
Decentralization is extending delegation to the lowest level. Comment.
Decentralization is extending delegation to the lowest level. Decentralization explains the manner, in which decision-making responsibilities are divided among hierarchical levels. Decentralization refers to delegation of authority throughout all the levels of the organisation.
Decision-making authority is shared with lowest levels and is consequently placed nearest to the point of action.
In other words, decision-making authority is pushed down the chain of command. Delegation is the process and decentralization is the end result.
For example, if the director gives the responsibility to the production head to complete the target of 32000 units and authorizes him to hire the workers, the production head further shares his responsibility with the manager to select the workers. And the manager shares his responsibility with supervisors, who are dealing with workers, authorizes them to select workers. Here, the responsibility is distributed at every level. That’s why we say systematic delegation leads to decentralization.
Neha runs a factory wherein she manufactures shoes. The business has been doing well and she intends to expand by diversifying into leather bags as well as western formal wear thereby making her company a complete provider of corporate wear. This will enable her to market her business unit as the one stop for working women. Which type of structure would you recommend for her expanded organization and why?
Divisional structure is recommended for Neha’s expanded organisation. Because it provides equal importance to all its products and other benefits are:
1. It facilitates expansion and growth as new divisions can be added without interrupting the existing operation.
2. It enables her to determine the profit margin of each product line and help her to plan accordingly.
The production manager asked the foreman to achieve a target production of 200 units per day, but he doesn’t give him the authority to requisition tools and materials from the stores department. Can the production manager blame the foreman if he is not able to achieve the desired target? Give reasons.
No, the production manager cannot blame the foreman, if he is not able to achieve the desired target, as the authority delegated to a subordinate should be equal to his responsibility. authority and responsibility of a subordinate should go hand in hand.
This principle suggests that if a subordinate is given the responsibility to perform a particular task in a proper manner, he should be given adequate authority to perform the task. Similarly, if a subordinate is given authority to do a particular task, he should be equally held responsible for doing the task in the proper manner.
In the above case, the production manager has not given authority to the foreman for the requisition of tools and materials from the stores department. Therefore foreman cannot be held responsible for not achieving the desired result. But, the directors can blame the production manager for not achieving the target.
Long Answer Type Questions
Why delegation is considered essential for effective organizing?
Delegation implies transfer of authority, from a superior to his subordinate. It is an essential concept for effective organization as it lowers the burden on the manager and thereby, facilitates the manager to focus on activities that command high priority. Also, the managers can extend his area of operations once he delegates the work to subordinates. In addition to this, it provides the subordinates with more opportunities for growth. It helps in efficient completion of tasks as the subordinates can now show their skills and exercise initiative. The following points highlight the importance of delegation in effective organizing.
Efficient Management: By empowering the employees, the managers are able to functionmore efficiently as they get more time to concentrate on important matters. Freedom from doing routine work provides them with opportunities to excel in new areas.
Employee Development: By delegating the work, managers empower his subordinates by providing them opportunities to apply their skills. Herein, the subordinates get a chance to prove his abilities, gain experience and develop his career. Thus, delegation in a way helps in preparing future managers.
Motivation: Along with improving the managerial and employee efficiency, delegation provides the employees with the psychological benefits. It acts as a motivational guide for the workers. It imparts a feeling of mutual trust and commitment between the superior and subordinate. With responsibility employees gain confidence and they get encouraged to give their best to the organization.
Facilitation of Growth: Delegation helps in the expansion of an organization by providing a ready workforce to take up leading positions in new ventures. Trained and experienced employees are able to play significant roles in the launch of new projects by replicating the work culture they have absorbed from existing units, in the newly set up branches.
Hierarchical Structure: Delegation forms the basis of the hierarchical structure of an organization. It decides the superior-subordinate chain and determines who has to report to whom. It clearly states down the reporting relationships which helps in smooth working of the organization.
Coordination: Delegation promotes coordination of work. It reduces overlapping of work by defining the reporting relationships. All the elements of delegation such as authority, responsibility and accountability helps in providing a clear working relationship, thereby, increasing efficiency.
What is divisional structure? Discuss its advantages and limitations.
Divisional structure refers to an arrangement of activities which are separated on the basis of products. There are different units and divisions which deal with varied products. Each division has its own divisional manager who supervises the whole unit and has the authority for it. Organizations that are large in size and deal in a diversified range of products or categories opt for this type of structure. Under each head of divisional structure, a functional structure develops itself, i.e. each divisional unit is further divided on the basis of its functions.
For example, a company dealing with varied products has divisional heads such as clothing, shoes and electronics. Now these units will have further functional departments such as, under shoes, there will be resource inputs, advertising, production, sales, etc. Similarly, under clothing also there will be departments of resources, advertising, production and sales. The same will be under the electronics division. Here, each division has to take care about its profit and loss and is responsible for its own work.
Following are a few prominent advantages of a divisional structure.
1. Product specialization helps in the development of varied skills in a divisional head and this prepares him for higher positions. This is because he gains experience in all functions related to a particular product.
2. Divisional heads are accountable for profits, as revenues and costs related to different departments can be easily identified and assigned to them. This provides a proper basis for performance measurement. It also helps in fixation of responsibility in cases of poor performance of the division and appropriate remedial action can be taken.
3. It promotes flexibility and initiative because each division functions as an autonomous unit which leads to faster decision making.
4. It facilitates expansion and growth as new divisions can be added without interrupting the existing operations by merely adding another divisional head and staff for the new product line.
A divisional structure has certain disadvantages as well. The following are some of the disadvantages of a divisional structure.
5. Conflict may arise among different divisions with reference to allocation of funds and further a
Particular division may seek to maximize its profits at the cost of other divisions.
6. It may lead to increase in costs since there may be a duplication of activities across products. Providing each division with separate set of similar functions increases expenditure.
7. It provides managers with the authority to supervise all activities related to a particular division. In course of time, such a manager may gain power and, in a bid, to assert his independence may ignore organizational interests.
FAQs
Does the term organizing has a special meaning while studying chapter 5 of 12 B. St.?
Yes, Here the term means establishing the superior subordinate relationships and creating a chain of superiors so that everybody knows whom to receive orders from and whom to give orders to.
Into how many sub topics or segments can chapter 5 of 12 B. St. be divided?
Mainly three:
1 Introduction, Steps and importance of organizing.
2. Different types of organizational structures.
3. Delegation and decentralizations.
What are the main questions from 12th Business Studies Chapter 5 in Exams?
This topic is examiner’s favorite topic for case studies. Case study can be asked regarding organization structure. They can also ask the concept of accountability – so, the elements of delegations must be thoroughly known.
What is the peculiar feature of chapter 5 Class 12 Business Studies?
Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 5 has many questions of distinguish types. For example – distinguish between delegation and decentralization, functional structure and divisional structure etc.