NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases in Hindi and English Medium to Study Online without downloading for academic session 2025-26 for all boards using NCERT Books. NCERT Books based on latest Curriculum 2025-26 is also available to download. Ask Your Questions or Reply to your friends by answering their questions via discussion forum.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 7
Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases Solutions
| Class: 12 | Science |
| Subject: | Biology |
| Chapter 7: | Human Health and Diseases |
| Content Mode: | Images, PDF and Videos |
| Academic Session: | 2025-26 |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Solutions in English
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases are given here to free download. NCERT Solutions 2025-26 are updated according to NCERT Books following latest CBSE Syllabus 2025-26. Join the discussion forum to ask your doubts and reply to questions asked by other users.
Extra Questions Class 12 Biology Chapter 7
What is meant by Vaccination?
A preparation of weakened or attenuated pathogen is introduced in the human body. Antibodies are formed against the pathogen. B and T memory cells are generated that recognises the pathogen quickly on subsequent exposure a kills it with quick and massive production of antibodies.
Define the type of types of Immunities?
Two types of Immunities.
Innate immunity: inherited by the organism from the parents and present at the time of birth.
Acquired Immunity: Acquired by a person after birth by vaccination or contacting the disease.
Important Terms related to Chapter 7
1. Addiction: A psychological attachment to effects like euphoria and temporary well-being associated with drugs and alcohol.
2. Interferon: The glycoproteins produced by our body cells in response to a viral infection.
3. Incubation Period: The time period between infection and tire appearance of symptoms.
4. Metastasis: The property in which the cancer cells spread to different sites through blood and develop secondary tumours.
5. Oncogenes: Viral genome which causes cancer/Cancer causing genes.
6. Retrovirus: A virus having RNA as genetic material and forms DNA by reverse transcription and then replicate e.g., Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).
7. Withdrawal Syndrome: If a drug dependent person stop taking drugs then his body stop functioning normally and he feels severe physical and psychological disturbance called withdrawal syndrome.
8. Contact Inhibition: It is a property of normal cells in which the cells stop dividing when comes in contact with its surrounding cells.
Infectious Diseases
Viral Diseases e.g., polio, common cold, measles, rabies
Bacterial diseases e.g., Typhoid, Pneumonia, Diptheria, Tetanus.
Fungal diseases e.g., Ring worm & Scabies
Helminthic diseases e.g. Ascariasis, Filariasis, Taeniasis
Protozoan diseases e.g. Malaria, Amoebiasis.
Prevention of Dengue and Chikungunya: Protection against mosquitoes by wearing long sleeves and full pants. Window and doors should have wire gauze screens, use mosquito repellents and there should be no stagnant water nearby.
Allergens
Substances to which immune system shows exaggerated response. e.g. mites in dust, pollens, animal dander, perfume, wool, nail polish and drugs.
Lymphoid Organs: Organs where lymphocytes are formed proliferate and mature are called lymphoid organs.
Bone Marrow: It is a primary lymphoid organs. Lymphocytes maturing here are called B-lymphocytes.
Thymus: Lymphocyte which mature in thymus are called T-lymphocyte.
In which way has the study of biology helped us to control infectious diseases?
Various advancements that have occurred in the field of biology have helped us gain a better understanding to fight against various infectious diseases. Biology has helped us study the life cycle of various parasites, pathogens, and vectors along with the modes of transmission of various diseases and the measures for controlling them. Vaccination programmes against several infectious diseases such as small pox, chicken pox, tuberculosis, etc. have helped eradicate these diseases. Biotechnology has helped in the preparation of newer and safer drugs and vaccines. Antibiotics have also played an important role in treating infectious diseases.
Important Questions on 12th Biology Chapter 7
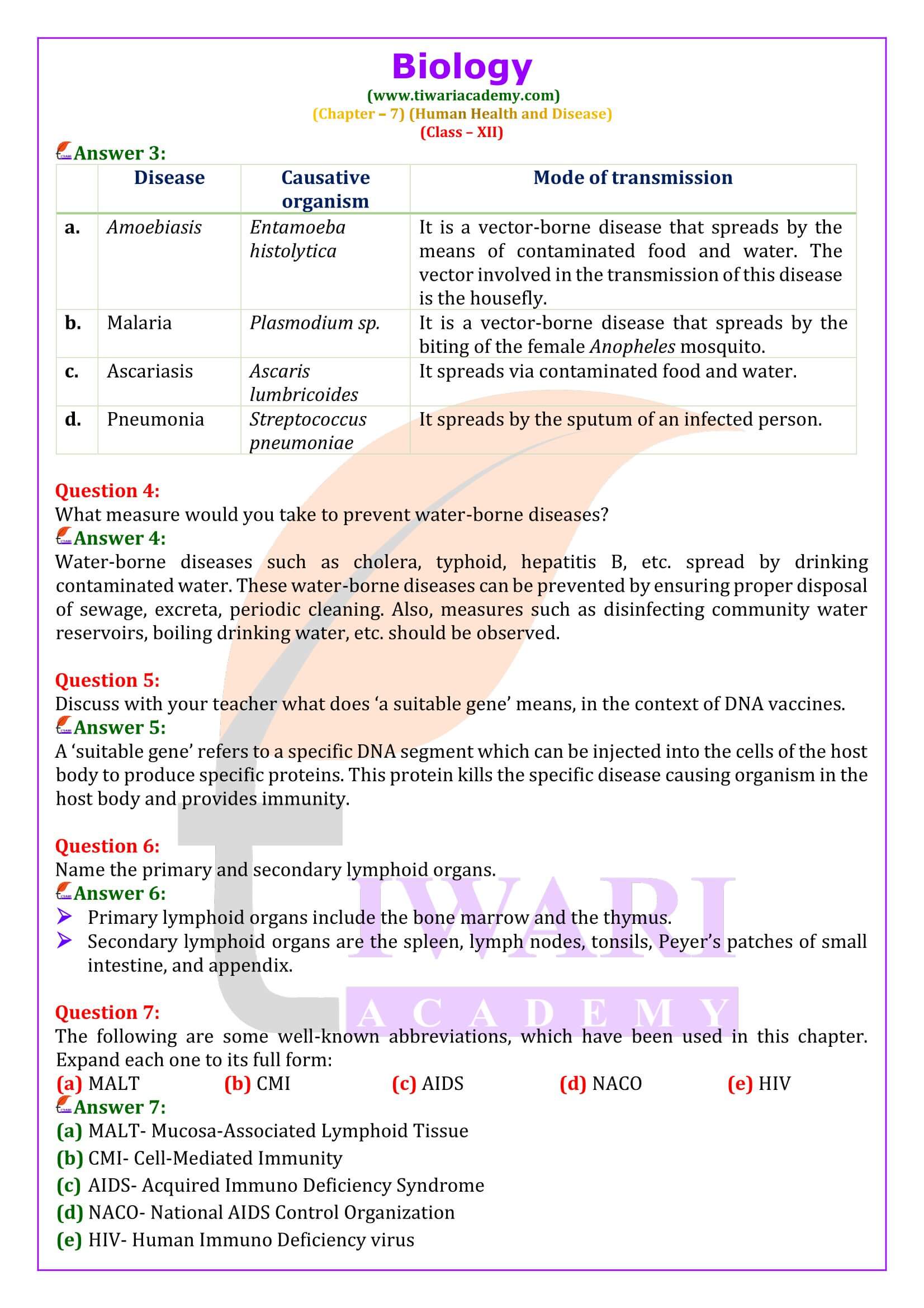
What measure would you take to prevent water-borne diseases?
Water-borne diseases such as cholera, typhoid, hepatitis B, etc. spread by drinking contaminated water. These water-borne diseases can be prevented by ensuring proper disposal of sewage, excreta, periodic cleaning. Also, measures such as disinfecting community water reservoirs, boiling drinking water, etc. should be observed.
Name the primary and secondary lymphoid organs.
Primary lymphoid organs include the bone marrow and the thymus. Secondary lymphoid organs are the spleen, lymph nodes, tonsils, Peyer’s patches of small intestine, and appendix.
Discuss with your teacher what does ‘a suitable gene’ means, in the context of DNA vaccines.
A ‘suitable gene’ refers to a specific DNA segment which can be injected into the cells of the host body to produce specific proteins. This protein kills the specific disease causing organism in the host body and provides immunity.
What are the various routes by which transmission of human immunodeficiency virus takes place?
AIDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome) is caused by the Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). It has the following modes of transmission: Unprotected sexual contact with an infected person. Transfusion of blood from a healthy to an infected person. Sharing infected needles and syringes. From an infected mother to a child through the placenta.
What is the mechanism by which the AIDS virus causes deficiency of immune system of the infected person?
AIDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome) is caused by the Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) via sexual or blood-blood contact. After entering the human body, the HIV virus attacks and enters the macrophages. Inside the macrophages, the RNA of the virus replicates with the help of enzyme reverse transcriptase and gives rise to viral DNA. Then, this viral DNA incorporates into the host DNA and directs the synthesis of virus particles. At the same time, HIV enters helper T- lymphocytes. It replicates and produces viral progeny there. These newly formed progeny viruses get released into the blood, attacking other healthy helper Tlymphocytes in the body. As a result, the number of T-lymphocytes in the body of an infected person decreases progressively, thereby decreasing the immunity of a person.
Explain what is meant by metastasis.
The property of metastasis is exhibited by malignant tumors. It is the pathological process of spreading cancerous cells to the different parts of the body. These cells divide uncontrollably, forming a mass of cells called tumor. From the tumor, some cells get sloughed off and enter into the blood stream. From the blood stream, these cells reach distant parts of the body and therefore, initiate the formation of new tumors by dividing actively.
Why is that once a person starts taking alcohol or drugs, it is difficult to get rid of this habit?
Drug and alcohol consumption has an inherent addictive nature associated with euphoria and a temporary feeling of well-being. Repeated intake of drugs increases the tolerance level of the body’s receptors, leading to more consumption of drugs.