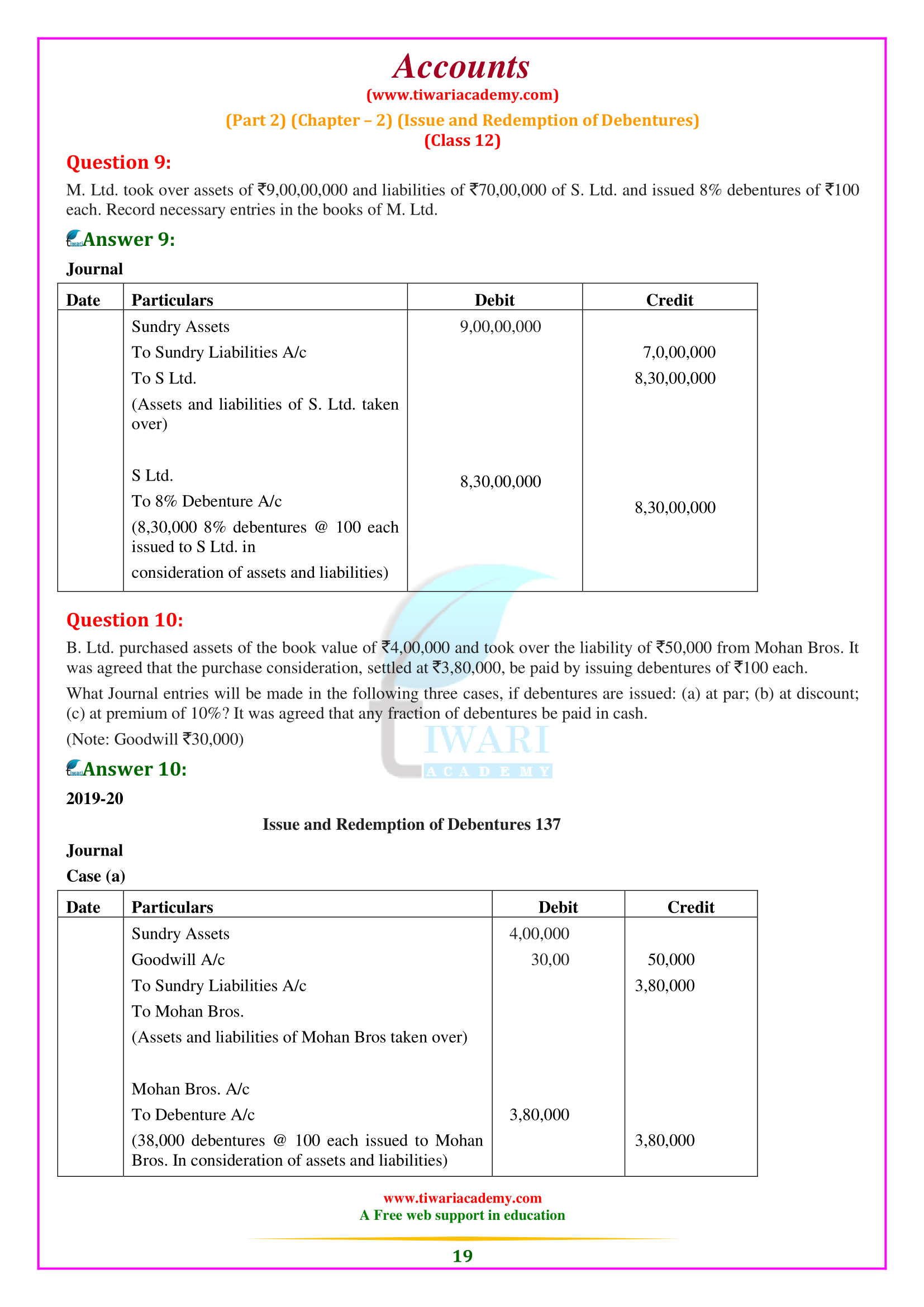
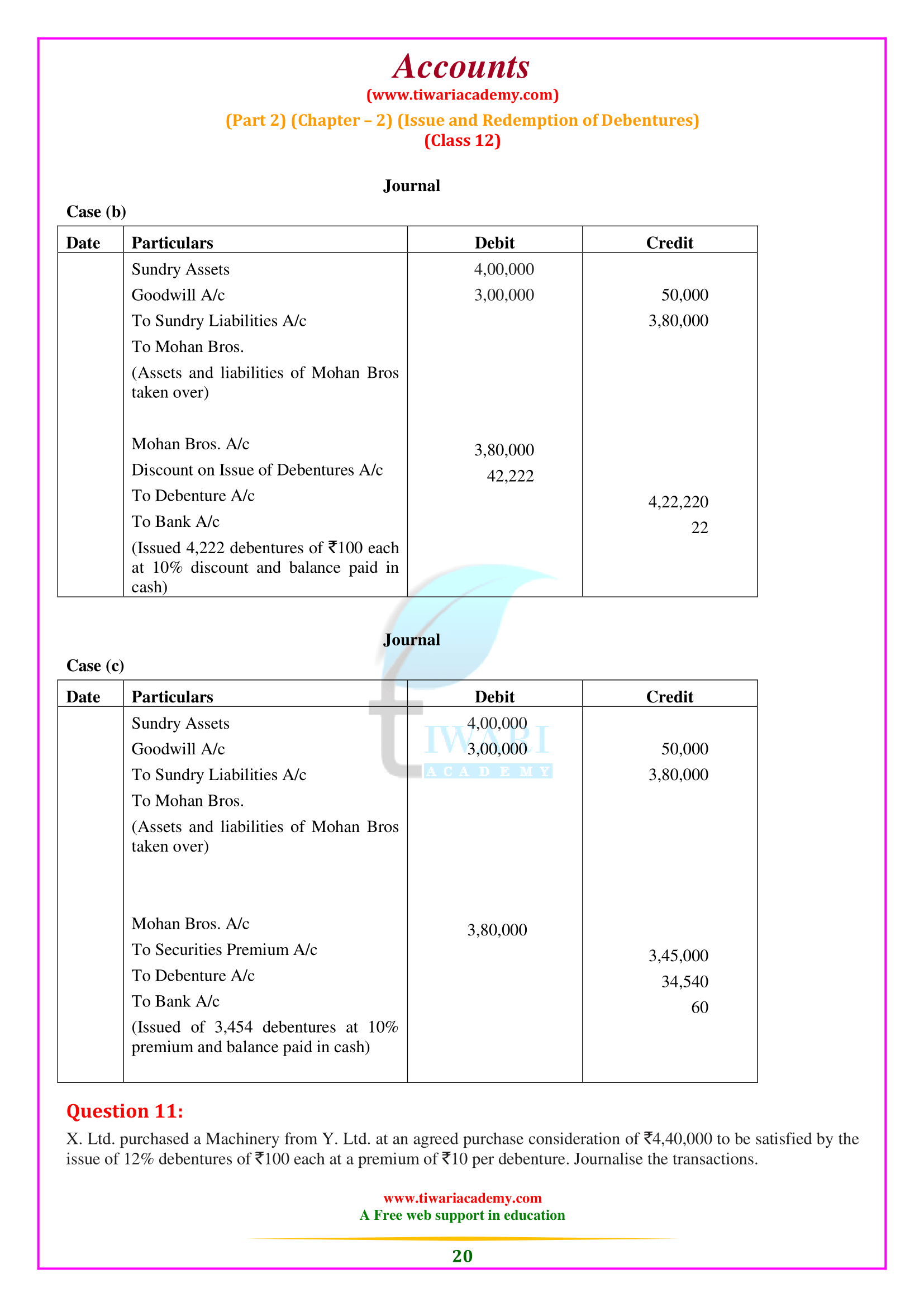
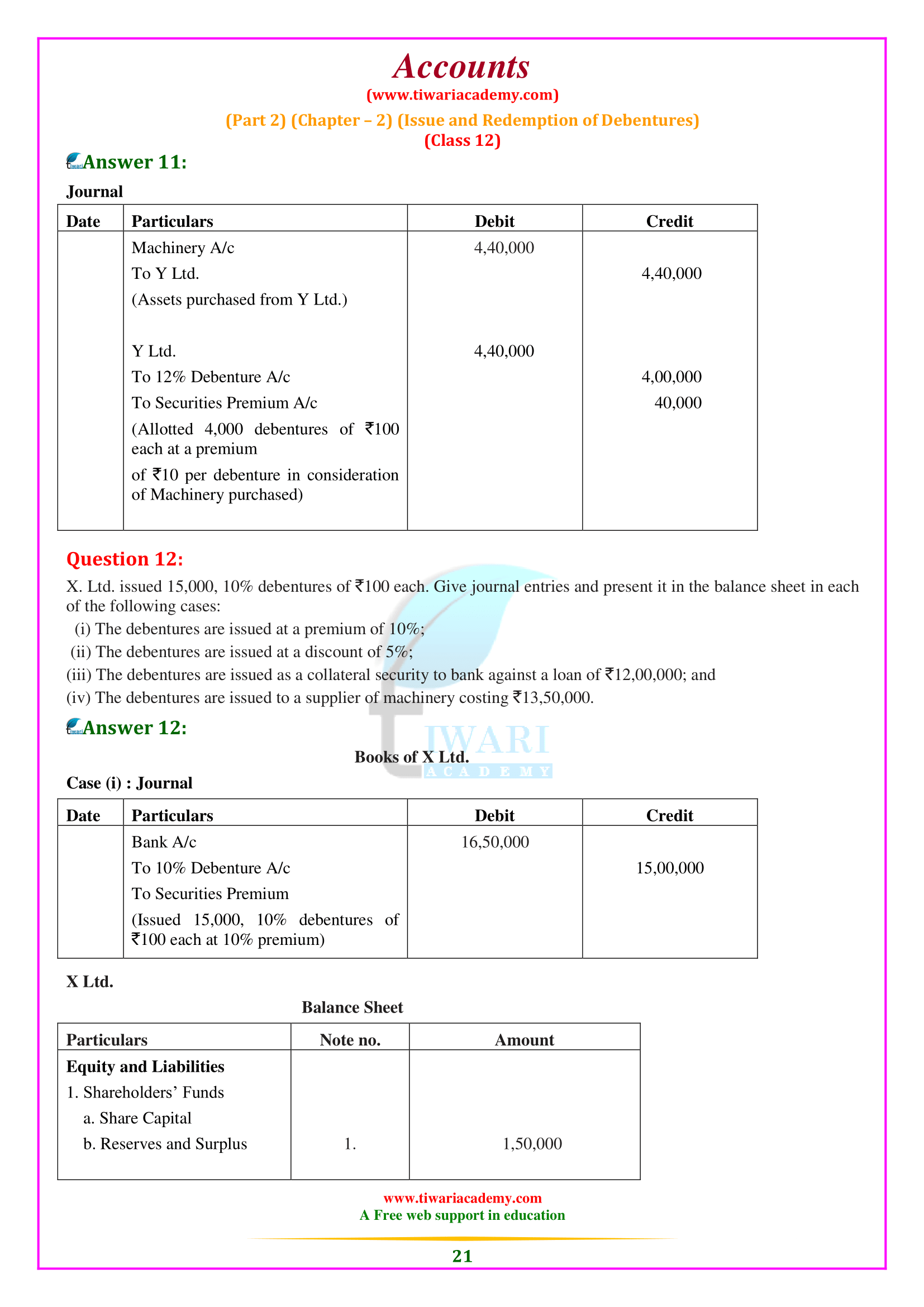
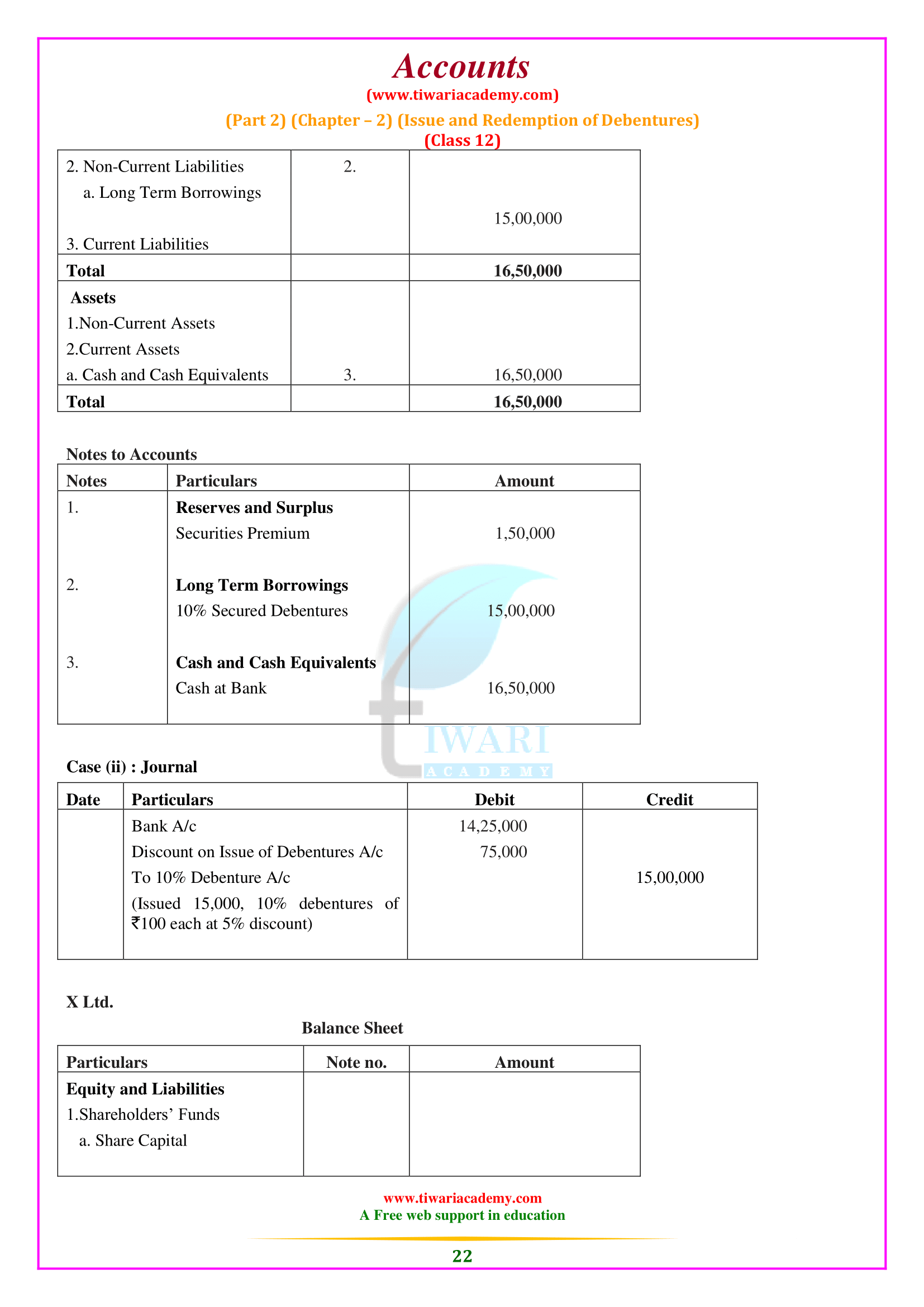
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Accountancy Part 2 Chapter 2 Issue and Redemption of Debentures. Clear your concepts about issue of debentures as well as redemption of debentures in almost all the conditions. Important questions and notes will help the students exploring more examples based on debentures and its redemption. Practice here with NCERT Question Answers and notes to prepare chapter 2 of part 2 Accounts Class 12.
Class 12 Accountancy Part 2 Chapter 2 Question Answers
Class 12 Accountancy Part 2 Chapter 2 Issue and Redemption of Debentures.
| Class: 12 | Accountancy (Part 2) |
| Chapter: 2 | Issue and Redemption of Debentures. |
| Contents: | NCERT Solutions and Notes |
What is Debenture?
The word “debenture” is derived from the Latin word “debere” which means to borrow. A debenture is a written instrument that recognizes a debt under the common seal of the company. It consists of a contract for repayment of principal after a specified period or at the company’s option, or on half-yearly or yearly dates initially payable for repayment of interest at a fixed rate. According to Section 2 (30) of the Corporation Law, 2013, “obligations” include the inventory of Observation, bonds, and security of any other company, whether or not it imposes any charges on the company’s assets.
What is a Bond?
Bond is also a debt recognition tool. Traditionally, the government issued bonds, but today, quasi-governmental and non-governmental organizations also issue bonds. The terms “obligations” and “bonds” are now used interchangeably.
- Ownership: A “share” represents a company’s ownership, whereas an obligation is just the acceptance of debt. A share is a share of equity, while an obligation is a share of borrowed capital.
- Return: The return on a stock is known as a dividend, while the return on a bond is called interest. The return rate on shares can vary from year to year, depending on the company’s earnings, but the interest rate on the bond is predetermined. The dividend payment is an appropriation of profits, while interest payments are a charge on profits, and it should be paid even if there is no profit.
- Amortization: Generally, the amount of shares is not withdrawn during the life of the company, whereas, in general, obligations are issued for a specified period and are repayable at the end of that period.
- Voting Rights: Shareholders enjoy voting rights, while bondholders generally do not enjoy any voting rights.
- Security: Shares are not guaranteed for any fee, while debentures are usually guaranteed, and there is a fixed or temporary charge on the company’s assets.
- Convertibility: Shares cannot be converted into bonds, while bonds can be converted into shares if the terms of issuance are so established, and in that case, they are known as convertible bonds.
Types of Debenture as per Security point of view
- (a) Secured Debentures: Secured Debentures refer to those obligations in which a charge is made on the company’s assets for payment in case of default. Charges can be fixed or floating. A fixed charge is made on a specific asset, while a floating charge is levied on its general assets. A fixed charge is made against assets placed by a company for use in operations that are not intended for sale, while the floating charge includes all assets assigned to secured creditors.
- (b) Unsecured Debentures: Unsecured Debentures do not have any specific charge on the company’s assets. However, a floating charge can be made on these obligations by default. Generally, these types of bonds are not issued.
Types of Debenture as per Tenure point of view
- Reimbursement Debentures: Reimbursement Debentures are paid at the end of a specific period, either in a lump sum or in installments during the company’s life. Bonds can be exchanged equally or with a premium.
- Irredeemable Debentures: Irredeemable Debentures are also known as permanent Debentures as the company does not undertake to pay the borrowed money by issuing such Debentures. These debentures are returned at the end of the liquidation or extended period of a business.
Types of Debenture as per Convertibility point of view
- Convertible Debentures: Convertible Debentures in capital shares or any other security, whether at the option of the company or in bondholders, are called convertible Debentures. These Debentures are fully convertible or partially convertible.
- Non-convertible Debentures: Debentures that cannot be converted into shares or any other security are called non-convertible Debentures. Most corporate Debentures fall into this category.
Types of Debenture as per Coupon Rate point of view
- (A) Debentures with a specific coupon rate: These Debentures are issued with a specific interest rate, called the coupon rate. The specified rate can be constant or temporary. The floating interest rate is usually labeled with the bank rate.
- (B) Zero-coupon rate Debentures: These Debentures do not have a specific interest rate. To compensate investors, such obligations are issued at a substantial discount. The difference between the nominal value with the issue price is counted as the amount of interest related to the obligations period.