NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Accountancy Part 2 Chapter 1 Accounting for Share Capital. Get here exercises question answers solved with suitable explanation. Questions are well described based on Textbooks of NCERT according to current CBSE Curriculum 2025-26. Extra Important questions are also given for better practice of this chapter. These questions also provide a complete revision of the chapter 1 of Class 12 Accounts Part 2.
Class 12 Accountancy Part 2 Chapter 1 Question Answers
| Class: 12 | Accountancy (Part 2) |
| Chapter: 1 | Accounting for Share Capital. |
| Contents: | NCERT Solutions and Notes |
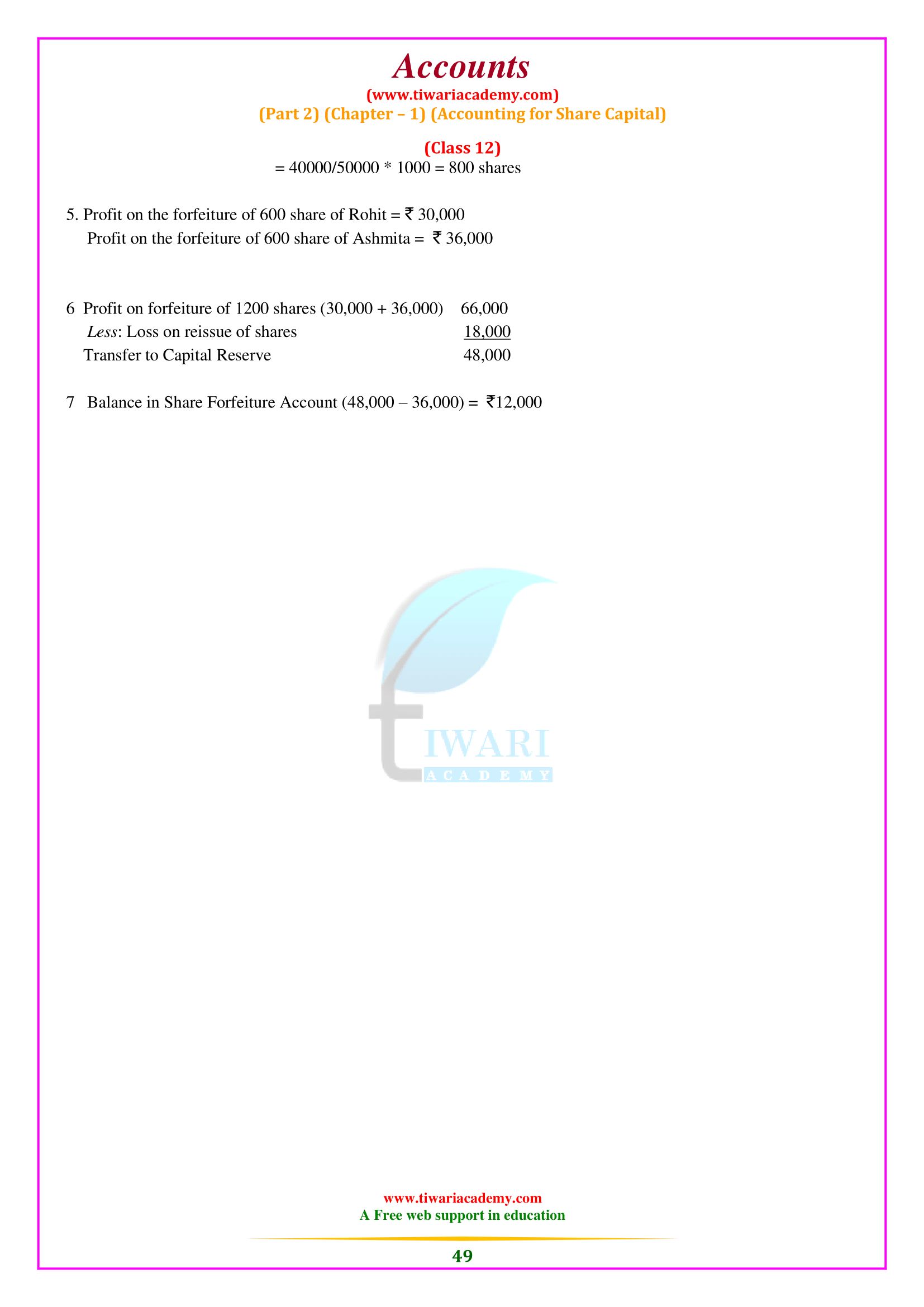
Features of a Company
A business can be seen as an association of people who contribute money or value of money to a standard list and use it for a common purpose. It is a legal person with a corporate legal entity other than its members (shareholders) and a common seal used for its signature. Therefore, it has specific characteristics that distinguish it from other forms of organization.
Main Points of Features of a Company
- Legal person: A company is formed under the provisions of law applicable at all times. Generally, in India, companies except banking and insurance companies are created and registered following the Companies Act, for which a separate law is provided.
- Separate legal entity: As we know that a company has a separate legal entity that is separate and distinct from its members. It can host and treat any property. You can enter into contracts and even open a bank account in your name.
- Limited Liability: As we know that the liability of the company’s members is limited to the unpaid amount of shares that they hold. When the companies limited by guarantee, their members’ liability is limited to the scope of the guarantee given by them for the dissolution of the company.
- Permanent Succession: The company, as a legal entity created by law, exists regardless of changes in its membership. A company can only be liquidated by law. The death, insolvency, or insolvency of any member of the company does not affect the company’s existence in any way. Members can come and go, but business continues.
Main Features of a Company
- General seal: The company, being a legal entity, cannot sign its name. Therefore, each company should have its seal, which serves as the official company’s signature. Any document which does not bear the common seal of the company is not binding on the company.
- Transferability of shares: The shares of the corporation are freely transferable. The transfer of shares does not require the company’s permission or the consent of any member of the company. But the company’s laws can be written in the manner in which the transfer of shares will take place.
- You can sue or file a lawsuit: A company that is a legal entity can enter into contracts and enforce contractual rights against others. When a breach of contract by the company, you can sue, and a lawsuit can be filed on your behalf.
Kinds of Companies
Companies can be classified according to the responsibility of their members or according to the number of members. Depending on the responsibility of their members, companies can be classified into the following three categories:
- Companies limited by shares: In this case, its members’ liability is limited to the nominal value of the shares they own. If a member gets the full amount of the shares, the company has no liability for the debt. There is no need to give a single salary for your personal property. However, if any liability is involved, it can be applied during the life of the business and liquidation.
- Limited Partnership by Guarantee: In this case, its members’ liability is limited to the amount they agree to contribute to the event of the dissolution of the partnership. Thus, the responsibility of the partners will arise only in the event of their dissolution.
- Unlimited companies: When there is no limit to its members’ liability, the company is called an unlimited company. When the company’s assets are less to pay its debts, its members’ personal property can be used for this purpose. In other words, creditors can claim their dues from their members. These companies are not located in India, even though the Companies Act permits it.