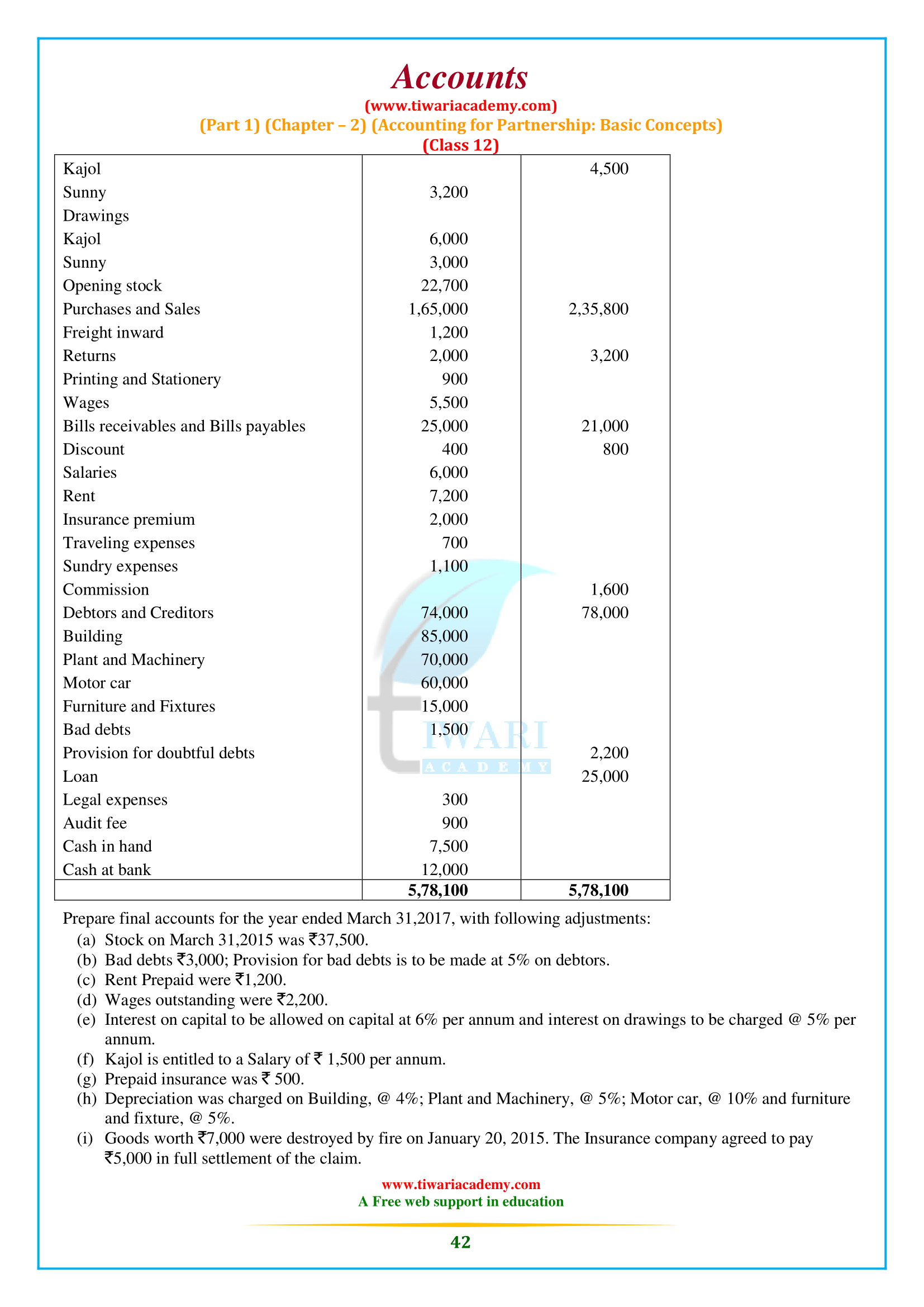
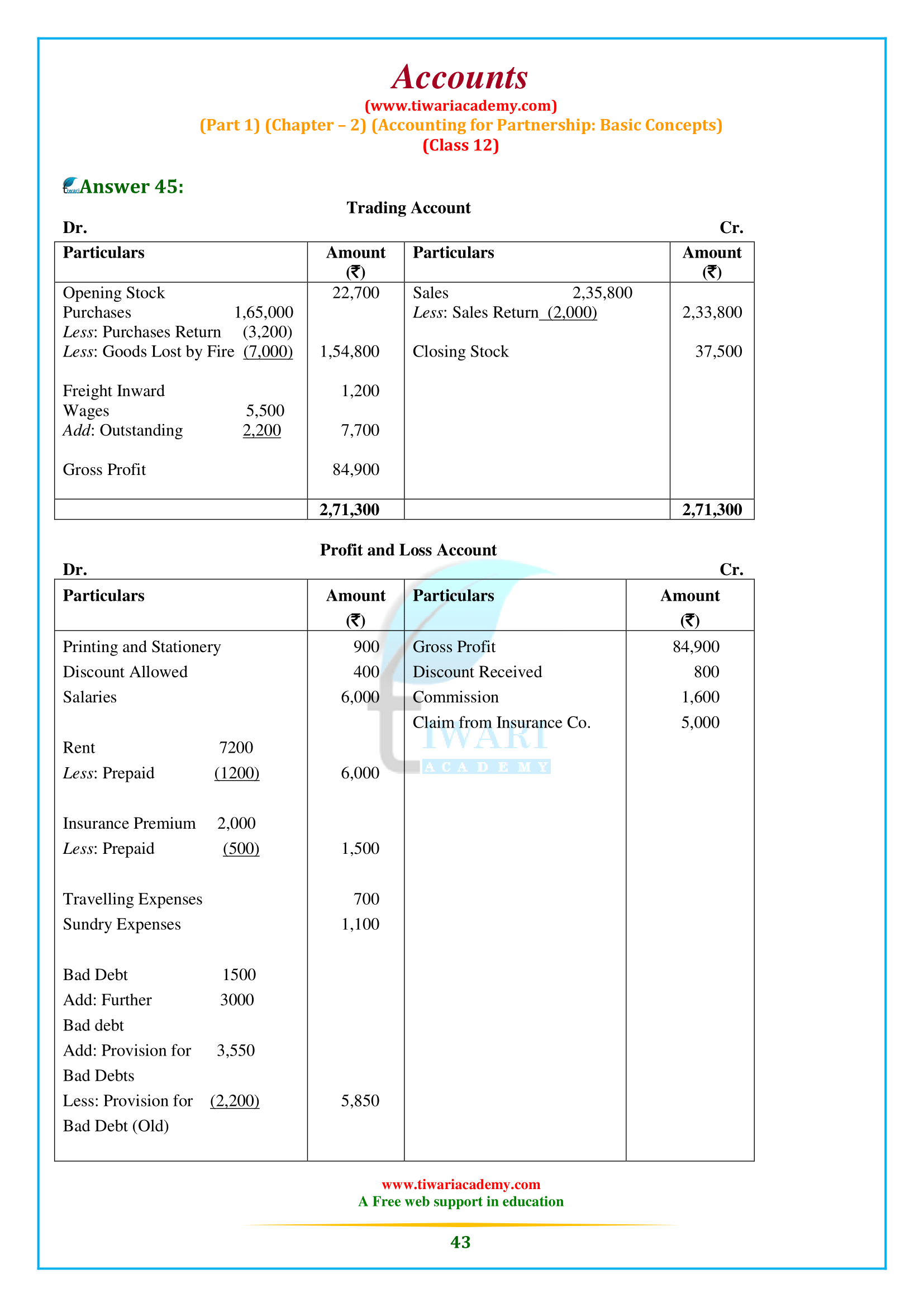
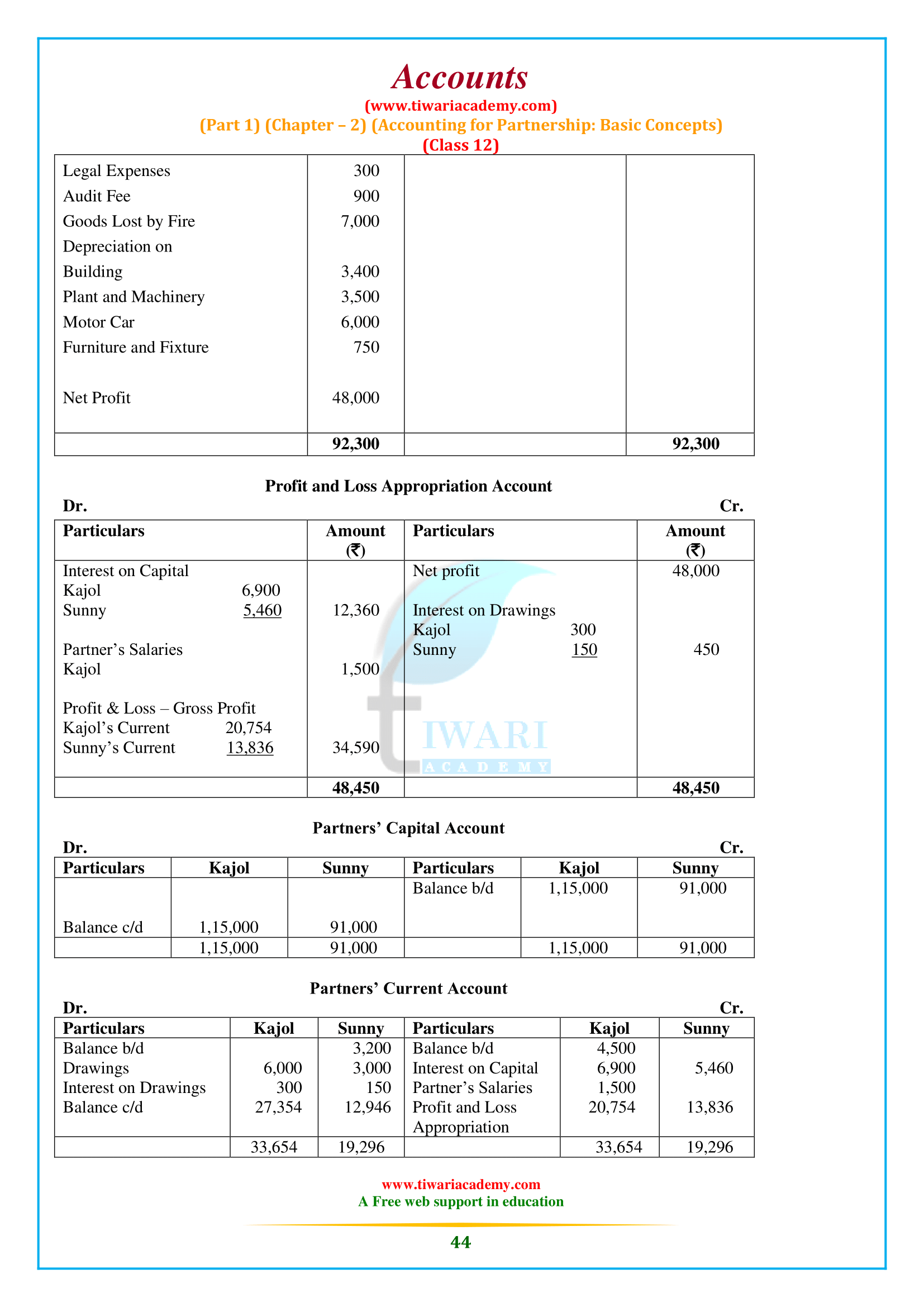
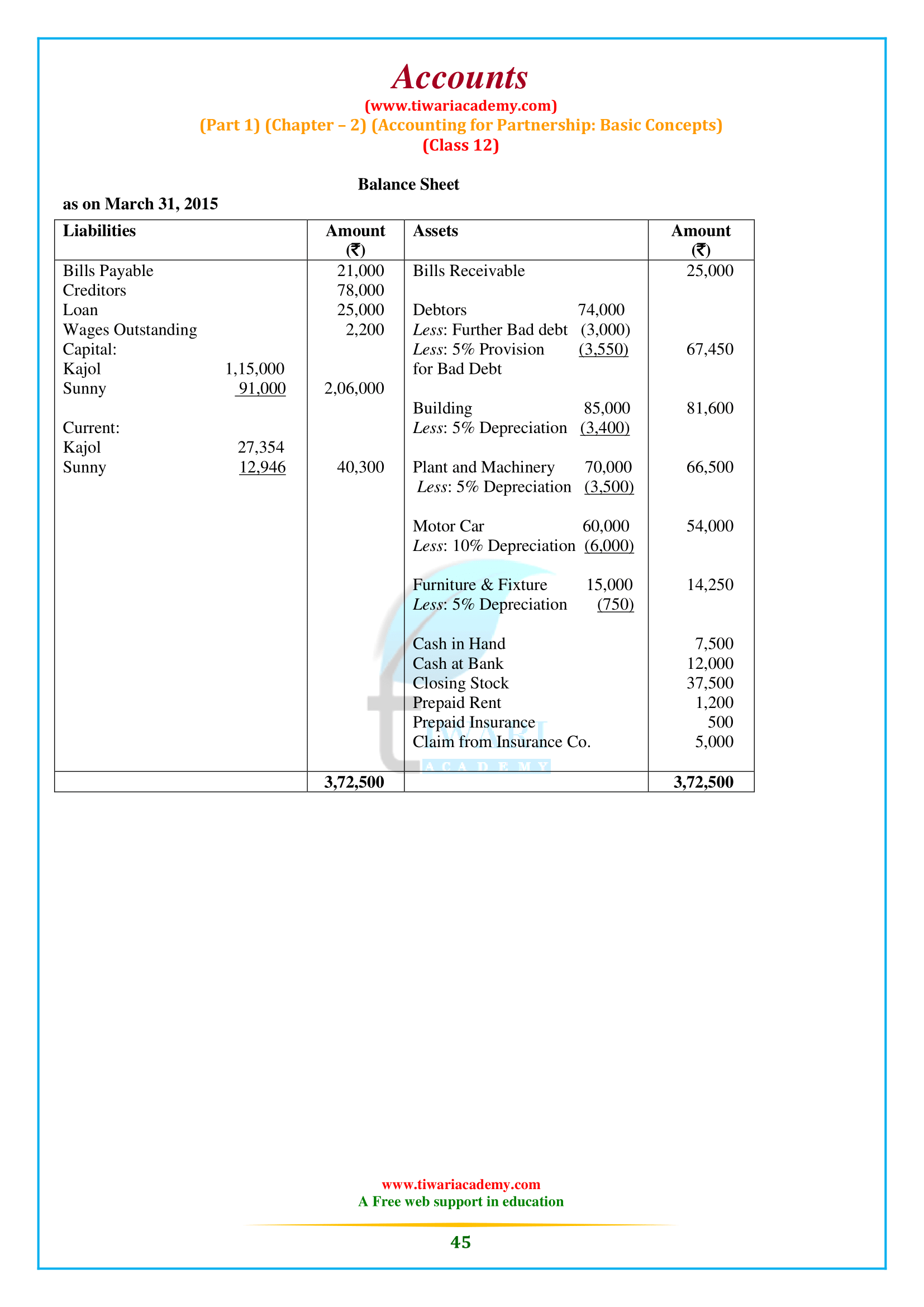
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Accountancy Part 1 Chapter 2 Accounting for Partnership: Basic Concepts. Question answers, short and long answers type questions, numerical type questions including all the questions of NCERT Textbook exercises are given here for the preparation of the exams. Study material related to chapter 2 of class 12 Accounts are also given in PDF file format.
Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 2 Question Answers
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 2 Accounting for Partnership Basic Concepts
| Class: 12 | Accountancy (Part 1) |
| Chapter: 2 | Accounting for Partnership: Basic Concepts |
| Contents: | NCERT Solutions and Notes |
The essential features of partnership
Two or more people
During the development of a partnership, there must be at least two people who come together for the same goal. In other words, the minimum number of partners in a company can be two. However, they have a maximum number limit. Under section 464 of the Companies Act 2013, the Central Government can determine the maximum number of partners in a company, but the number of partners cannot exceed 100. The central government has set the maximum number of partners in a company to be 50 years old.
Agreement
A partnership is the result of an agreement between two or more people to do business and share its profit and loss. The agreement becomes the basis of the relationship between the partners. Such an agreement does not need to be done in writing. A verbal agreement is equally valid. But to avoid controversy, it is preferred that
The partners have a written agreement.
Business
There must be an agreement to conduct some business. Mere co-ownership of a property is not equivalent to a partnership. For example, if Rohit and Mohit jointly purchase a parcel of land, they become co-owners of the property, not partners. Nevertheless, if they are buying and selling land to make a profit, they will be called partners.
Mutuality
A company’s business can act on behalf of all partners or any of them. This statement has two crucial implications. First, each partner has the right to participate in the conduct of its business affairs. Second, there is a mutual agency relationship between all the partners. Each partner doing the business is the principal and agent for all other partners. You can bind other partners with their acts, and you are also bound by the acts of other partners concerning the company’s business. The relationship of the mutual agency is so essential that it can be said that there will be no relationship if the element of mutual agency is absent.
Profit-sharing
Another vital element of a partnership is that there should be an agreement between the partners to share the company’s profits and losses. Although the definition contained in the Association Law describes the partnership as the relationship between those who agree to share a company’s profits, participation in losses is inherent. Thus, profit sharing and 2020–21. Society Accounting: Basics 63 is essential. If some people join hands for some charitable activity, it will not be considered a union.
Liability of partners
Each partner is jointly and severally liable with all other partners and jointly and severally liable before the third party for all the firm’s functions while he is a partner. Not only this, the liability of a partner for the functions of the firm is also unlimited. This implies that your assets can also be used to pay the company’s debt.
Provisions of Partnership Act Relevant for Accounting
The important provisions affecting partnership accounts are as follows:
- Profit-sharing relationship: If the partnership deed does not say anything about the profit-sharing relationship, then its profits and losses should be shared equally by the partners, regardless of their capital contribution to the company.
- Interest on capital: No partner can claim any interest in the amount of capital contributed by him as a law in the company. However, interests may be permitted when the partners expressly agree. Therefore, no interest is paid on the principal if the company deed is silent on the subject.
- Interest on drawing: If there is no mention in the deed, no interest will be charged on the partners’ drawing.
- Interest on loan: If a partner has given a loan to the company for business purposes, he will be entitled to receive interest on the loan amount at 6 percent per annum.
- Remuneration for the firm’s work: No partner is entitled to receive a salary or other remuneration for participating in the operation of the firm’s business unless the Deed of Society has a provision for the same.
Why it is considered desirable to make the partnership agreement in writing Class 12 Accounts Chapter 2?
The Partnership agreement can be either oral or written. The Partnership Act does not require that the agreement must be in writing. But wherever it is in writing, the document, which contains terms of the agreement is called ‘Partnership Deed’. But a written agreement is better than oral agreement and therefore helps in settling disputes between the partners. It has to be duly signed and registered under Partnership Act.
What do you understand by partnership according to 12th Accounts Chapter 2?
When two or more persons join hands to set up a business and share its profits and losses, they are said to be in partnership.
What is meant by a firm in Class 12 Accounts Chapter 2?
Persons who have entered into partnership with one another are individually called “partners” and collectively called “firm”.
What is a partnership deed in 12 Accountancy Chapter 2?
Partnership arise as a result of agreements between partners. The agreement may be oral or written. Partnership law does not require that the agreement be in writing. But wherever it is in writing, the document, which includes the terms of the agreement, is called the “Partnership Deeds”.