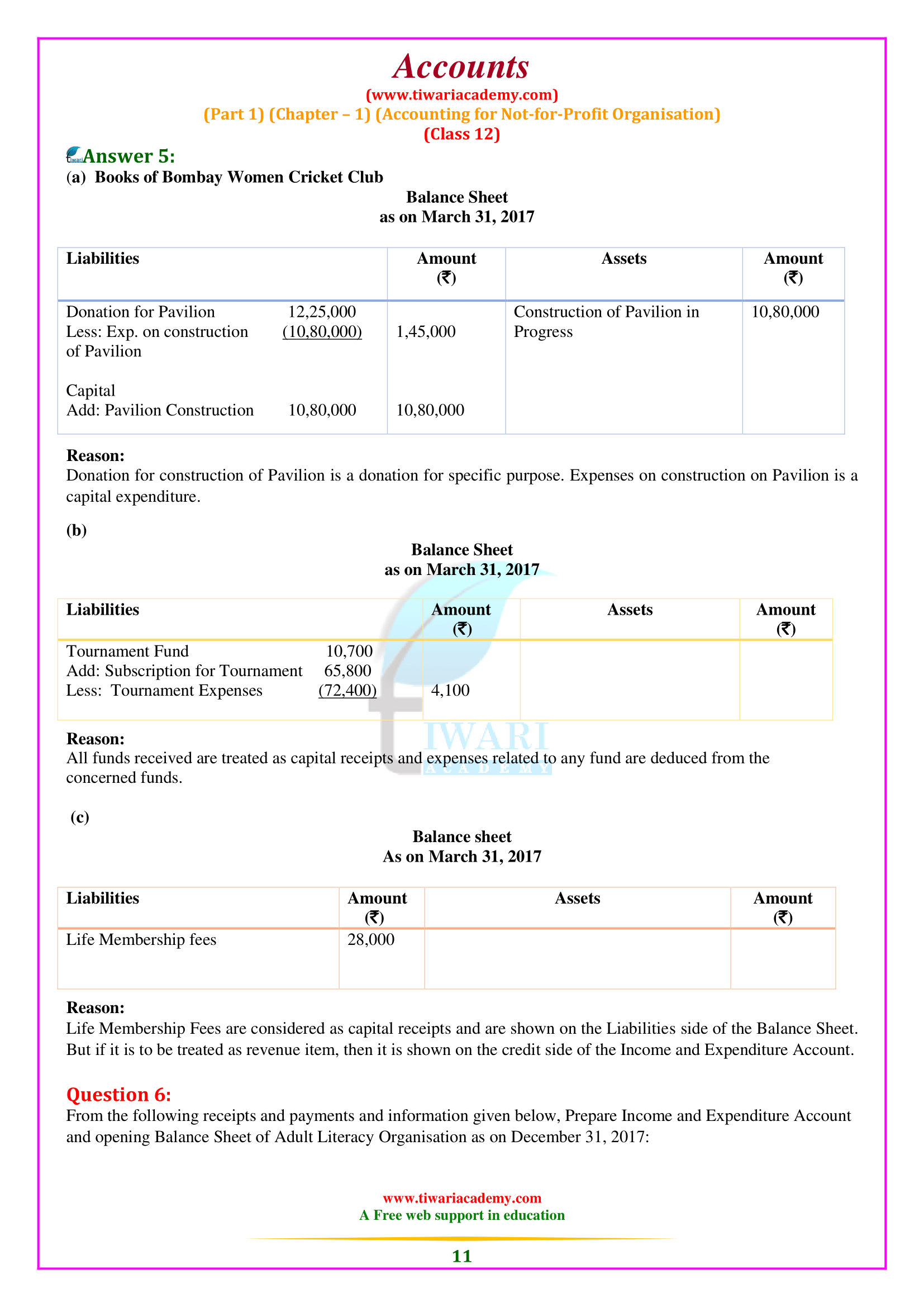
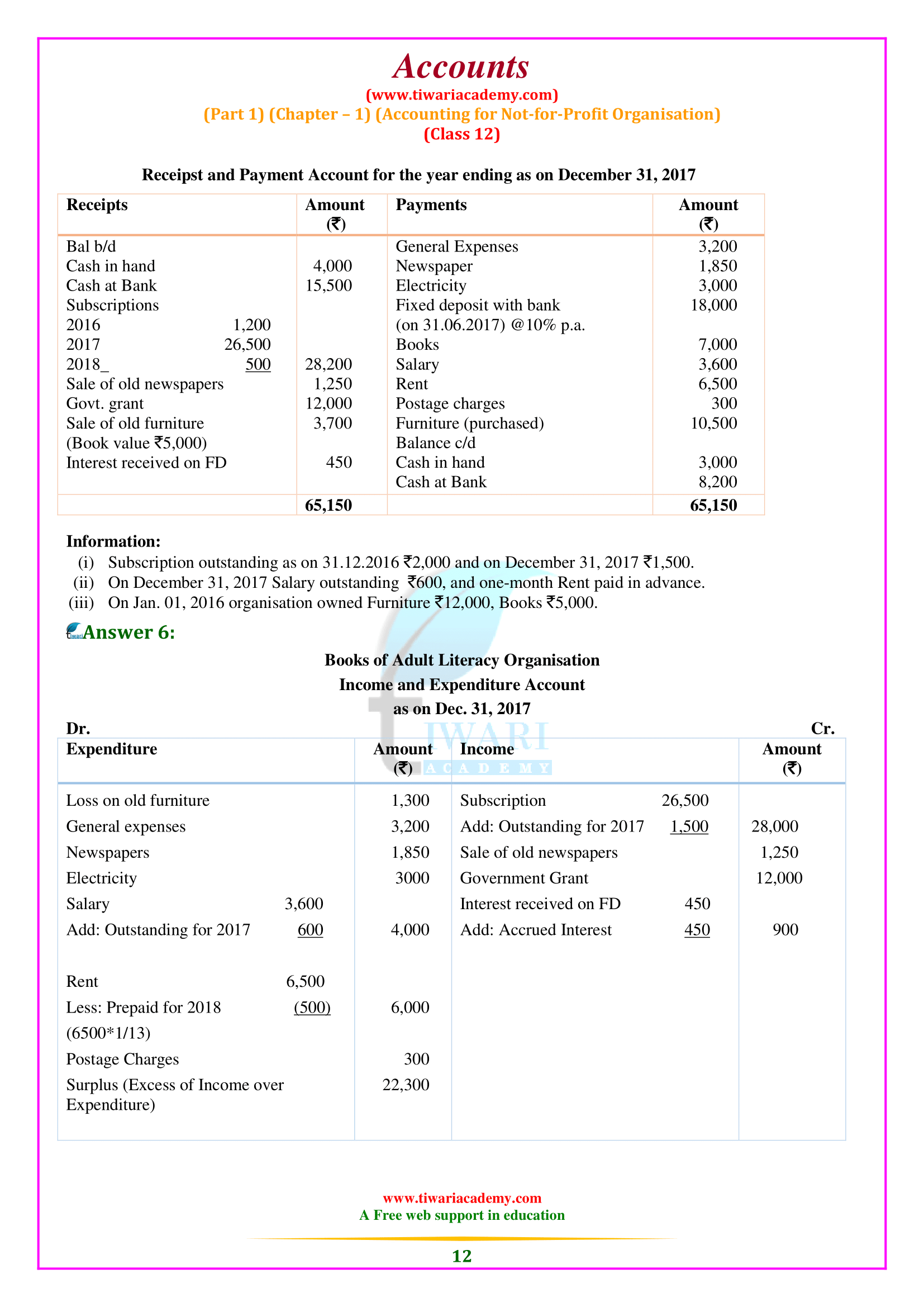
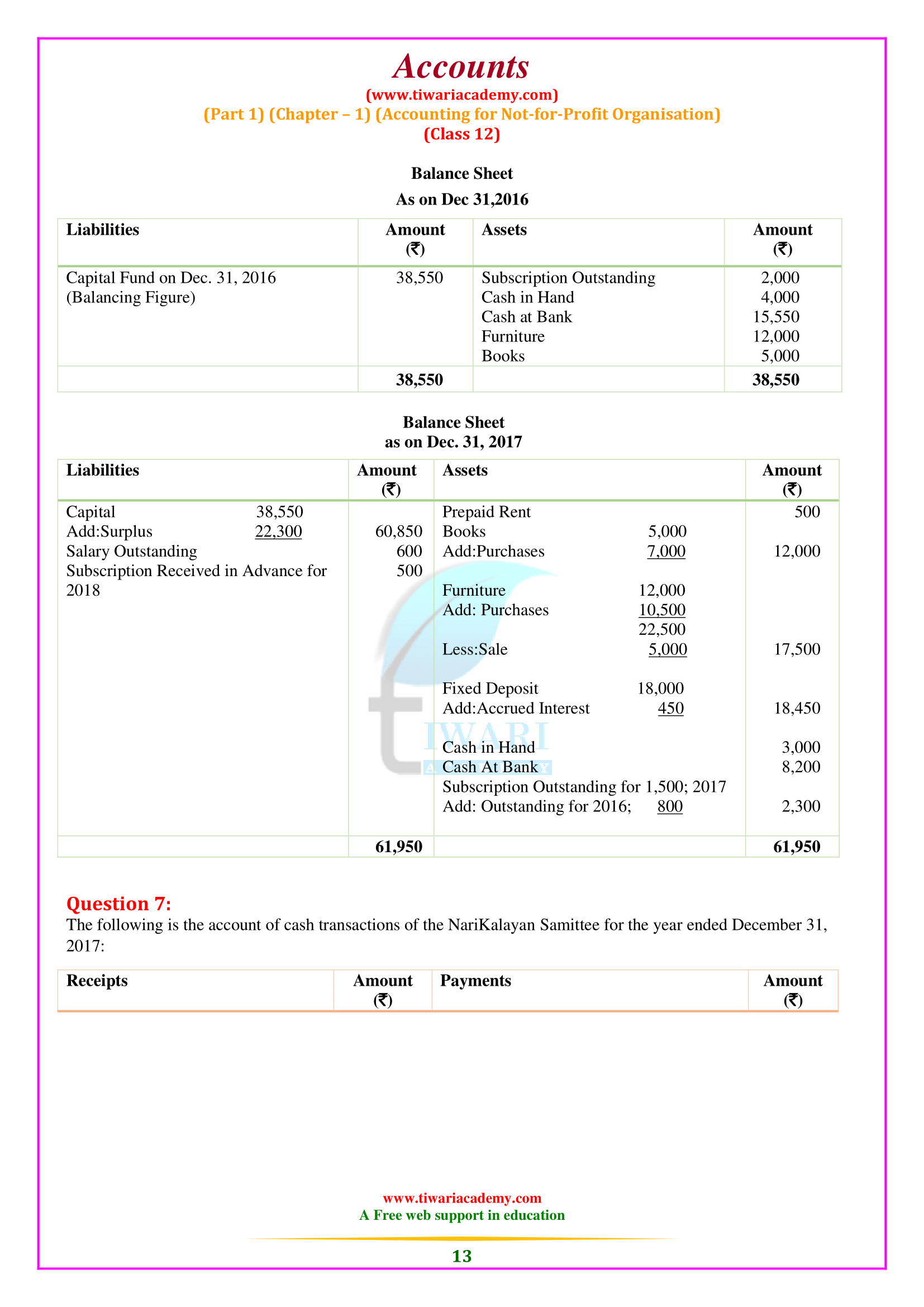
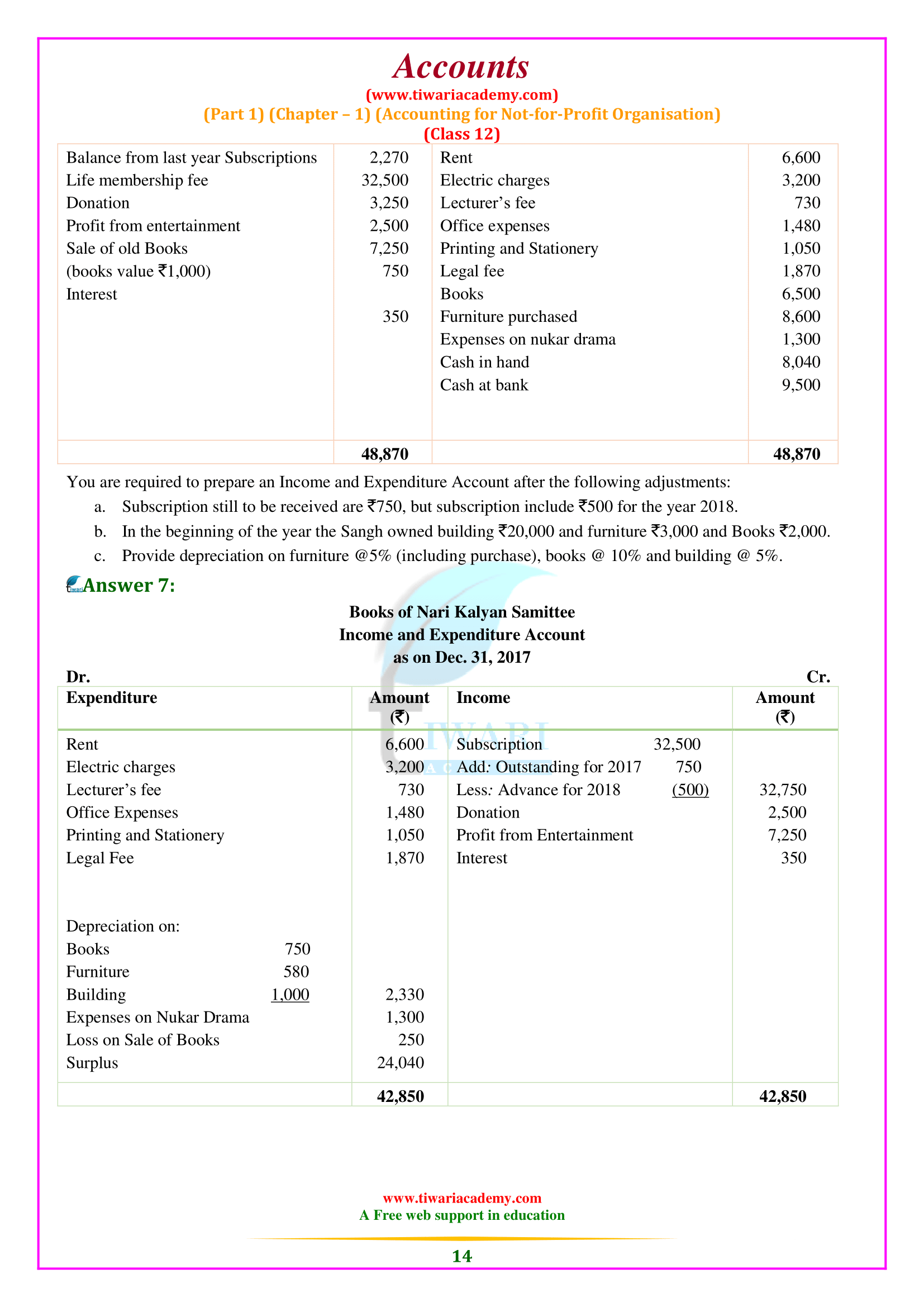
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Accountancy Part 1 Chapter 1 Accounting for Not-for-profit Organisation in English Medium free to download. All the question answers given at the end exercises are solved here for the academic session 2025-26. Extra questions based on 12th Accounts part 1 chapter 1 are also given for the preparation of CBSE and other board Exams.
Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 Question Answers
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Accountancy Part 1Chapter 1
| Class: 12 | Accountancy (Part 1) |
| Chapter: 1 | Accounting for Not-for-profit Organisation |
| Contents: | NCERT Solutions and Extra Questions |
The main characteristics of Not-for-Profit Organisation
- 1. Non-profit organizations are formed to provide services to a specific group or general public, such as education, health care, entertainment, sports, etc. without considering caste, creed, and color. Your sole goal is to provide a service free or at a nominal cost, not a profit.
- 2. These are organized as charitable societies or trusts, and members of that organization are called members.
- 3. Its affairs are usually managed by a management / executive committee elected by its members.
- 4. The primary sources of income for these organizations are member membership, donations, wills, etc.
- 5. Funds raised by non-profit organizations through various sources are deposited into capital funds or general funds. The surplus generated as income over expenses is not distributed among the members.
- 6. These organizations earn their reputation based on their contribution to society’s welfare and not on the satisfaction of customers or owners.
- 7. These organizations’ accounting information is for current and prospective taxpayers and compliance with legal requirements.
Receipt and Payment Account
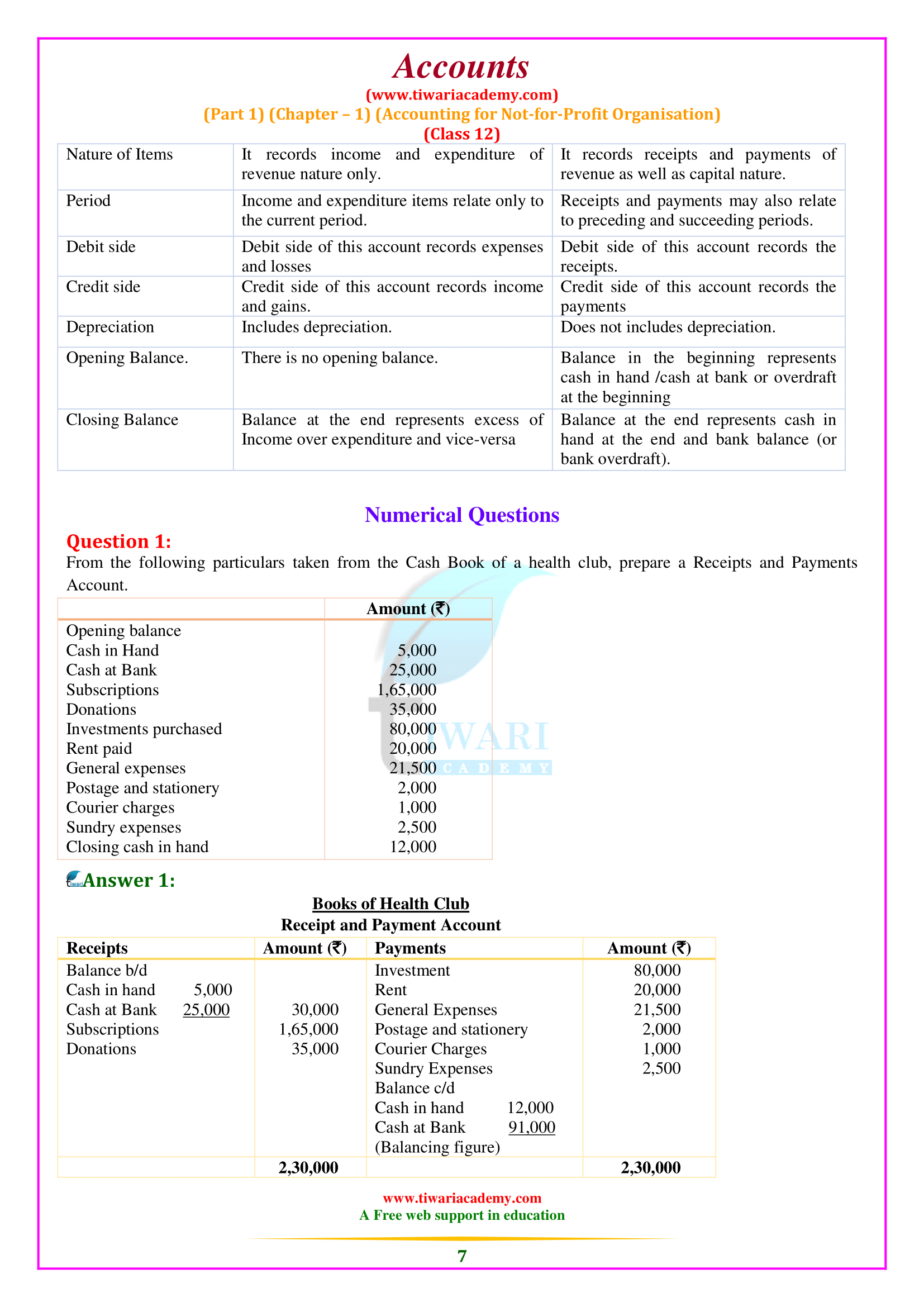
It is prepared based on cash receipts and payments recorded in the cash book at the end of the accounting year. It is a summary of bank and cash transactions under various headings. For example, subscriptions received from members of different dates appearing on the debit side of the cash book will be displayed as an item along with their total amount towards receipts and payments account receivables. Similarly, the payment of salary, rent, and electricity charges from time to time is recorded on the cash book’s credit side. However, the total salary, total rent paid, and total electricity fee is paid by the year of receipt, and payments appear on Bill’s payment side.
Therefore, receipts and payment accounts provide a summary picture of various receipts and payments, whether they are of the current period, the previous period, or the next period, or whether they are of a capital or income nature. It should be noted that this account does not show any non-cash items, such as depreciation. Initial balance upon receipt and The payment account represents the cash on hand/cash in the bank shown in favor of receivables, and the closing balance of this account represents the cash on hand and the bank balance at the end of the year, which appears on the side of the loan receipts and payment Account. However, if it is a bank overdraft at the end, it will be indicated on the debit side as the last item. Let us look at the cash book of the Golden Cricket Club shown in the example of how the total amount of each receipt and payment has been calculated.
Steps in the Preparation of Receipt and Payment Account
- Take the beginning balance on hand and cash in the bank and enter them on the debit side. If there is a bank overdraft at the beginning of the year, enter it on the account’s credit side.
- Show the total amount of all income on your debit side regardless of their nature (either equity or income) and whether they relate to past, present, and future periods.
- Show the total amount of all payments on behalf of your creditor, regardless of their nature (either principal or income) and related to past, present, and future periods.
- Any receivables and expenses payable should not be recorded in this account, as they do not include cash flows or outflows.
- Find out the difference between the total on the debit side and the total on the account’s credit side and enter the same on the credit side as the closing side/cash balance. However, if the total on the credit side is more than the total on the debit side, the banks show that the difference in debit in the form of overdraft and close the account.
What are the main terms to read in Class 12 Accounts Chapter 1.
The main terms are as follows:
1. Not-for-Profit Organisation.
2. Income and Expenditure Account
3. Receipts and Payments Account
4. Entrance Fee
5. Special Receipts
6. Life Membership
7. Subscription
8. Donation
9. Incidental Trading Activity
10. Legacy
What is meant by a Not-for-profit Organisation in Chapter 1 of 12th Accounts?
Not-for-Profit Organisations refer to the organisations that are for used for the welfare of the society and are set up as charitable institutions which function without any profit motive.
What are the main sources of income in Not-for-profit Organisation in Class 12 Accounts Chapter 1?
The main sources of income of Not-for-profit organisations are:
1. Subscriptions from members
2. Donations
3. Legacies
4. Grantin-aid
5. Income from investments
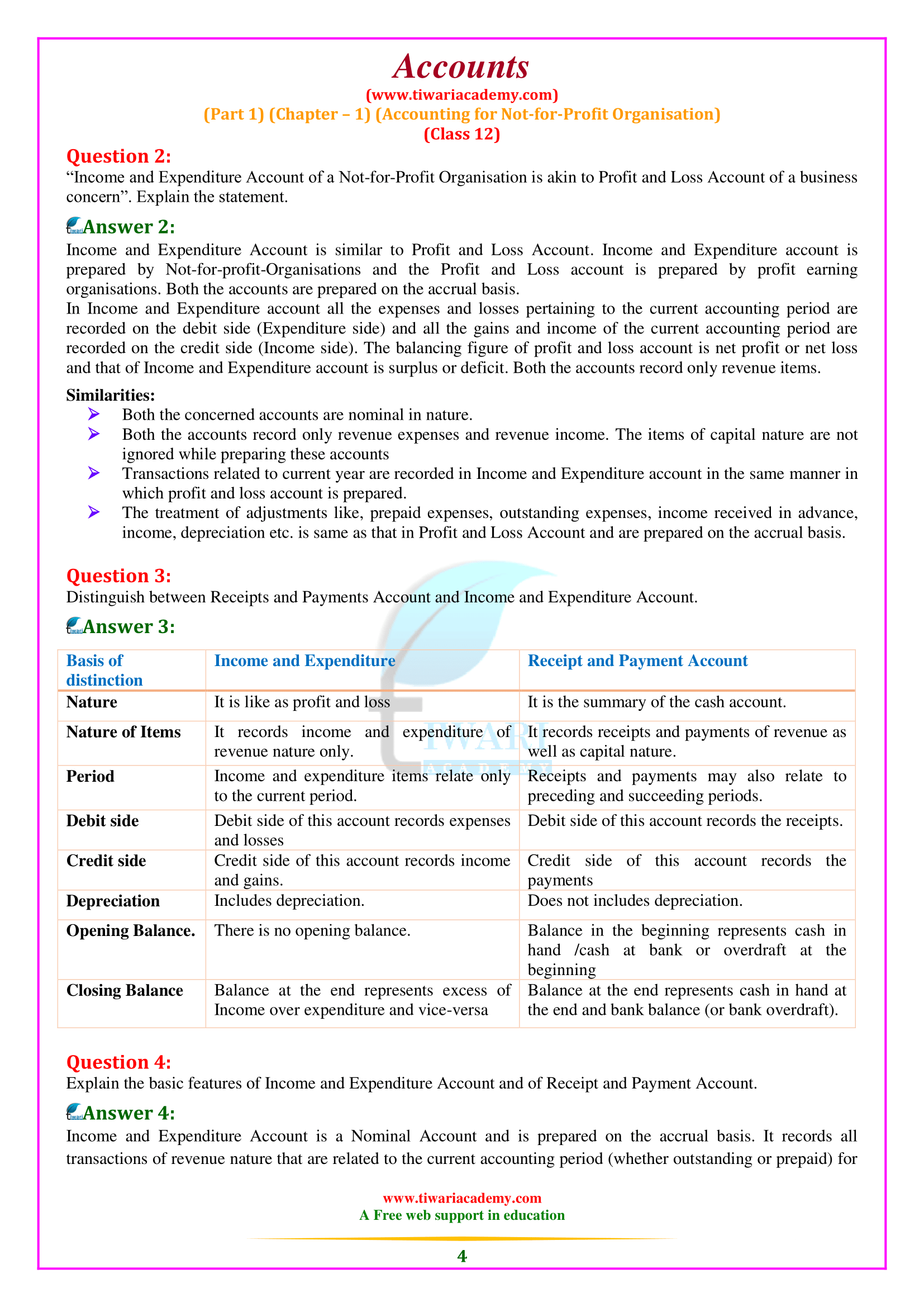
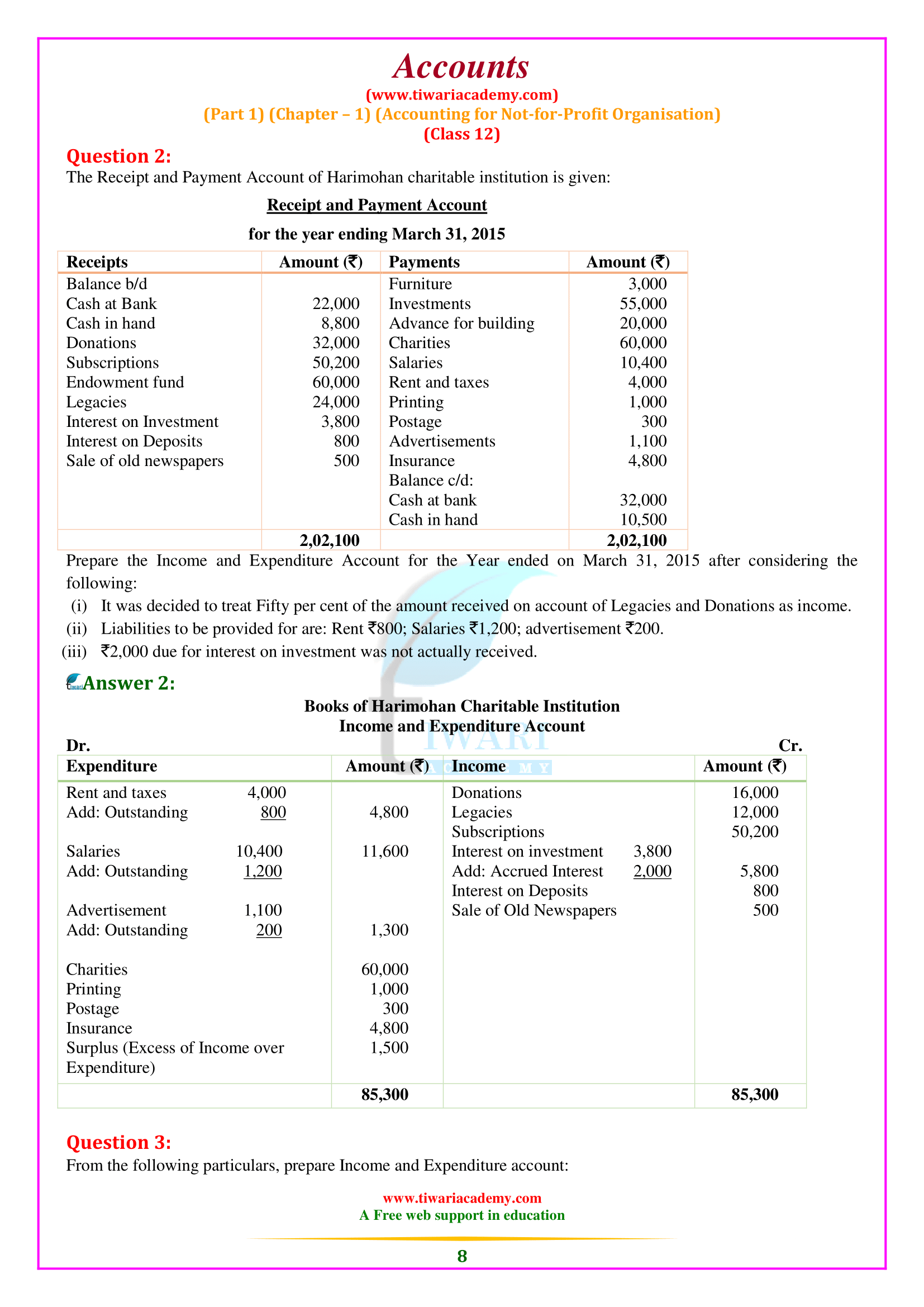
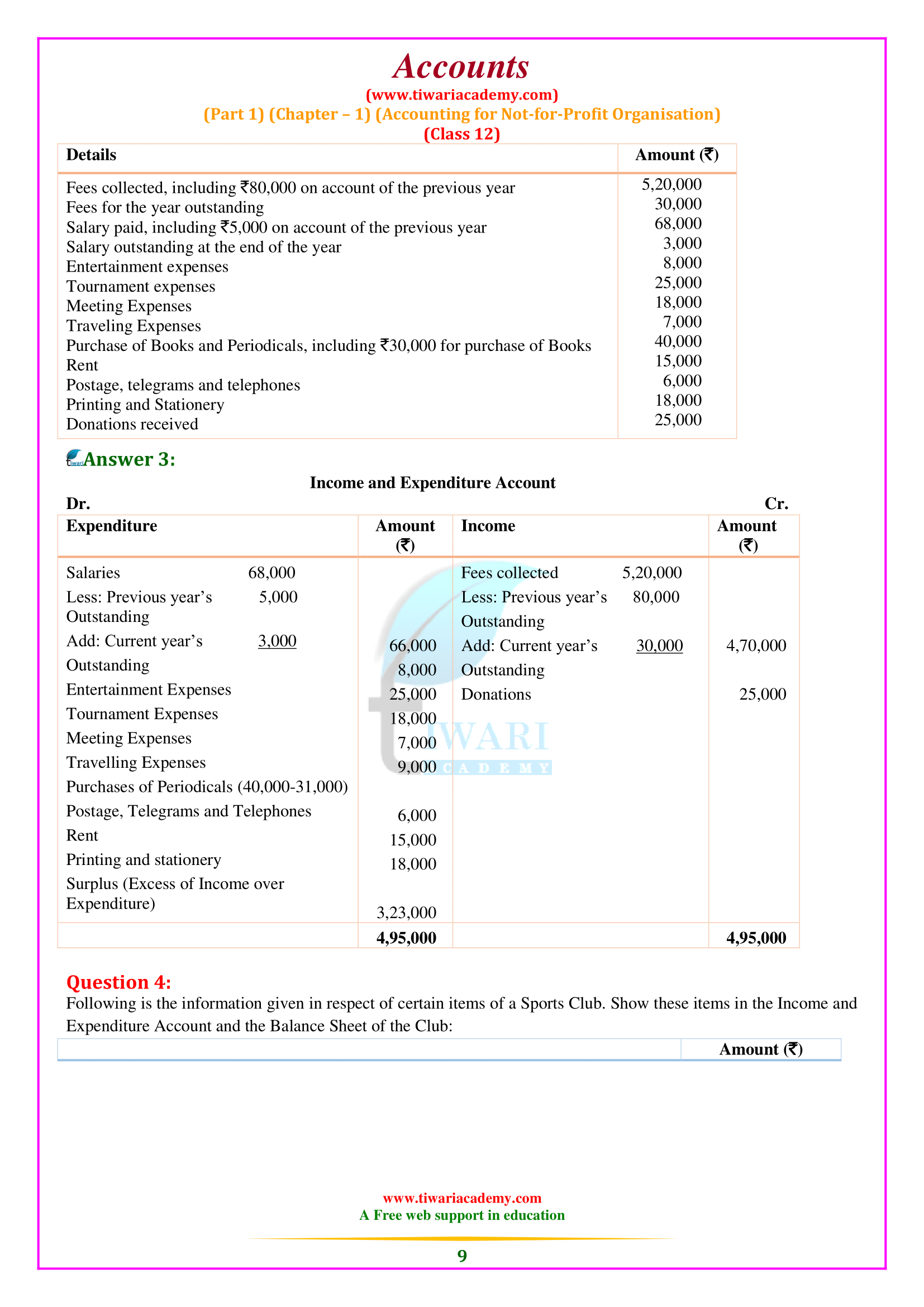
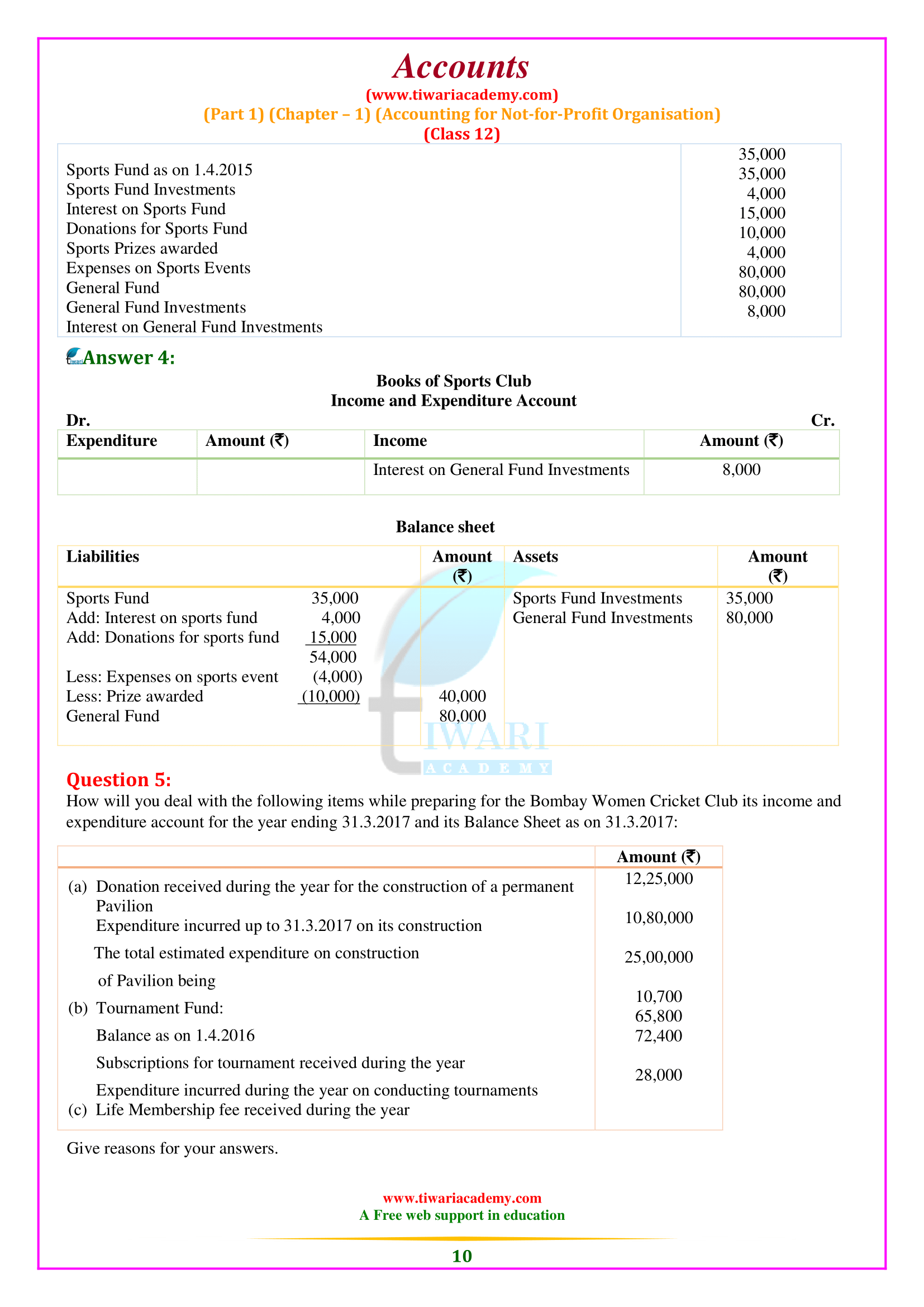
What is the meaning of Receipt and Payment Account according to 12th Accounts Chapter 1?
The Receipt and Payment Account is the summary of cash and bank transactions which helps in the preparation of Income and Expenditure Account and the Balance Sheet. Besides, it is a legal requirement as the Receipts and Payments Account has also to be submitted to the Registrar of Societies along with the Income and Expenditure Account, and the Balance Sheet. All cash receipts are recorded on the Receipts side (i.e. Debit side) and all cash payments are recorded on the Payments side (i.e. Credit side) of Receipts and Payments Account. It begins with the opening balance of cash and bank and ends with the closing balances of cash and bank (balancing figure) at the end of the accounting period.