NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Hydrocarbons in Hindi and English Medium updated for new academic session 2025-26. Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 MCQ, Exercise, Intext Question Answers, Extra Important Question Answers are given here in PDF and Video.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 NCERT Book
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Hindi Medium
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Revision Book
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Study Material 1
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Study Material 2
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Assignment
- Class 11 Chemistry NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 all Subjects NCERT Solutions
Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons occur naturally and form the basis of crude oil, natural gas, coal, and other important energy sources. The term ‘hydrocarbon’ is self-explanatory which means compounds of carbon and hydrogen only. Hydrocarbons play a key role in our daily life. You must be familiar with the terms ‘LPG’ and ‘CNG’ used as fuels. LPG is the abbreviated form of liquefied petroleum gas whereas CNG stands for compressed natural gas.
Classification of Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons are of different types. Depending upon the types of carbon-carbon bonds present, they can be classified into three main categories:
- (A) Saturated
- (B) Unsaturated and
- (C) Aromatic hydrocarbons
Alkanes
alkanes are saturated open chain hydrocarbons containing carbon – carbon single bonds. Methane (CH₄) is the first member of this family. Methane is a gas found in coal mines and marshy places. If you replace one hydrogen atom of methane by carbon and join the required number of hydrogens to satisfy the tetravalence of the other carbon atom, you get C₂H₆. This hydrocarbon with molecular formula C₂H₆ is known as ethane. Thus you can consider C₂ H₆ as derived from CH₄ by replacing one hydrogen atom by -CH₃ group. General formula for alkanes is CₙH₂ₙ₊₂.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 MCQ
Arrange the halogens F₂, Cl₂, Br₂, I₂, in order of their increasing reactivity with alkanes.
The increasing order of reduction of alkyl halides with zinc and dilute HCl is
Arrange the following hydrogen halides in order of their decreasing reactivity with propene.
Arrange the following carbanions in order of their decreasing stability: (1) H₃C – C ≡ C⁻ (2) H – C ≡ C⁻ (3) H₃C – CH₂⁻
Preparation
Petroleum and natural gas are the main sources of alkanes. However, alkanes can be prepared by following methods:
From Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
Dihydrogen gas adds to alkenes and alkynes in the presence of finely divided catalysts like platinum, palladium or nickel to form alkanes. This process is called hydrogenation.
CH₂ = CH₂ + H₂ ⟶ CH₃¬¬¬¬ – CH₃
Ethene Ethane
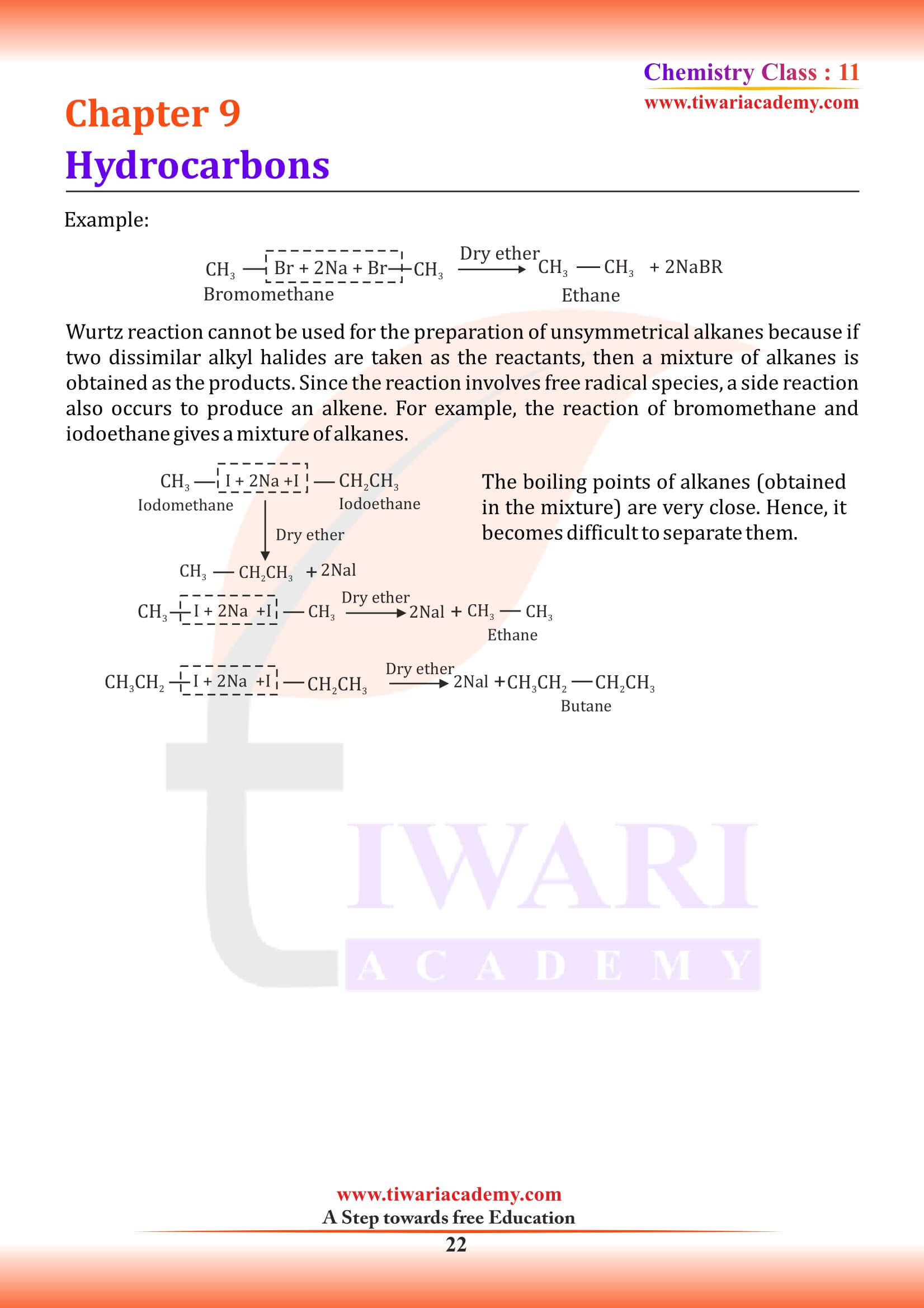
From Alkyl Halides
Alkyl halides (except fluorides) on reduction with zinc and dilute hydrochloric acid give alkanes.
CH₃ – Cl + H₂ ⟶ CH₄ + HCl
Chloromethane Methane
From carboxylic acids Sodium salts of carboxylic acids on heating with soda lime (mixture of sodium hydroxide and calcium oxide) give alkanes containing one carbon atom less than the carboxylic acid. This process of elimination of carbon dioxide from a carboxylic acid is known as decarboxylation.
CH₃COO⁻Na⁺ + NaOH ⟶ CH₄ + Na₂CO₃
Physical Properties
Alkanes are almost non-polar molecules because of the covalent nature of C-C and C-H bonds and due to very little difference of electronegativity between carbon and hydrogen atoms. C₁ to C₄ are gases, C₄ to C₁₇ are liquids and those containing 18 carbon atoms or more are solids at 298 K. They are colourless and odourless.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 MCQ with Answers
Which of the following reactions of methane is incomplete combustion
In an electrophilic substitution reaction of nitrobenzene, the presence of nitro group
Which of the following are correct?
The molecules having dipole moment are
Chemical Properties
alkanes are generally inert towards acids, bases, oxidising and reducing agents.
Combustion
Alkanes on heating in the presence of air or dioxygen are completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water with the evolution of large amount of heat.
CH₄ (g) 2O₂ ⟶ (g) CO₂ (g) 2H₂O(l)
ALKENES
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one double bond. If there is one double bond between two carbon atoms in alkenes, they must possess two hydrogen atoms less than alkanes. Hence, general formula for alkenes is CₙH₂ₙ. Alkenes are also known as olefins (oil forming) since the first member, ethylene or ethene (C₂H₄) was found to form an oily liquid on reaction with chlorine.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 Important Extra Questions
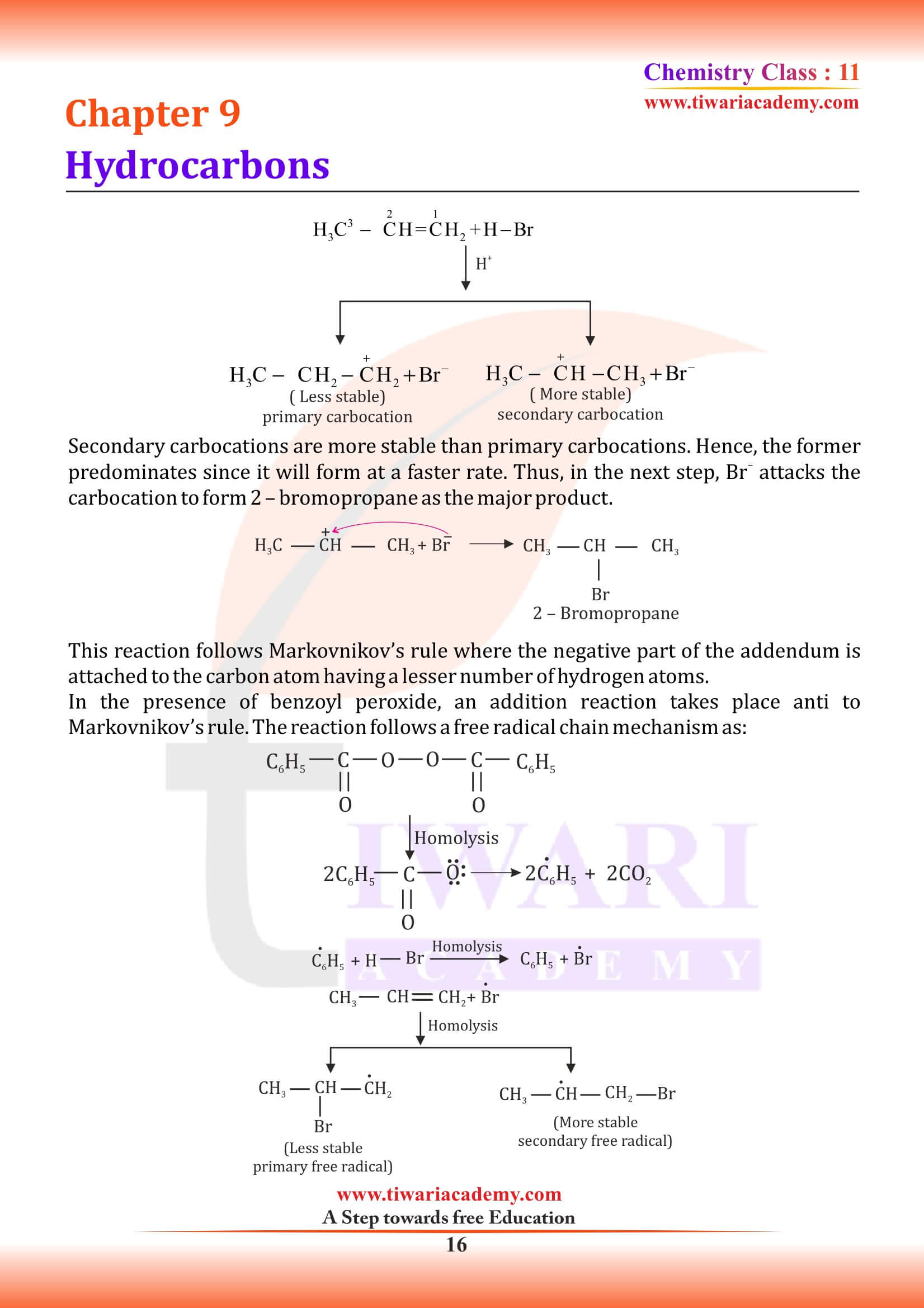
Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain.
Both alkenes and arenes are electron-rich. Therefore, undergo electrophilic reactions. Olefins undergo addition reactions because addition of a reagent to an olefin gives a more stable product as sp² hybridisation changes to sp³ hybridisation. Addition to the double bond of an arene would give a product with less or no resonance stability hence addition is difficult arenes. On the other hand, in substitution reaction resonance stabilization is retained therefore, arenes undergo substitution reaction.
Rotation around carbon-carbon single bond of ethane is not completely free. Justify the statement.
The rotation about C—C bond is restricted because of repulsion between electron cloud of C—H bonds on either carbon atom.
Despite their – I effect, halogens are o- and p-directing in haloarenes. Explain.
Halogens attached to benzene rings exert –I and +R effect. +R effect dominates –I effect and increases the electron density at ortho and para positions of the benzene ring with respect to halogens.
Physical Properties
Alkenes as a class resemble alkanes in physical properties, except in types of isomerism and difference in polar nature. The first three members are gases, the next fourteen are liquids and the higher ones are solids. Ethene is a colourless gas with a faint sweet smell. All other alkenes are colourless and odourless, insoluble in water but fairly soluble in nonpolar solvents like benzene, petroleum ether.
Chemical Properties
Alkenes are the rich source of loosely held pi (p) electrons, due to which they show addition reactions in which the electrophiles add on to the carbon-carbon double bond to form the addition products. Some reagents also add by free radical mechanism. There are cases when under special conditions, alkenes also undergo free radical substitution reactions. Oxidation and ozonolysis reactions are also quite prominent in alkenes.