NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure in Hindi and English Medium exercise and intext questions answers prepared for new CBSE session 2025-26. Get here the PDF and video related to class 11 chemistry chapter 4 MCQ all concepts.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 NCERT Book
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Hindi Medium
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Revision Book
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Study Material 1
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Study Material 2
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Study Material 3
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Assignment 1
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Assignment 2
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Assignment 3
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Assignment 4
- Class 11 Chemistry NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 all Subjects NCERT Solutions
Chemical Bonding
The attractive force which holds various constituents (atoms, ions, etc.) together in different chemical species is called a chemical bond.
Types of Chemical Bonding. There are three primary types of bonding:
- (A) Ionic bonding or electrovalent bond
- (B) Covalent bonding
- (C) Metallic bonding
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 MCQ
Polarity in a molecule and hence the dipole moment depends primarily on electronegativity of the constituent atoms and shape of a molecule. Which of the following has the highest dipole moment?
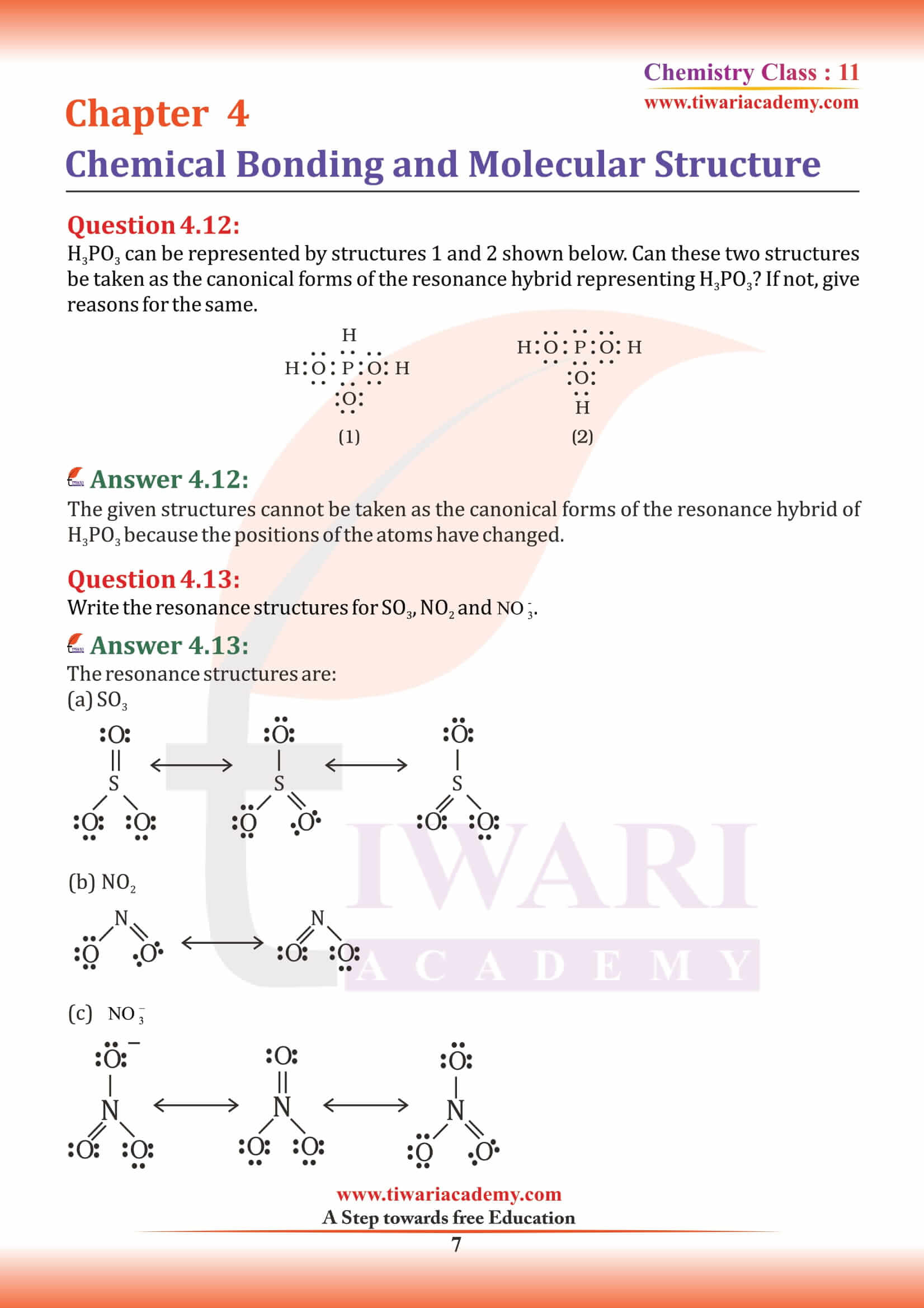
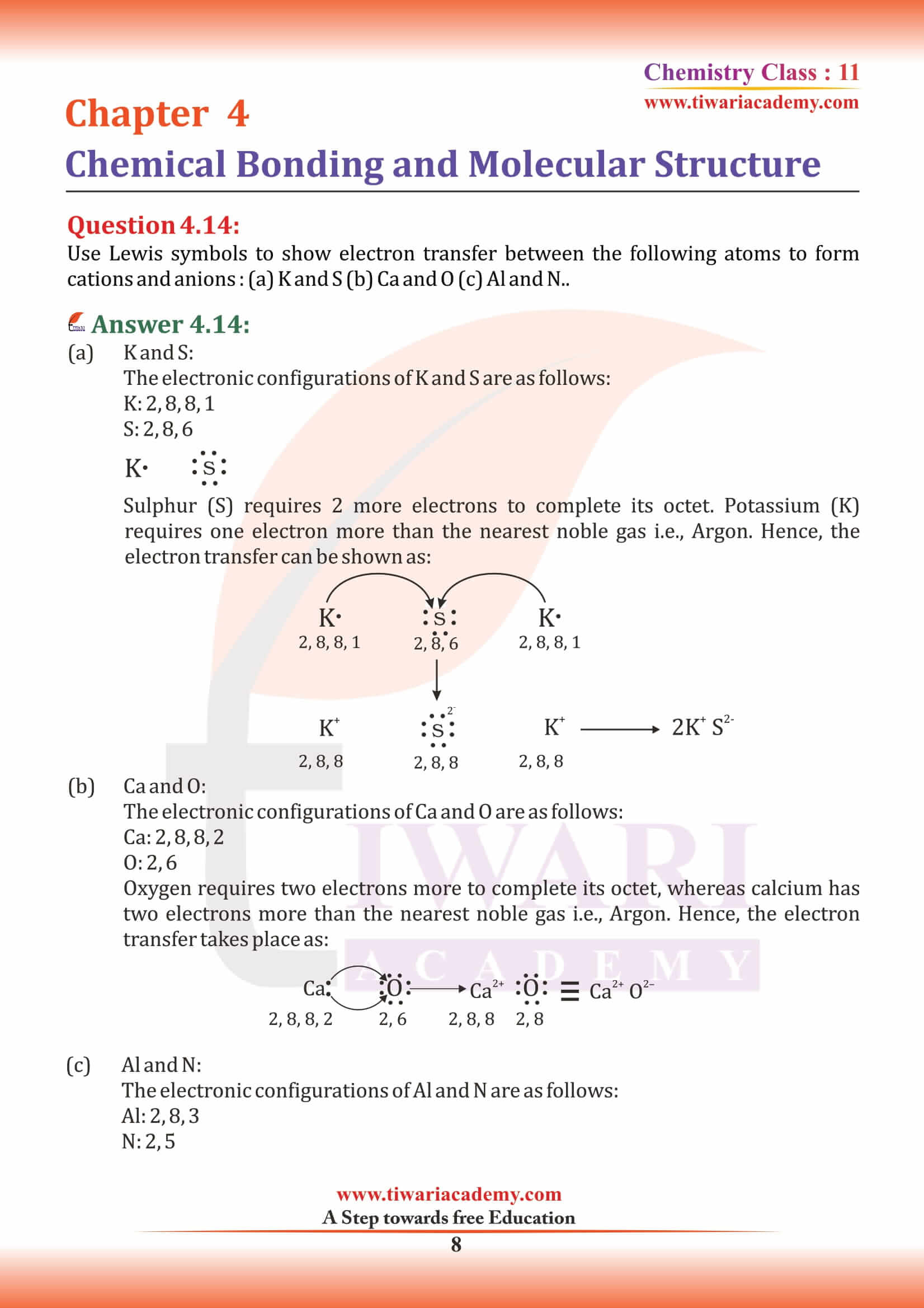
The types of hybrid orbitals of nitrogen in NO₂⁺, NO₃⁻ and NH₄⁺ respectively are expected to be
In PO₄³⁻ ion the formal charge on the oxygen atom of P–O bond is
Which of the following species has tetrahedral geometry?
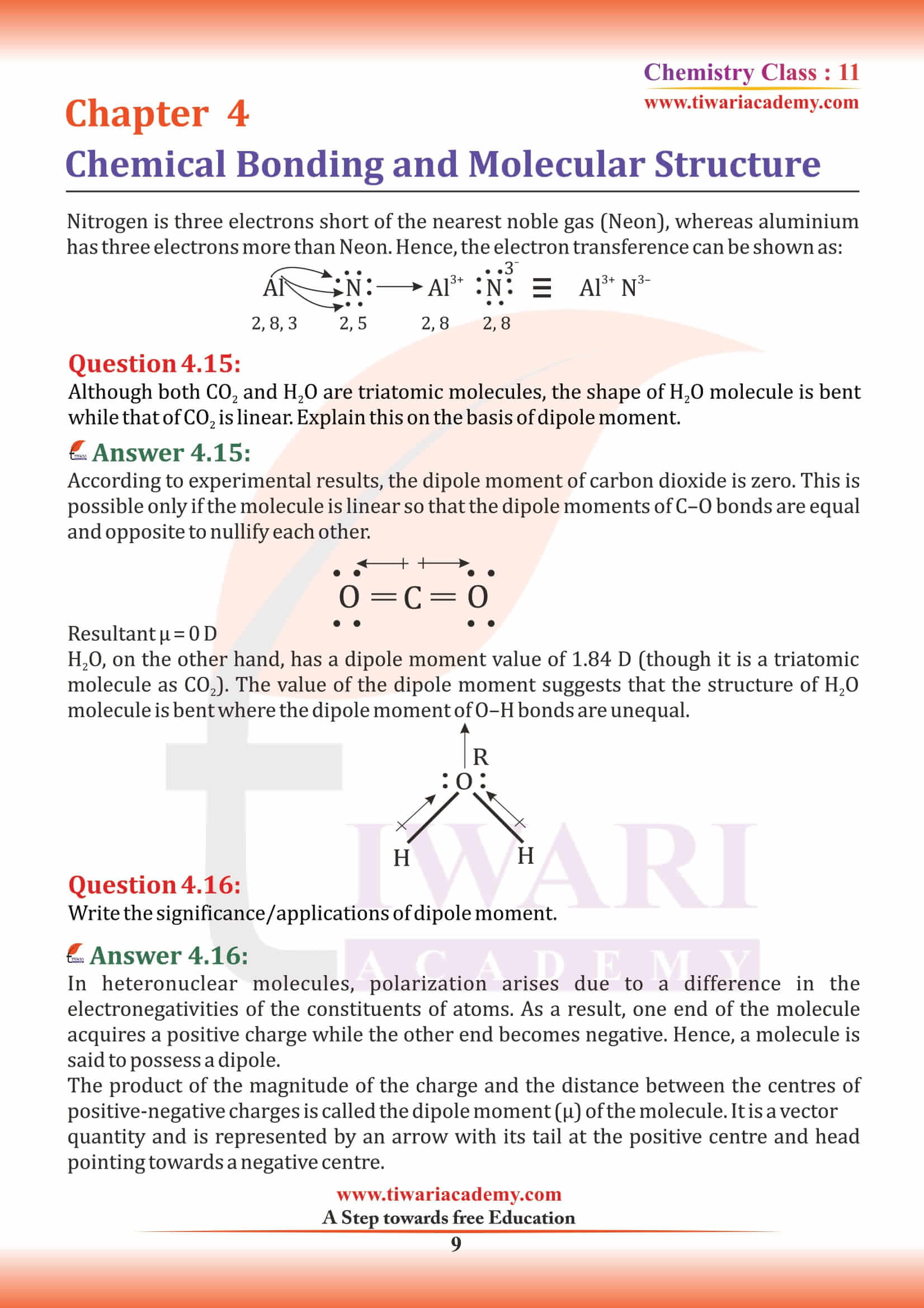
Ionic Bonding or Electrovalent Bond
The bond formed, as a result of the electrostatic attraction between the positive and negative ions was termed as the electrovalent bond. The electrovalence is thus equal to the number of unit charge(s) on the ion.
Examples: MgCl₂, CaCl₂, MgO, Na₂S, CaH₂, AlF₃, NaH, KH, K₂O, KI, RbCl, NaBr, CaH₂ etc.
Covalent Bonding
when two atoms share one electron pair they are said to be joined by a single covalent bond.
Examples: H₂, O₂, and N₂.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 MCQ for Practice
In which of the following substances will hydrogen bond be strongest?
Which of the following angle corresponds to sp² hybridization?
Metallic bonding
Metallic bonds are formed when the charge is spread over a larger distance as compared to the size of single atoms in solids. Mostly, in the periodic table, left elements form metallic bonds, for example, zinc and copper.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Important Extra Questions
What is an ionic bond? With two suitable examples explain the difference between an ionic and a covalent bond?
An example of an ionic bond is the chemical compound Sodium Chloride (NaCl). The difference between an ionic and a covalent bond are an ionic bond essentially donates an electron to the other atom participating in the bond, while electrons in a covalent bond are shared equally between the atoms.
Covalent bonds are directional bonds while ionic bonds are non-directional.
Ionic bonds are non-directional because it is the electrostatic force between two opposite charges, hence bonding direction does not matter whereas covalent is directional as attraction is in a specific direction and at an angle relative to the bonding atoms.
Explain covalent bond with suitable example.
A covalent bond consists of the mutual sharing of one or more pairs of electrons between two atoms. These electrons are simultaneously attracted by the two atomic nuclei. A covalent bond forms when the difference between the electro negativities of two atoms is too small for an electron transfer to occur to form ions. Covalent compound examples include water, ammonia, chlorine gas, and nitrogen gas.
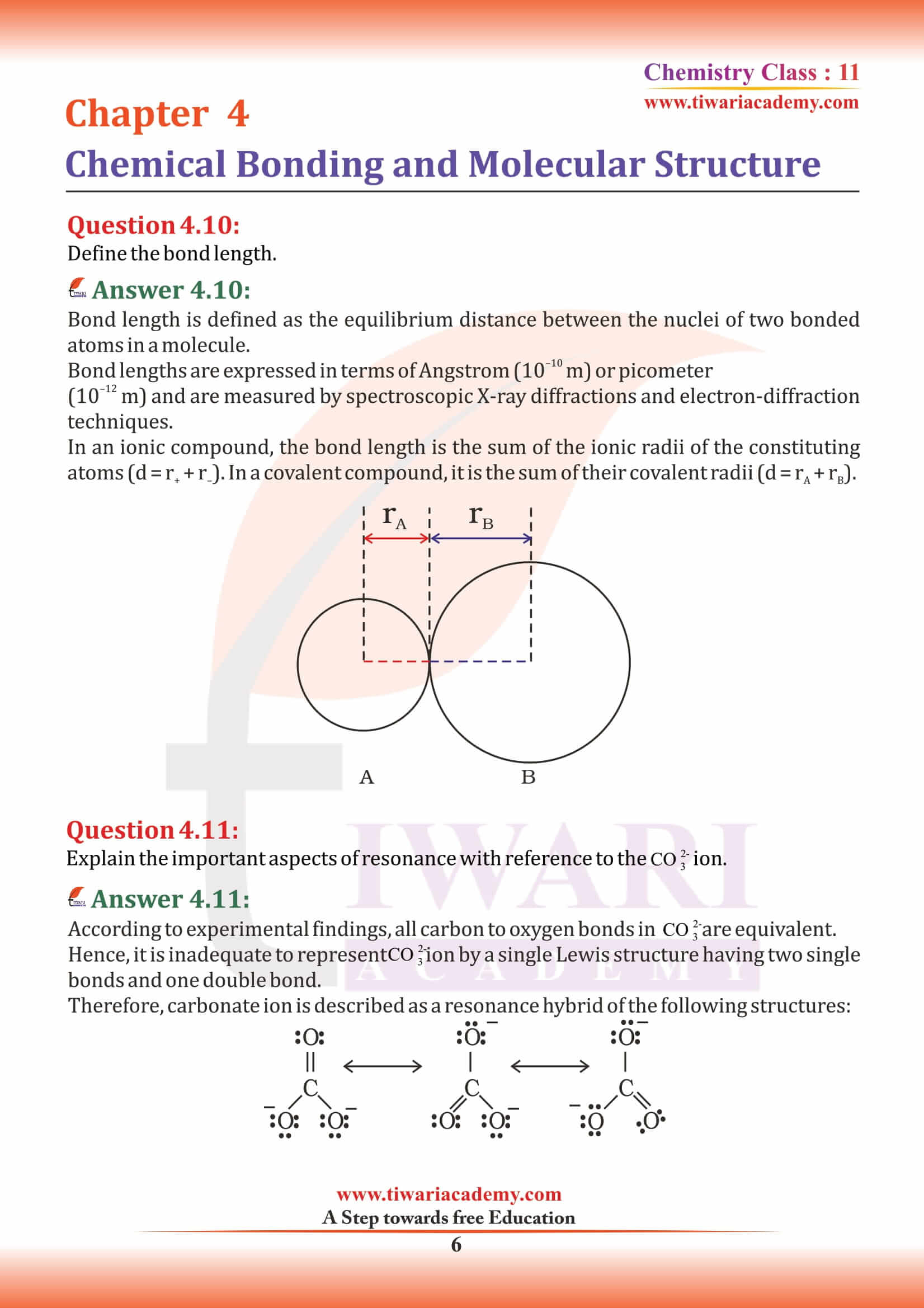
Bond Length
In molecular geometry, bond length or bond distance is defined as the average distance between nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule. It is a transferable property of a bond between atoms of fixed types, relatively independent of the rest of the molecule.
Bond Angle
The bond angle is defined as the average angle between the orbitals containing bonding electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule. For example: In a linear model, atoms are connected in a straight line. The bond angles are set at 180°.
Bond Order
In the Lewis description of covalent bond, the Bond Order is given by the number of bonds between the two atoms in a molecule. The bond order, for example in H₂ (with a single shared electron pair), in O₂ (with two shared electron pairs) and in N₂ (with three shared electron pairs) is 1, 2, 3 respectively.