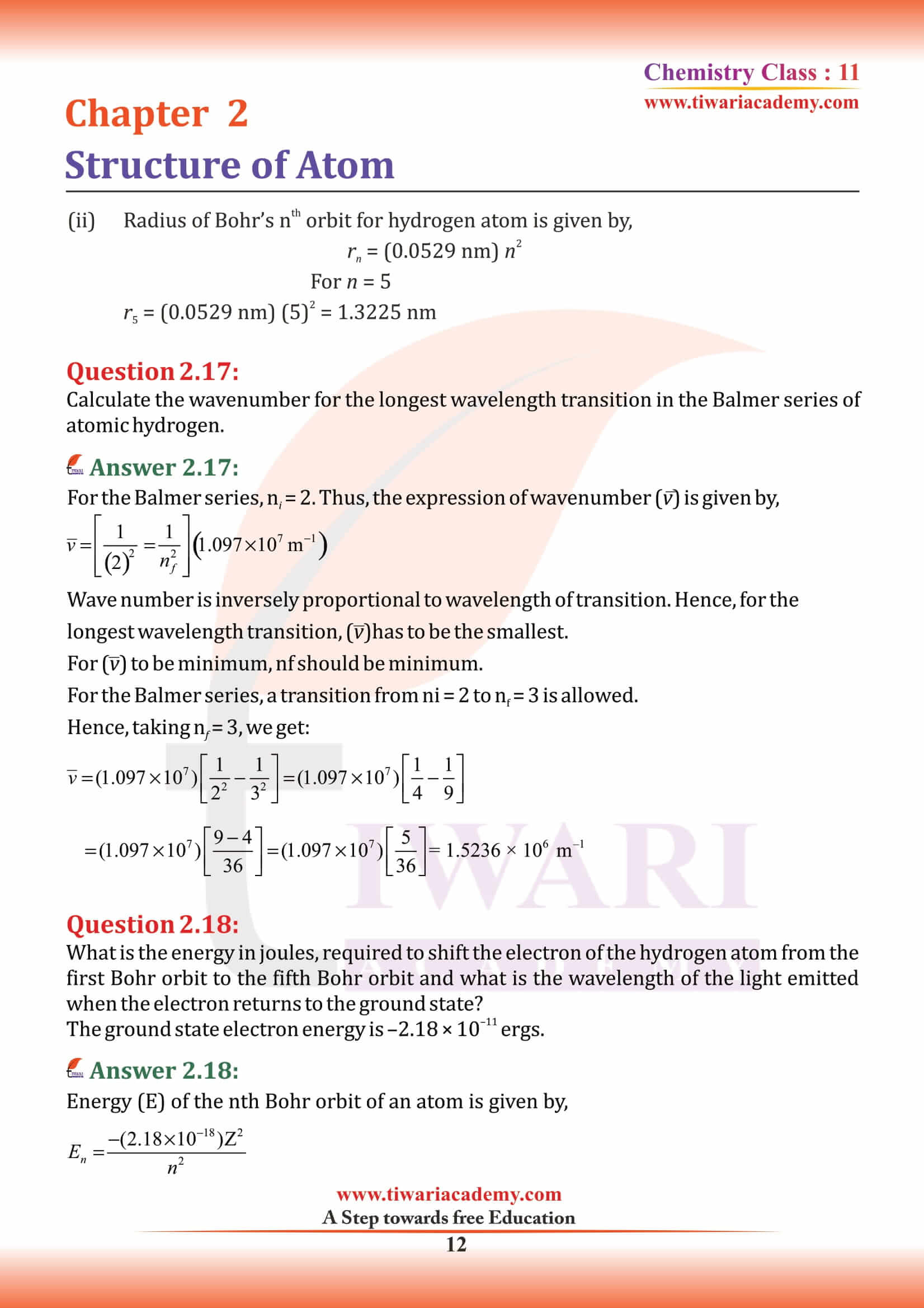
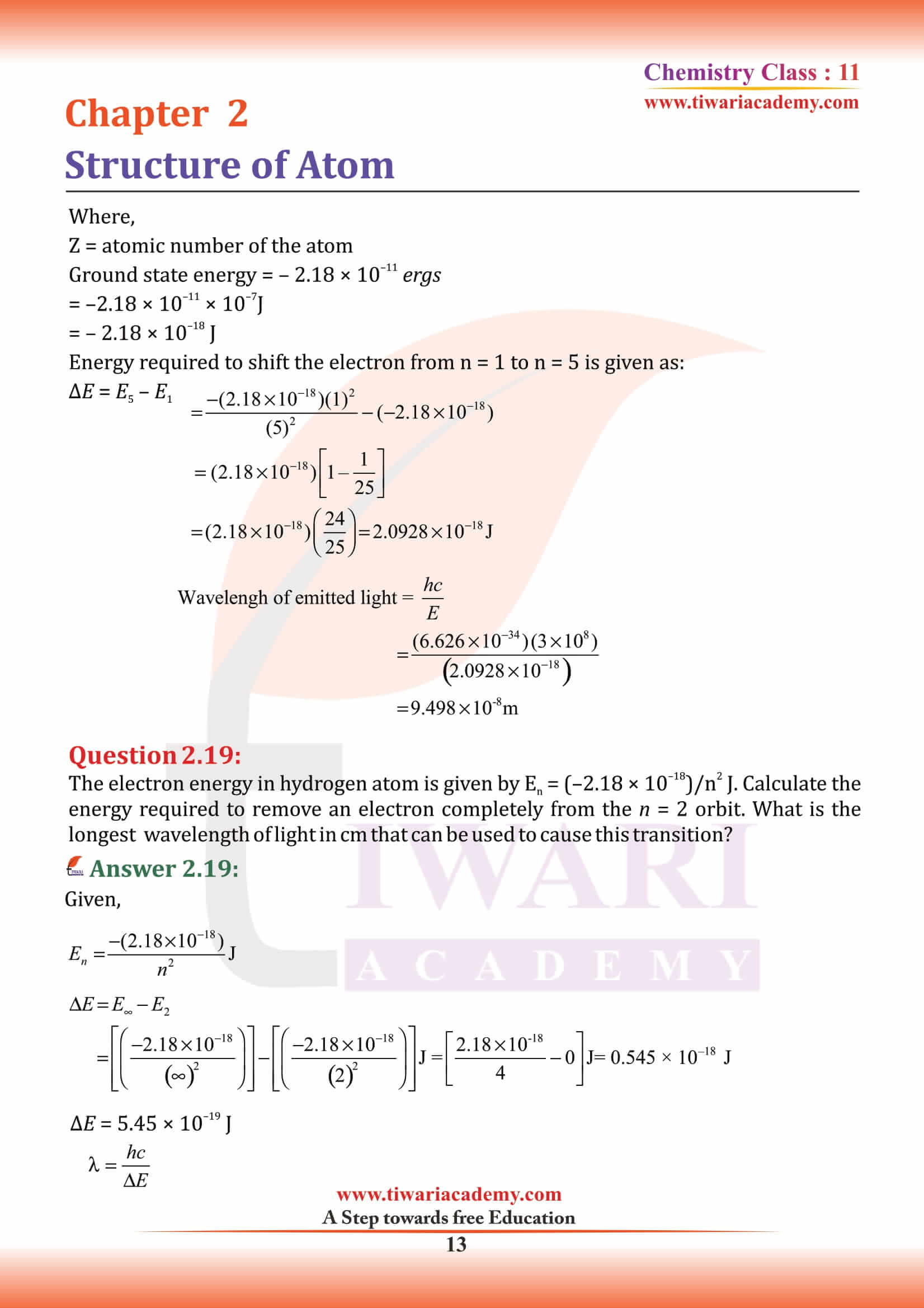
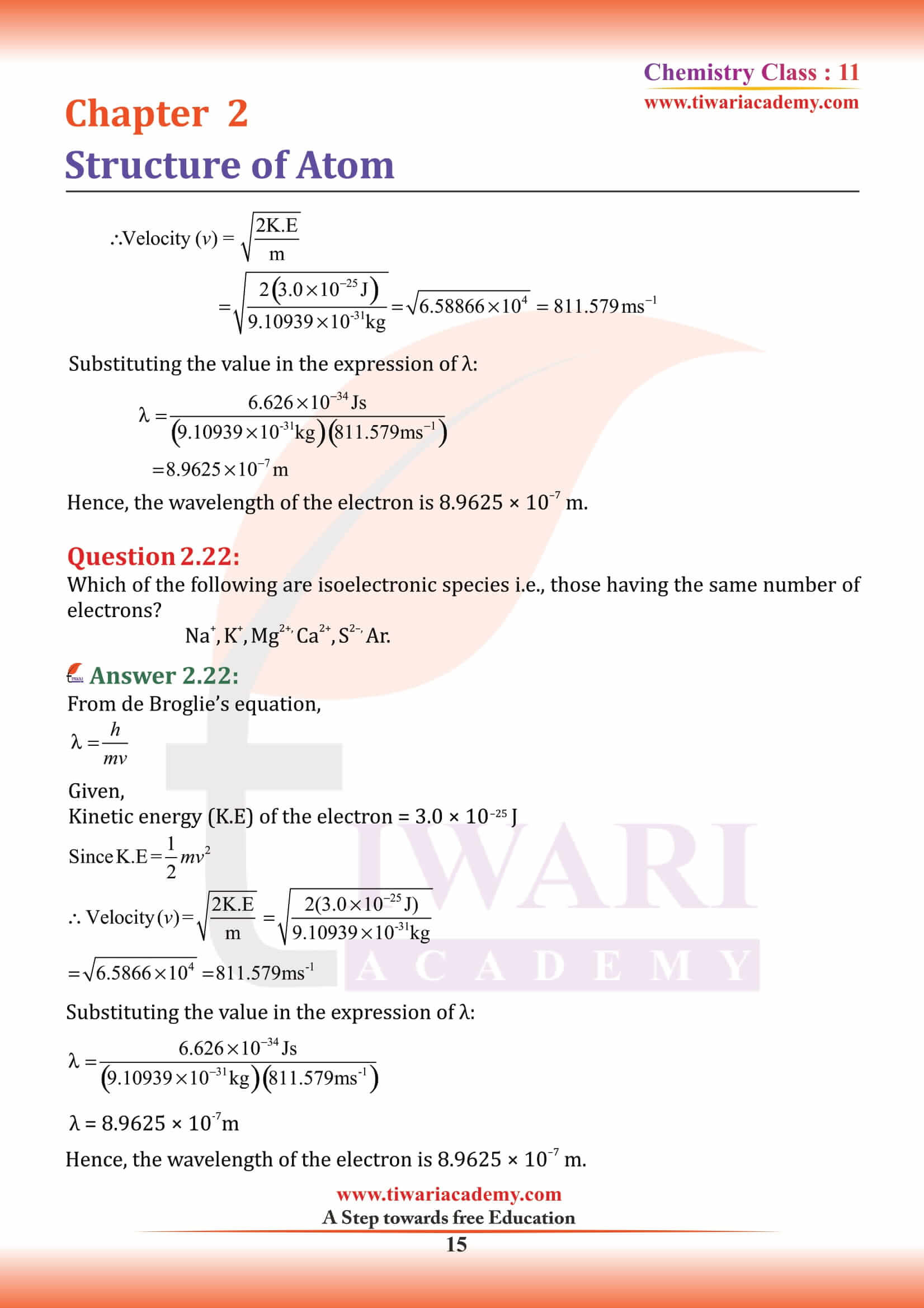
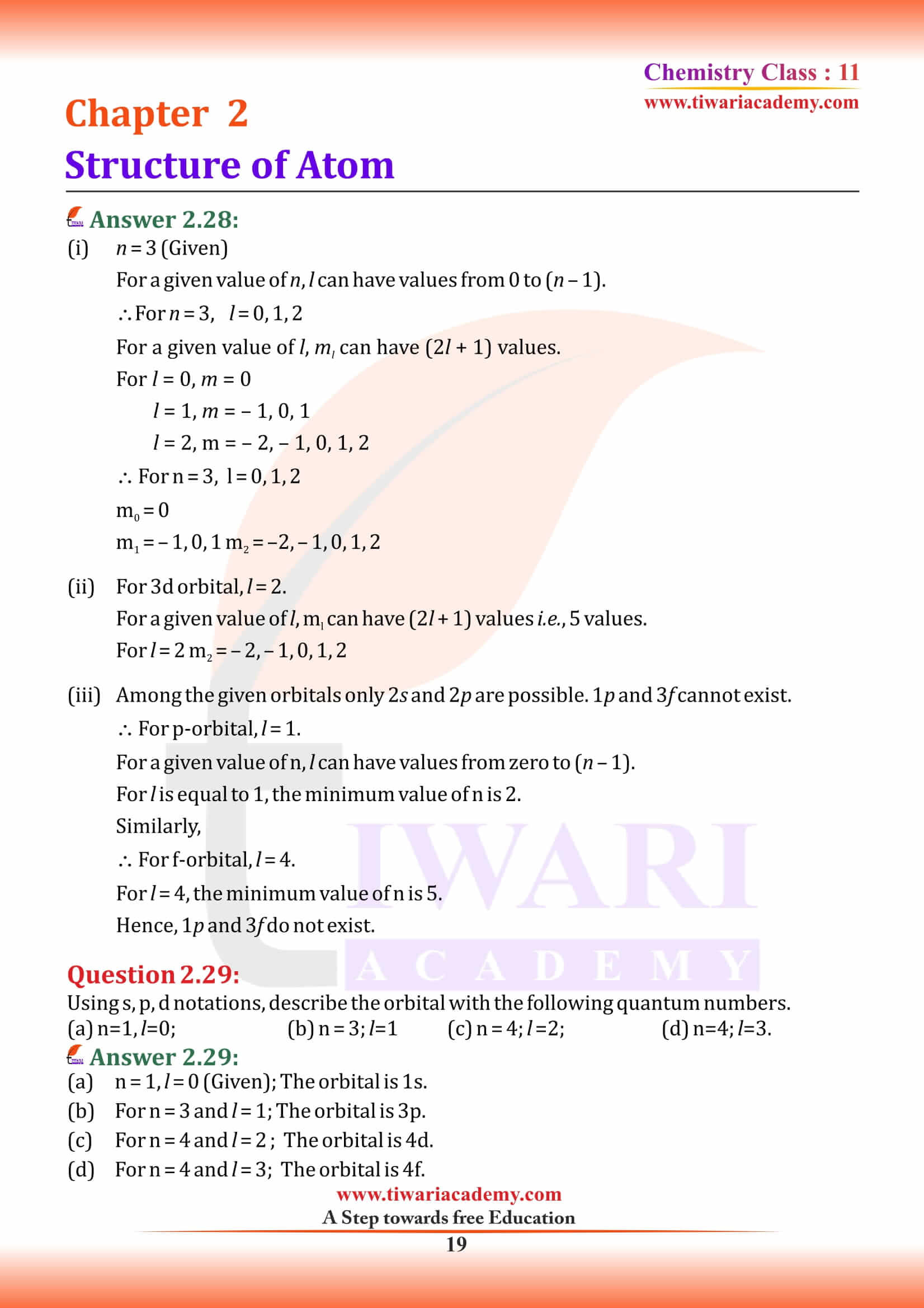
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Structure of Atom in Hindi and English Medium MCQ updated for new academic session based on new edition NCERT Books 2025-26. Class 11 Chemistry chapter 2 solutions, exercises and intext questions are equally useful for CBSE and State board students.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 NCERT Book
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Hindi Medium
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Revision Book
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Study Material 1
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Study Material 2
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Study Material 3
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Assignment 1
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Assignment 2
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Assignment 3
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Assignment 4
- Class 11 Chemistry NCERT Solutions
- Class 11 all Subjects NCERT Solutions
Structure of Atom
Primarily, the atomic structure of matter is made up of protons, electrons and neutrons. The protons and neutrons make up the nucleus of the atom, which is surrounded by the electrons belonging to the atom. The atomic number of an element describes the total number of protons in its nucleus.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 MCQ
Which of the following element has least number of electrons in its M-shell?
The electronic configuration of an element is 1s², 2s² 2p⁶, 3s² 3p⁶ 3d⁵, 4s¹. It represents
Atoms with same mass number but different atomic numbers are called
In Hydrogen atom, energy of first excited state is – 3.4 eV. Then find out KE of same orbit of Hydrogen atom
What is an Electron?
An electron is a negatively charged subatomic particle. It can be either free (not attached to any atom), or bound to the nucleus of an atom. the charge on the electron to be – 1.6 × 10–19 C. The present accepted value of electrical charge is – 1.602176 × 10–19 C. Electrons in atoms exist in spherical shells of various radii, representing energy levels. The larger the spherical shell, the higher the energy contained in the electron. Electron is discovered by English physicist J. J. Thomson in 1897.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 MCQ for Exams
The total number of orbitals in a shell having principal quantum n is
In which of the following Bohr’s stationary state, the electron will be at maximum distance from the nucleus?
The line spectrum of hydrogen obtained in the visible region of light corresponds to
The magnetic quantum number specifies
What is Proton?
Proton, stable subatomic particle that has a positive charge equal in magnitude to a unit of electron charge and a rest mass of 1.67262 × 10⁻²⁷ kg, which is 1,836 times the mass of an electron. Ernest Rutherford discovered protons in 1920.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Important Extra Questions
What is the structure of atoms?
Atoms consist of three basic particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons. The nucleus (center) of the atom contains the protons (positively charged) and the neutrons (no charge). The outermost regions of the atom are called electron shells and contain the electrons (negatively charged).
What are the 4 types of atoms?
Different Kinds of Atoms:
Atoms are made of tiny particles called protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons clump together to form a central nucleus. The electrons move in a cloud-like region around the nucleus. On the bases of physical and chemical properties we can categorized atoms as:
- Stable
- Isotopes
- Radioactive
- Ions
- Antimatter.
What are the four principles of Bohr’s model?
Main Points of the Bohr Model are:
- Electrons orbit the nucleus in orbits that have a set size and energy.
- The energy of the orbit is related to its size.
- The lowest energy is found in the smallest orbit.
- Radiation is absorbed or emitted when an electron moves from one orbit to another.
What are the Neutral subatomic particles?
Neutral subatomic particle that is a constituent of every atomic nucleus except ordinary hydrogen. It has no electric charge and a rest mass equal to 1.67493 × 10⁻²⁷ kg marginally greater than that of the proton but nearly 1,839 times greater than that of the electron. Sir James Chadwick, the British Physicist discovered neutrons in 1932.
Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number
Atomic Number
The number of protons present in the nucleus is equal to atomic number (Z). For example, the number of protons in the hydrogen nucleus is 1, in sodium atom it is 11, therefore their atomic numbers are 1 and 11 respectively.
Atomic Mass Number
Together, the number of protons and the number of neutrons determine an element’s mass number: mass number = protons + neutrons. If you want to calculate how many neutrons an atom has, you can simply subtract the number of protons, or atomic number, from the mass number.
Isobars and Isotopes
Isobars
Isobars are the atoms with same mass number but different atomic number for example, ¹⁴C₆ and ¹⁴N₇.
Isotopes
Atoms with identical atomic number but different atomic mass number are known as Isotopes. chemical properties of atoms are controlled by the number of electrons, which are determined by the number of protons in the nucleus. Number of neutrons present in the nucleus have very little effect on the chemical properties of an element. Therefore, all the isotopes of a given element show same chemical behaviour.