NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control and Coordination in Hindi and English Medium for CBSE 2025-26 exams. The question answers of chapter 6 class 10th science are revised according to new syllabus and NCERT textbooks issued for academic year 2025-26.
Prepare of Class 10 Science for Board Exam
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Question Answers
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Exercises Solutions
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Intext Exercises
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 in Hindi Medium
Class 10 Science Book Download in PDF
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Board Questions
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 MCQ
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Extra Questions
Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions
Class 10 all Subjects Solutions
In NCERT Class 10 Science, Chapter 6 Control and Coordination, we focus on study about nervous system, endocrine system, and how organisms control and coordinate various functions in their bodies.
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Questions in Detail
- What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
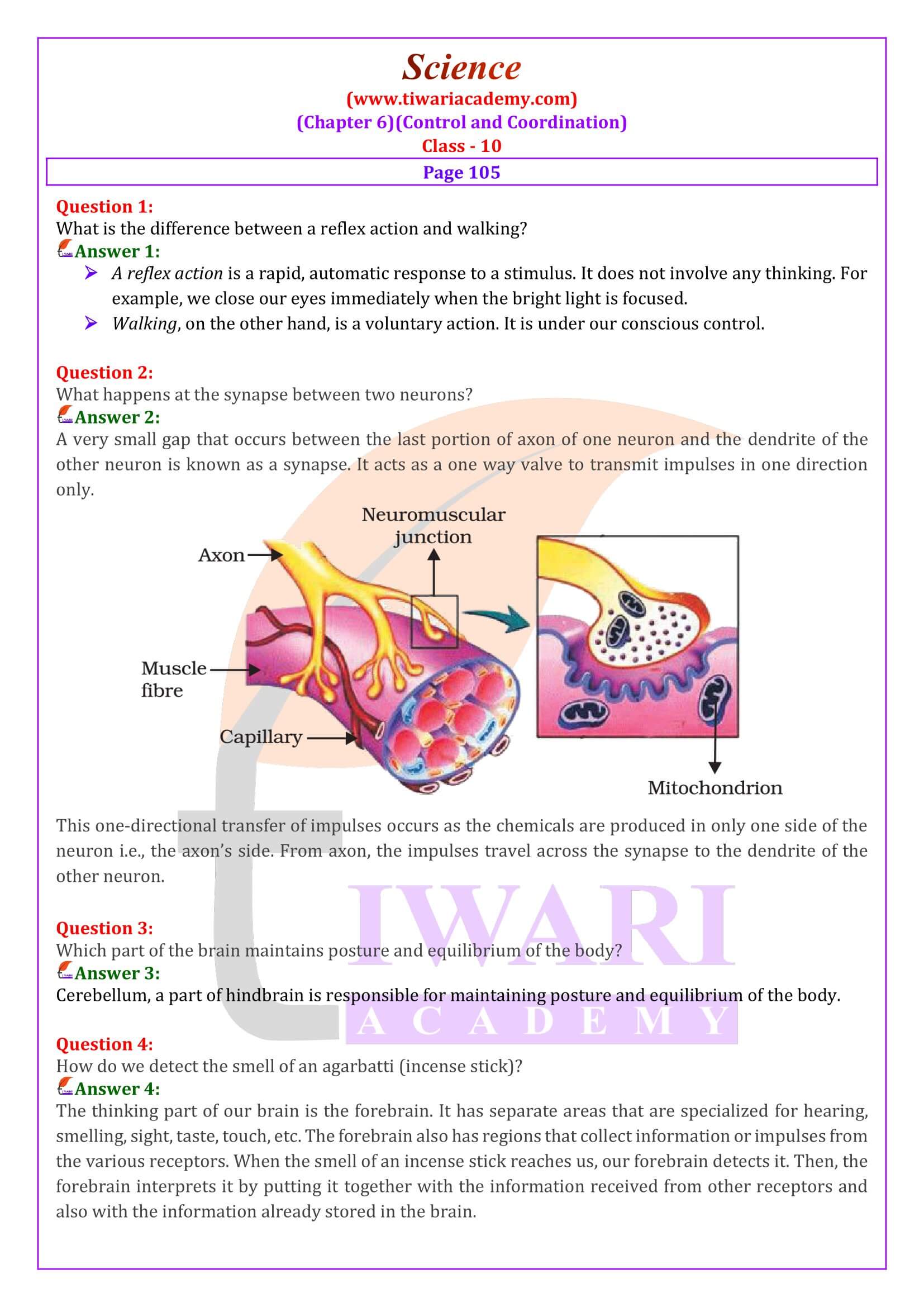
- What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
- Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
- How do we detect the smell of an Agarbatti (Incense Stick)?
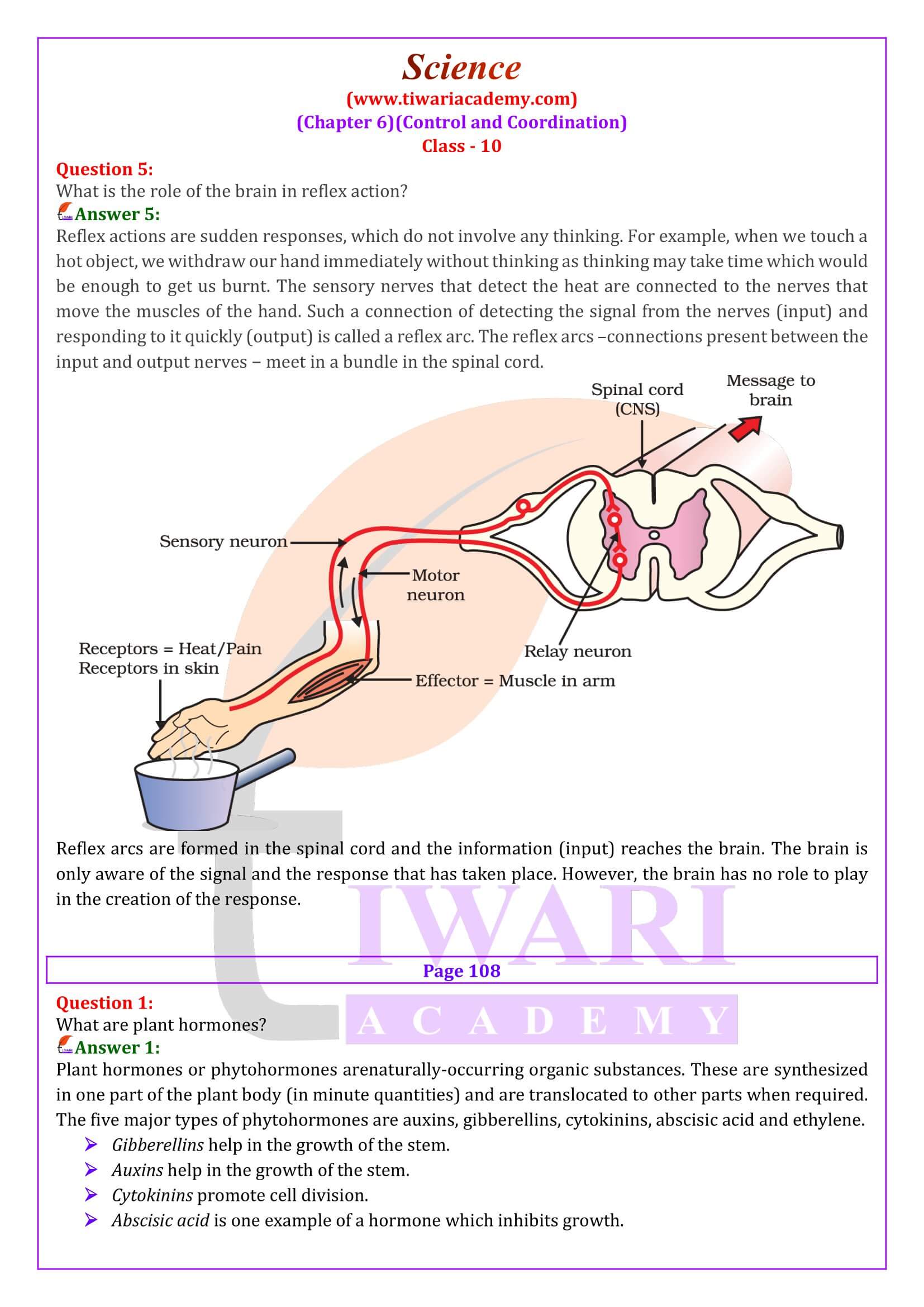
- What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
- What are plant hormones?
- How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
- Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
- How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
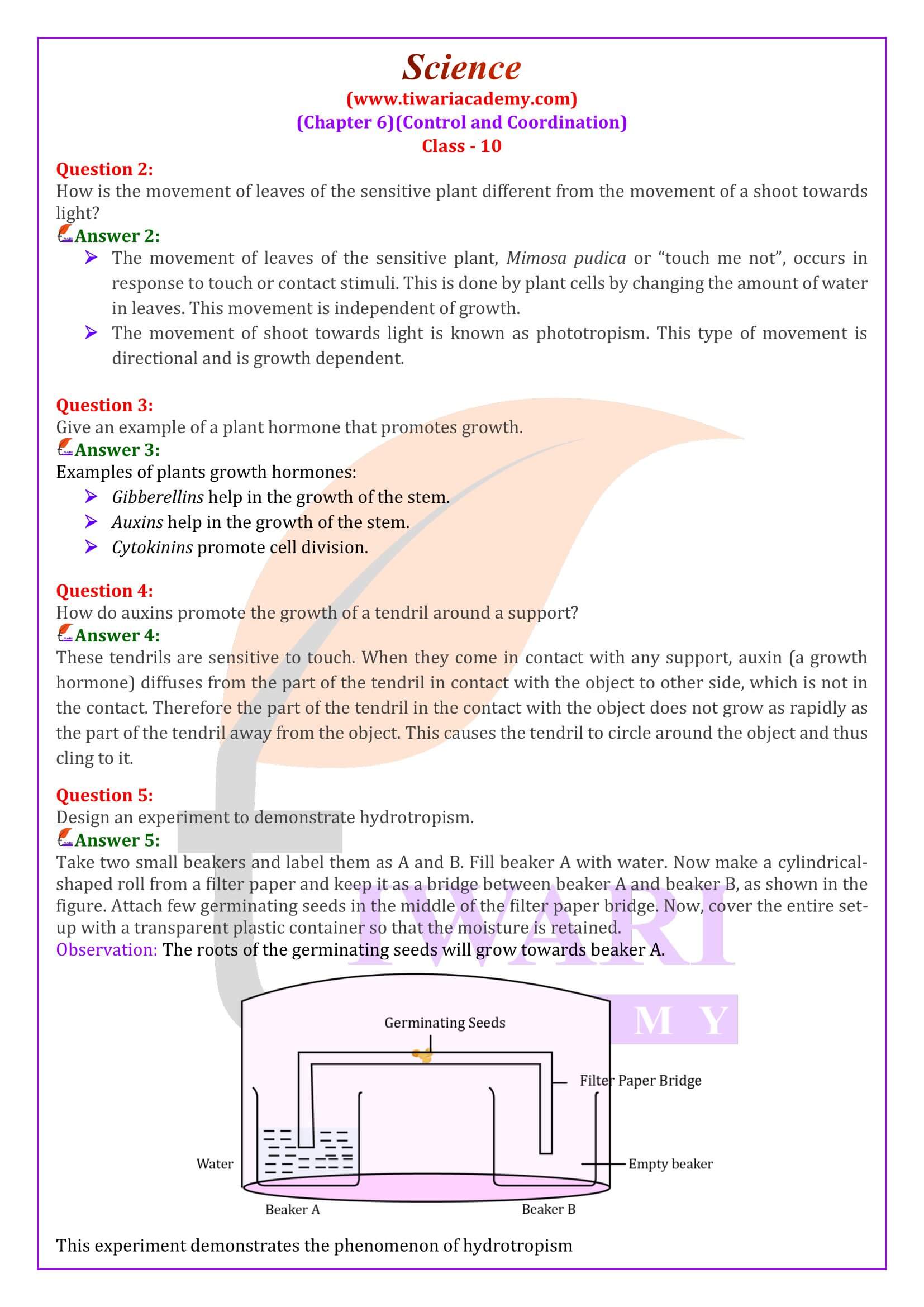
- Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
- How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
- Why is the use of iodised salt advisable?
- How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
- Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
- What is the function of receptors in our body?
- Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function.
- How does phototropism occur in plants?
- Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
- How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
- What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism?
- How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
- Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in animals.
- What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our legs?
| Class: 10 | Science – Biology |
| Chapter 6: | Control and Coordination |
| Content: | Exercise and Intext Questions |
| Content Type: | Text, PDF and Videos Format |
| Session: | CBSE 2025-26 |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
The main topics covered in this chapter are Introduction to Control and Coordination and the need for control and coordination in organisms. Overview of the nervous system and the endocrine system.
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Answers in Hindi and English Medium
- Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Exercises
- Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Intext Questions
- Class 10 Science Chapter 6 in Hindi
- Class 10 Science Chapter 6 in PDF
- Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Board Questions
- Class 10 Science Chapter 6 MCQ
- Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Extra Questions
- Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 all Subjects Solutions
The brief summary of class 10 science chapter 6 is as follows:
- Introduction to Control and Coordination: The chapter 6 of 10th science, begins by discussing the concept of movement in living organisms, distinguishing between movements caused by growth (as in plants) and those not connected to growth (as in animals). It emphasizes the importance of movement as a response to environmental changes and the necessity for controlled movement in response to various stimuli.
- Nervous and Muscular Tissues in Animals: This chapter explains how control and coordination in animals are facilitated by nervous and muscular tissues. It describes the structure of neurons, the transmission of nerve impulses, and the role of synapses in this process.
- Sensory Reception and Response: 10th science chapter 6 delves into how sensory information is detected by receptors located in sense organs and how this information triggers electrical impulses in nerve cells, leading to appropriate responses.
- Reflex Actions: The concept of reflex actions is explored, highlighting how these are quick, involuntary responses to stimuli. The chapter 6 of 10th science discusses the reflex arc and its efficiency in providing rapid responses without the need for conscious thought.
- Human Brain and Spinal Cord: The role of the human brain and spinal cord in control and coordination is examined. The brain is described as the main coordinating center, integrating sensory information and facilitating voluntary actions. The spinal cord’s role in reflex actions and as a conduit for information to and from the brain is also discussed.
- Functions of Different Brain Regions: Chapter 6, of class 10 science, breaks down the functions of various parts of the brain, including the fore-brain, mid-brain, and hind-brain. It details how different brain regions are responsible for processing sensory information, voluntary actions, and involuntary actions like blood pressure regulation and digestion.
- Role of the Cerebellum: The cerebellum’s function in maintaining posture, balance, and precision in voluntary actions is highlighted.
- Class 10 Science chapter 6 provides an overview of the key concepts related to control and coordination in living organisms, particularly focusing on the nervous system and brain functions in humans.
The topics covered under the nervous system are the Structure and function of neurons (nerve cells). Generation and transmission of nerve impulses. Parts of the human nervous system (central nervous system and peripheral nervous system). Role of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Reflex actions and their significance.
How sensory organs detect external stimuli (light, sound, chemicals, etc.). Role of sense organs in gathering information about the environment. The senses that we tend to think of as exclusive to animals, which also exist in plants: they see, hear, smell, and taste, and of course respond to touch.

The brain is the most complex part of the human body. The human brain performs activities like intelligence, interpreter of the senses, initiator of body movement, and controller of behavior. Structure and functions of different parts of the brain (forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain). Control of various body functions by different regions of the brain. The importance of the brain in regulating activities like thinking, memory, and emotions.
The endocrine system and its components (endocrine glands). Role of hormones in the body. Key endocrine glands such as the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, pancreas, and gonads. Functions of hormones produced by these glands. Hormones in Animals, Hormones involved in growth, metabolism, and reproduction. Role of hormones like insulin and glucagon in blood sugar regulation. Control of growth hormones and sex hormones.
Class 10 Science chapter 6 helps students understand how living organisms, including humans and plants, control and coordinate various physiological processes to adapt to their surroundings and maintain internal balance. It provides a fundamental understanding of the nervous and endocrine systems and their roles in regulating bodily functions.
Preparing for NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 6, Control and Coordination, requires a strategic approach to ensure a thorough understanding of the concepts. Here are some effective strategies for better preparation- Read the Chapter Thoroughly, and begin by reading the chapter from start to finish.
This will give you an overall idea of the topics covered and their sequence. Make Notes while reading, make concise notes summarizing key points, definitions, and important concepts. Understand the Basics, Focus on understanding the basics of the nervous system and the endocrine system. Pay attention to the structure and function of neurons, glands, and hormones.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7
All the Offline Apps and NCERT Solutions are based on latest CBSE Syllabus. 10th Science Biology solutions of questions given in Hindi Medium are free to view online or download in PDF format.
Download Offline Apps to use it without internet. Class X Science chapter 7 intext questions answers on Page 119 or Page 122 or Page 125 and Exercises answers in English as well as Hindi Medium free to download in PDF file format.
Use of diagrams and flowcharts to help students to understand topics in a better way. Create diagrams and flowcharts to visualize the structures and processes discussed in the chapter. Drawing diagrams can help you remember complex concepts. Analyze diagrams and figures, and pay close attention to any diagrams, figures, or labeled illustrations provided in the chapter. Understand the parts and their functions.
Understand the structure and function of sensory organs (eyes, ears, etc.) and how they detect stimuli. Practice relating these to real-life examples. Learn about reflex actions and understand the concept of reflex actions and how they occur. Be prepared to explain the reflex arc and its components. Memorize Key Hormones, Memorize the names and functions of important hormones produced by various endocrine glands. Mnemonics can be helpful for this.

Solve sample questions and exercises provided at the end of the chapter or in your textbook. Use additional resources, if you find certain concepts challenging, refer to additional resources such as online tutorials, videos, or reference books to gain a deeper understanding. Teach or Discuss with Peers, explaining concepts to others or discussing them with peers can reinforce your understanding. It also helps you remember the material better.
Allocate specific time slots for studying class 10 chapter 6 in your overall study schedule. Consistency is key to effective learning. Revise Regularly, Periodic revision is crucial. Revisit your notes and practice questions to reinforce your memory. Seek Clarification, if you have doubts or find certain topics confusing, don’t hesitate to seek clarification from your teacher or tutor.
10th Science Chapter 6 Answers in English & Hindi Medium
All Subjects NCERT Solutions for class 10 are in PDF and Free to download. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control and Coordination Intext questions and chapter end exercises question answers are given below to free download. All the answers are updated for session 2025-26 based on latest NCERT Books following the current CBSE Syllabus.
Practice Previous Year’s Questions, solve previous years’ question papers to get a sense of the types of questions that may appear in the board exams. Remember that understanding the concepts is more important than rote memorization. Use these strategies to build a strong foundation in Chapter 6, as it forms the basis for understanding more advanced biology concepts in the future.
Difference between Voluntary and Involuntary Actions
Voluntary Actions
The actions are under the will or consciousness of the individual. They may or may not involve information from receptors or sense organs. Impulses originate in the brain. Every voluntary action occurs under conscious directions from brain. The actions employ voluntary muscles. Voluntary actions do not occur in the form of an arc. Mainly three parts are involved brain, efferent neuron and effector organ.
Involuntary Actions
Actions occur without consulting the will. Involuntary actions always occur in response to stimuli picked up by receptors. Impulses originate in the region of receptors. Brain is seldom consulted consciously through an involuntary action always involves spinal cord or brain for transfer of information from afferent neurons to efferent neurons. The actions employ involuntary muscles but occasionally voluntary muscles also get involved.
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Extra Question Answers
How does over production of hormones controlled? Give one example.
Endocrine glands or ductless glands produce hormones and directly pour their secretion in the blood. These glands do not go on producing hormones. Their secretion is controlled by feedback information system. Thus their over production of hormones is controlled.
For example, a hormone called TSH is secreted by pituitary gland. TSH stimulates the production of thyroxine from the thyroid gland. But if there is over production of thyroxine hormone, this hormone acts on pituitary gland and controls the production of TSH. As a result, the production of thyroxine by the thyroid gland is controlled. Thus, TSH and thyroxine control the level of each other. This mechanism of opposing effect is called feedback mechanism.
Differentiate between sensory neurons and motor neurons.
Sensory neurons carry sensory impulse from receptors to the nerve cell body or to the region which receives sensory impulses. Whereas motor neurons carry information of action to be carried by the conserved voluntary muscles.
How is brain protected in our body?
Human brain is lodged in a bony case, the cranium which protects it from injuries. It is wrapped in three sheets of connective tissue, known as meninges. The space between the meninges is filled with cerebrospinal fluid which helps in absorption of shocks.
Name the part of the brain responsible for precision of voluntary action and maintaining body posture and balance of the body.
Fore-brain is responsible for precision of voluntary action.
Cerebellum is responsible for maintaining the posture and keeping balance of the body.
What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
Reflex actions are controlled by spinal cord, although the information input also goes on to reach the brain. However, conditioned reflexes (based on previous experiences), such as salivation after seeing good food are controlled by cerebral cortex of brain.
How does adrenaline help an athlete to prepare for running?
Adrenaline causes the heart beat faster, resulting in supply of more oxygen. It causes reduction in supply of blood to the digestive system and skin. This diverts the blood to our skeletal muscle. The breathing rate also increases. All these responses together help an athlete to prepare for running.
What is meant by Tropic movement? Why do tropic movements takes place in plants?
The directional (tropic) response of plants shown by the plants towards or away of the stimulus such as light, water, gravity, etc. is known as tropism.
Tropic movements in plants are growth related. Plants respond to stimuli slowly by growing in a particular direction, either towards stimulus or away from. This growth causing tropic movement is regulated by the plant hormone called auxin.
Questions for Practice
Question:
State the function of any three of the structural and functional unit of nervous system.
Answer:
Nervous system: Main parts of nervous system are: (i) Central nervous system, (ii) Peripheral nervous system, (iii) Autonomous System.
(i) Central Nervous System: It consist of
(a) Brain receives information carrying impulses from all the sensory organs (by sensory nerves) of the body and also from the spinal cord. The brain respond to the information by sending its own instructions (through motor nerves) to the muscles and glands to act accordingly. The brain also stores information and act as organ of thought and intelligence.
(b) Spinal cord: It is concerned with spinal reflex actions and the conduction of nerve impulses to and from the brain.
(ii) Peripheral Nervous system: it is composed of cranial nerves (nerves from the brain) and the spinal nerves. Both of these consist of sensory and motor neurons. So, they carry sensations to and messages from the brain and the spinal cord.
(iii) Autonomous Nervous System: It is that part of the peripheral nervous system which controls the activities of the internal organs such as stomach, heart-beat, etc. automatically even without our thinking about them. Its nerves are attached to the smooth muscles and control the activities of internal organs of the body involuntarily, many these nerves are connected with the mid- brain and hind-brain.
To help students prepare for exams, the platform may offer sample papers and previous years’ question papers. Solving these papers can help students familiarize themselves with the exam pattern and practice answering questions effectively. Many online education platforms, like Tiwari Academy, have doubt-clearing sessions where students can ask questions related to the chapter, and educators or experts will provide explanations and clarifications.
Questions from Board Papers
Question 1:
(a) If the cerebellum is not functioning properly, state the activities of our body that are affected.
(b) how do muscles move?
Answer 1:
(a) Cerebellum is not functioning properly may affect-
(i)Walking in straight line
(ii)Riding a cycle
(iii)Maintaining the posture and balance of the body
(iv)Movement is very coordinate, the patient sways in walking and tend to fall towards the affected side.
(v)It is responsible for precision of voluntary actions.
(b) When the decision to move is conveyed by a nerve to a muscle, it has to act. In response to nervous electrical impulses. The special proteins of the muscle change both their shape and their arrangement in the cell. This new arrangement of these proteins give the muscle cells a shorter form that causes movement of the muscle.
Interactive quizzes and tests can help students assess their knowledge and track their progress. These quizzes may be designed to simulate the format of actual exams. Class 10 Science Chapter 6 involve complex diagrams and illustrations related to the nervous system, sense organs, and hormone regulation. Tiwari Academy provide labeled diagrams and explanations to help students understand these concepts better.
Question:
“Use of iodised salt is essential”. List three reasons to justify this statement.
Answer:
(i) Iodised salt supplies sufficient amount of iodine through our diet, even in the areas where iodine is not available naturally through water or otherwise in diet.
(ii) Iodine is necessary for the thyroid glands to make thyroxine hormone.
(iii) Proper supply of iodine maintains thyroxine level that regulates carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism to provide the best balance for growth.
(iv) Deficiency of iodine causes many diseases such as Goitre.
Diagrams related to the nervous system, sense organs, and hormone regulation are often included in the examination. Students may be asked to label these diagrams or explain specific parts and their functions. Reflex actions, a key topic in chapter 6 of 10th Science, are frequently examined. Questions may require students to explain the sequence of events in a reflex arc or discuss the significance of reflexes in protecting the body.
The chapter 6 of 10th Science covers the endocrine system and hormones. Students may be asked to identify hormones, their sources, and their functions. Additionally, questions related to the regulation of bodily functions by hormones are common. Some questions may require students to compare and contrast the roles of the nervous system and the endocrine system in control and coordination.
Understanding these differences is crucial for answering such questions accurately. To assess a student’s application of knowledge, examination questions may present scenarios or case studies related to control and coordination. Students may need to analyze these situations and explain how the body responds.
Important Questions on 10th Science Chapter 6
What is the function of receptors in our body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
Receptors are sensory structures (organs/tissues or cells) present all over the body. The receptors are either grouped in case of eye or ear, or scattered in case of skin. Functions of receptors: They sense the external stimuli such as heat or pain. They also trigger an impulse in the sensory neuron which sends message to the spinal cord. When the receptors are damaged, the external stimuli transferring signals to the brain are not felt. For example, in the case of damaged receptors, if we accidentally touch any hot object, then our hands might get burnt as damaged receptors cannot perceive the external stimuli of heat and pain.
How does phototropism occur in plants?
The movement of plant in response to light is called phototropism. Stem shows positive phototropism as follows: When growing plants detect light, a hormone called auxin, synthesised at the shoot tip, helps the cells to grow longer. When light is coming from one side of the plant, auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot. This concentration of auxin stimulates the cells to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light. Thus, the plant appears to bend towards light.
Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
The reflex arc connections between the input and output nerves meet in a bundle in the spinal cord. In fact, nerves from all over the body meet in a bundle in the spinal cord on their way to the brain. In case of any injury to the spinal cord, the signals coming from the nerves as well as the signals coming to the receptors will be disrupted.
How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Plants respond to stimuli by showing movements. The growth, development, and responses to the environment in plants is controlled and coordinated by a special class of chemical substances known as hormones. These hormones are produced in one part of the plant body and are translocated to other needy parts. For example, a hormone produced in roots is translocated to other parts when required. The five major types of phytohormone are auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, and ethylene. These phytohormones are either growth promoters (such as auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, and ethylene) or growth inhibitors such as abscisic acid.
What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism?
The maintenance of the body functions in response to changes in the body by working together of various integrated body systems is known as coordination. All the movements that occur in response to stimuli are carefully coordinated and controlled. In animals, the control and coordination movements are provided by nervous and muscular systems. The nervous system sends messages to and away from the brain. The spinal cord plays an important role in the relay of messages. In the absence of this system of control and coordination, our body will not be able to function properly. For example, when we accidentally touch a hot utensil, we immediately withdraw our hand. In the absence of nerve transmission, we will not withdraw our hand and may get burnt.
How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
Involuntary actions cannot be consciously controlled. For example, we cannot consciously control the movement of food in the alimentary canal or pumping of blood through heart. These actions are however directly under the control of the brain. On the other hand, the reflex actions such as closing of eyes immediately when bright light is focused show sudden response and do not involve any thinking. This means that unlike involuntary actions, the reflex actions are not under the control of brain.
What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
A reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus. It does not involve any thinking. For example, we close our eyes immediately when the bright light is focused. Walking, on the other hand, is a voluntary action. It is under our conscious control.
Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
Cerebellum, a part of hindbrain is responsible for maintaining posture and equilibrium of the body.
What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
Reflex actions are sudden responses, which do not involve any thinking. For example, when we touch a hot object, we withdraw our hand immediately without thinking as thinking may take time which would be enough to get us burnt. The sensory nerves that detect the heat are connected to the nerves that move the muscles of the hand. Such a connection of detecting the signal from the nerves (input) and responding to it quickly (output) is called a reflex arc. The reflex arcs –connections present between the input and output nerves − meet in a bundle in the spinal cord. Reflex arcs are formed in the spinal cord and the information (input) reaches the brain. The brain is only aware of the signal and the response that has taken place. However, the brain has no role to play in the creation of the response.
What are plant hormones?
Plant hormones or phytohormones arenaturally-occurring organic substances. These are synthesized in one part of the plant body (in minute quantities) and are translocated to other parts when required. The five major types of phytohormones are auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid and ethylene. Gibberellins help in the growth of the stem. Auxins help in the growth of the stem. Cytokinins promote cell division. Abscisic acid is one example of a hormone which inhibits growth.
How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
These tendrils are sensitive to touch. When they come in contact with any support, auxin (a growth hormone) diffuses from the part of the tendril in contact with the object to other side, which is not in the contact. Therefore the part of the tendril in the contact with the object does not grow as rapidly as the part of the tendril away from the object. This causes the tendril to circle around the object and thus cling to it.
How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Chemical coordination takes place in animals with the help of hormones. Hormone is the chemical messenger that regulates the physiological processes in living organisms. It is secreted by glands. The regulation of physiological processes and control and coordination by hormones comes under the endocrine system. The nervous system along with the endocrine system in our body controls and coordinates the physiological processes.
How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
Adrenalin is a hormone secreted by the adrenal glands in case of any danger or emergency or any kinds of stress. It is secreted directly into the blood and is transported to different parts of the body. When secreted in large amounts, it speeds up the heartbeat and hence supplies more oxygen to the muscles. The breathing rate also increases due to contractions of diaphragm and rib muscles. It also increases the blood pressure. All these responses enable the body to deal with any stress or emergency.
Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Diabetes is a disease in which the level of sugar in the blood is too high. Insulin, a hormone secreted by the pancreas, helps in regulating the blood sugar levels. This is the reason why diabetic patients are treated by giving injections of insulin.
Class 10 Science chapter 6 bridges the gap between biology and physiology. Students may encounter interdisciplinary questions that require them to integrate knowledge of control and coordination with related concepts in physics or chemistry. A strong understanding of control and coordination is essential for students who plan to pursue biology or related fields in the future. This chapter serves as a foundation for more advanced studies.
Students can typically access these resources at their own pace, allowing them to study at a speed that suits their learning style and schedule. Many platforms, including Tiwari Academy, offer mobile apps, making it convenient for students to access study materials, videos, and practice questions on their smartphones or tablets. Some platforms have online communities or forums where students can interact with peers, discuss doubts, and share study strategies.
How can Tiwari Academy help the students in preparation for NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 6?
Tiwari Academy’s offerings as online education platforms, website, apps for Android and iOS for iPhone and iPad. They typically offer various resources and support to help students prepare for chapters like NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 6, Control and Coordination. Here are ways in which Tiwari Academy or similar platforms may assist students in their preparation.
Tiwari Academy provide comprehensive chapter notes that summarize key concepts, definitions, and important points from Chapter 6. These notes can serve as a quick reference for students. The platform offer video tutorials that explain complex topics from the chapter in an easy-to-understand manner. Visual aids can help students grasp concepts more effectively. Tiwari Academy provides a variety of practice questions and exercises related to Chapter 6. These questions can help students test their understanding of the material and improve their problem-solving skills.
To get the most accurate and up-to-date information on how Tiwari Academy specifically helps students with NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 6 or any other chapter, I recommend visiting their official website or contacting them directly. They have introduced new features or resources.
From the examination point of view, what is the importance of NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 6?
NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 6, Control and Coordination, is important from an examination point of view for several reasons. This chapter typically carries a significant weightage in the Class 10 Science examination conducted by various educational boards, including the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) in Bharat. This means that a notable portion of the exam paper is dedicated to questions from this chapter.
Class 10 Science chapter 6 covers fundamental concepts related to control and coordination in organisms, including the nervous system, sensory organs, reflex actions, and the endocrine system. These concepts are essential building blocks for understanding more advanced biology topics in higher classes. Many of the concepts discussed in this chapter have practical applications in real life. Students may encounter questions that ask them to relate the principles of control and coordination to everyday situations.
To excel in the examination, students should thoroughly study NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 6, practice solving questions from the chapter, and understand the underlying concepts. Additionally, reviewing previous years’ question papers and sample papers can provide valuable insights into the types of questions that may be asked in the exam.
How many questions are in between chapter 6 and the back exercise of chapter 6 of 10th standard Science?
There are 14 (5 questions on page number 119, 5 questions on page number 122, 4 questions on page number 125) questions between chapter 6 of class 10th Science and 12 questions in the back exercise of chapter 6 of class 10th Science.
Are there any questions in chapter 6 of grade 10th Science that are important for the exams?
There are 26 questions in chapter 6 of grade 10th Science out of which questions 1, 2, 3 (page number 119), questions 2, 4 (page number 122), questions 1, 2, 3 (page number 125), and questions 4, 5, 10, 11, 12 of back exercise of chapter 6 of class 10th Science are important. Students can’t skip these questions for the exams as they are significant.
Is chapter 6 of class 10th Science interesting?
Yes, chapter 6 of class 10th Science is interesting. Students study the following interesting topics in this chapter:
- 1. Animals – Nervous System
- 2. What happens in Reflex Actions?
- 3. Human Brain
- 4. How are these Tissues protected?
- 5. How does the Nervous Tissue cause Action?
- 6. Coordination in Plants
- 7. Immediate Response to Stimulus
- 8. Movement Due to Growth
- 9. Hormones in Animals
Why are activities given in chapter 6 of grade 10th Science?
Chapter 6 of grade 10th Science has four activities. Activities are given in chapter 6 of grade 10th Science because activities help students to understand the chapter practically and easily. Activities help teachers also to teach the chapter with the help of some practical examples.