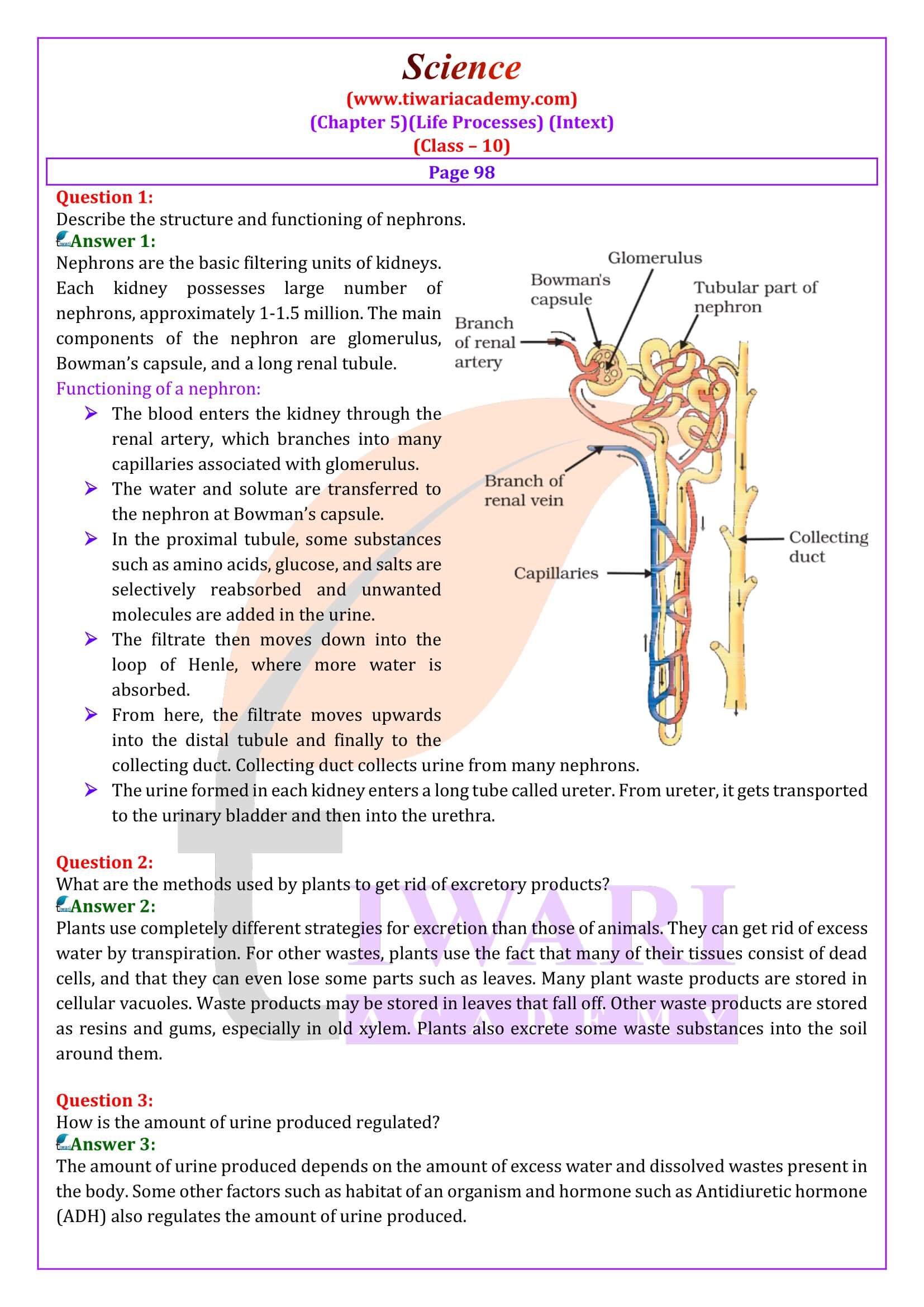
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Life Processes in Hindi and English Medium updated for CBSE 2025-26. Get the revised question answers of chapter 5 class 10th science based on new syllabus and latest textbooks issued for academic session 2025-26.
Easy Way to Prepare Class 10 Science for Exams
Question Answers of Class 10 Science Chapter 5
Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Exercises Solutions
Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Intext Exercises
Class 10 Science Chapter 5 MCQ
Class 10 Science Chapter 5 in Hindi Medium
Class 10 Science Book Download in PDF
Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Board Questions
Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Extra Questions
Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions
Class 10 all Subjects Solutions
In NCERT Class 10 Science, Chapter 5 Life Processes. This chapter explores the fundamental processes that occur in living organisms to maintain life, whether they are microorganisms, plants, or animals. Go through summary of the chapter to simplify the topic.
Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Answers in Detail
- Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans?
- What criteria do we use to decide whether something is alive?
- What are outside raw materials used for by an organism?
- What processes would you consider essential for maintaining life?
- What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition?
- Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
- What is the role of the acid in our stomach?
- What is the function of digestive enzymes?
- How is the small intestine designed to absorb digested food?
- What advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
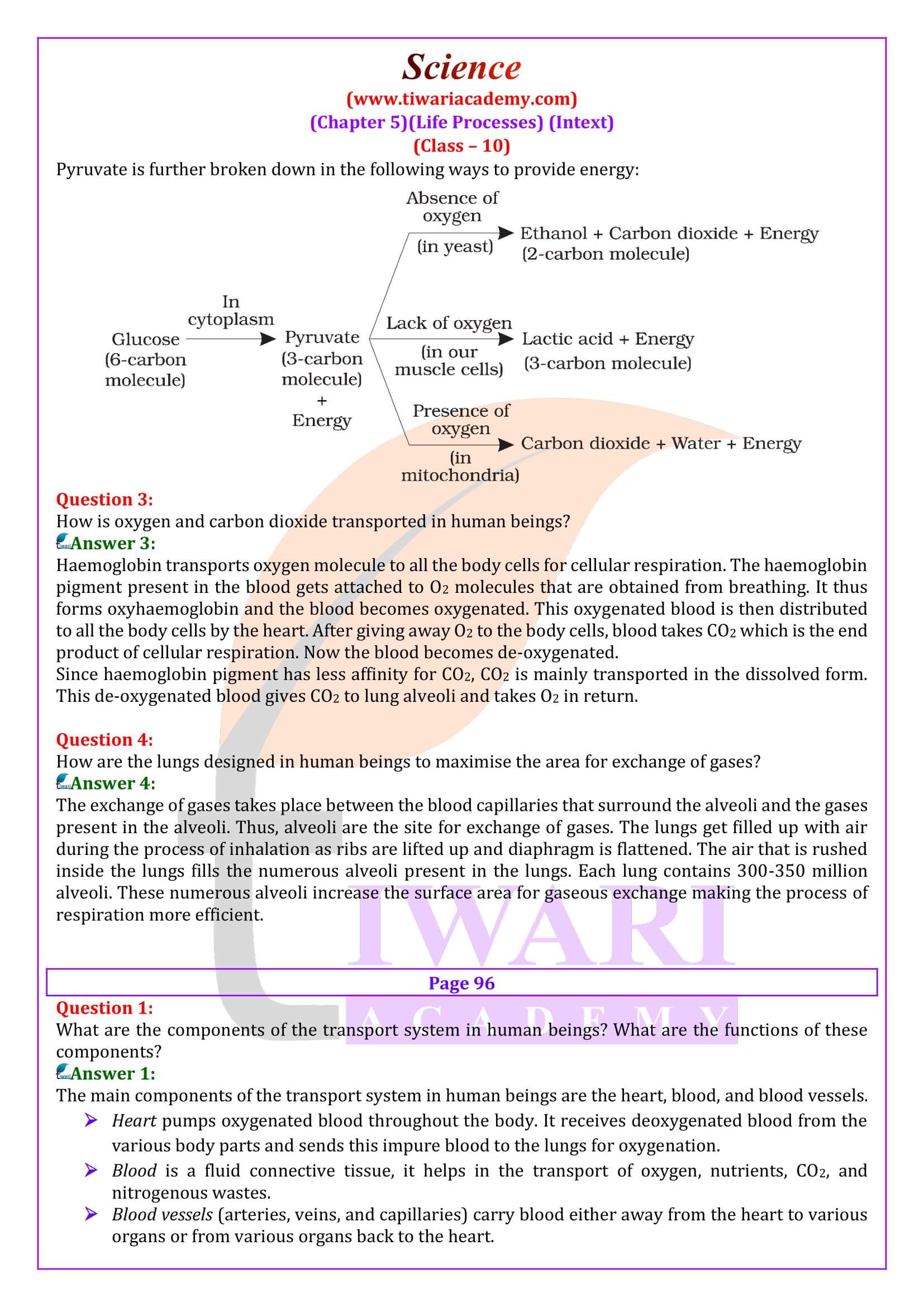
- What are the different ways in which glucose is oxidised to provide energy in various organisms?
- How is oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in human beings?
- How are the lungs designed in human beings to maximise the area for exchange of gases?
- What are the components of the transport system in human beings?
- Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds?
- What are the components of the transport system in highly organised plants?
- How are water and minerals transported in plants?
- How is food transported in plants?
- Describe the structure and functioning of nephrons.
- What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products?
- How is the amount of urine produced regulated?
- How are fats digested in our bodies? Where does this process take place?
- What is the role of saliva in the digestion of food?
- What are the necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition and what are its byproducts?
- What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
- How are the alveoli designed to maximise the exchange of gases?
- What would be the consequences of a deficiency of haemoglobin in our bodies?
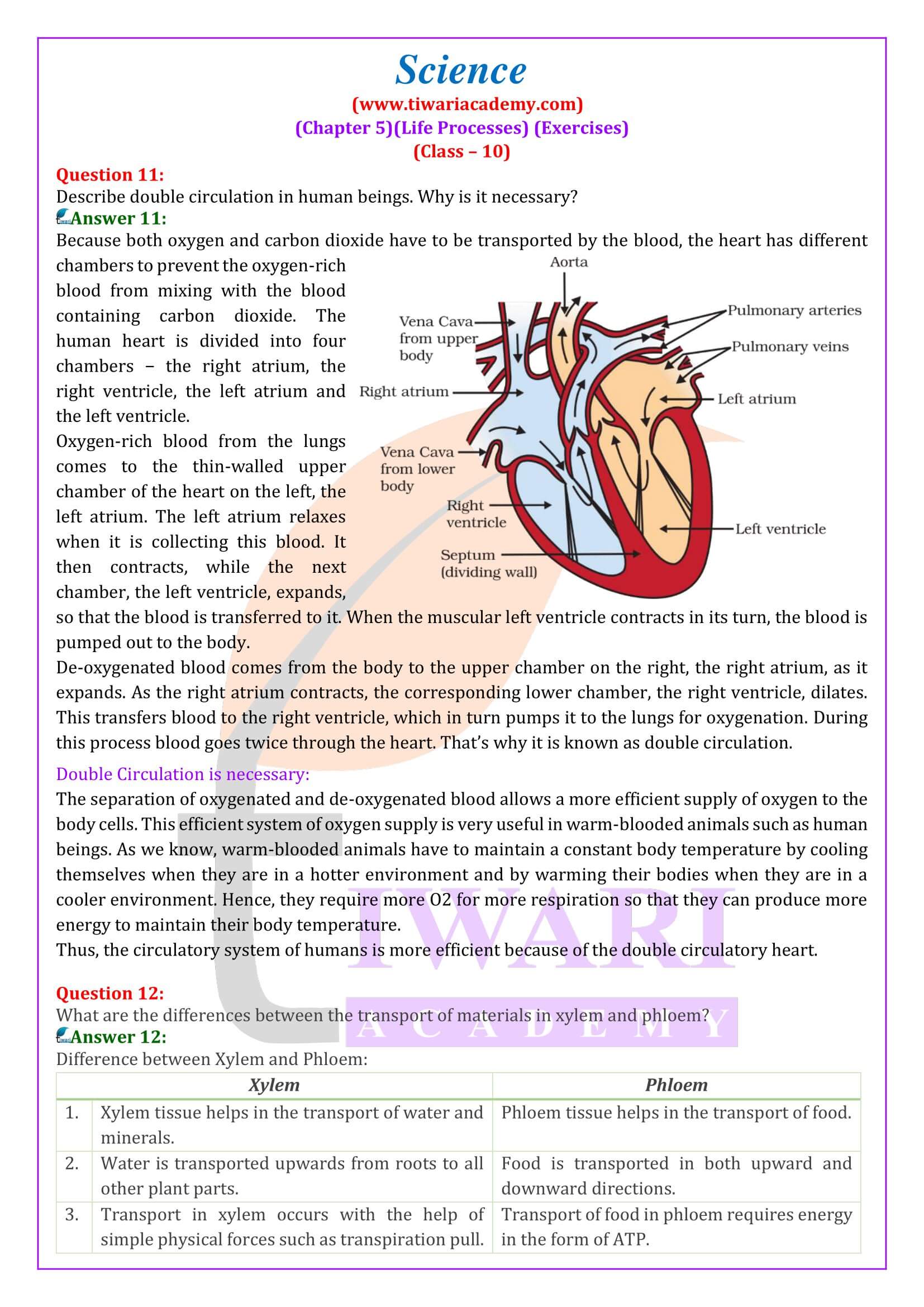
- Describe double circulation of blood in human beings. Why is it necessary?
- What are the differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem?
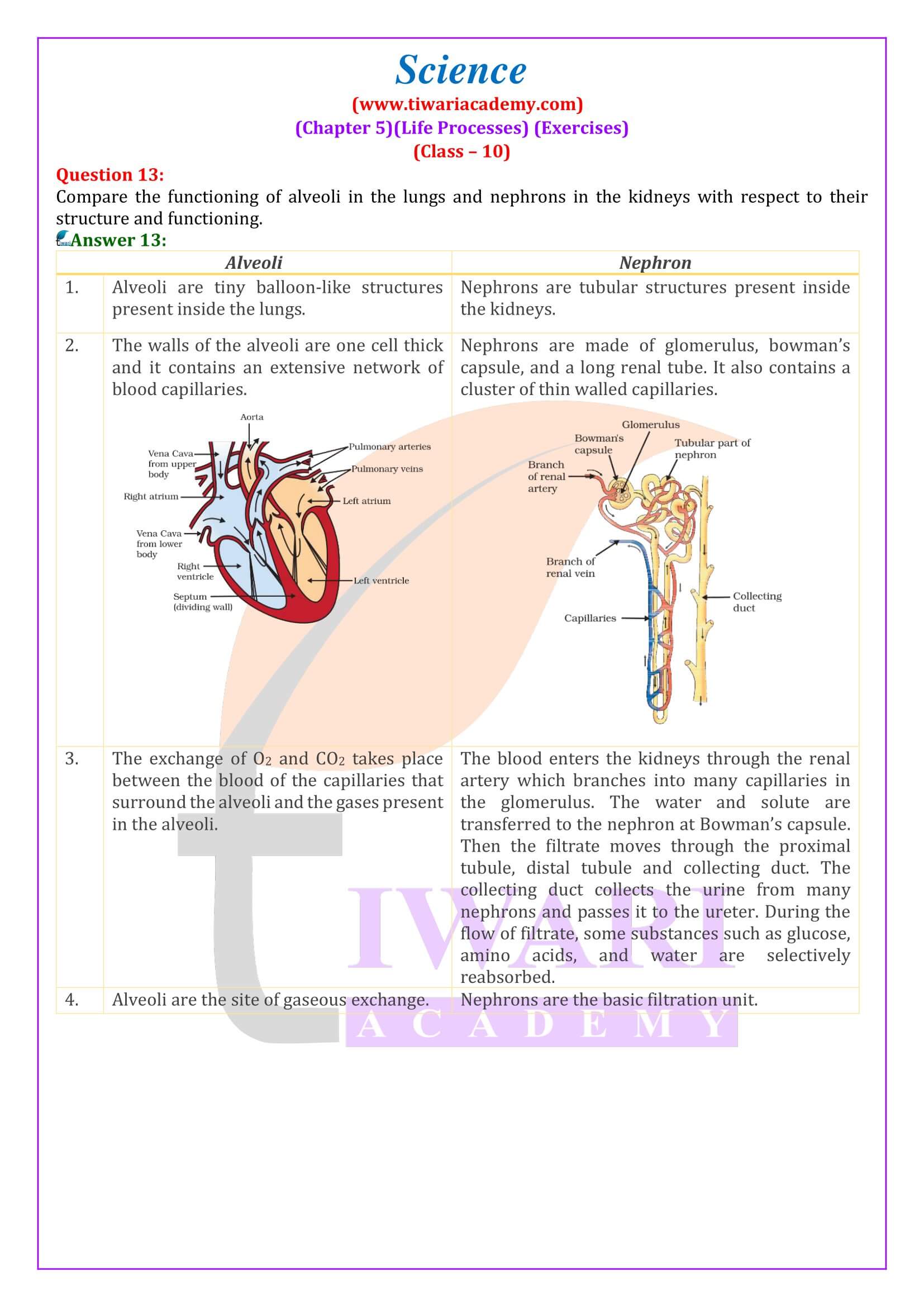
- Compare the functioning of alveoli in the lungs and nephrons in the kidneys with respect to their structure and functioning.
| Class: 10 | Science – Biology |
| Chapter 5: | Life Processes |
| Content: | NCERT Exercise Solution |
| Content Type: | PDF and Videos Format |
| Session: | CBSE 2025-26 |
| Medium: | Hindi and English Medium |
To maintain life all living species require energy which they get in the form of food from different sources. Understanding the concept of life processes that are essential for the survival of living organisms.
Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Answers in Hindi and English Medium
- Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Exercises
- Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Intext Questions
- Class 10 Science Chapter 5 in Hindi
- Class 10 Science Chapter 5 in PDF
- Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Board Questions
- Class 10 Science Chapter 5 MCQ
- Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Extra Questions
- Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 all Subjects Solutions
Nutrition in Plants and Animals
Modes of nutrition in plants, including autotrophic nutrition (photosynthesis). The structure and function of chloroplasts. The process of capturing light energy to convert it into chemical energy (glucose). Modes of nutrition in animals, including heterotrophic nutrition. The digestive system in humans and its components. Digestion and absorption of food in the human digestive system. The role of various digestive enzymes.
Respiration in Organisms
The food material taken in during the process of nutrition is used in cells to provide energy for various life processes. Diverse organisms do this in different ways – some use oxygen to break down glucose completely into carbon dioxide and water, and some use other pathways that do not involve oxygen. The process of respiration in plants and animals. The respiratory system in humans and its components. Cellular respiration: The breakdown of glucose to release energy (ATP). Aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Basic differences between Aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Respiratory organs in plants, micro-organisms, animals, and humans.
Transportation in Plants and Animals
The need for transportation of substances in plants. The structure and function of the vascular tissue (xylem and phloem). How water and minerals are transported through the plant. The process of transpiration and its significance.
The circulatory system in humans and its components (heart, blood vessels, blood). The functions of blood, include the transportation of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products. The structure and function of the heart. The concept of double circulation.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5
NCERT Solutions given on inside the chapter 5 of 10th Science intext question and all other questions answers in Hindi Medium free to study online or download in PDF file format. UP Board Solutions and NCERT textbook solutions or Solutions Apps for class 10 all subjects are also given. Class X Science chapter 5 all intext question answers given on Page 95 or Page 101 or Page 105 or Page 110 or Page 112 or Exercises in Hindi and English Medium updated for 2025-26.
Excretion in Organisms, plants, and animals
The biological process involved in the removal of these harmful metabolic wastes from the body is called excretion. Different organisms use varied strategies to do this. The importance of excretion in living organisms. The excretory system in humans (kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra). The formation of urine and its composition. Role of the skin and lungs in excretion.
Focus on Key Concepts of Life Processes
Nutrition in plants: Understand the process of photosynthesis, including the role of chloroplasts and factors affecting photosynthesis.
Nutrition in animals: Learn about the components of the human digestive system and the functions of digestive enzymes.
Respiration: Comprehend cellular respiration, aerobic vs. anaerobic respiration, and the structure of the respiratory system.
Transportation: Understand the vascular tissue in plants (xylem and phloem) and the circulatory system components in humans.
Excretion: Study the human excretory system, including the role of kidneys and the composition of urine.
Control and Coordination: Explore the nervous system, reflex actions, and the endocrine system.
Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Practice Tests with Answers
Preparation Method for Board Exams
Create flashcards for important terms, processes, and concepts. Use these flashcards for quick revision and self-quizzing. Practice drawing diagrams of the digestive system, respiratory system, and circulatory system to reinforce your understanding.
Answer the exercise questions at the end of class 10 science chapter 5. These questions are designed to test your comprehension of the material. If you have doubts or questions about any topic within the chapter, don’t hesitate to ask your teacher for clarification or seek help from peers or online resources.
In addition to the NCERT textbook, consider using reference books, online tutorials, and educational websites to reinforce your understanding of life processes. Create concept maps or mind maps to visualize the relationships between different processes and concepts within the chapter.
Practice taking mock tests or sample papers to assess your knowledge and time management skills. Regularly review the chapter to reinforce your understanding. Don’t wait until the last minute to revise. Consistency in your study routine is key. Allocate dedicated study time for this chapter regularly rather than cramming.
By following strategies, given here, and maintaining a disciplined study routine, you can prepare for NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 5 effectively and perform well in your exams. Understanding the processes of life is fundamental to biology and lays the foundation for more advanced studies in the subject.
Tiwari Academy provide a wide range of practice questions and exercises related to Chapter 5. These questions are designed to help students test their understanding of the material and improve their problem-solving skills. To help students prepare for exams, Tiwari Academy offer sample papers and previous year’s question papers for Class 10 Science.
Solving these papers can give students a sense of the exam pattern and help them practice answering questions effectively. Many online platforms, including Tiwari Academy, offer doubt-clearing sessions where students can ask questions related to the chapter, and experts or educators will provide explanations and clarifications. Interactive quizzes and tests can help students assess their knowledge and track their progress. These quizzes are often designed to mimic the format of actual exams.
10th Science Chapter 5 Answers in English & Hindi Medium
NCERT book solutions for 10 Science Chapter 5 question answers which are given inside the book and at the end of chapters are given below. All the solutions are free to use and updated for new academic session. NCERT Solutions Offline Apps for class 10 Science in Hindi and English Medium based on latest CBSE Syllabus are available to free download.
The excretory system, a key topic in chapter 5 of 10th science, often appears in the examination. Questions related to the structure and function of excretory organs and the importance of excretion are common. Understanding how plants carry out life processes, such as photosynthesis, respiration, and transportation of water and nutrients, is essential. Questions related to these processes in plants are frequently included in the exam.
Tiwari Academy also offer additional resources such as revision notes, mind maps, and mnemonic techniques to aid in memory retention. Self-Paced Learning: Students can typically access these resources at their own pace, allowing them to study at a speed that suits their learning style and schedule. This platforms offer Android and iOS apps for iPad and iPhone, making it convenient for students to access study materials and practice questions on their smartphones or tablets.
Some platforms have online communities or forums where students can interact with peers, discuss doubts, and share study strategies. To get the most accurate and up-to-date information on how Tiwari Academy specifically helps students with NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 5 or any other chapter, I recommend visiting their official website directly.
The concepts introduced in class 10 science chapter 5 serve as a foundation for more advanced biology topics that students may encounter in higher education. A strong understanding of life processes is essential for students who wish to pursue biology or related fields in the future. It includes diagrams and illustrations related to processes like photosynthesis and transportation in plants. Students may be asked to label diagrams or explain concepts using them in the examination.
Questions for Practice
Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Extra Question Answers
Some finger like projection are present in the inner wall of small intestine. Write their name. Why are they important?
The fingers-like structure present on the inner surface of the small intestine are called Villi. About five millions of villi are present in the intestines, thus they increase the absorptive surface of the intestine considerably and facilitate quick absorption of the digested food. Each villi contains a network of blood capillaries with a central lacteal vessel (lymph vessel).
Which is the internal energy reserve in plants? Do the animals have the same energy reserve? Justify your answer.
Carbohydrates are utilized for providing energy to the plants and are stored in the form of starch, which serves as the internal energy reserve to be used as and when required by the plant. In animals, carbohydrates are reserved in the form of glycogen, as internal energy reserve. The carbohydrates like starch (in plants) and glycogen (in animals) serve as the internal energy reserve because they are polymer of glucose and their hydrolysis provide glucose molecules to provide energy at the time of need.
What are nutrients?
Nutrients are substances which an organism obtains from its surroundings and uses it either as an energy source or source of material required for growth and maintenance of the body.
Explain the structure of stomata. Write functions of guard cells.
i). The outermost layer of cell i.e., usually the epidermis is not continuous at some place e.g., on the surface of leaves or green herbaceous stems. The epidermis of the young shoot and leaves contains numerous minute pores called stomata. Each stomata opening is surrounded by two semilunar cells known as the guard cells. The term ‘stomata’ (plural – stomata) is applied to the stomatal opening plus the guard cells. The guard cells are living and contains chloroplast. Their inner walls (wall towards opening) are thicker and outer walls thinner.
ii). Function of guard cells: the guard cells regulate the opening and closing of the stomatal pore. The guard cells swell when water flows into them causing the stomatal pore to open. Because inflow of water in guard cells causes the stretching and bulging of outer thin walls in converse shape. This drags thick walls apart leading to opening of the pore. When there is outflow of water from guard cells, the outer thin walls come to their original position resulting in closure of stomatal pore.
Write major functions of stomata present in the epidermis.
Major functions of stomata are:
1. Stomata are essential for exchange of gases between the plants and the atmosphere-Oxygen and carbon dioxide.
2. Normally, plants eliminate excessive water in the form of vapour through stomatal openings. The process is called transpiration.
3. When there is shortage of water, stomatal openings get closed. Thus, reduce water lose. Stomatal opening also close down during night. Thus, stomata regulate water lose from plants i.e., they regulate transpiration.
Stomata remains closed during the day in desert plants. How they get carbon dioxide for photosynthesis?
In desert, temperature is very high so stomata are closed to reduce the loss of water due to transpiration. Therefore, desert plants are adapted to take up carbon dioxide at night when stomata are open. This CO2, taken up in night, prepare an intermediate compound. This intermediate compound is acted upon by the energy absorbed by the chlorophyll during the day to prepare food
Explain parasitic mode of nutrition with two examples.
Parasitic mode of nutrition: Some organisms derive their nutrition from other plants or animals (hosts). This is known as parasitic mode of nutrition and such organisms are called parasites. Some parasites are ectoparasite. They lived outside of the body of the host and derive their nutrition, the host such as cuscuta, leech, blood sucking mosquitoes etc. are ectoparasite. Some parasites live in the body of the host called endoparasites. For example: tapeworm, some fungi, etc.
How does nutrition takes place in Paramoecium?
Paramoecium is unicellular animal which has a definite shape (slipper – like).
Paramoecium takes in food at a specific point (through oral groove to mouth to gullet). Food such as bacteria or very small organisms are moved to the specific spot (ingestion point) by the movement of cilia which are present all over the single-celled body.
From the gullet a food vacuole is formed which starts circulating in the endoplasm. During circulation food is digested by enzymes. The digested food diffuses into the cytoplasm and undigested food is thrown out through the pore.
What is emulsification?
Emulsification means a fine dispersion of one liquid in another. In reference to digestion of food, breakdown of large fat globules in the small intestine by the bile juice from liver into fine smaller fat globules so to increase the efficiency of enzyme action, is called emulsification.
Practical experiments related to life processes are commonly included in the CBSE board exam. Students are expected to understand the principles behind these experiments and may be asked to predict outcomes or interpret results. The chapter 5 of 10th science typically includes a mix of long and short answer questions. Short-answer questions may require concise explanations, while long-answer questions may demand a more in-depth understanding of the topic.
Question 1:
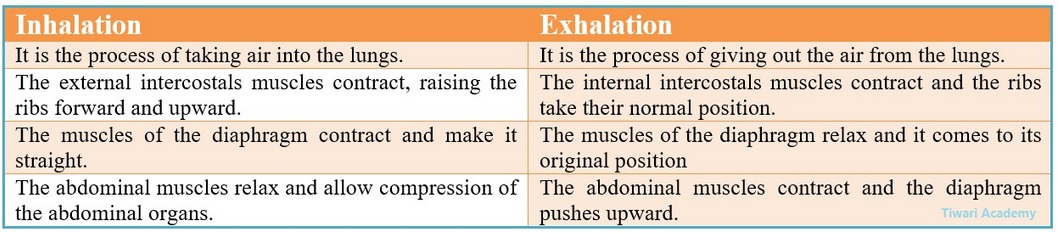
“The breathing cycle is rhythemic whereas exchange of gases is a continuous process” Justify the statement. Differentiate between Inhalation and Exhalation.
Answer 1:
The blood brings carbon dioxide form the body parts to be released into the alveoli, and the oxygen in the alveolar cavity is taken up in the alveolar blood vessels to be transported to all the cells in the body. This forms the breathing cycle (taking in air and given out air) is rhythmic. But during breathing cycle, when air is taken in and let out.
The lungs always contain a residual volume of air. So that there is sufficient time for oxygen to be absorbed and for the carbon dioxide to be released. Thus, there is some gap in between inspiration (taking in air) and expiration (given out air) during breathing cycle but exchange of gases continuous.
Question 2:
What are the basic materials used during photosynthesis? Write chemical equation for photosynthesis.
Answer 2:
Materials used in photosynthesis are (a) Carbon Dioxide and (b) Water. Chemical equation of photosynthesis.
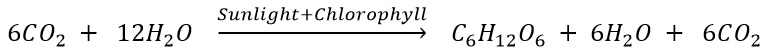
Questions from Board Papers
Question 1:
Explain the process of nutrition in amoeba with the help of diagrams.
Answer 1:
Engulfing of Food: Amoeba obtains food by phagocytosis (a type of holozoic nutrition). Amoeba engulfs the food by forming pseudopodia.
1. Two pseudopodia start growing from opposite sides of food particle. They completely encircle the food and their lips touch each other.
2. The membranes of both the pseudopodia dissolve at the point of touching and the food is encaptured into the Amoeba (one cell body) in a bag known as food vacuole.
3. Digestion of food: Inside the food vacuole, complex substances of the food are broken down into simpler ones. The digested simple substances diffuse from food vacuole into cytoplasm.
4. The remaining undigested material is moved near the surface of the single-celled body of amoeba and thrown out.
Example of other unicellular organisms are Paramoecium and Euglena. Pseudopodia also help amoeba in locomotion.

Question 2:
a) Where are salivary glands located in human beings?
b) Name the enzyme found in saliva. State the role of saliva in the digestion of food.
Answer 2:
Salivary glands secrete their secretion called saliva in the mouth cavity. There are three pairs of salivary glands located in the mouth. Saliva Amylase enzyme.
Role Or Function of saliva:
1. Saliva moisten the food thus help in chewing of food by the teeth.
2. Human saliva contains an enzyme called salivary amylase that converts starch into maltose (a sugar).
3. Saliva also helps in swolling and passage of food chewed food through the food canal which has soft lining.
Important Questions on 10th Science Chapter 5
How are fats digested in our bodies? Where does this process take place?
Fats are present in the form of large globules in the small intestine. The small intestine gets the secretions in the form of bile juice and pancreatic juice respectively from the liver and the pancreas. The bile salts (from the liver) break down the large fat globules into smaller globules so that the pancreatic enzymes can easily act on them. This is referred to as emulsification of fats. It takes place in the small intestine.
What is the role of saliva in the digestion of food?
Saliva is secreted by the salivary glands, located under the tongue. It makes the food soft for easy swallowing. It contains a digestive enzyme called salivary amylase, which breaks down starch into sugar.
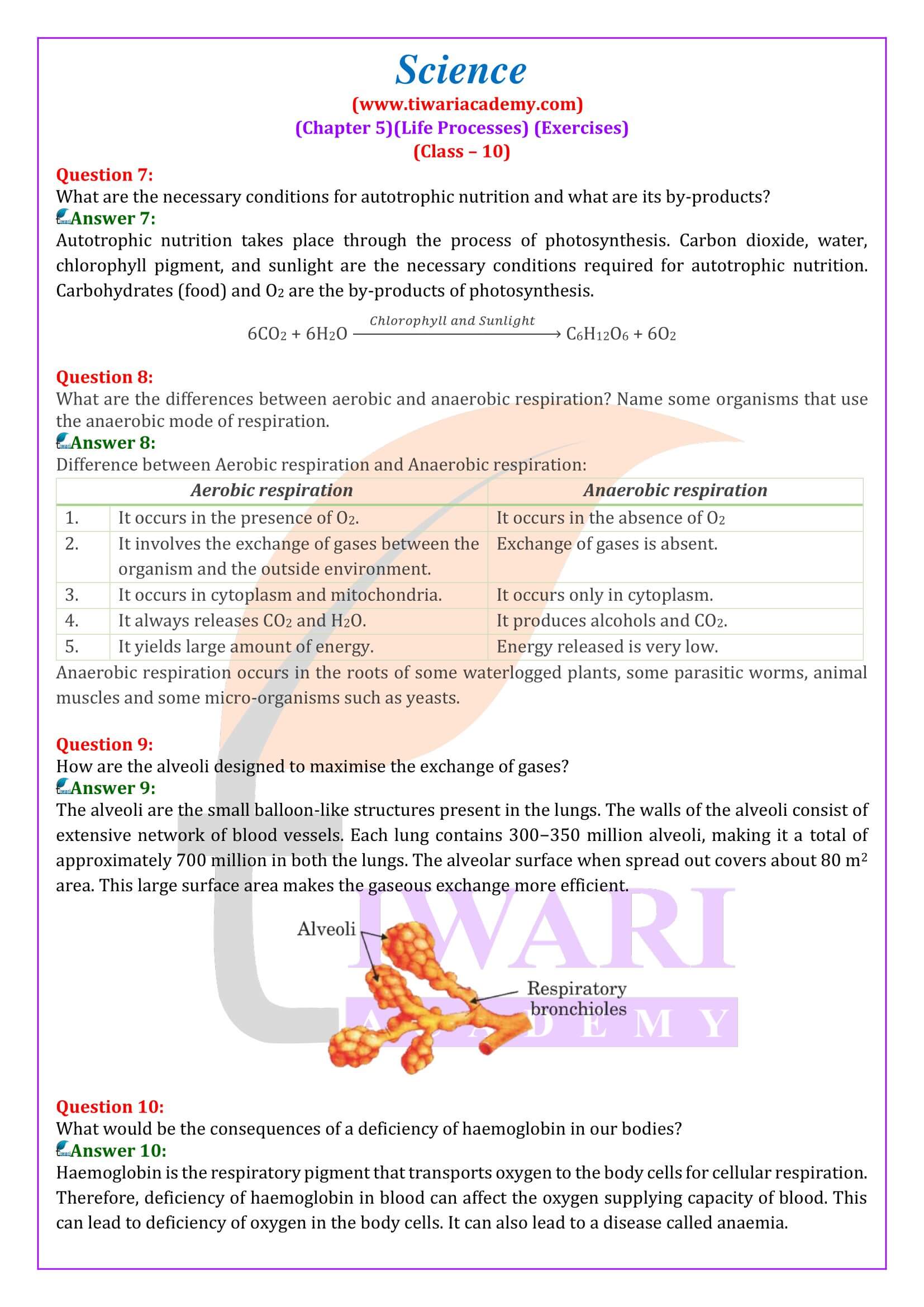
How are the alveoli designed to maximise the exchange of gases?
The alveoli are the small balloon-like structures present in the lungs. The walls of the alveoli consist of extensive network of blood vessels. Each lung contains 300−350 million alveoli, making it a total of approximately 700 million in both the lungs. The alveolar surface when spread out covers about 80 m² area. This large surface area makes the gaseous exchange more efficient.
What would be the consequences of a deficiency of haemoglobin in our bodies?
Haemoglobin is the respiratory pigment that transports oxygen to the body cells for cellular respiration. Therefore, deficiency of haemoglobin in blood can affect the oxygen supplying capacity of blood. This can lead to deficiency of oxygen in the body cells. It can also lead to a disease called anaemia.
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans?
In multi-cellular organisms, all the cells may not be in direct contact with the surrounding environment. Thus, simple diffusion will not meet the requirements of all the cells.
What criteria do we use to decide whether something is alive?
Any visible movement such as walking, breathing, or growing is generally used to decide whether something is alive or not. However, a living organism can also have movements, which are not visible to the naked eye. Therefore, the presence of molecular movement inside the organisms used to decide whether something is alive or not.
What are outside raw materials used for by an organism?
An organism uses outside raw materials mostly in the form of food (Since life on earth depends on carbon based molecules, most of these food sources are also carbon-based) and oxygen. The raw materials required by an organism can be quite varied depending on the complexity of the organism and its environment.
What is the role of the acid in our stomach?
Role of the acid (HCl) in our stomach: Kills germs present in the food and makes the food acidic, so that pepsin can digest protein.
How is the small intestine designed to absorb digested food?
The small intestine has millions of tiny finger-like projections called villi. These villi increase the surface area for food absorption. Within these villi, many blood vessels are present that absorb the digested food and carry it to the blood stream. From the blood stream, the absorbed food is delivered to each and every cell of the body.
How are the lungs designed in human beings to maximise the area for exchange of gases?
The exchange of gases takes place between the blood capillaries that surround the alveoli and the gases present in the alveoli. Thus, alveoli are the site for exchange of gases. The lungs get filled up with air during the process of inhalation as ribs are lifted up and diaphragm is flattened. The air that is rushed inside the lungs fills the numerous alveoli present in the lungs. Each lung contains 300-350 million alveoli. These numerous alveoli increase the surface area for gaseous exchange making the process of respiration more efficient.
Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds?
Warm-blooded animals such as birds and mammals maintain a constant body temperature by cooling themselves when they are in a hotter environment and by warming their bodies when they are in a cooler environment. Hence, these animals require more oxygen (O2) for more cellular respiration so that they can produce more energy to maintain their body temperature. Thus, it is necessary for them to separate oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood, so that their circulatory system is more efficient and can maintain their constant body temperature.
What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products?
Plants use completely different strategies for excretion than those of animals. They can get rid of excess water by transpiration. For other wastes, plants use the fact that many of their tissues consist of dead cells, and that they can even lose some parts such as leaves. Many plant waste products are stored in cellular vacuoles. Waste products may be stored in leaves that fall off. Other waste products are stored as resins and gums, especially in old xylem. Plants also excrete some waste substances into the soil around them.
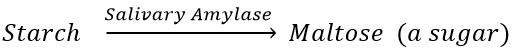
Summary of 10th Science Chapter 5 Life Processess
Introduction to Life Processes: The chapter 5, of 10th Science, begins by exploring what differentiates living beings from non-living things, focusing on the concept of molecular movements essential for life. Class 10 science chapter 5 Life Processess discusses the controversy around whether viruses are alive, given their lack of molecular movement outside a host cell.
- Nutrition: The chapter covers different modes of nutrition, including autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition. It explains how organisms fulfill their energy and material requirements, with a focus on the digestion of fats, the role of saliva in digestion, and the conditions necessary for autotrophic nutrition.
- Respiration: The process of respiration is detailed, including the breakdown of organic compounds like glucose to release energy. This topic of class 10 science chapter 5, discusses aerobic and anaerobic respiration and the role of the circulatory system in humans and vascular tissues in plants for transporting materials.
- Circulatory System in Humans: The structure and function of the human heart are explained, emphasizing its role in preventing the mixing of oxygen-rich and carbon dioxide-rich blood. The process of blood circulation, including the various roles of different heart functions, its chambers and valves, is described.
- Excretion and Waste Removal: The chapter covers how human beings and plants get rid of waste materials. It explains the role of nephrons in the kidneys for excretion in humans and various techniques used by plants for waste removal.
- Transportation in Human Beings: The efficiency of gas exchange in the lungs due to their large surface area is highlighted. The chapter also discusses the transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide in humans and compares it with the transportation system in plants.
- Digestion and Absorption: The process of digestion in the small intestine, including the role of liver and pancreas secretions, is explained. The chapter also discusses how different animals have varying lengths of the small intestine based on their diet.
- Activities and Exercises: The chapter includes various activities and questions to reinforce the concepts covered, such as experiments with lime water to understand respiration and visits to health centers to learn about haemoglobin levels.
What is the importance of NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 5 in Board Exams?
In the context of examinations for Class 10 Science, including board exams, NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 5, Life Processes, is of significant importance. Here’s why this chapter holds importance from an examination point of view. NCERT textbooks are the primary source of information for many board exams, including the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) in Bharat. Chapter 5, Life Processes, often carries a substantial weightage in the question paper. This means that a significant portion of the marks in the science exam is allocated to questions related to this chapter.
The concepts covered in this chapter are fundamental to understanding how living organisms function. Topics such as nutrition, respiration, transportation in plants and animals, and excretion are essential components of biology. Questions based on these topics are likely to appear on the exam. The chapter delves into practical aspects of how living organisms obtain and utilize energy, which is crucial for their survival and growth. Questions may require students to apply their knowledge of these processes to real-life scenarios.
In addition to theoretical knowledge, questions may assess a student’s ability to apply the concepts learned in the chapter to practical situations or scenarios. To excel in the examination, students should thoroughly study NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 5, practice solving questions, and understand the underlying concepts. Additionally, reviewing previous years’ question papers and sample papers can provide insights into the types of questions that may be asked in the exam.
How does Tiwari Academy help in preparation for NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 5?
Tiwari Academy is an online education platform that provides resources and assistance to students preparing for various exams, including NCERT (National Council of Educational Research and Training) Class 10 Science. Tiwari Academy provides comprehensive chapter-wise notes that cover all the key concepts, formulas and important points from NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 5 (and other chapters). These notes serve as a quick reference for students to understand and revise the chapter’s content. The platform offer video tutorials that explain complex concepts in a visually engaging manner. These tutorials can help students grasp difficult topics more easily.
How student can prepare NCERT class 10 science chapter 5 in a better way?
To prepare for NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 5, Life Processes, effectively and score well in exams, students should read the Chapter thoroughly. Start by reading the entire chapter from your NCERT textbook. Understand the concepts, definitions, and key terms presented in the chapter. As you read, make concise notes summarizing important points, definitions, and processes. These notes will be helpful at the exam time. Pay special attention to the chapter’s diagrams, flowcharts, and illustrations. These visuals often simplify complex processes, making them easier to understand.
How many questions are there in chapter 5 of 10th Science Biology?
There are 34 questions in chapter 5 of class 10th Science. 21 questions are in between the chapter, and 13 questions are in the back exercise of chapter 5. All questions are nice, interesting, and logical. Chapter 5 is a chapter of biology.
Which questions of chapter 5 of class 10th Science teacher can give in the exams?
Chapter 5 of grade 10th Science is important from the exam point of view. Every year questions come from chapter 5 in the exams. There are 34 questions in chapter 5. All the questions of this chapter are significant and can come in the exams. But the most important questions of this chapter that teachers can give in the exams are questions 1, 4 (page number 95), questions 1, 3, 5 (page numbers 101), questions 1, 2, 4 (page number 105), questions 1, 2, 4, 5 (page number 110), questions 1, 2 (page number 112), and from back exercise questions 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 are important.
Does the chapter 5 of class 10th Science take less time for preparation?
Chapter 5 of class 10th Science is very lengthy. Students need a maximum of 15-20 days to complete chapter 5 (Life Processes) of grade 10th Science if they give 1-2 hours per day to this chapter. This time depends on many things like student’s working speed, efficiency, capability, etc.
Is chapter 5 of class 10th Science Solutions easy?
Yes, chapter 5 of class 10th Science is complex. Most of the students face problems while solving the questions of this chapter and also in theory part of this chapter. This chapter is interesting, and logical. This chapter requires complete concentration. Also, this chapter helps in increasing the thinking ability of students.