NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Human eye and colorful world in Hindi and English Medium for CBSE 2025-26. All the question answers and solutions of chapter 10 class 10th science are revised according to new syllabus and latest textbooks issued for academic session 2025-26.
Revision for Class 10 Science
Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Solutions
Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Exercises Solutions
Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Intext Exercises
Class 10 Science Chapter 10 MCQ
Class 10 Science Chapter 10 in Hindi Medium
Class 10 Science Book Download in PDF
Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Board Questions
Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Extra Questions
Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions
Class 10 all Subjects Solutions
Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Questions in Detail
- Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Important Questions
- Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Board Questions
- Class 10 Science Chapter 10 MCQ
- What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye?
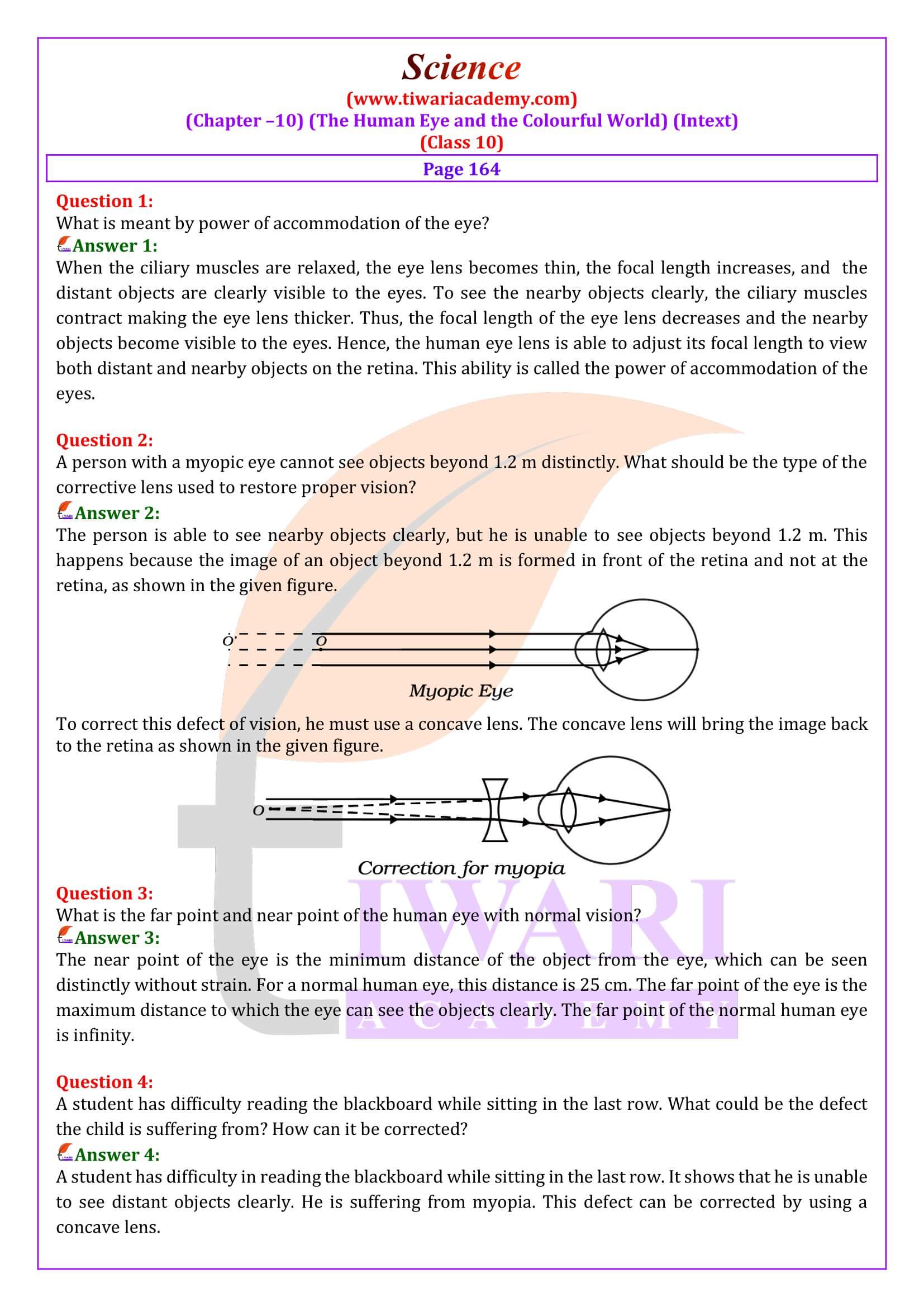
- A person with a myopic eye cannot see objects beyond 1.2 m distinctly. What should be the type of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision?
- What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision?
- A student has difficulty reading the blackboard while sitting in the last row. What could be the defect the child is suffering from? How can it be corrected?
- A person needs a lens of power –5.5 dioptres for correcting his distant vision. For correcting his near vision he needs a lens of power +1.5 dioptre. What is the focal length of the lens required for correcting (i) distant vision, and (ii) near vision?
- The far point of a myopic person is 80 cm in front of the eye. What is the nature and power of the lens required to correct the problem?
- Make a diagram to show how hypermetropia is corrected. The near point of a hypermetropic eye is 1 m. What is the power of the lens required to correct this defect?
- Why is a normal eye not able to see clearly the objects placed closer than 25 cm?
- What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye?
- Why do stars twinkle?
- Explain why the planets do not twinkle?
- Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?
| Class: 10 | Science |
| Chapter 10: | Human eye and colorful world |
| Content: | Intext and Exercise Answers |
| Content Mode: | PDF and Videos format |
| Session: | CBSE 2025-26 |
| Medium: | English and Hindi Medium |
Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Answers in Hindi and English Medium
- Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Exercises
- Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Intext Questions
- Class 10 Science Chapter 10 in Hindi
- Class 10 Science Chapter 10 in PDF
- Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Board Questions
- Class 10 Science Chapter 10 MCQ
- Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Extra Questions
- Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions
- Class 10 all Subjects Solutions
Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Study Material
Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Brief Introduction
Introduction to the Human Eye: The class 10 Science chapter 10 begins by relating the concepts of refraction and lenses, previously discussed, to the human eye. It emphasizes the eye’s role in vision, describing it as a camera-like organ with a lens that forms images on the retina. The cornea, iris, and pupil are mentioned as key components in controlling the amount of light entering the eye.
Power of Accommodation: The eye’s ability to adjust its lens’s focal length, known as accommodation, is explained. This process allows us to see objects at different distances. Class 10 Science chapter 10 discusses the near point (the closest distance for clear vision, typically about 25 cm for young adults) and the far point (the farthest point of clear vision, ideally infinity).
Defects of Vision and their Correction: Common refractive defects like myopia (near-sightedness), hypermetropia (far-sightedness), and presbyopia are detailed. Each condition is explained with its causes and corrective measures, typically involving the use of suitable lenses.
Eye Donation and Social Impact: Class 10 Science chapter 10 touches on the importance of eye donation, highlighting how donated eyes can cure corneal blindness and aid in medical research. It emphasizes that eye donation is a simple, quick process that doesn’t cause disfigurement.
Refraction of Light through a Prism: The chapter 10 of 10th science concludes with an exploration of how light refracts through a prism, different from refraction through a rectangular slab. An activity is described to help understand this concept.
NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World explores the functioning of the human eye, optical instruments, and various phenomena related to light and colors. Here are the main topics covered in this chapter. Structure and function of the human eye, overview of the structure of the human eye, including the cornea, iris, lens, retina, and optic nerve. Explanation of how the eye works as an optical instrument. Power of Accommodation, and the concept of the power of accommodation and its role in adjusting focus on objects at different distances.
Defects of Vision and their Correction
Common vision defects, including myopia (nearsightedness) and hypermetropia (farsightedness). How these defects are corrected using suitable lenses (concave and convex lenses). Refraction of light through a prism, when a white light passes through a prism it is separated into seven colors. Formation of a spectrum. Atmospheric refraction, explanation of the apparent bending of light due to atmospheric refraction. Effects of atmospheric refraction on the apparent position of celestial objects.
Scattering of Light
Explanation of the scattering of light by particles in the atmosphere. The blue color of the sky during the daytime. Tyndall effect, and explanation of the Tyndall effect, which is the scattering of light by colloidal particles. Examples of the Tyndall effect in daily life. Applications of scattering of light, and explanation of why the color of the Sun appears reddish during sunrise and sunset. Understanding the color of the sky during sunrise and sunset.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10
Class X Science chapter 10 intext questions on Page 190 and chapter end Exercises in English Medium. Download Solutions in Hindi Medium updated for CBSE session 2025-26. These solutions are applicable for UP Board High School students also. Download here the UP Board Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 in Hindi Medium. Important and Extra Questions based on Chapter 10 of 10th Science are also given with proper answers.
Formation of Images by Spherical Lenses
Principles of image formation by convex and concave lenses. Use of ray diagrams to determine the position and nature of the image formed by lenses. Nature, position, and magnification of the image, explanation of how the nature (real or virtual), position, and size (magnification) of the image formed by a lens depend on the object’s position. Power of a lens, and the concept of the power of a lens and its units. Calculation of the power of a lens. Prescription of lenses, and how to prescribe corrective lenses for vision defects? Using the lens formula to determine the power of prescribed lenses.
All NCERT question answers and Offline Apps are free to download or use online without downloading. Solutions are available online as well as offline in PDF form to free download. Download NCERT Solution Offline Apps for class x other subjects also. NCERT Solutions and all the study material on Tiwari Academy is free to use without any login or password.
Explanation of how multiple images can be formed by multiple reflections or refractions. The eye defects and how they are corrected using lenses, a detailed explanation of how myopia (nearsightedness) and hypermetropia (farsightedness) occur, and how they are corrected using appropriate lenses. This chapter provides insights into the functioning of the human eye, the behavior of light, and various optical phenomena, all of which are essential topics in the field of optics and vision. Understanding these concepts is important for a well-rounded knowledge of physics and its practical applications.
Preparing for NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World requires a structured approach and a focus on understanding the concepts related to optics and the human eye. To prepare effectively some guidelines are given here. Read the chapter thoroughly, Students should read the entire chapter from the NCERT book. Pay attention to explanations, diagrams, and examples provided. Make concise notes while reading. Summarize key points, definitions, and formulas. Highlight important terms and concepts.
Understand the Structure of the Human Eye
Pay close attention to the structure and functioning of the human eye. Understand the role of each part, such as the cornea, iris, lens, and retina. Learn about accommodation and vision defects, and study the concept of accommodation, which allows the eye to focus on objects at different distances. Understand common vision defects, including myopia (nearsightedness) and hypermetropia (farsightedness), and how they occur. Familiarize yourself with optical phenomena, and learn about optical phenomena like dispersion (formation of a spectrum by a prism), atmospheric refraction, and the Tyndall effect. Understand how these phenomena contribute to the colors we observe in the environment.
Practice Drawing Ray Diagrams
Practice drawing ray diagrams to understand image formation by convex and concave lenses. Pay attention to image characteristics (real, virtual, magnified, diminished, etc.). Use these diagrams to solve numerical problems related to lenses. Study the lens formula and power of lenses, and understand the lens formula and how it relates to object distance, image distance, and focal length. Learn how to calculate the power of a lens using the lens formula.
Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Extra Question Answer
What is hypermetropia? What are the two causes of this defect of vision? How can this defect of the eye be corrected?
Hypermetropia or long-sightedness: It is a vision defect in which a person can see the distant object clearly but cannot see the nearby objects clearly.
Cause of hypermetropia: This defect arises due to either of the following two reasons:
(i) The eyeball becomes too small along its axis so that the distance between the eye lens and the retina is reduced.
(ii) The focal length of the eye lens becomes too large resulting in the low converging power of the eye lens.
Correction of hypermetropia: A hypermetropia eye is corrected by using a convex lens of suitable focal length. This lens diverges the rays such that the rays coming from normal near point N appear to come after refraction, from near point N’ of the defected eye. That is a virtual image of the object placed at N is formed at N’. Then the eye lens forms a clear image at the retina.
What is presbyopia? Write two causes of this defect.
Presbyopia: this defect is similar to hypermetropia i.e., a person having this defect cannot see nearby objects distinctly, but can see distant objects without any difficulty. This defect differs from hypermetropia in the cause by which it is produced. It usually occurs in elderly persons. Due to the stiffening of the ciliary muscles, the eye lens loses flexibility and hence the accommodating power of the eye lens decreases.
“Stars appear higher than they actually are.” Give reason.
Since the atmosphere bends starlight towards the normal, the apparent position of the star is slightly different from its actual position. The stars appear slightly higher (above) than their actual position when viewed near the horizon.
Why is the colour of the clear sky blue? Explain.
The blue colour of the sky is due to the scattering of the sunlight by the molecules of the atmosphere. The molecules of air, such as N2 and O2, have sizes smaller than the wavelength of visible light. As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, these molecules absorb some amount of sunlight and re-emit it. They scatter blue light of shorter wavelength more strongly than red light of longer wavelength. When we look at the sky, the scattered light enters our eyes and this light contains blue light in a larger proportion. This is why, the sky appears blue.
Learn about the Prescribing of Corrective Lenses
Understand how optometrists prescribe corrective lenses for vision defects. This involves using the lens formula and understanding the concept of power. Solve numerical problems related to lenses, image formation, power of lenses, and vision correction. Pay attention to units and follow the sign conventions for lenses. Use visual aids and simulations, use online simulations and visual aids to better understand optical phenomena and eye-related concepts.
10th Science Chapter 10 Answers in English & Hindi Medium
Class 10 Science Physics Chapter 10 Human eye and colorful world intext questions given on page 190 Answers and chapter end exercises answers are given below in updated form for new academic session 2025-26. Download UP Board Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 with important Questions and intext questions in Hindi and English. Visit to Discussion Forum to ask your doubts and discuss the facts asked by other uses.
Experiment with Prism and Light Dispersion
If possible, conduct simple experiments with prisms to observe the dispersion of light into its constituent colors. Solve previous years’ board exam questions related to this chapter to get a sense of the types of questions that are commonly asked. Regular revision is essential. Dedicate time to revise your notes, diagrams, and important concepts from the chapter. Take mock tests or practice tests to assess your understanding of the chapter. Simulate exam conditions to improve time management. By following these steps and focusing on a deep understanding of the concepts, you can prepare effectively for NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World. Remember to practice regularly and seek help from your teacher or classmates if you face any difficulties or have questions.
Questions for Practice
Question 1:
What is myopia? State two reasons due to which this defect is caused.
Answer 1:
Myopia or short-nearsightedness: It is a vision defect in which a person can see nearby objects clearly but cannot see the distant objects clearly beyond a certain point. This defect is common among children.
Cause of Myopia: This defect arises due to either of the following two reasons:
(i) The eyeball gets elongated along its axis so that the distance between the eye lens and the retina becomes larger.
(ii) The focal length of the eye lens becomes too short due to the excessive curvature of cornea.
Correction of Myopia: A myopia eye is corrected by using a concave lens of focal length equal to the far point F from the eye. This lens diverges the parallel rays from distant object as if they are coming from the far point F. Finally, the eye lens forms a clear image at the retina.
Question 2:
What will be the colour of sky in the absence of atmosphere? or “The sky appears dark to passengers flying at very high altitudes.” Give reason.
Answer 2:
In the absence of any atmosphere, there will be no scattering of sunlight and the sky will appear dark. The sky appears dark to passengers or astronauts flying at high altitudes, as scattering is not prominent at such heights due to thin atmosphere.
Tiwari Academy is a valuable online resource that assists students in their preparation for NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World and other subjects as well. Here’s how Tiwari Academy can be helpful. Tiwari Academy provides detailed solutions to the exercises and questions found in the NCERT textbook. This helps students understand the correct way to solve problems and verify their answers.
Tiwari Academy offers supplementary practice questions and exercises that go beyond what’s provided in the NCERT textbook. These extra questions allow students to further practice and reinforce their understanding of the chapter. It also provide comprehensive explanatory notes and study materials that simplify complex concepts. These materials can be beneficial for students who need additional explanations and examples.
Questions from Board Papers
Question 1:
Why do we see stars appear twinkling, whereas planets do not twinkle?
or
A star sometimes appears brighter and some other times fainter. What is this defect called? State reason for this effect.
Answer 1:
Twinkling of stars: The apparent position of a star is slightly different from the actual position due to refraction of starlight by the atmosphere. Further, this apparent position is not stationary but keeps on changing due to the change in atmospheric conditions like density, temperature, etc. the path of the rays of light coming from the stars goes on varying slightly. The amount of light entering our eyes from a particular star increases or decreases randomly with time. Sometimes, the star appears bright and other times, it appears fainter. This gives rise to the twinkling effect of the star.
Tiwari Academy, offers video tutorials on various topics. These videos help students visualize and understand challenging concepts more effectively. It includes interactive simulations and animations related to the concepts in chapter 10 of 10th science. These tools can make learning more engaging and help students grasp abstract ideas. Tiwari Academy provides mock tests and sample question papers for Class 10 Science. These resources allow students to practice under exam-like conditions and assess their preparation level.
NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World is of significant importance from the examination point of view for several reasons. Chapters in the NCERT syllabus are designed to carry weightage in board exams. Chapter 10, like other chapters, contributes to your score in the science subject. This chapter covers fundamental concepts related to optics, the human eye, and the behavior of light. A strong grasp of these concepts is crucial for understanding more advanced topics in physics.
The planets do not show twinkling effect: As the planets are much closer to the earth, the amount of light received from them is much greater and the fluctuations caused in the amount of light due to atmospheric refraction are negligible as compared to the amount of light received from them.
Commonly Asked Questions
Questions related to the structure and functioning of the human eye, vision defects, image formation by lenses, and optical phenomena are commonly asked in board exams. Drawing accurate ray diagrams for image formation by lenses and understanding their characteristics (real, virtual, magnified, diminished, etc.) is a skill that is often tested in science exams. Numerical problems related to lenses, image formation, and the power of lenses are frequently included in exams. Students need to apply the lens formula and understand the sign conventions.
Question 2:
What is astigmatism? How is it caused? How is it corrected? Or What is astigmatism and how is this vision defect counteracted?
Answer 2:
Astigmatism: It is a defect of vision in which a person cannot simultaneously see both the horizontal and vertical views of an object with same clarity.
Cause of astigmatism: This defect occurs when the cornea of the eye is not perfectly spherical. This results in objects in one direction being well focussed while those in perpendicular direction are not well focussed.
Dispersion and Optical Phenomena
Concepts related to dispersion of light, formation of a spectrum, atmospheric refraction, and the Tyndall effect are part of this chapter and are potential topics for exam questions. Knowledge of common vision defects (myopia and hypermetropia) and how they are corrected using lenses is essential for answering questions related to vision and optics.
Important Questions on 10th Science Chapter 10
What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye?
Since the size of eyes cannot increase or decrease, the image distance remains constant. When we increase the distance of an object from the eye, the image distance in the eye does not change. The increase in the object distance is compensated by the change in the focal length of the eye lens. The focal length of the eyes changes in such a way that the image is always formed at the retina of the eye.
Why do stars twinkle?
Stars emit their own light and they twinkle due to the atmospheric refraction of light. Stars are very far away from the earth. Hence, they are considered as point sources of light. When the light coming from stars enters the earth’s atmosphere, it gets refracted at different levels because of the variation in the air density at different levels of the atmosphere. When the star light refracted by the atmosphere comes more towards us, it appears brighter than when it comes less towards us. Therefore, it appears as if the stars are twinkling at night.
Explain why the planets do not twinkle?
Planets do not twinkle because they appear larger in size than the stars as they are relatively closer to earth. Planets can be considered as a collection of a large number of point-size sources of light. The different parts of these planets produce either brighter or dimmer effect in such a way that the average of brighter and dimmer effect is zero. Hence, the twinkling effects of the planets are nullified and they do not twinkle.
Why does the Sun appear reddish early in the morning?
During sunrise, the light rays coming from the Sun have to travel a greater distance in the earth’s atmosphere before reaching our eyes. In this journey, the shorter wavelengths of lights are scattered out and only longer wavelengths are able to reach our eyes. Since blue colour has a shorter wavelength and red colour has a longer wavelength, the red colour is able to reach our eyes after the atmospheric scattering of light. Therefore, the Sun appears reddish early in the morning.
Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?
The sky appears dark instead of blue to an astronaut because there is no atmosphere in the outer space that can scatter the sunlight. As the sunlight is not scattered, no scattered light reach the eyes of the astronauts and the sky appears black to them.
What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye?
When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thin, the focal length increases, and the distant objects are clearly visible to the eyes. To see the nearby objects clearly, the ciliary muscles contract making the eye lens thicker. Thus, the focal length of the eye lens decreases and the nearby objects become visible to the eyes. Hence, the human eye lens is able to adjust its focal length to view both distant and nearby objects on the retina. This ability is called the power of accommodation of the eyes.
What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision?
The near point of the eye is the minimum distance of the object from the eye, which can be seen distinctly without strain. For a normal human eye, this distance is 25 cm. The far point of the eye is the maximum distance to which the eye can see the objects clearly. The far point of the normal human eye is infinity.
A student has difficulty reading the blackboard while sitting in the last row. What could be the defect the child is suffering from? How can it be corrected?
A student has difficulty in reading the blackboard while sitting in the last row. It shows that he is unable to see distant objects clearly. He is suffering from myopia. This defect can be corrected by using a concave lens.
Correction of astigmatism: Astigmatism can be corrected by using cylindrical lenses. They have different curvatures in horizontal and vertical directions and so they can be oriented suitably to compensate for the irregularities in the cornea.
Real-Life Applications based on 10th Science chapter 10
Understanding the principles of the human eye and optics has practical applications in fields like ophthalmology, photography, and the design of optical instruments. Questions may be framed around these applications. Given that this chapter combines theoretical concepts with practical aspects, students who have a good grasp of the subject matter can score well in both theory and numerical problems. A strong foundation in optics and the principles of light is essential for those students who plan to pursue further studies in science and engineering.
In conclusion, NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World is indeed important from the examination point of view. It covers fundamental concepts related to optics and vision, and a good score in this chapter contributes to your overall performance in the science subject. Therefore, it is advisable to dedicate sufficient time and effort to prepare effectively for this chapter.
Is chapter 10 of class 10th Science interesting to learn?
Yes, chapter 10 of class 10th Science is very interesting. Students will study many interesting topics in this chapter. Topics which students study in chapter 10 are:
- 1. The Human Eye
- 2. Power of Accommodation
- 3. Defects of vision and their correction
- 4. Myopia
- 5. Hypermetropia
- 6. Presbyopia
- 7. Refraction of light through a prism
- 8. Dispersion of white light by a glass prism
- 9. Atmospheric refraction
- 10. Twinkling of stars
- 11. Advance sunrise and delayed sunset
- 12. Scattering of light
- 13. Tyndall Effect
- 14. Why is the color of the clear Sky Blue?
- 15. Colour of the Sun at Sunrise and Sunset.
How many days are needed to complete chapter 10 of class 10th Science?
Students need a maximum of 8-10 days to complete chapter 10 (The Human Eye and The Colourful World) of grade 10th Science if they give 2 hours per day to this chapter. This time is an approximate time. This time can vary because no students can have the same working speed, capability, efficiency, etc.
How many activities are there in chapter 10 of grade 10th Science?
There are 3 activities in chapter 10 of grade 10th Science. All the activities are nice, interesting, and logical. These activities help students to understand the chapter easily and practically. Students enjoy doing these activities in school.
Is chapter 10 of grade 10th Science important for the board exams?
Yes, chapter 10 of grade 10th Science is important from the exam point of view. Every year questions come from chapter 10 in the exams. There are 17 questions in chapter 10. All the questions of this chapter are significant and can come in the exams. This chapter is not very lengthy and not very short.