NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 3 Landforms and Life updated and modified for academic session 2025-26. The question answers of Class 6 Social Science Exploring Society – India and Beyond India Beyond Geography Chapter 3 is given here based on NEP 2020.
Class 6 Social Science Chapter 3 Landforms and Life Question Answers
Landforms and Life: Introduction to Landforms
Landforms are natural features on Earth’s surface that vary greatly from place to place. The three main types of landforms are mountains, plateaus, and plains. These landforms are formed over millions of years and have a significant impact on the environment and the way people live. As you travel across different regions, such as from Jharkhand to Uttarakhand in India, you’ll notice changes in the landscape due to the presence of these landforms. Each landform has its unique climate, vegetation, and animal life, and humans have adapted to live in all these different environments.

Mountains: The Majestic Heights
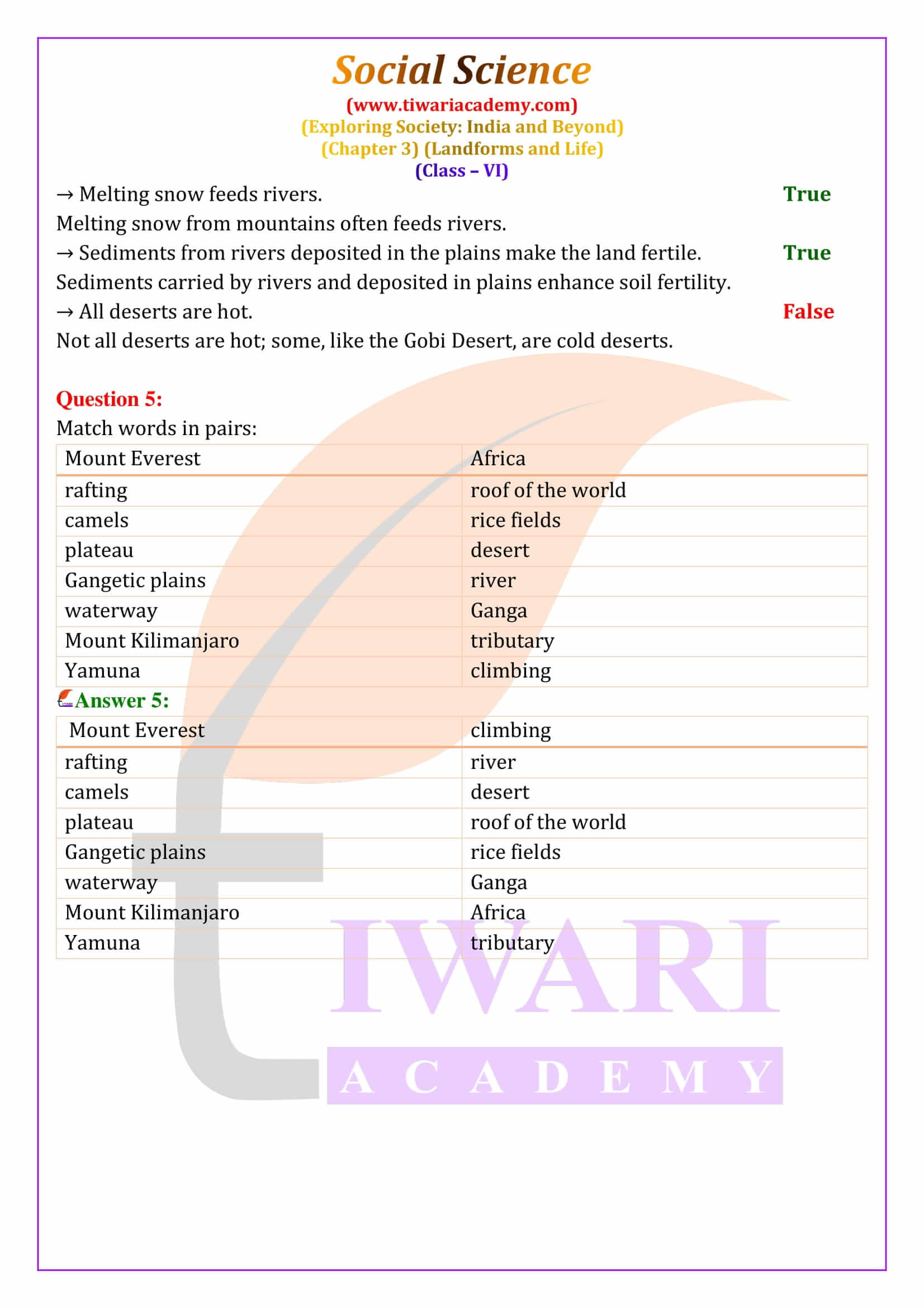
Mountains are towering landforms with steep slopes and a narrow peak. They are often found in long chains or ranges, such as the Himalayas in Asia or the Andes in South America. Mountains can be covered in snow at high altitudes, which melts in the summer to feed rivers. Some of the world’s tallest mountains, like Mount Everest and Mount Kanchenjunga, are part of the Himalayan range. Mountains are rich in natural resources and are home to a variety of wildlife, including animals like the snow leopard and the yak. People living in mountainous regions often rely on activities like farming, herding, and tourism for their livelihood.
Life in the Mountains
Living in the mountains comes with its challenges. The rugged terrain and steep slopes make farming difficult, but people have found ways to cultivate the land by creating terraces on the slopes. Many mountain communities also depend on tourism, as visitors are drawn to the fresh air, scenic views, and opportunities for outdoor activities like skiing and mountaineering. However, mountain life can be dangerous due to natural hazards like landslides, avalanches, and flash floods. Despite these challenges, many people continue to live in the mountains, adapting to the harsh conditions with resilience and ingenuity.
Plateaus: Elevated Plains
Plateaus are flat, elevated areas of land that rise sharply above the surrounding landscape. Some plateaus, like the Tibetan Plateau, are known as the “Roof of the World” because of their high elevation. Others, like the Deccan Plateau in India, are rich in minerals and have been formed through volcanic activity. Plateaus are important sources of minerals like coal, iron, and gold, making mining a major economic activity in these regions. However, the rocky soil of plateaus often makes them less suitable for farming, except for volcanic plateaus, which have fertile black soil.
Life on Plateaus
While plateaus may not be as fertile as plains, they still support a variety of human activities. In addition to mining, people on plateaus often engage in farming and herding. Some plateaus are also famous for their stunning waterfalls, such as the Victoria Falls in Africa and the Jog Falls in India. The diverse landscapes of plateaus offer opportunities for tourism as well. However, the harsh climate and rocky terrain can make life on plateaus challenging, and people living in these regions must adapt to these conditions.
Plains: The Fertile Lands
Plains are vast, flat areas of land that are usually very fertile, making them ideal for agriculture. Many of the world’s earliest civilizations developed in the fertile plains around rivers, where the soil was rich and suitable for growing crops. In India, the Ganga Plain supports a large population and is known for its agricultural productivity. People in the plains grow a variety of crops, including rice, wheat, and cotton, and the plains are also home to diverse wildlife. The flat terrain of plains makes them ideal for transportation and trade, further contributing to their importance in human society.
The Diversity of Landforms
The Earth’s surface is made up of a complex variety of landforms, each offering different challenges and opportunities for human life. From the towering mountains to the elevated plateaus and the fertile plains, each landform has shaped the way people live, work, and interact with their environment. Understanding these landforms helps us appreciate the diversity of life on Earth and the ways in which humans have adapted to their surroundings. Whether it’s the resilience of mountain communities or the agricultural productivity of the plains, the connection between landforms and life is a fundamental aspect of our world.