NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 Grassroots Democracy – Part 3: Local Government in Urban Areas revised for academic session 2025-26. Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 Exploring Society – India and Beyond India Beyond in Civics (Political Science) Section Question Answers according to National Education Policy 2020.
Class 6 Social Science Chapter 12 Grassroots Democracy – Part 3: Local Government in Urban Areas Question Answers
Grassroots Democracy Part 3: Local Government in Urban Areas – Introduction
Urban local bodies are a part of the local government system in cities and towns. Unlike rural areas, where governance is handled by Panchayati Raj institutions, urban areas are managed by these urban local bodies. These bodies are crucial because they bring governance closer to the people, allowing residents to have a direct say in how their cities and towns are managed. The urban governance system is more complex due to the diverse and densely populated nature of cities, which requires more structured and organized administration.

Functions of Urban Local Bodies
Urban local bodies perform various functions that are essential for the smooth functioning of cities and towns. They are responsible for maintaining infrastructure, collecting and disposing of waste, managing water supply, and ensuring proper sanitation. Additionally, they oversee the implementation of government schemes, collect local taxes, and ensure public health and safety. These bodies also play a role in planning and managing the economic and social development of their areas, making them key players in urban governance.
Structure of Urban Local Bodies
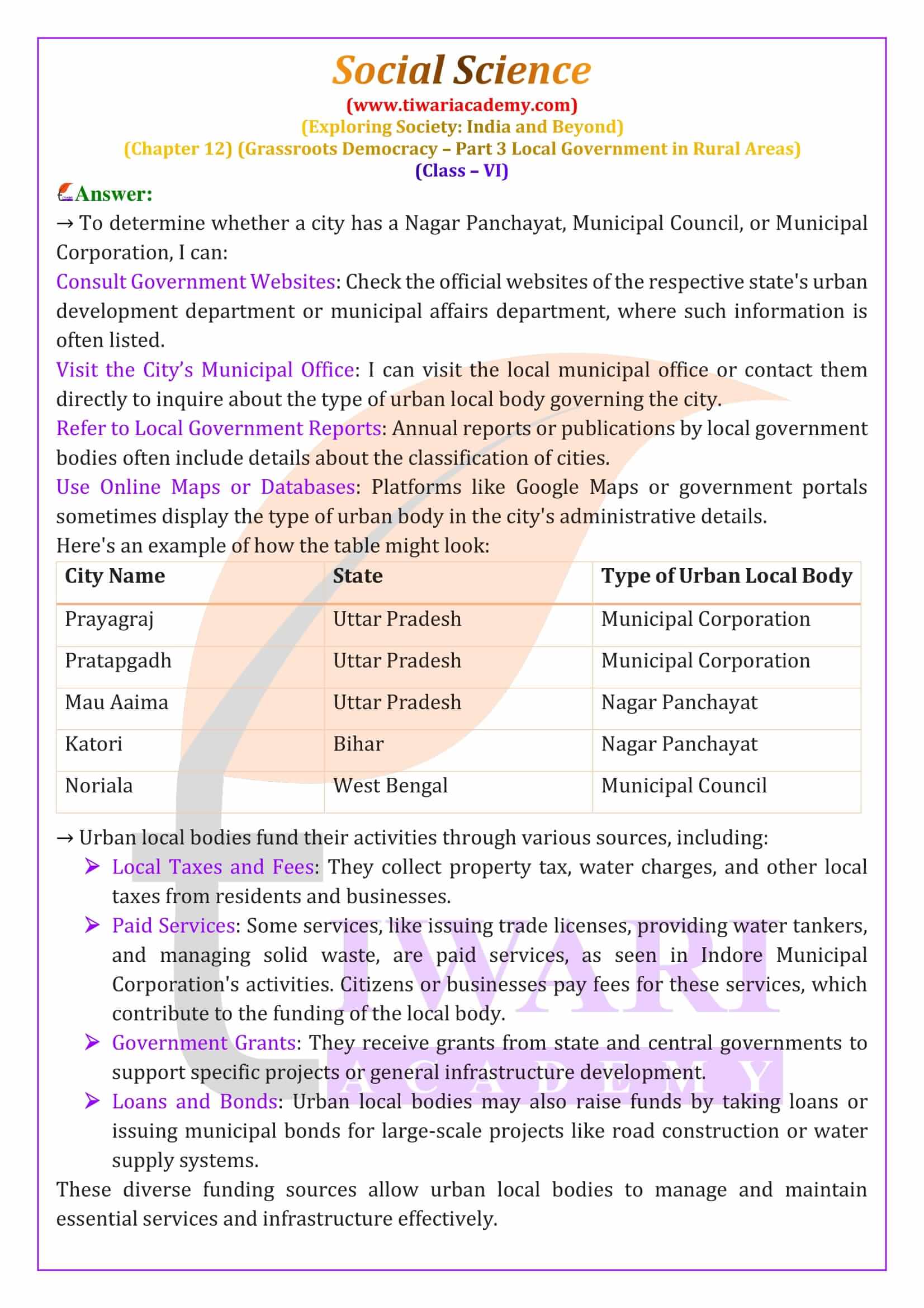
Cities and towns are divided into smaller units called ‘wards.’ Each ward has its own committee that is responsible for addressing local issues and ensuring that the area is well-maintained. The size and structure of urban local bodies vary depending on the population of the area. Large cities with populations over one million have Municipal Corporations, while smaller towns have Municipal Councils or Nagar Panchayats. These different bodies ensure that urban governance is tailored to the needs of the population.
Citizen Participation in Urban Governance
For urban local bodies to function effectively, it is important for citizens to actively participate in the governance process. This includes following rules and guidelines set by these bodies, such as waste segregation, reporting issues like water leaks or road damage, and participating in community decisions. Active citizen participation helps ensure that urban areas are well-maintained and that the needs of the community are met. It also fosters a sense of responsibility among residents, making them more invested in the well-being of their city.
Challenges in Urban Governance
Managing a city or town is a complex task that comes with many challenges. Urban areas are often crowded and diverse, with people from different backgrounds living close together. This diversity can make it difficult to address the needs of all residents. Additionally, cities face issues like traffic congestion, pollution, and inadequate housing, which require effective planning and management. Urban local bodies must work hard to overcome these challenges and ensure that cities are livable for everyone.
Examples of Urban Local Bodies in Action
The chapter provides examples of how urban local bodies work in practice. For instance, the Greater Chennai Corporation, established in 1688, is the oldest municipal body in India and has played a key role in the development of Chennai. Another example is the Indore Municipal Corporation, which has been recognized as the cleanest city in India under the Swachh Survekshan scheme. These examples show how effective urban governance can lead to significant improvements in city life.
The Role of Citizens
The chapter 12 concludes by emphasizing the importance of both urban local bodies and citizen participation in maintaining and improving urban areas. It highlights that while these bodies are responsible for governance, it is up to the citizens to support their efforts by being responsible and active members of the community. By working together, urban local bodies and citizens can create cities and towns that are clean, safe, and vibrant places to live.