NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 10 Grassroots Democracy — Part 1: Governance is updated for academic session 2025-26. The question answers of Class 6 Social Science Chapter 10 Exploring Society – India and Beyond India Beyond in Civics (Political Science) Section are given here to solve exercises.
Class 6 Social Science Chapter 10 Grassroots Democracy 1: Governance Question Answers
Grassroots Democracy Part 1: Understanding Governance
Governance is the process of creating rules and ensuring they are followed to maintain order in society. When people live together, disagreements and disorder can happen, so rules become necessary. Just like schools, roads, and workplaces have rules, society also needs rules to function properly. The system or group of people who make these rules and ensure they are followed is called the government. Some of these rules are more important and are called laws. These laws and rules can change over time, and citizens have a say in how these rules are made and changed.

The Three Branches of Government
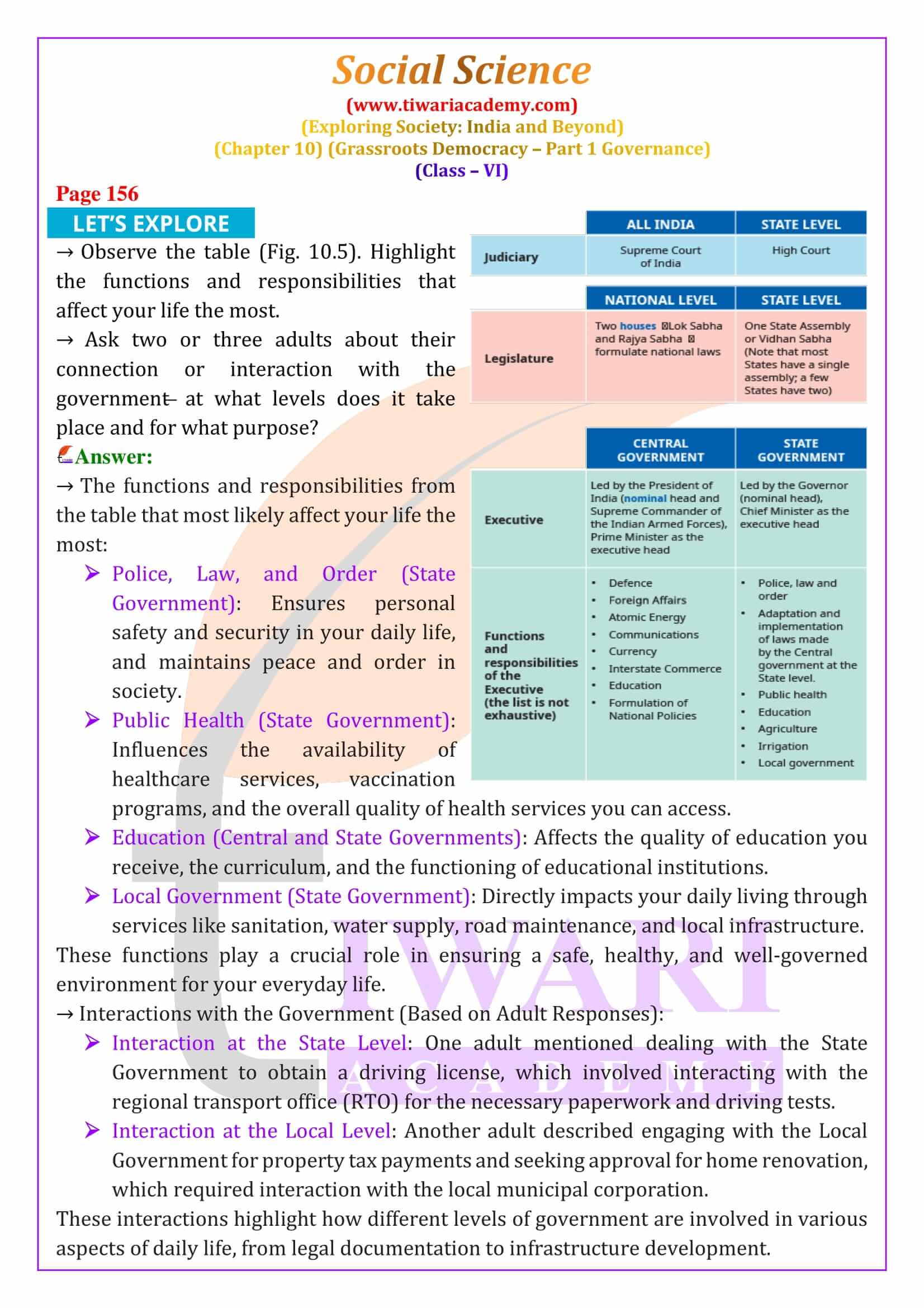
Governments around the world usually have three main parts, called branches or organs, which work together. These are the legislature, the executive, and the judiciary. The legislature makes the laws, the executive implements them, and the judiciary checks if the laws are followed correctly and decides on punishments if they are broken. For example, if someone steals money online (cyber crime), the legislature creates laws to stop it, the executive (like the police) catches the criminals, and the judiciary decides their punishment.
Separation of Powers
For good governance, these three branches should be separate but work together. This separation is called the “separation of powers” and helps ensure that no one branch becomes too powerful. Each branch checks the others to keep a balance. For instance, if the legislature makes a law, the judiciary can review it to ensure it is fair, and the executive must enforce it correctly. This system prevents any one group from controlling the entire government and helps protect the rights of the people.
Three Levels of Government
In India, the government works at three levels: local, state, and national. The local government deals with issues in towns or villages, the state government handles problems within a state, and the central government takes care of matters that affect the entire country. For example, if there is a flood in a small town, the local government might help. If the flood affects many towns, the state government steps in. If it’s a big disaster, the central government might send help too. Each level of government has specific responsibilities, and they all work together to manage the country.
Democracy and Representation
Democracy means “rule by the people.” In a democracy, people vote for representatives who make decisions on their behalf. In India, these representatives are called MLAs (Members of Legislative Assembly) at the state level and MPs (Members of Parliament) at the national level. These representatives discuss problems and make laws in assemblies. This system of electing representatives is called representative democracy. It allows people to have a say in how they are governed, even if they cannot participate directly in every decision.
Grassroots Democracy
Grassroots democracy means involving ordinary citizens in decision-making processes. It allows people at the base level, such as in villages or small communities, to have a voice in decisions that affect them. This is important in a large democracy like India, where decisions made at the top levels of government might not always address local issues. Grassroots democracy helps ensure that the needs and concerns of all citizens, no matter where they live, are considered in governance.
The Importance of Democracy
Democracy is not just about voting; it is about ensuring equality, justice, and respect for all people. It provides a framework where laws and decisions are made by representatives chosen by the people. Democracy also ensures that the government is accountable to the people and that citizens have the right to express their opinions and participate in governance. This system helps maintain peace and fairness in society, making sure that everyone has a voice in how their country is run.