NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Curiosity Chapter 5 Measurement of Length and Motion in Hindi and English Medium revised for session 2025-26. All the question answers of class 6 science chapter 5 are given here in simplified format.
Class 6 Science Curiosity Chapter 5 Measurement of Length and Motion
Measurement of Length
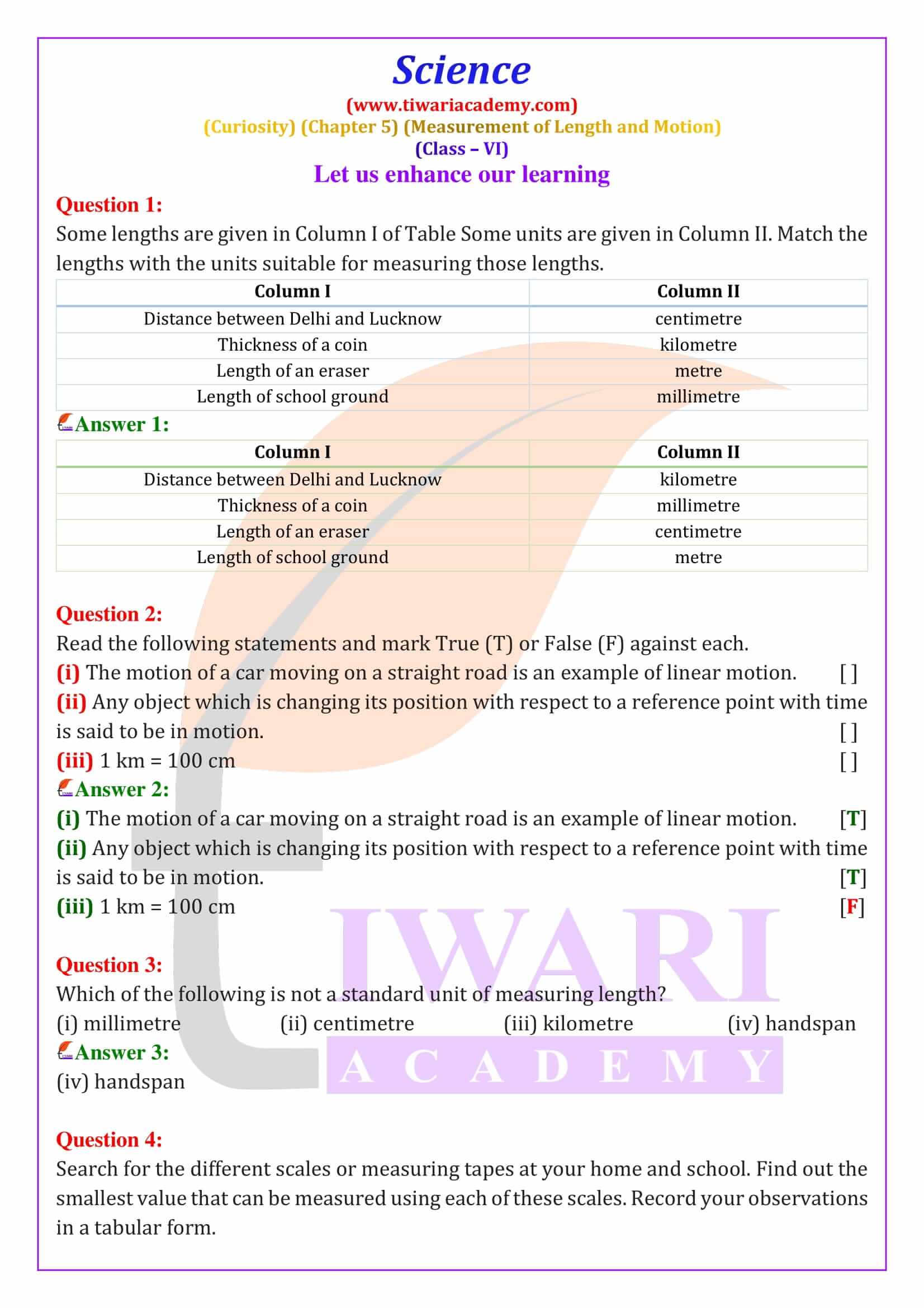
Chapter 5 of Class 6 Science introduces students to the fundamental concepts of measuring length and motion. The chapter begins with a story of a girl named Deepa and her friends, who explore various traditional and modern methods of measuring length. They experiment with using body parts like hand-spans and find the inconsistencies due to different sizes. This leads them to understand the need for standard units of measurement, which are consistent and universally accepted.

Traditional and Standard Units
The chapter 5 explores various traditional units of length used in ancient India, such as angula (finger width) and dhanusa (bow length). It highlights the evolution of these units into the International System of Units (SI units), where the metre is the standard unit of length. The metre is further divided into centimetres and millimetres for smaller measurements and kilometres for larger distances. This system ensures that measurements are consistent and accurate across different regions and applications.
Correct Measurement Techniques
Students learn the correct techniques for measuring lengths using scales and measuring tapes. The chapter 5, of 6th science, emphasizes the importance of placing the scale properly along the object and viewing the measurement from the correct angle to avoid parallax error. It also provides solutions for measuring with broken or unclear scales, ensuring accurate results despite imperfections in measuring tools.
Measuring Curved Lines and Describing Position
Class 6 Science chapter 5 solutions also covers methods for measuring curved lines using flexible measuring tapes or threads. This technique is essential for measuring non-linear objects accurately. Additionally, the concept of a reference point is introduced to describe the position of objects. This helps students understand how distances are relative and how to specify locations using a common reference point, ensuring clear and unambiguous communication.
Motion and Types of Motion
Students explore the concepts of motion by observing objects around them. They learn that an object is in motion if its position changes with respect to a reference point over time. The chapter categorizes different types of motion: linear motion (straight-line path), circular motion (circular path), and oscillatory motion (back and forth movement). Each type of motion is explained with practical examples, helping students relate theoretical concepts to real-world observations.
Practical Activities and Real-World Applications
The chapter 5, of class 6 science Curiosity, includes various activities that encourage students to measure objects, observe different types of motion, and think critically about their observations. These activities, such as measuring lengths with scales, identifying types of motion in a park, and designing a card game for unit conversions, make learning interactive and engaging. The practical applications of these concepts in everyday life are emphasized, reinforcing the importance of accurate measurements and understanding motion.